Abstract
Background
Transposons constitute the major fractions of repetitive sequences in eukaryotes, and have been crucial in the shaping of current genomes. Transposons are generally divided into two classes according to the mechanism underlying their transposition: RNA intermediate class 1 and DNA intermediate class 2. CACTA is a class 2 transposon superfamily, which is found exclusively in plants. As some transposons, including the CACTA superfamily, are highly abundant in plant species, and their nucleotide sequences are highly conserved within a family, they can be utilized as genetic markers, using a slightly modified version of the conventional AFLP protocol. Rim2 /Hipa is a CACTA transposon family having 16 bp consensus TIR sequences to be present in high copy numbers in rice genome. This research was carried out in order to develop a Rim2/Hipa CACTA-AFLP or Rim2/Hipa CACTA-TD (transposon display, hereafter Rim2/Hipa-TD) protocol for the study of genetic markers in map construction and the study of genetic diversity in rice.
Results
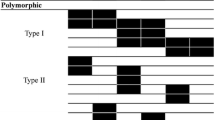
Rim2/Hipa-TD generated ample polymorphic profiles among the different rice accessions, and the amplification profiles were highly reproducible between different thermocyclers and Taq polymerases. These amplification profiles allowed for clear distinction between two different ecotypes, Japonica and Indica, of Oryza sativa. In the analysis of RIL populations, the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers were found to be segregated largely in a dominant manner, although in a few cases, non-parental bands were observed in the segregating populations. Upon linkage analysis, the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers were found to be distributed in the regions proximal to the centromeres of the chromosomes. The distribution of the Rim2/Hipa CACTA elements was surveyed in 15 different Oryza species via Rim2/Hipa-TD. While Rim2/Hipa-TD yielded ample amplification profiles between 100 to 700 bp in the AA diploid Oryza species, other species having BB, CC, EE, BBCC and CCDD, profiles demonstrated that most of the amplified fragments were larger than 400 bp, and that our methods were insufficient to clearly distinguish between these fragments. However, the overall amplification profiles between species in the Oryza genus were fully distinct. Phenetic relationships among the AA diploid Oryza species, as evidenced by the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers, were matched with their geographical distributions.
Conclusion
The abundance of the Rim2/Hipa TIR sequences is very informative since the Rim2/Hipa-TD produced high polymorphic profiles with ample reproducibility within a species as well as between species in the Oryza genus. Therefore, Rim2/Hipa-TD markers can be useful in the development of high-density of genetic map around the centromeric regions. Rim2/Hipa-TD may also prove useful in evaluations of genetic variation and species relationships in the Oryza species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Transposable elements (TEs) constitute a large fraction of plant genomes, and exert critical effects on the formation of the current genomes [1]. With the genome sequences available from a few model species, the differential amplification of TEs helps to explain the C-value paradox in cereal grass species [2]. The TEs have also proven to be a robust source of allelic and subsequent genetic diversity in plants [3, 4].
Two classes of transposable elements, classes 1 and 2, have been delineated in plants [5]. Class 1 TEs integrate into host chromosomes via RNA intermediates, using element- encoded reverse-transcriptase, culminating in the production of highly abundant copies in the host genome [2]. The class 1 TEs include the retro-elements, the long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons, the long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs, also known as non-LTR retrotransposons), and the short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs). Class 2 elements transpose via DNA intermediates, usually resulting in relatively low copy numbers (usually <100 copies per genome) [6]. The class 2 elements are also characterized by short terminal inverted repeats (TIRs), and are divided into two groups, autonomous and non-autonomous elements, depending on their transposability. Autonomous elements, such as Ac and Spm, transpose themselves autonomously, as they harbor all the genes necessary for transposition. Non-autonomous elements, including Ds and dSpm, only transpose in the presence of autonomous elements in the genome, as they are usually derivatives of autonomous elements, or possess defects in critical regulatory sequences [7]. Another family of class 2 TE, MITEs (miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements) were found in plants [8, 9]. Unlike other DNA elements, MITEs are present in very high copy numbers in the genome [1]. However, the mechanisms by which they achieve these high copies have yet to be clearly elucidated [10]. CACTA is another family of transposable elements present at high copy numbers in plants [11]. CACTA was first isolated in maize as a subfamily of En/Spm [12], and its name was designated by virtue of its inverted repeats, which terminate in a conserved CACTA motif.
Regardless of its small genome, the Oryza species contains all classes of TEs [13]. TEs of both classes have been found to contribute 19.9% of the 910 kb of the rice genome sequence, as evidenced by a high-resolution computer-based survey [14]. While the number of elements in the class 2 TEs outnumbered the class 1 TEs (166 to 22), class 1 TEs constituted a greater sequence contribution (12.2% to 6.6%). Mao et al. [13] also noted a variety of TE elements occurring in a survey of 73,000 sequence-tagged-connectors (STC), which can be converted to one STC for every 9 kb across the 430 Mb rice genome, and found that 6848 STCs shared homology with regions of the known TE sequences. A CACTA-like element was identified in rice from a RNA transcript, Rim2, in response to the fungal pathogen, Magnaporthe grisea [31]. Upon subsequent analysis, the Rim2 transcript was revealed to belong to the CACTA superfamily, and designated as a Rim2/Hipa element [21]. The Rim2/Hipa element was estimated to be present several hundred copies or more in the rice genome.
Phenotypic changes due to TE mobilization have provided powerful genetic and molecular tools for the discovery and isolation of genes, using both forward and reverse genetic strategies [15, 16]. MITE-transposon display (MITE-TD), a modification of conventional AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphism) techniques [17, 18] using the consensus sequences of the MITE transposons, demonstrated high allelic variations occurring in a segregating maize mapping population [3, 4]. The MITE-TD technique proved quite efficient in the construction of recombinant genetic maps. More recently, the MITE-TD technique was approved as an effective method for the evaluation of genetic diversity and species relationships in the Oryza species [19, 20]. We have modified the MITE-TD, allowing us to utilize the Rim2/Hipa CACTA consensus sequences [21] to develop a new set of transposon display (TD) markers in rice. Here, we report the detailed protocols with regard to Rim2/Hipa-TD in the Oryza species.
Results
Amplification profiles in O. sativa
As shown in Figure 1, Rim2/Hipa-TD generated multiple bands with abundant polymorphic profiles among the O. sativa accessions. The overall amplification profiles were similar to the AFLP profiles. Depending on primer combinations, the number of amplified fragments ranged from 60 to 80 bands, in a size range from 100 to 700 bp. The number of amplified bands was reduced by increasing the number of selective bases, and the best resolution was obtained with 2 selective bases, as shown in Figure 1. In Figure 1, we can see the disparity in many of the major bands of the Indica and Japonica ecotypes, although we were not, at that time, attempting to differentiate between O. sativa ecotypes. In order to verify the reproducibility of this technique, Rim2/Hipa-TD was conducted on two different thermocyclers, using different brands of Taq DNA polymerases, in 5 different primer combinations. In all of these trials, the amplification profiles were proved to be highly reproducible, as shown in Figure 2.
Segregation and chromosomal distribution of the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers
Segregation of the highly polymorphic bands was assessed using F5 plants derived from an inter-specific hybrid between O. sativa Ilpoombyeo/O.rufipogon W254 (Fig. 3). There were 50 and 45 recordable markers being segregated in the AT and CA primer combinations, respectively. As we were unable to ascertain whether these markers were dominant or co-dominant using the F5 population, we utilized Rim2/Hipa-TD to analyze the F2 population. Most of the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers were found to be segregated as dominant markers, with the exception of a few co-dominantly segregated markers. However, the co-dominant segregating markers constituted less than 1% of the total segregating markers. In Figure 3, the segregating markers indicated by stars were odd, since they were found to be present in both parents. We also attempted to confirm the segregation pattern in the F14 RIL lines (M/G lines) derived from an intra-specific hybrid, during which we also observed one or two odd segregating markers in each primer set amplification (data not shown). Whether or not these odd markers were derived from transposon movement after hybridization remains unknown.
Figure 4 displays the chromosomal distribution of the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers in chromosome 1 of rice using the F14 M/G RIL lines, in which the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers are distributed proximal half to the centromere in both arms, which was also observed similarly in other chromosomes.
Diversity and distribution of Rim2/Hipa-TD markers in Oryza genus
The distribution of the Rim2/Hipa elements was evaluated by Rim2/Hipa-TD in 15 different Oryza species, 8 of which were AA diploids and 7 of which were found to be other genomes, including BB, CC, EE, BBCC, and CCDD (Fig. 5). Although the Rim2/Hipa-TD generated ample amplification profiles among the AA diploid Oryza species, the other species exhibited amplified fragments which, in general, were larger than 400 bp, and these fragments could not be clearly distinguished. These results were consistent with the results obtained with other primer combinations. Among the AA diploid species, amplification profiles were distinct between species, with the notable exceptions of O. glaberrima and O. barthii. O. barthii, however, is believed to be a direct ancestor of O. glaberrima [22].
Overall profiles were also fairly consistent with the geographical distribution of the Oryza species in Asia (O. sativa, O. rufipogon, O. nivara), Africa (O. glaberrima, O. barthii, O. longistaminata), and Australia (O. meridionalis). This was confirmed by the phenetic dendrogram [Fig. 6]. The phenetic relationship between AA diploid Oryza species, as shown in Figure 6, was similar to those obtained by RFLP [23] and AFLP [24]. The Oryza species, except for the AA diploids, could not be included in the phenetic analysis, as the Rim2/Hipa-TD marker bands in these species were difficult to match with their corresponding homologous bands in the AA diploids (Fig. 5).
Phenetic dendrogram of the AA diploid Oryza species based on the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers. The numbers in the horizontal bar at the bottom represent the genetic similarity at the corresponding nodes. The numbers at the nodes represent bootstrap values in each node. The countries in the right column are the origins of each accession.
Discussion
The CACTA transposon superfamily is abundant in most plants. Similar sequence organization has been observed in its terminal regions which are flanked by short TIRs of 10 – 28 bp in size, which terminate in a CACTA sequence motif [11, 12]. Using representational difference analysis (RDA), a CACTA-like transposon, hipa, was identified in the rice genome [25], which had previously been characterized as Rim2 [21]. Although rice has the smallest genome among cereal grass species, various transposon types can be found in the rice genome. In a survey of 910 kb of the rice genomic sequences, class 1 and 2 transposons together constitute approximately 20% of the genome, and CACTA transposons alone contribute 0.5% to these total transposons [14]. Based on cloning and data mining in 230 Mb of the rice genome, the Rim2/Hippa CACTA element was estimated to comprise about 600–700 elements of the entire rice genome [21], suggesting that there would be several thousands of the CACTA elements in the entire rice genome. We have utilized the unusually high copy numbers of the Rim2/Hipa CACTA transposons and the sequence conservation TIRs of the Rim2/Hippa element as genetic markers, using the conventional AFLP protocol, with minor modifications [17].
Conventional AFLP detects restriction site polymorphisms by adaptor ligation to the restricted ends, and selective amplification of restriction fragments using complementary primers to the adaptors. Rather than using two different restriction enzymes, TD employs a single restriction enzyme (usually Mse I). Therefore, in addition to the restriction site polymorphisms which flank the transposons, TD also detects polymorphisms of the presence or absence of transposons at specific loci. This constitutes a marked advantage when TDs are utilized for genetic markers, as the integration or excision of transposons can induce allelic diversity in the genes [3, 4]. Kanazawa et al. [26] also noted that the presence or absence of MITE elements in the Stowaway family was significantly associated with speciation in the AA diploid Oryza species. The advantages of the AFLP technique over other molecular markers include the reproducibility of the AFLP profile, as well as its ability to detect multiple loci within a PCR amplification. The amplification of the Rim2/Hipa- TD was also proved to be highly reproducible, which we confirmed by conducting trials with different thermocyclers and Taq DNA polymerases, and the resolution profile was equivalent to that of AFLP. As primers with two selective bases result in optimum amplification, 16 primer combinations are possible. The average number of amplified fragments in each primer combination is approximately 50 – 60, when surveying over 800 fragments. Therefore, Rim2/Hipa-TD appears to be another effective protocol for the genetic analysis of Oryza species, as is shown in Figure 5.
The large number of segregation markers detected in the inter- and intra-specific hybrid mapping populations represents a very favorable circumstance for Rim2/Hipa-TD, especially with regard to the construction of genetic maps and the tagging of genes of interest. However, its dominant segregation characteristics may limit the use of Rim2/Hipa-TD in the F2 population, although the band intensity enables us to differentiate between homozygotic and heterozygotic genotypes. This intensity-differentiating typing method should be carefully scored, as unequivocal genotyping has proved impossible for some markers, as illustrated by Lee et al's experiences with maize F2 mapping using MITE-TD [27]. One notable feature of the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers is their distribution of regions proximal to the centromeres in both arms (Fig. 4), which was unexpected since the Stowaway MITE Pangrangja markers were also evenly distributed among 12 linkage groups in rice [28]. In the linkage analysis of Heartbreaker MITE markers in maize, the MITE markers were determined to be evenly distributed in all 10 linkage groups [3]. Therefore, the chromosomal distribution of the Rim2/Hipa CACTA and MITE transposons may be different in rice. Chromosomal localization of other transposons, such as MITEs and SINEs, is being under investigated with the F14 M/G RIL lines.
The appearance of non-parental bands is also intriguing. Although we did not, in our analysis, attempt to calculate the frequency of non-parental bands, similar results were reported in a RIL mapping population of maize with Heartbreaker MITE-TD markers [3]. In that study, the frequency of non-parental fragments ranged from 0.2 % to 2.5%, depending on the enzyme/primer combination, and the authors explained this non-parental band appearance in terms of the loss of some degree of parental variation over subsequent generations of inbreeding. The mutations in the restriction sites were also proposed to explain the appearance of non-parental bands. Therefore, further analyses of our materials are warranted. The frequency of and mechanisms underlying the appearance of non-parental bands requires determination in future research.
The distribution of the Rim2/Hipa CACTA elements among Oryza species is particularly prominent in AA genome diploid species, which was corroborated by the results of Southern hybridization using Rim2/Hipa CACTA element [21, 25]. In the current study, the Rim2/Hipa TIR sequence for TD analysis was derived from the sequences of O. sativa var. Nipponbare in the NCBI data base. Therefore, poor amplification in species with other genomes may derive from these slight differences in the TIR sequences, resulting in the reduction of primer annealing at the target sites during PCR amplification. Similar results have also been reported by Park et al., in an analysis of Oryza species using a Stowaway MITE Pangrangja element [29]. In Southern analysis with the Pangrangja probe, more abundant copies of the Pangrangja sequences were found among AA diploids than in any other Oryza species. Subsequent TD analysis with the Pangrangja primer also indicated that the amplified profiles were more prominent in the AA diploid species than in any other species [20]. In the CACTA superfamily, several subfamilies, namely, Casper, Mandrake, Isaac, Baldwin, Jorge, Enac, and TAT-1, were isolated and characterized in the Gramineae species [11]. As all of them shared the CACTA nucleotide, containing TIR sequences and constituting significant fractions of the cereal genomes, the amplification profile in the current study may represent these CACTA subfamilies.
Conclusion
The Rim2/Hipa-TD generated abundant polymorphisms between different O. sativa ecotypes. Many segregating markers in inter- and intra-specific hybrids were distributed to regions proximal to the centromeres of the rice chromosomes. The phenetic relationship occurring among AA diploid Oryza species, as based on the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers, matched well with their geographical distributions, and this was corroborated with results obtained with other marker systems. Therefore, the Rim2/Hipa-TD technique will provide another effective protocol for the development of linkage maps and phenetic analyses in rice.
Methods
Plant materials and DNA extraction
A few representative accessions were analyzed from each of 13 Oryza species (Table 1). The seeds of Oryza species, kindly provided by Dr. M.T. Jackson, at the Genetic Resources Center, International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Philippines, were germinated in a nursery field. Plant DNA was extracted from young leaves according to the method described by Dellaporta et al. [30].
Transposon Display with Rim2/Hipa CACTA transposon
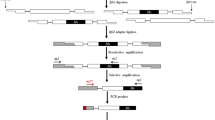
The MITE-AFLP protocols of Casa et al. [3] and Park et al. [20] were modified for the CACTA transposon display. Using the basic information provided by He et al. [31], the CACTA primer and adaptors were designed from consensus sequences obtained from the GenBank database. The primer and sequence information are shown in Table 2.
The genomic DNA (100 ng) was fully digested with Mse I endonuclease, and the adaptor was ligated with the digested DNA in a volume of 20 μl at 22° for 3 hours. Pre-amplification was carried out with the KRMIP-0 primer and with either Rim2/Hipa MAP primer. The PCR reaction was carried out with 0.5 μM of each primer, 0.2 mM dNTP, 1.5 mM MgCl2, and 1.5 units of Taq Pol (Biotool, Spain) in a total volume of 50 μl. PCR reaction control was as follows: one cycle of 72° for 2 min and 94° for 3 min; 25 cycles of 94° for 30 sec, 56° for 30 sec, 72° for 1 min; and a final extension at 72° for 5 min before completion of the reaction. For selective amplification, the pre-amplified products were diluted by 50-fold. Three μl of the dilution was mixed with 0.5 μM of Rim2/Hipa MAP primer, 0.5 μM of one of the Mse I selective primers, 0.2 mM dNTP, 1.5 mM MgCl2, and 1 unit of Taq Pol (Biotool, Spain) in a total volume of 30 μl. PCR reaction control was as follows one cycle at 94° for 5 min; ten "touchdown" cycles of 94° for 30 sec, 64° for 30 sec, and 72° for 1 min with a decrease in annealing temperature to 1° in each cycle; 26 cycles of 94° for 30 sec, 56° for 30 sec, 72° for 1 min; and once at 72° for 5 min to terminate the reaction.
Electrophoresis and fragment detection
Five μl of the final reaction was mixed with 10 μl of electrophoresis loading-buffer (98% formamide, 0.02% BPH, 0.02% Xylene C, and 5 mM of NaOH). After being denatured and immediately cooled, two μl of the sample was loaded into 6% denaturing (7.5 M urea) acrylamide-bisacrylamide gel (19:1) in 1× TBE buffer and electrophoresed at 1800 volts and 60 watts for 130 min. Then, the separated fragments were visualized with the silver-staining kit (Promega, USA).
Genetic inheritance of the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers
Genetic inheritance of the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers was analyzed using F2 and F5 populations derived from a cross between O. sativa var. Ilpoombyeo (Japonica type variety) and O. rufipogon W259. Chromosomal distributions of the Rim2/Hipa-TD markers were analyzed with a RIL population (M/G RILs) derived from an intra-specific cross between O. sativa var. Milyang (Tongil type, Indica/Japonica) and O. sativa var. Gihobyeo (Japonica variety) since a SSR framemap had already been developed with the M/G RILs [32]. Linkage analysis was performed using Mapmaker version 3.0 [33].
Phenetic cluster analysis
Presence or absence of the marker bands were recorded as a binary code, 1 or 0, in each accession. Then, a phenetic dendrogram was constructed on the basis of Nei and Li's algorithm [34] using the arithmetic average option in the NTSYS-pc program [35]. The bootstrapping was done using the 'WINBOOT' program developed at IRRI [36].
Abbreviations
- TE:
-
transposable elements
- AFLP:
-
amplified fragments length polymorphism
- TD:
-
transposon display
- MITE:
-
miniature-inverted transposable element
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
References
Wessler SR, Bureau T, White S: LTR-retrotransposons and MITEs : important players in the evolution of plant genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995, 5: 814-821. 10.1016/0959-437X(95)80016-X.
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL: Plant retrotransposons. Ann Rev Genet. 1995, 33: 479-532. 10.1146/annurev.genet.33.1.479.
Casa A, Brouwer C, Nagel A, Wang L, Zhang Q, Kresovich A, Wessler SR: The MITE family Heartbreaker (Hbr): Molecular markers in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000, 97: 10083-10089. 10.1073/pnas.97.18.10083.
Wessler SR, Nagel A, Casa A: Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements help to create diversity in maize and rice. Rice genetics IV. Proc. 4th Int Rice Genetics Symposium, 22–27. Edited by: Khush GS, Brar DS, Hardy B. 2000, International Rice Research Institute, Los Baňos, The Philippines, October
Flavell AJ, Pearce SR, Kumar A: Plant transposable elements and the genome. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994, 4: 838-844. 10.1016/0959-437X(94)90068-X.
Kunze R, Saedler H, Lönnig WE: Plant transposable elements. Adv Bot Res. 1997, 27: 331-370.
Federoff NV: About maize transposable elements and development. Cell. 1989, 56: 181-191. 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90891-X.
Bureau T, Wessler SR: Stowaway : a new family of inverted repeat elements associated with genes of both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants. Plant Cell. 1994, 6: 907-916. 10.1105/tpc.6.6.907.
Bureau T, Wessler SR: Mobile inverted-repeat elements of the Tourist family are associated with genes of many cereal grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994, 91: 1411-1415.
Feschotte C, Swamy L, Wessler SR: Genome-wide analysis of Mariner -like transposable elements in rice reveals complex relationships with Stowaway miniature inverted repeat transposable elements (MITEs). Genetics. 2003, 163: 747-758.
Wicker T, Guyot R, Yahiaouri N, Keller B: CACTA transposons in Triticeae. A diverse family of high-copy repetitive elements. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132: 52-63. 10.1104/pp.102.015743.
Pereira A, Cuypers H, Gieral A, Sommers ZS, Saedler H: Molecular analysis of the En/Spm transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1986, 5: 835-841.
Mao L, Wood TC, Yu Y, Muhammad A, Budiman MA, Tomkins J, Woo S-S, Sasnowski M, Presting G, Frisch D, Goff S, Dean RA, Wing RA: Rice transposable elements: A survey of 73,000 sequence-tagged-connectors. Genome Res. 2000, 10: 982-990. 10.1101/gr.10.7.982.
Turcotte K, Srinivasan S, Bureau T: Survey of transposable elements from rice genome sequences. Plant J. 2001, 25: 169-179. 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00945.x.
Bensen RJ, Johal GS, Crane VC, Tossberg JT, Schnable PS, Meely RB, Briggs SP: Cloning and characterization of the maize An1 gene. Plant Cell. 1995, 7: 75-84. 10.1105/tpc.7.1.75.
Das L, Martienssen R: Site-selected transposon mutagenesis at the hcf106 locus in maize. Plant Cell. 1995, 7: 287-294. 10.1105/tpc.7.3.287.
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijers A, Pot J, Oeleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M: AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23: 4407-4414.
DeKeukeleire P, Maes T, Sauer M, Zethof J, Van Montagu M, Gerats T: Analysis by transposon display of the behaviour of the dTph1 element family during ontogeny and inbreeding of Petunia hybrida. Mol Gen Genomics. 2001, 265: 72-81. 10.1007/s004380000390.
Park KC, Kim NH, Cho YS, Kang KH, Lee JK, Kim N-S: Genetic variations of AA genome Oryza species measured by MITE-AFLP. Theor Appl Genet. 2003, 107: 203-209. 10.1007/s00122-003-1252-x.
Park KC, Lee JK, Kim NH, Shin YB, Lee J-H, and Kim N-S: Genetic variation in Oryza species detected by MITE-AFLP. Genes Genet Syst. 2003, 78: 235-243. 10.1266/ggs.78.235.
Wang G-D, Tian P-F, Cheng ZK, Wu G, Jiang J-M, Li D-B, Li Q, He Z-H: Genomic characterization of Rim2/Hipa elements reveals a CACTA-like transposon superfamily with unique features in the rice genome. Mol Gen Genomics. 2003, 270: 234-242. 10.1007/s00438-003-0918-z.
Vaughan DA: The wild relatives of rice: a genetic resources handbook. 1994, International Rice Research Institute, Los Baňos, The Philippines
Wang ZM, Second G, Tanksley SD: Polymorphism and phylogenetic relationships among species in the genus Oryza as determined by analysis of nuclear RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet. 1992, 83: 565-581. 10.1007/BF00226900.
Aggarwal RK, Brar DS, Nandi S, Hwang N, Khush GS: Phylogenetic relationships among Oryza species revealed by AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet. 1999, 98: 1320-1328. 10.1007/s001220051198.
Panaud O, Vitte C, Hivert J, Muzlak S, Talag J, Brar D, Sarr A: Characterization of transposable elements in the genome of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using representational difference analysis (RDA). Mol Gen Genomics. 2002, 268: 113-121. 10.1007/s00438-002-0734-x.
Kanazawa A, Akimoto M, Morishima H, Shimamoto Y: Inter- intra-specific distribution of Stowaway transposable elements in AA-genome species in rice. Theor Appl Genet. 2000, 101: 327-335. 10.1007/s001220051487.
Lee JK, Park JY, Choi SH, Kim JH, Choi JK, Min H-K, Park C-H, Kim N-S: Genetic mapping of maize with the intermated Mo17 × KW7 population using MITE-AFLP and SSR markers. Kor J Genet. 2004, 26: 63-72.
Park KC, Lee JK, Kwon SJ, Shin JH, Lee J-H, Yang C-I, Kim N-S: Distribution of MITE transposons in rice genome. Kor J Breed. 2004, 36: 200-206.
Park KC, Jeong CS, Song MT, Kim N-S: A new MITE family, Pangrangja, in Gramineae species. Mol Cells. 2003, 15: 373-380.
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB: A simple and rapid method for plant DNA preparation. Version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1983, 1: 19-21.
He Z-H, Dong H-T, Dong J-X, Li D-B, Ronald PC: The rice Rim2 transcript accumulates in response to Magnaporthe grisea and its predicted protein product shares similarity with TNP2-loke proteins encoded by CACTA transposons. Mol Gen Genet. 2000, 264: 2-10. 10.1007/s004380000278.
Cho YG, McCouch SR, Kuiper M, Kang MR, Pot J, Groenen JTM, Eun MY: Integrating map of AFLP, SSLP and RFLP markers using a recombinant inbred population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet. 1998, 97: 370-380. 10.1007/s001220050907.
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander ES: Constructing genetic maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0. Whitehead Institute Technological Report. 1992, Cambridge, MA, 3
Nei M, Li W: Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1979, 76: 371-385.
Roholf FJ: NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 1.8. Exter Software, New York. 1992
YAP IV, Nelson RJ: WINBOOT: a program for performing bootstrap analysis of binary data to determine the confidence limits of UPGMA-based dendrograms. International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) Discussion Paper Series No. 14. 1996
SSR frame map of rice chromosome 1. [http://ricelab.plbr.cornell.edu]
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant to NSK from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea, through the Crop Functional Genomics Center (Project Number CG3122). Thanks are also extended to Drs. Thomas Bureau and Myung-Hyun Wang for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors' contributions
SJK conducted most of the TD analysis, designed the experiment, and prepared the illustrations for the manuscript. JHK performed the TD analysis. KCP mined the TE sequences in the GenBank database and designed the primers used in the Rim2/Hipa-TD analysis. JKL analyzed the obtained data and participated in the discussion for preparing the manuscript. NSK was the principal investigator of the project and prepared the manuscript
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, SJ., Park, KC., Kim, JH. et al. Rim 2/Hipa CACTA transposon display ; A new genetic marker technique in Oryza species. BMC Genet 6, 15 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-6-15
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-6-15