Abstract
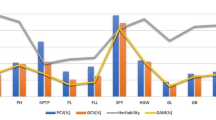
Ten elite inbred lines (four japonica, six indica), chosen from those widely used in the hybrid rice breeding program at Human Hybrid Rice Research Center in China, were crossed to produce all possible hybrids excluding reciprocals. The 45 F1 hybrids along with the ten parents were evaluated for eight traits of agronomic importance, including yield potential, in a replicated field trial. The ten parents were analyzed with 100 arbitrary decamer oligonucleotide primers and 22 microsatellite (simple sequence repeats, SSRs) primer sets via polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Out of the 100 random primers used, 74 were informative and amplified 202 non-redundant bands (variants) with a mean of 2.73 bands per polymorphic primer. All 22 microsatellite primer sets representing 23 loci in the rice genome showed polymorphisms among the ten parents and revealed 90 alleles with an average of 3.91 per SSR locus. Cluster analysis based on Nei's genetic distance calculated from the 291 (202 RAPDs, 89 SSRs) non-redundant variants separated the ten parental lines into two major groups that corresponds to indica and japonica subspecies, which is consistent with the pedigree information. Strong heterosis was observed in hybrids for most of the traits examined. For the 43 diallel crosses (excluding 2 crosses not heading), yield potential, its components (including panicles per plant, spikelets per panicle and 1000-grain weight) and their heterosis in F1 hybrids showed a significant positive correlation with genetic distance. When separate analyses were performed for the three subsets, yield potential and its heterosis showed significant positive correlations with genetic distance for the 15 indica x indica crosses and the 6 japonica x japonica crosses; however, yield potential and its heterosis were not correlated with genetic distance for the 22 indica x japonica crosses. Results indicated that genetic distance measures based on RAPDs and SSRs may be useful for predicting yield potential and heterosis of intra-subspecific hybrids, but not inter-subspecies hybrids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AI-Janabi SM, Honeycutt RJ, McClelland M, Sobral BWS (1993) A genetic linkage map of Saccharum spontaneum L. ‘SES 208’. Genetics 134:1249–1260
Barzen E, Mechelke W, Ritter E, Schulte-Kappert E, Salamini F (1995) An extended map of the sugar beet genome containing RFLP and RAPD loci. Theor Appl Genet 90:189–193
Boppenmaier J, Melchinger AE, Brunklaus-Jung E, Geiger HH, Herrmann RG (1992) Genetic distance for RFLPs in European maize inbreds. I. Relation to performance of flint x dent crosses for forage traits. Crop Sci 32:895–902
Borokova IG, Steffenson BJ, Jin Y, Rasmussen JB, Kilian A, Kleinhofs A, Rossnagel BG, Kao KN (1995) Identification of molecular markers linked to the stem rust resistance gene rpg4 in barley. Phytopathology 85:181–185
Cai Q, Guy CL, Moore GA (1994) Extension of the linkage map in citrus using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers and RFLP mapping of cold-acclimation-responsive loci. Theor Appl Genet 89:606–614
Cho YG, Blair MW, Panaud O, McCouch SR (1996) Cloning and mapping of variety-specific rice genomic DNA sequences: amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLP) from silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Genome (in press)
Chunwongse J, Bunn TB, Crossman C, Jiang J, Tanksley SD (1994) Chromsomal localization and molecular-marker tagging of the powdery mildew resistance gene (lv) in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 89:76–79
Dudley JW, Saghai Maroof MA, Rufener GK (1991) Molecular marker and grouping of parents in maize breeding programs. Crop Sci 31:718–723
Deng H, Wang G (1984) A study on prediction of heterosis in crops (in Chinese). Hunan Agric Sci 3:1–5
Giovannoni JJ, Wing RA, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD (1991) Isolation of molecular markers from specific chromosomal intervals using DNA pools from existing mapping populations. Nucleic Acids Res 19:6553–6558
Godshalk EB, Lee M, Lamkey KR (1990) Relationship of restriction fragment length polymorphisms to single-cross hybrid performance of maize. Theor Appl Genet 80:273–289
Ikehashi H, Araki H (1985) Genetics of F1 sterility in remote crosses of rice. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Rice genetics. IRRI, Manila, Philippines, pp 119–130
Jain A, Bhatia S, Banga SS, Prakash S, Lakshmikumaran M (1994) Potential use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique to study the genetic diversity in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) and its relationship to heterosis. Theor Appl Genet 88:116–122
Jennings PR (1966) Evaluation of partial sterility in indica x japonica rice hybrids. IRRI Technol Bull 5
Lee M, Godshalk EB, Lamkey KR, Woodman WW (1989) Association of restriction fragment length polymorphisms among maize inbreds with agronomic performance of their crosses. Crop Sci 29: 1067–1071
Lefebvre V, Palloix A, Caranta C, Pochard E (1995) Construction of an intraspecific intergrated linkage map of pepper using molecular markers and doubled-haploid progenies. Genome 38:112–121
Li ZB, Xiao YH, Zhu YH, Li RQ, Liu CL, Wang JM (1982) The study and practice of hybrid rice (in Chinese). Shanghai Academic and Technical Press, Shanghai, China
Lin SC, Yuan LP (1980) Hybrid rice breeding in China. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Innovative approaches to rice breeding. IRRI, Manila, Philippines, pp 35–51
Link W, Dixkens C, Singh M, Schwall M, Melchinger AE (1995) Genetic diversity in European and Mediterranean faba bean germ plasm revealed by RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:27–32
Martin GB, Williams JGK, Tanksley SD (1991) Rapid identification of markers linked to a Pseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and near-isogeneic lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2336–2340
Martin JM, Talbert LE, Lanning SP, Blake NK (1995) Hybrid performance in wheat as related to parental diversity. Crop Sci 35: 104–108
Melchinger AE, Lee M, Lamkey KR, Woodman WW (1990a) Genetic diversity for restriction fragment length polymorphisms: relation to estimated genetic effects in maize inbreds. Crop Sci 30:1033–1040
Melchinger AE, Lee M, Lamkey KR, Hallauer AR, Woodman WW (1990b) Genetic diversity for restriction fragment length polymorphisms and heterosis for two diallel sets of maize inbreds. Theor Appl Genet 80:488–496
Melchinger AE, Boppenmaier J, Dhillon BS, Pollmer WG, Hermann RG (1992) Genetic diversity for RFLPs in European maize inbreds: II. Relation to performance of hybrids within versus between heterotic groups for forage traits. Theor Appl Genet 84: 672–681
Moser H, Lee M (1994) RFLP variation and genealogical distance, multivariate distance, heterosis, and genetic variance in oats. Theor Appl Genet 87:947–956
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Oka HI (1974) Analysis of genes controlling F1 sterility in rice by the use of isogenic lines. Genetics 77:521–534
Oka HI (1988) Functions and genetic bases of reproductive barriers. In: Oka HI (ed) Origin of cultivated rice. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, pp 181–209
Panaud O, Chen XL, McCouch SR (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet (in press)
Peng JY, Glaszmann JC, Virmani SS (1988) Heterosis and isozyme divergence in indica rice. Crop Sci 28:561–563
Ren J, McFerson JR, Li R, Kresovich S, Lamboy WF (1995) Identities and relationships among Chinese vegetable brassicas as determined by random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 120:548–555
Ronald PC, Albano B, Tabien R, Abenes L, Wu K, Tanksley SD (1992) Genetic and physical analysis of the rice bacterial blight resistances locus, Xa-21. Mol Gen Genet 236:113–120
Wang ZY, Second G, Tanksley SD (1992) Polymorphism and phylogenetic relationships among species in the genus Oryza as determined by analysis of nuclear RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 83: 565–581
Wu KS, Tanksley SD (1993) Abundance, polymorphism and genetic mapping of microsatellites in rice. Mol Gen Genet 241:225–235
Xiao J (1989) Compatibility of six rice varieties with indica and japonica. Int Rice Res Newsl 14:6
Xiao J, Yuan LP (1988) The heterosis of F1 hybrids between indica and japonica and their relationship with their parents (in Chinese). Hybrid Rice 9:5–9
Xie FM (1993) Hybrid performance and genetic distance as revealed by RFLPs in rice (Oryza sativa L.) PhD thesis, Texas A & M University. College Station, Tex.
Yuan LP (1985) Exploration of super-high yielding hybrid rice (in Chinese). Hybrid Rice 3:1–3
Yuan LP (1987) Strategy for hybrid rice breeding (in Chinese). Hybrid Rice 1:1–4
Yuan LP, Cheng HX (1986) Hybrid rice breeding and cultivation (in Chinese) Hunan Science and Technology Press, Hunan, China
Yuan LP, Virmani SS, Mao CX (1989) Hybrid rice: achievements and outlook. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Progress in irrigated rice research. IRRI, Manila, Philippines, pp 219–235
Zhang QF, Gao YJ, Yang SH, Ragab RA, Saghi Maroof MA, Li ZB (1994) A diallel analysis of heterosis in elite hybrid rice based on RFLPs and microsatellites. Theor Appl Genet 89:185–192
Zhang QF, Gao YJ, Yang SH, Saghai Maroof MA, Yang SH, Li JX (1995) Molecular divergence and hybrid performance in rice. Mol Breed 1:133–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by F. Salamini
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, J., Li, J., Yuan, L. et al. Genetic diversity and its relationship to hybrid performance and heterosis in rice as revealed by PCR-based markers. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 92, 637–643 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226083
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226083