Abstract
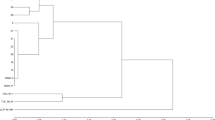
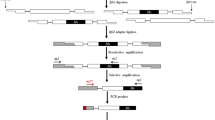
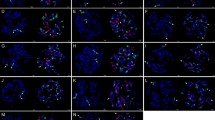
In recent years, transposon insertion polymorphisms have been utilized as molecular markers, and a range of techniques tailored towards identification of insertion sites of various transposable elements have been developed. In the present paper we describe the application of a recently developedDcMaster transposon display system to analyse the genetic diversity of Polish breeding materials of carrot (Daucus carota) and to identify polymorphisms useful for hybrid seed purity testing. Using 3 sets of breeding materials (each consisting of the cytoplasmic male sterility stock, the maintainer, the pollinator, and the corresponding F1 hybrid), we identified 56 DcMTD markers.DcMaster insertion sites proved to be highly polymorphic in cultivated carrot, as 79% of all insertion sites differentiated between individual plants. Fourteen stock-specific DcMTD markers were further selected as potentially useful for hybrid seed purity testing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boerner T, Linke B, Nothnagel T, Scheike R, Schulz B, Steinborn R, et al. 1995. Inheritance of nuclear and cytoplasmic factors affecting male sterility inDaucus carota. In: Kück U, Wricke G, eds. Genetic mechanisms for hybrid breeding, Oxford/Berlin: Blackwell Scientific: 111–122.
Bradeen JM, Bach CI, Briard M, LeClerc V, Grzebelus D, Senalik DA, Simon PW, 2002. Molecular diversity analysis of cultivated carrot (Daucus carota L.) and wildDaucus populations reveals a genetically nonstructured composition. J Am Soc Hort Sci 127: 383–391.
Bradeen JM, Simon PW, 1998. Conversion of an AFLP fragment linked to the carrotY 2 locus to a simple, codominant PCR-based marker form. Theor Appl Genet 97: 960–967.
Briard M, LeClerc V, Grzebelus D, Senalik D, Simon PW, 2000. Modified protocols for rapid carrot genomic DNA extraction and AFLP anaysis using silver stain or radioisotopes. Plant Mol Biol Rep 18: 235–241.
Capy P, Bazin C, Higuet D, Langin T, 1998. Dynamics and evolution of transposable elements. Austin: Landes Bioscience.
Casa AM, Mitchel SE, Smith OS, Register III JC, Wessler SR, Kresovich S, 2002. Evaluation ofHbr (MITE) markers for assessment of genetic relationships among maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 104: 104–110.
Chang R-Y, O’Donoughue LS, Bureau TE, 2001. Inter-MITE polymorphisms (IMP): a high throughput transposon-based genome mapping and fingerprinting approach. Theor Appl Genet 102: 773–781.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N, 1987. Isolation of RNA by the single-step acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction method. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159.
Diers BW, McVetty PBE, Osborn TC, 1996. Relationship between heterosis and genetic distance based on restriction fragment length polymorphism markers in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Crop Sci 36: 79–83.
Felsenstein J, 2004. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) version 3.6. Seattle: Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington.
Flavell AJ, Knox MR, Pearce SR, Ellis THN, 1998. Retrotransposon-based insertion polymorphisms (RBIP) for high throughput marker analysis. Plant J 16: 643–650.
Grzebelus D, Jagosz B, Simon PW, 2007. The DcMaster Transposon Display maps polymorphic insertion sites in the carrot (Daucus carota L.) genome. Gene 390: 67–74.
Grzebelus D, Yau Y-Y, Simon PW, 2006.Master: a novel family of PIF/Harbinger-like transposable elements identified in carrot (Daucus carota L.). Mol Genet Genomics 275: 450–459.
Grzebelus D, Senalik D, Jagosz B, Simon PW, Michalik B, 2001. The use of AFLP markers for the identification of carrot breeding lines and F1 hybrids. Plant Breeding 120: 526–528.
Grzebelus D, Szklarczyk M, Michalik B, 1997. The use of RAPD markers for genotype identification of carrot lines and F1 hybrids. J Appl Genet 38A: 33–41.
Kalendar R, Grob T, Regina M, Suoniemi A, Schulman A, 1999. IRAP and REMAP: two new retrotransposon-based DNA fingerprinting techniques. Theor Appl Genet 98: 704–711.
Kwon S-J, Park K-C, Kim J-H, Lee JK, Kim N-S, 2005.Rim2/Hipa CACTA transposon display: a new genetic marker technique inOzyza species. BMC Genetics 6: 15 doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-15.
Le QH, Bureau T, 2004. Prediction and quality assessment of transposon insertion display data. BioTechniques 36: 222–228.
Leigh F, Kalendar R, Lea V, Lee D, Donini P, Schulman AH, 2003. Comparison of the utility of barley retrotransposon families for genetic analysis by molecular marker techniques. Mol Genet Genomics 269: 464–474.
Nakajima Y, Oeda K, Yamamoto T, 1998. Characterization of genetic diversity of nuclear and mitochondrial genomes inDaucus varieties by RAPD and AFLP. Plant Cell Rep 17: 848–853.
Rubatzky VE, Quiros CF, Simon PW, 1999. Carrot and related vegetable Umbelliferae. Wallingford: CABI Publishing.
Shim SI, Jørgensen RB, 2000. Genetic structure in cultivated and wild carrot (Daucus carota L.) revealed by AFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 101: 227–233.
Stein M, Nothnagel T, 1995. Some remarks on carrot breeding (Daucus carota sativus Hoffm.). Plant Breeding 114: 1–11.
Van den Broeck D, Maes T, Sauer M, Zethof J, De Keukeleire P, D’Hauw M, et al. 1998. Transposon Display identifies individual transposable elements in high copy number lines. Plant J 13: 121–129.
Waugh R, McLean K, Flavell AJ, Pearce SR, Kumar A, Thomas BT, Powell W, 1997. Genetic distribution of BARE-1 retrotransposable elements in the barley genome revealed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphisms (S-SAP). Mol Genet Genomics 253: 687–694.
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan L, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD, 1996. Genetic diversity and its relationship to hybrid performance and heterosis in rice as revealed by PCR-based markers. Theor Appl Genet 92: 637–643.
Yephremov A, Saedler H, 2000. Display and isolation of transposon-flanking sequences starting from genomic DNA or RNA. Plant J 21: 495–505.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macko, A., Grzebelus, D. DcMaster transposon display markers as a tool for diversity evaluation of carrot breeding materials and for hybrid seed purity testing. J Appl Genet 49, 33–39 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195246
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195246