Summary
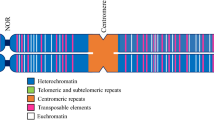
Giemsa dark bands, G-bands, are a derived chromatin character that evolved along the chromosomes of early chordates. They are facultative heterochromatin reflecting acquisition of a late replication mechanism to repress tissue-specific genes. Subsequently, R-bands, the primitive chromatin state, became directionally GC rich as evidenced by Q-banding of mammalian and avian chromosomes. Contrary to predictions from the neutral mutation theory, noncoding DNA is positionally constrained along the banding pattern with short interspersed repeats in R-bands and long interspersed repeats in G-bands. Chromosomes seem dynamically stable: the banding pattern and gene arrangement along several human and murine autosomes has remained constant for 100 million years, whereas much of the noncoding DNA, especially retroposons, has changed. Several coding sequence attributes and probably mutation rates are determined more by where a gene lives than by what it does. R-band exons in homeotherms but not G-band exons have directionally acquired GC-rich wobble bases and the corresponding codon usage: CpG islands in mammals are specific to R-band exons, exons not facultatively heterochromatinized, and are independent of the tissue expression pattern of the gene. The dynamic organization of noncoding DNA suggests a feedback loop that could influence codon usage and stabilize the chromosome’s chromatin pattern: DNA sequences determine affinities of → proteins that together form → a chromatin that modulates → rate constants for DNA modification that determine → DNA sequences. Theories of hierarchical selection and molecular ecology show how selection can act on Darwinian units of noncoding DNA at the genome level thus creating positionally constrained DNA and contributing minimal genetic load at the individual level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros PF, Sumner AT (1987) Correlation of pachytene chromomers and metaphase bands of human chromosomes, and distinctive properties of telomeric regions. Cytogenet Cell Genet 44:223–228
Ansari HA, Takagi N, Sasaki M (1986) Interordinal conservation of chromosome banding pattern inGallus domesticus (Galliformes) andMelopsittacus undulatus (Psittaciformes). Cytogenet Cell Genet 43:6–9
Aota S-I, Ikemura T (1986) Diversity in G+C content at the third position of codons in vertebrate genes and its cause. Nucleic Acids Res 14:6345–6355
Ashley T (1988) G-band position effects on meiotic synapsis and crossing over. Genetics 118:307–317
Ashley T, Russell LB (1986) A new type of nonhomologous synapsis in T(X;4) 1R1 translocation male mice. Cytogenet Cell Genet 43:194–200
Baker TG (1963) A quantitative and cytological study of germ cells in human ovaries. Proc Soc Lond Ser B 158:417–433
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1985) Codon usage and genome composition. J Mol Evol 22:363–365
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1986a) The human genome and its evolutionary context. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 41:479–487
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1986b) Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol 24:1–11
Bernardi G, Olofsson B, Filipski J, Zerial J, Salinas J, Cuny G, Meunier-Rotival M, Rodier M (1985) The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science 228:953–958
Bianchi MS, Bianchi NO, Pantelias GE, Wolff S (1985) The mechanism and pattern of banding induced by restriction endonucleases in human chromosomes. Chromosoma 91:131–136
Bird AP (1986) CpG rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature 321:209–213
Bird AP (1987) CpG islands as gene markers in the vertebrate nucleus. Trends Genet 3:342–347
Bouchard RA (1982) Moderately repetitive DNA in evolution. Int Rev Cytol 76:113–193
Britten RJ, Baron WF, Stout DB, Davidson EH (1986) Sources and evolution of humanAlu repeated sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4770–4774
Brown RAW, Bird AP (1986) Long-range restriction site mapping of mammalian genomic DNA. Nature 322:477–481
Bulmer M (1987) Coevolution of codon usage and transfer RNA abundance. Nature 325:728–730
Calza RE, Eckhardt LA, DelGiudice T, Schildkraut CL (1984) Changes in gene position are accompanied by a change in time of replication. Cell 36:689–696
Camargo M, Cervenka J (1982) Patterns of DNA replication of human chromosomes. II. Replication map and replication model. Am J Hum Genet 34:737–780
Cavalier-Smith T (1985) The evolution of genome size. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Chandley AC (1986) A model for effective pairing and recombination at meiosis based on early replicating sites (R-bands) along chromosomes. Hum Genet 72:50–57
Comings DE (1978) Mechanisms of chromosome banding and implications for chromosome structure. Annu Rev Genet 12:25–46
Comings DE, Avelino E (1975) Mechanisms of chromosome banding VII. Interaction of methylene blue with DNA and chromatin. Chromosoma 51:365–379
Comings D, Harris D, Okada TA, Holmquist GP (1977) Nuclear proteins IV. Deficiency of non-histone proteins inDrosophila virilis and mouse heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 105:349–365
Comings DE, Kovacs BW, Avelino E, Harris DC (1975) Mechanisms of chromosome banding. V. Quinacrine banding. Chromosoma 50:111–145
Cox EC (1972) On the organizations of higher chromosomes. Nature New Biol 239:133–134
Crow JF, Kimura M (1970) An introduction to popualtion genetics theory. Harper and Row, New York
Cuny G, Soriano P, Macay G, Bernardi G (1981) The major components of the mouse and human genomes. 1. Preparation, basic properties and compositional heterogeneity. Eur J Biochem 115:227–223
D’Alisa RM, Korf BR, Gershey EL (1979) T antigen banding on chromosomes of simian virus 40 infected muntjac cells. Cytogenet Cell Genet 24:27–36
Dawkins R (1976) The selfish gene. Oxford University Press
Deininger PL, Daniels GR (1986) The recent evolution of mammalian repetitive DNA elements. Trends Genet 2:76–80
Doolittle WF, Sapienza C (1980) Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature 284:601–603
Dover G (1982) Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299:111–117
Dover GA (1986) Molecular drive in multigene families: how biological novelties arise, spread and are assimilated. Trends Genet 2:159–165
Dubey DD, Raman R (1987) Factors influencing replicon organization in tissues having different S-phase durations in the mole rat,Bandicota bengalensis. Chromosoma 95:285–289
Dutrillaux B (1979) Chromosomal evolution in primates: tentative phylogeny formMicrocebus murinus (Prosimian) to man. Hum Genet 48:251–314
Economou-Pachnis A, Tsichlis PN (1985) Insertion of an Alu SINE in the human homologue of the Mlvi-2 locus. Nucleic Acids Res 13:8379–8387
Eden FC, Hendrick JP (1978) Unusual organization of DNA sequences in the chicken. Biochemistry 17:5835
Endoh H, Okada N (1986) Total DNA transcription in vitro: a procedure to detect highly repetitive and transcribable sequences with tRNA-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:251–255
Epplen JT, Leipoldt M, Engel W, Schmidtke J (1978) DNA sequence organisation in avian genomes. Chromosoma 69: 307–321
Fang JS, Jagiello GM (1988) An analysis of the chromomere map and chiasmata characteristics of human diplotene spermatocytes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 47:52–57
Filipski J (1988a) Why the rate of silent codon substitutions is variable within a vertebrate’s genome. J Theor Biol 134:159–164
Filipski J (1988b) Sequence-based phylogeny in eukaryotic genomes. Nature 334:572
Filipski J, Salinas J, Rodier F (1987) Two distinct compositional classes of vertebrate gene-bearing DNA stretches, their structures and possible evolutionary origin. DNA 6:109–118
Fink GR (1987) Pseudogenes in yeast? Cell 49:5–6
Funderud S, Andreassen R, Haugli F (1979) DNA replication inPhysarum polycephalum: electron microscopic and autoradiographic analysis of replicating DNA from defined stages of the S-period. Nucleic Acids Res 6:1417–1431
Furano AV, Somerville CC, Tsichlis PN, D’Ambrosio E (1986) Target sites for the transposition of rat long interspersed repeated DNA elements (LINEs) are not random. Nucleic Acids Res 14:3717–3726
Ganner E, Evans HJ (1971) The relationship between patterns of DNA replication and quinacrine fluorescence in the human complement. Chromosoma 35:326–341
Gardiner-Garden M, Frommer M (1987) CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol 196:261–282
Goldman MA (1988) The chromatin domain as a unit of gene regulation. BioEssays 9:50–55
Goldman MA, Holmquist GP, Gray MC, Caston LA, Nag A (1984) Replication timing of mammalian genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science 224:686–692
Gottesfeld J, Bloomer LS (1982) Assembly of transcriptionally active 5s RNA gene chromatin in vitro. Cell 28:781–791
Grantham R, Gautier G, Gouy G, Mercier M, Pare A (1980) Codon catalog usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res 8:r49-r62
Haldane JBS (1957) The cost of natural selection. J Genet 55: 511–524
Hand R (1978) Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell 15:317–325
Hardison RC, Printz R (1985) Variability within the rabbit C repeats and sequences shared with other SINEs. Nucleic Acids Res 13:1073–1088
Hatton KS, Dhar V, Brown EH, Iqbal MA, Stuart S, Didamo VT, Schildkraut CL (1988a) The replication program of active and inactive multigene families in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 8:2149–2158
Hatton KS, Dhar V, Gahn TA, Brown EH, Mager D, Schildkraut CL (1988b) The temporal order of replication of multigene families reflects chromosomal location and transcriptional activity. In: Cancer cells 6. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories. Cold Spring Harbor NY, pp 335–340
Heartlein MW, Stroh H, Ellin M, Latt SA (1987) Chromosome instability associated with human alphoid DNA transfected into the Chinese hamster genome. Am J Hum Genet 41:A122
Hoehn H (1975) Functional implications of differential chromosome banding. Am J Hum Genet 27:676–686
Holmquist GP (1987a) Role of replication time in the control of tissue-specific gene expression. Am J Hum Genet 40:151–173
Holmquist GP (1987b) The magic of cytogenetic technology. In: Obe G, Basler A (eds) Cytogenetics. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 31–47
Holmquist GP (1988a) DNA sequences in G-bands and R-bands. In: Adolph KW (ed) Chromosomes and chromatin. CRC Press, Boca Raton FL, pp 76–121
Holmquist GP (1988b) Mobile genetic elements in G-band and R-band DNA. In: Daniel A (ed) The cytogenetics of mammalian autosomal rearrangmeents. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 803–834
Holmquist GP, Caston LA (1986) Replication time of inter-spersed repetitive seuquences. Biochim Biophys Acta 868:164–177
Holmquist GP, Dancis B (1979) Telomere replication, kinetochore organizers, and satellite DNA evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4566–4570
Holmquist G, Gray M, Porter T, Jordan J (1982) Characterization of Giemsa dark- and light-band DNA. Cell 31:121–129
Hwu HR, Robers JW, Davidson EH, Britten RJ (1986) Insertion and/or deletion of many repeated DNA sequences in human and higher ape evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3875–3879
Ikemura T (1985) Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol 22:13–34
Ikemura T, Aota S (1988) Global variation in G+C content along vertebrate genome DNA: possible correlation with chromosome band structures. J Mol Biol 203:1–13
Iqbal MA, Plumb M, Stein J, Stein G, Schildkraut CL (1984) Coordinate replication of members of the multigene family of core and H1 human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7723–7727
Iqbal MA, Chinsky J, Didamo V, Schildkraut CL (1987) Replication of proto-oncogenes early during the S phase in mammalian cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res 15:87–103
John B, Miklos GLG (1979) Functional aspects of satellite DNA and heterochromatin. Int Rev Cytol 58:1–114
Kerem BS, Goitein R, Diamond G, Cedar H, Marcus M (1984) Mapping of DNAase I sensitive regions on mitotic chromosomes. Cell 38:493–499
Kettmann R, Meunier-Rotival M, Cortadas J, Cuny G, Ghysdael J, Mammerickx M, Burney A, Bernardi G (1979) Integration of bovine leukemia virus DNA in the bovine genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4822–4826
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kimura M, Maruyama T (1969) The substitutional load in a finite population. Heredity 24:101–114
Kominami R, Muramatsu M, Moriwaki K (1983) A mouse type 2Alu sequence (M2) is mobile in the genome. Nature 301:87–89
Korenberg JR, Rykowski MC (1988) Human genome organization: Alu, Lines, and the molecular structure of metaphase chromosome bands. Chromosoma 53:391–400
Kowalski J, Cheevers WP (1976) Synthesis of high molecular weight DNA strands during S phase. J Mol Biol 104:603–615
Kuhn EM, Therman E, Denniston C (1985) Mitotic chiasmata, gene density, and oncogenes. Hum Genet 70:1–5
Kuro-o M, Ikebe C, Kohno S (1986) Cytogenetic studies of Hynobiidae (Urodelia). Cytogenet Cell Genet 43:14–18
Latt, SA (1975) Flourescence analysis of late DNA replication in human metaphase chromosomes. Somatic Cell Genet 1:293–321
Latt SA, Brodie S, Munroe SH (1974) Optical studies of complexes of quinacrine with DNA and chromatin: implications for the fluorescence of cytological chromosome preparations. Chromosoma 49:17–40
Lau YF, Arrighi FE (1981) Studies of mammalian chromosome replication. II. Evidence for the existence of defined chromosome replicating units. Chromosome 83:721–741
Leadon SA, Zolan ME, Hanawalt PC (1983) Restricted repair of aflatoxin B1 induced damage in alpha DNA of monkey cells. Nucleic Acids Res 11:5675–5689
Lewin B (1980) Eucaryotic chromosomes: gene expression. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Lewontin RC (1974) The genetic basis of evolutionary change. Columbia University Press, New York
Macaya G, Theiry JP, Bernardi G (1976) An approach to the organization of eukaryotic genomes at a molecular level. J Mol Biol 108:237–254
Madhani HD, Bohr VA, Hanawalt PC (1986) Differential DNA repair in transcriptionally active and inactive proto-oncogenes: c-ab1 and c-mos. Cell 45:417–423
Manuelidis L, Ward DC (1984) Chromosomal and nuclear distribution of the 1.9-kb human DNA repeat segment. Chromosoma 91:28–38
Marchionni MA, Roufa DJ (1981) Replication of viral DNA sequences integrated within the chromatin of SV-40-transformed Chinese hamster lung cells. Cell 26:245–258
Martin CH, Meyerowitz EM (1986) Characterization of the boundaries between adjacent rapidly and slowly evolving genomic regions inDrosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 8654–8658
Martin SL, Voliva CF, Hardies SC, Edgell MH, Hutchison III CA (1985) Tempo and mode of concerted evolution in the L1 repeat family of mice. Mol Biol Evol 2:217–140
Matsumoto KI, Murakami K, Okada N (1986) Gene for lysine tRNA may be a progenitor of the highly repetitive and transcribable sequences present in the salmon genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3156–3160
Mellon I, Bohr VA, Smith CA, Hanawalt PC (1986) Preferential DNA repair of an active gene in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8878–8822
Mizuno S, Macgregor HC (1974) Chromosomes, DNA sequences, and evolution in salamanders of the genusPlethodon. Chromosoma 48:239–296
Mouchiroud D, Fichant G, Bernardi G (1987) Compositional compartmentalization and gene composition in the genome of vertebrates. J Mol Evol 26:198–204
Muto A, Osawa S (1987) The guanine and cytosine content of genomic DNA and bacterial evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:166–169
O’Brien SJ, Reeves RH, Simonson JM, Eichelberger MA, Nash WG (1984) Parallels of genomic organization and of endogenous retrovirus organization in cat and man. Dev Genet 4:341–354
Odum EP (1969) The strategy of ecosystem development. Science 164:262–270
Ohno S (1972) Evolutional reason for having so much junk DNA. In: Pfeiffer RA (ed) Modern aspects of cytogenetics: constitutive heterochromatin in man. F.K. Schattauer Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 169–190
Okada TA, Comings DE (1974) Mechanisms of chromosome banding III. Similarity between G-bands of mitotic chromosomes and chromomeres of meiotic chromosomes. Chromosoma 48:65–71
Olofsson B, Bernardi G (1983) Organization of nucleotide sequences in the chicken genome. Eur J Biochem 130:241–245
Olson JS (1958) Rates of succession and soil changes on southern Lake Michigan sand dunes. Bot Gaz 119:125–170
Orgel LE, Crick FHC (1980) Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature 284:604–607
Perkins DD, Barry EG (1977) The cytogenetics of neurospora. Annu Rev Genet 19:133–224
Perrin P, Bernardi G (1987) Directional fixation of mutations in vertebrate evolution. J Mol Evol 26:301–310
Rogers JH (1985) The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol 93:187–279
Sahasrabuddhe CG, Pathak S, Hsu TC (1978) Responses of mammalian metaphase chromosomes to endonuclease digestion. Chromosoma 69:331–338
Sakamoto K, Okada N (1985) Rodent type 2 Alu family, rat identifier sequence, rabbit C-family and bovine or goat 73-bp repeat may have evolved from tRNA genes. J Mol Evol 22:134–140
Salinas J, Zerial M, Filipski J, Crepin M, Bernardi G (1987) Nonrandom distribution of MMTV proviral sequences in the mouse genome. Nucleic Acids Res 15:3009–3022
Sawada I, Schmid CW (1986) Primate evolution of the alpha-globin gene cluster and its Alu-like repeats. J Mol Biol 192:693–709
Sawyer JR, Hozier JC (1986) High resolution of mouse chromosomes: banding conservation between man and mouse. Science 232:1632–1635
Schempp W, Schmid M (1981) Chromosome banding in amphibia VI. BrdU-replication patterns in Anura and demonstration of XX/XY sex chromosomes inRana esculenta. Chromosoma 83:711–720
Schimke RT, Sherwood SW, Hill AB, Johnston RN (1986) Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2157–2161
Schmid CW, Jelinek WR (1982) The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science 216:1065–1070
Schmid M (1980) Replication banding in Amphibia. IV. Differentiation of GC- and AT-rich chromosome regions in Anura. Chromosoma 77:83–103
Schmid M, de Almeida CG (1988) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. Chromosoma 96:283–290
Schonberg SA, Fukuyama K, Hara N, Epstein AL (1987) Monoclonal antibodies to human nuclear proteins as probes for human chromosome structure. Am J Hum Genet 41:A138
Schweizer D (1981) Counterstain-enhanced chromosome banding. Hum Genet 57:1–14
Seuanez HN (1979) The phylogeny of human chromosomes. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Shiraishi Y, Taguchi T, Ohta Y, Hirai K (1985) Chromosomal localization of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome in Bloom’s syndrome B-lymphoblastoid cell lines transformed with EBV. Chromosoma 93:157–164
Smith JM (1968) “Haldane’s dilemma” and the rate of evolution. Nature 219:114–116
Solomon MJ, Strauss F, Varshavsky A (1986) A mammalian high mobility group protein recognizes any stretch of six A-T base pairs in duplex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1276–1280
Sonigo P, Wain-Hobson S, Bougueleret L, Tiollais P, Jacob F (1987) Nucleotide sequence and evolution of ETn elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3768–3771
Soriano P, Macaya G, Bernardi G (1981) The major components of the mouse and human genomes. Eur J Biochem 115: 235–239
Soriano P, Meunier-Rotival M, Bernardi G (1983) The distribution of interspersed repeats is nonuniform and conserved in the mouse and human genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:1816–1820
Stanton LW, Schwab M, Bishop JM (1986) Nucleotide sequence of the human N-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1772–1776
Stineman M (1981) Chromosomal replication inDrosophila virilis III. Organization of active origins in the highly polytene salivary gland cells. Chromosoma 82:289–307
Stock AD, Mengden GA (1975) Chromosome banding pattern conservatism in birds and nonhomology of chromosome banding patterns between birds, turtles, snakes and amphibians. Chromosoma 50:69–77
Strayer D, Heintz N, Roeder R, Gillespie D (1983) Three organizations of human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4770–4774
Sueoka N (1988) Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2653–2657
Tanford C (1961) Physical chemistry of macromolecules. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Thiery JP, Macaya G, Bernardi G (1976) An analysis of eukaryotic genomes by density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol 108:219–235
Trabuchet G, Chebloune Y, Savatier P, Lachuer J, Faure C, Verdier G, Nigon VM (1987) Recent insertion of anAlu sequence in the beta-globin gene cluster of the gorilla. J Mol Evol 25:288–291
Vizard DL, Rosenberg NL (1984) Temporal replication of an interspersed repeated sequence of mouse DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 782:402–407
von Kiel K, Hameister H, Sommssich IE, Adolph S (1985) Early replication banding reveals a strongly conserved functional pattern in mammalian chromosomes. Chromosoma 93:69–76
Weiner AM, Deininger PL, Efstratiadis A (1986) Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem 55:631–661
Willard C, Nguyen HT, Schmid CW (1987) Existence of at least three distinctAlu subfamilies. J Mol Evol 26:180–186
Yunis JJ (1981) Mid-prophase human chromosomes. The attainment of 2,000 bands. Hum Genet 56:293–298
Zolan ME, Cortopassi GA, Smith CA, Hanawalt PC (1982) Deficient repair of chemical adducts in alpha DNA of monkey cells. Cell 28:613–619
Zuckerkandl E (1976) Evolutionary processes and evolutionary noise at the molecular level II. A selectionist model for random fixations in proteins. J Mol Evol 7:269–311
Zuckerkandl E (1986) Polite DNA: functional density and functional compatibility in genomes. J Mol Evol 24:12–27
Zuckerkandl E, Pauling L (1965) Molecules as documents of evolutionary history. J Theor Biol 8:357–366
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holmquist, G.P. Evolution of chromosome bands: Molecular ecology of noncoding DNA. J Mol Evol 28, 469–486 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02602928
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02602928