Abstract
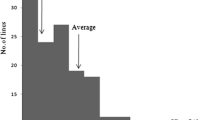
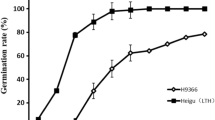
A doubled haploid population, derived from anther culture of F1 hybrid between a typicalindica cv. and ajaponica cv. has been used to investigate the seedling cold tolerance (SCT) in growth cabinet. By dynamically analyzing every day’s survival percentages of the parents and DH lines under 7-d cold plus 9-d normal temperature condition, the quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for SCT have been mapped based on a molecular linkage map constructed from this population. The results show that two parents had significant differences in SCT and the segregation of SCT in DH lines was basically a continuous distribution with most serious injury on the 6th d of the cold treatment. A total of 4 QTLs for SCT have been identified on chromosomes 1, 2, 3 and 4 respectively. The additive effects of qSCT-1, qSCT-2 and qSCT-3 have been contributed by thejaponica cv JX17, but that of qSCT-4 has been contributed by theindica cv ZYQ8. The mechanism of SCT seems complicated since the above 4 QTLs detected at different stages during the treatment. Further study on the genotypes for these SCT QTLs in the DH lines shows transgressive segregation. It is demonstrated that the lines with stronger SCT over JXI7 have 3–4 loci for SCT. Integration of these QTLs into an appropriate variety may lead to a successful rice breeding program for cold tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang, Y., Current status of rice cold tolerance researches in Asia, Journal of Yunan Agr. Uni., 1998, 13(1): 135.
Li, C. C., Rutger, J. N., Inheritance of cool temperature seedling vigor in rice and its relationship with other agronomic characters, Crop Sci., 1980, 20: 295.
Xiong, Z. M., Zhu, X. D., Shao, D. F. et al., The study on early testing technology for rice cold tolerance, Journal of Zhangjing Agr. Science (in Chinese), 1984, 6: 276.
Xu, Y. B., Shen, Z. T., Genetic study on cold tolerance at seedling stage betweenindica andjaponica rices, Scientia Agr. Sinica (in Chinese), 1989, 22(5): 14.
Yan, C. G., Li, X., Yu, H. X. et al., Identification of a QTL for cold tolerance at early seedling stage via RFLP markers in rice (O. Sativa L.), CRRN, 1998, 6. 4: 1.
He, P., Shen, L. S., Lu, C. F., et al., Genetic analysis and mapping the anther culture response genes in rice (Oryza satiza L.), Acta Genetica Sinica, 1998, 25(4): 337.
McCouch, S. R., Cho, Y. G., Yano, M. et al., Report on QTL nomenclature, Rice Genet. Newslett., 1997, 14: 11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, Q., Zeng, D., He, P. et al. QTL analysis of the rice seedling cold tolerance in a double haploid population derived from anther culture of a hybrid betweenindica andjaponica rice. Chin. Sci. Bull. 45, 448–453 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02884949
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02884949