Abstract
Background
Neoporphyra haitanensis, a major marine crop native to southern China, grows in the harsh intertidal habitats of rocky coasts. The thallus can tolerate fluctuating and extreme environmental stresses, for example, repeated desiccation/rehydration due to the turning tides. It is also a typical model system for investigating stress tolerance mechanisms in intertidal seaweed. The basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors play important roles in the regulation of plants’ responses to environmental stress stimuli. However, little information is available regarding the bZIP family in the marine crop Nh. haitanensis.
Results
We identified 19 bZIP genes in the Nh. haitanensis genome and described their conserved domains. Based on phylogenetic analysis, these 19 NhhbZIP genes, distributed unevenly on the 11 superscaffolds, were divided into four groups. In each group, there were analogous exon/intron numbers and motif compositions, along with diverse exon lengths. Cross-species collinearity analysis indicated that 17 and 9 NhhbZIP genes were orthologous to bZIP genes in Neopyropia yezoensis and Porphyra umbilicalis, respectively. Evidence from RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data showed that the majority of NhhbZIP genes (73.68%) exhibited transcript abundance in all treatments. Furthermore, genes NN 2, 4 and 5 showed significantly altered expression in response to moderate dehydration, severe dehydration, and rehydration, respectively. Gene co-expression network analysis of the representative genes was carried out, followed by gene set enrichment analysis. Two NhhbZIP genes collectively responding to dehydration and rehydration and their co-expressing genes mainly participated in DNA repair, DNA metabolic process, and regulation of helicase activity. Two specific NhhbZIP genes responding to severe dehydration and their corresponding network genes were mainly involved in macromolecule modification, cellular catabolic process, and transmembrane transport. Three specific NhhbZIP genes responding to rehydration and their co-expression gene networks were mainly involved in the regulation of the cell cycle process and defense response.
Conclusions
This study provides new insights into the structural composition, evolution, and function of the NhhbZIP gene family. Our results will help us to further study the functions of bZIP genes in response to dehydration and rehydration in Nh. haitanensis and improve Nh. haitanensis in southern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Water deficit or desiccation is one of the main abiotic stresses seriously affecting plant growth and development and reducing crop production. To better survive under such harsh stress conditions, plants have evolved diverse defense mechanisms at the morphological and physiological levels driven by the regulation of stress-related gene expression [1, 2]. Transcription factors and epigenetic regulation play key roles in orchestrating gene expression and stress response when plants are exposed to extreme environmental stress conditions [3].
The basic leucine zipper (bZIP) family is one of the largest and most diverse transcription factor families [4] and is widely distributed in eukaryotes [5]. They usually possess a highly conserved 40–80 amino acid bZIP domain, which is typically composed of two structural features: a basic DNA-binding region and a leucine zipper region [5]. The basic region is highly conserved and composed of nuclear localization signals and an invariant N-X7-R/K motif that binds to target DNA [6], while the leucine zipper region is variable and is composed of a heptad repeat of leucine or other large hydrophobic amino acids that are involved in dimer formation in the bZIP proteins [6,7,8].
Several studies have shown that the bZIP gene family plays a vital role in many biological processes, including tissue and organ differentiation [9], metabolic activity [10], floral development [11], embryogenesis [12], and seed maturation [13]. Furthermore, bZIP proteins are also involved in the regulation of plants’ responses to abiotic and biotic stressors, such as osmotic, cold, drought, and high salinity stress. SlAREB overexpression in Arabidopsis thaliana and tomato results in enhanced tolerance to water deficit and high salinity stress [14]. In tomato, silencing SlbZIP1 results in reduced tolerance to salt and drought stress [15]; SlAREB1 overexpression increases salt stress tolerance [16]. Similar results have been observed for OsbZIP23 and OsbZIP72 in transgenic rice [17, 18] and for the GmbZIP2 gene in soybean [19].
With the availability of whole genome sequences in various plant species, genome-wide surveys of the bZIP gene family have been completed in several plants. For example, 78 bZIP genes were found in Arabidopsis [8], 160 in soybean [20], 136 in Brassica rapa [21], and 86 in poplar [22]. However, genome-wide characterization of the bZIP gene family in seaweed nori has not yet been reported. Neoporphyra haitanensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta), an endemic species, is an economically important marine crop that is widely cultivated along the coast of South China. At the present time, the total annual harvest of Nh. haitanensis comprises approximately 75% of all seaweed nori production in China [23]. As sessile organisms grown in harsh intertidal habitats, Nh. haitanensis is periodically exposed to air and unavoidably encounters dramatic changes in abiotic environmental conditions, such as temperature, light, desiccation/rehydration, and osmotic pressure [24,25,26]. This species has evolved with high adaptation to the harsh stresses of the intertidal zone habitat. Neoporphyra haitanensis is thus a typical model system for studying stress tolerance mechanisms in intertidal seaweed. Some progress have been achieved regarding the response of Nh. haitanensis blades to various abiotic stresses, and numerous genes, proteins, and metabolites have been identified using a single omics or multi-omics approach [26,27,28,29]. However, little information is available regarding the bZIP gene family in Nh. haitanensis. Recently, the genome sequences of Nh. haitanensis have been reported [30, 31], providing an opportunity to study the characteristics, evolution, and expression of the bZIP gene family at the genome level. Here, all members of the bZIP gene family were identified from the available Nh. haitanensis genome. We conducted systematic analyses of the bZIP genes in Nh. haitanensis, including their characteristics, phylogenetic relationships, sequence structure, pseudomolecule location, gene duplication, and synteny analysis across species. In addition, based on the RNA-seq data, the differential expression profiles of the bZIP genes were determined under dehydration and rehydration stress conditions. Furthermore, gene co-expression network analysis of the dehydration/rehydration responsive genes was carried out, followed by gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of the co-expression gene sets. Our study is the first to report on the bZIP gene family in Nh. haitanensis, which will provide valuable information for future studies on the function of bZIP genes in this important marine crop and aid in a further understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying abiotic stress tolerance in intertidal red seaweed.
Results
Identification and characterization of the bZIP gene family in Nh. haitanensis
Initially, we identified 13 Nh. haitanensis bZIP genes using a Hidden Markov Model search (e-value < e− 5). We then used BLAST to search the Nh. haitanensis genome database with bZIP sequences from Cyanidioschyzon merolae, Galdieria sulphuraria, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and A. thaliana as queries. Finally, 19 bZIP genes were identified in the Nh. haitanensis genome, further confirmed using the SMART database (Additional file 1: Table S1), and named NhhbZIP1–NhhbZIP19. Furthermore, the amino acid sequences of the conserved bZIP domain from each member were extracted, and multiple sequence alignment was performed as described in [32]. As shown in Fig. 1, the conserved bZIP domain consists of a basic DNA-binding region and an adjacent leucine zipper structure. The basic DNA-binding region is composed of an invariable N-X7-R motif, whereas the leucine zipper region contains heptad repeats of leucine (L) or other hydrophobic amino acids. The highly conserved leucine residues are occasionally substituted for amino acids, including alanine, methionine, and valine. Our results are similar to those of previous research on Arabidopsis [6, 8].
The gene characteristics, including molecular weight (MW), coding sequence length (CDS), and isoelectric point (pI), were determined (Additional file 1: Table S1). The full length of the 19 predicted NhhbZIP proteins ranged from 63 (NhhbZIP8) to 1031 (NhhbZIP2) amino acid residues, with the CDS ranging from 192 to 3096 bp. The MW of the proteins varied from 7.26 kDa (NhhbZIP8) to 106.8 kDa (NhhbZIP2), and the pI was distributed from 4.84 (NhhbZIP13) to 11.35 (NhhbZIP8).
Visualization of multiple sequence alignment of the Neoporphyra haitanensis basic leucine zipper (NhhbZIP) transcription factor family domains. The cumulative height of the letter piles at each position demonstrates the conservation of the sequence at that position (measured in bits). The height of a single letter in the letter piles corresponds to the relative frequency of the related amino acids at that position
Phylogenetic relationships and classification of NhhbZIP genes
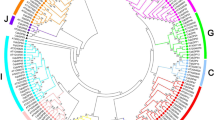
To study the evolutionary relationships and classification of the bZIP family members, we constructed an unrooted Maximum Likelihood (ML) tree using the full-length amino acid sequences of 19 NhhbZIPs and five other plant bZIPs. As shown in Fig. 2, all bZIP genes were divided into 14 groups according to the classification in A. thaliana [6, 8]. Herein the NhhbZIP genes were separated into four groups. Group N was the biggest group, including 12 genes of the NhhbZIP family; whereas group J had only one member. Group N was not homologous to A. thaliana bZIP genes. Meanwhile, most bZIP genes of the other four algae (Neopyropia yezoensis, Cy. merolae, Ectocarpus siliculosus, and Cl. reinhardtii) were also grouped into group N, revealing that the bZIP gene family was relatively conserved across different algae species. These results suggest that the differentiation in the bZIP family in Nh. haitanensis and other algae is lower than that in A. thaliana.
Phylogenetic analysis of the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) proteins from six different plant species (Neoporphyra haitanensis, Neopyropia yezoensis, Cyanidioschyzon merolae, Ectocarpus siliculosus, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and Arabidopsis thaliana). The phylogenetic tree includes 19 bZIP genes from Nh. haitanensis, 19 from Ny. yezoensis, 4 from Cy. merolae, 9 from E. siliculosus, 19 from Cl. reinhardtii, and 78 from A. thaliana. All bZIP genes from multiple species were classified into groups a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, m, n, and s. Group N represents the bZIP genes from five algae species that cannot be classified. Different colors are used to represent different groups. The numbers beside all branches represent bootstrap values generated from 1000 replicates
Sequence structure analysis of the NhhbZIP gene family
To study the sequence structure of the Nh. haitanensis bZIP family, we examined the exon-intron structure of each member. In general, most NhhbZIP genes from the same group shared a similar exon/intron number (Fig. 3). The results showed that 14 (73.7%) of 19 NhhbZIP genes had no introns, most of which belonged to group N. Among the intron containing genes, the intron number varied from 1 to 2. The intron number in the genes of the same group varied only slightly, mostly from 0 to 2. The number of exons showed little variation (from 1 to 3) among the different NhhbZIP groups, indicating that there were relatively smaller differences among the 19 NhhbZIP genes. However, the exon lengths in the genes of the same group exhibited significant variation.
To provide insight into the divergence and function of NhhbZIP proteins, conserved motifs were predicted using MEME software. A total of 10 conserved motifs in the NhhbZIPs were identified (Fig. 4). As expected, all Nh. haitanensis bZIP members contained motif 1, which was annotated as the bZIP domain. The other motifs had no specific annotation information. Most NhhbZIP proteins within the same group had similar motif compositions. For example, group N harbored motifs 1 and 6, except for NhhbZIP8 and NhhbZIP18; all the members of group S shared motifs 1 and 6; group I possessed almost all kinds of motifs; and group J had only motifs 1 and 6. Motifs 1 and 6 widely exist in most NhhbZIP proteins. Notably, five motifs, namely motifs 3, 4, 8, 9, and 10, were found only in group I.
Location of superscaffolds and gene duplication events of NhhbZIP genes
As shown in Fig. 5, all 19 NhhbZIP genes were unevenly dispersed on the 11 superscaffolds. Specific regions showed a relatively high density of NhhbZIP genes. For example, SDUX01000004.1 had the most NhhbZIP genes (9), followed by SDUX01000007.1 with 4 and SDUX01000001.1 with 3. No genes were located on superscaffolds SDUX01000003.1, SDUX01000005.1, SDUX01000009.1, SDUX01000010.1, and SDUX01000011.1. To explore the evolutionary regulation of the NhhbZIP gene family, we analyzed the gene duplication events among the genes, including tandem and segmental duplication events. No tandem or segmental duplication events were found in the NhhbZIP gene family, revealing that the evolution of NhhbZIP genes was not driven by tandem or segmental duplication.
Cross-species collinearity analysis
To analyze the collinearity relationship of the bZIP family genes among Nh. haitanensis and several other algae, we generated seven comparative bZIP synteny maps comparing Nh. haitanensis and seven representative algae, namely five red algae (Cy. merolae, Chondrus crispus, Porphyra umbilicalis, Ny. yezoensis, and Porphyridium purpureum), one brown algae (E. siliculosus), and one green algae (Cl. reinhardtii). As shown in Fig. 6, 18 NhhbZIP genes exhibited syntenic relationships with 16 Ny. yezoensis genes and 9 Po. umbilicalis genes (Additional file 2: Table S2). Nevertheless, no such syntenic relationship was identified between the Nh. haitanensis genes and any other algae (Cy. merolae, E. siliculosus, Cl. reinhardtii, Ch. crispus, and Pr. purpureum) genes. There were 17 pairs of orthologous genes between Nh. haitanensis and Ny. yezoensis and 9 orthologous gene pairs between Nh. haitanensis and Po. umbilicalis. These results indicate that Nh. haitanensis had a relatively closer phylogenetic relationship with Ny. yezoensis and Po. umbilicalis compared to other algae.
Notably, there was great synteny between the Nh. haitanensis genes and Ny. yezoensis genes, compared to those found in the other six algae. This is consistent with the fact that both Nh. haitanensis and Ny. yezoensis belong to Pyropia sensu lato. In addition, eight Nh. haitanensis bZIP genes were collectively syntenic with Ny. yezoensis and Po. umbilicalis genes. However, there was no such relationship with the genes from the other five algae, indicating that these bZIP genes remained in Neoporphyra, Neopyropia, and Porphyra and were lost in the remaining algae analyzed.
To explore the divergence of orthologous gene pairs between Nh. haitanensis and other algae, the non-synonymous (Ka)/synonymous (Ks) ratios of the syntenic gene pairs were calculated on the basis of comparative bZIP synteny maps. The Ka/Ks ratios of all orthologous gene pairs were less than 1, with the highest in the NhhbZIP1_BU14_0513s0012 pair (Ka/Ks = 0.30).
Expression profiles of NhhbZIP genes during dehydration and rehydration
To investigate expression patterns of the bZIP genes in Nh. haitanensis in response to dehydration and rehydration, we analyzed the expression changes of these genes under dehydration and rehydration treatments, based on the RNA-seq data obtained from Wang et al. [26]. As shown in Fig. 7, five NhhbZIP genes had no expression or exhibited low expression in all treatments. Other NhhbZIP genes showed specific expression patterns in response to dehydration and rehydration treatments in Nh. haitanensis. The expression of seven NhhbZIP genes (NhhbZIP1, NhhbZIP5, NhhbZIP11, NhhbZIP12, NhhbZIP14, NhhbZIP18, and NhhbZIP19) was positively associated with the degree of water loss, i.e., the gene expression levels increased with increased dehydration and then decreased in subsequent rehydration. In contrast, one NhhbZIP gene (NhhbZIP7) showed decreased expression as the degree of dehydration deepened and then increased expression during rehydration. The expression of NhhbZIP9 increased with increased dehydration stress, and the increase was maintained during rehydration. NhhbZIP17 exhibited increased expression in the moderate dehydration treatment (AWC70), which then gradually decreased in the severe dehydration (AWC20) and rehydration treatment (AWC20_REH), whereas two NhhbZIP genes (NhhbZIP6 and NhhbZIP16) showed contrasting expression patterns.
We then used the DESeq2 method to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) among the various treatments. According to the results, there were two DEGs between the control group (AWC100) and AWC70 (downregulated in AWC70), followed by four genes between AWC100 and AWC20 (two downregulated and two upregulated in AWC20) and by five genes between AWC100 and AWC20_REH (four downregulated and one upregulated in AWC20_REH) (Additional file 3: Table S3). Subsequently, the three groups of DEGs were compared. As shown in Additional file 6: Fig. S1, two specific NhhbZIP genes were only differentially regulated between AWC100 and AWC20 (upregulated in AWC20), and three specific NhhbZIP genes were only involved in the response to rehydration (two downregulated and one upregulated in AWC20_REH). In addition, two NhhbZIP genes were collectively downregulated in the three groups of DEGs, revealing that they were collectively involved in the response to moderate dehydration, severe dehydration, and rehydration. To verify the accuracy of RNA-seq data, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis was used to detect the expression of six randomly selected bZIP genes following dehydration and rehydration treatments. As shown in Fig. 8, the qRT-PCR results were basically congruent with the RNA-seq data. However, the bZIP gene (NhhbZIP5) showed downregulated expression in response to moderate dehydration and severe dehydration and then upregulated expression in response to rehydration, which was contradictory to the RNA-seq data.
Heatmap diagram showing the expression profiles of Neoporphyra haitanensis basic leucine zipper (NhhbZIP) genes in response to dehydration and rehydration treatments. AWC100, AWC70, AWC20, and AWC20_REH represent 100% absolute water content, 70% absolute water content, 20% absolute water content, and rehydrated 30 min after 80% water content was lost, respectively. The color bar represents gene transcript abundance values normalized to log10
Expression patterns of six Neoporphyra haitanensis basic leucine zipper (NhhbZIP) genes under dehydration and rehydration conditions based on RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The X-axis represents different stress conditions. The Y-axis represents the relative expression levels and the normalized expression data (FPKM) from the qRT-PCR analysis and RNA-seq data, respectively. The error bars indicate the standard deviations from the three biological replicates
Gene co-expression analysis
To construct a co-expression network centered on the two shared DEGs responding to dehydration and rehydration, the two specific DEGs responding to severe dehydration, and the three specific DEGs responding to rehydration, the RNA-seq data of eight samples were used for gene co-expression analysis using the Weighted Correlation Network Analysis (WGCNA) method. Seven co-expression networks were generated (Fig. 9, Additional file 4: Table S4), in which the network centering on NhhbZIP6 was the largest (1953 genes). In contrast, the network centered on NhhbZIP14 had the least genes (132 genes).
Transcription factor-focused co-expression network of two shared genes responding to dehydration and rehydration, two specific genes responding to severe dehydration, and three specific genes responding to rehydration. Dots denote genes, and lines indicate that they have a co-expression relationship
To further elucidate the biological processes in which these genes may be involved, GO enrichment tests were conducted on the seven sets of co-expression genes described above (Fig. 10). Two shared DEGs (NhhbZIP6 and NhhbZIP10) share 43 significantly enriched GO terms, mainly including DNA repair, DNA replication, DNA metabolic process, cellular response to stress, cellular response to DNA damage stimulus, and regulation of helicase activity. This implies that the two genes might play crucial roles in the regulation of the cellular response to dehydration and rehydration treatments.
With respect to the two specific DEGs responding to severe dehydration, NhhbZIP14 and the genes in its network were enriched in macromolecule modification, protein ubiquitination, proteolysis, phosphorylation, and protein modification by small protein conjugation. NhhbZIP19 and its co-expression gene network were enriched in GO terms, including cellular catabolic process, transmembrane transport, lipid catabolic process, carbohydrate metabolic process, and other biological processes. Interestingly, the two severe dehydration-responsive genes showed the same expression pattern across the different stress conditions.
Regarding the three specific DEGs responding to rehydration, the networks centered on NhhbZIP11 and NhhbZIP18 shared the most enriched GO terms, such as nuclear division, organelle fission, regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization, regulation of cell cycle process, and reproductive process. Meanwhile, NhhbZIP11 and NhhbZIP18 also had the same expression profile across stress conditions. In addition, NhhbZIP9 and its co-expression gene network were enriched in the defense response to other organisms, defense response, nucleobase-containing compound biosynthetic process, and regulation of the RNA metabolic process.
Discussion
Neoporphyra haitanensis, an important marine crop native to China, thrives in the challenging habitat of the intertidal zone, and it has therefore evolved a set of protective mechanisms that make this species highly adaptable to harsh stresses. The bZIP gene family has been reported to participate in a variety of biological processes, such as plant growth and development and response to biotic and abiotic stress [20]. Although the bZIP gene family has been found in many plant species, systematic research on the bZIP gene family in Nh. haitanensis is relatively lacking.
Here, 19 bZIP family genes were identified in the Nh. haitanensis genome (53 Mb) [30]. Furthermore, 19 bZIP family genes were identified in the Ny. yezoensis genome (108 Mb) [33], 4 in Cy. merolae (17 Mb), 20 in Ga. sulphuraria (14 Mb), 23 in Po. umbilicalis (88 Mb), 18 in Ch. crispus (105 Mb), 18 in Pr. purpureum (22 Mb), 9 in E. siliculosus (196 Mb), and 19 in Cl. reinhardtii (111 Mb) from their genome databases and the PlnTFDB and Phytozome databases. These data suggest that there is no direct relationship between the number of bZIP family genes and the genome size of these algae.
Phylogenetic analysis showed that the Nh. haitanensis bZIP family could be divided into four groups based on an unrooted ML tree that compared NhhbZIP family members with five other plant bZIP genes (Fig. 2). This is less than the number of groups in most higher plants [20, 22, 34]. As described in the results, group N was not present in A. thaliana, so the majority of bZIP genes from five algae species could not be classified. Thus we segregated these unclassified bZIP genes into a group designated as N (Fig. 2). Furthermore, gene structure analysis indicated that most members located in the same group showed similar exon/intron numbers (Fig. 3). About 74% of the NhhbZIP genes had no introns, which is higher than that in most higher plants, such as apple, sorghum, and soybean [4, 20, 35]. Exon/intron gain/loss plays an important role in the diversification of multiple gene families [36], and it was also observed in the present study. For instance, NhhbZIP3 had three exons, while the paralogous gene, NhhbZIP10, had two, revealing a loss of an exon in the evolutionary process. A similar situation was also reported in soybean and apple bZIP families [4, 20]. These losses may derive from chromosomal rearrangements and fusions and can potentially cause the emergence of functionally distinct paralogs [37]. These lines of evidence indicate that exon/intron gain/loss might be the main driving force behind the diversity of bZIP genes in Nh. haitanensis. Interestingly, the lengths of exons in the genes of the same group showed significant variation in Nh. haitanensis. Several studies found that with the relatively large bZIP gene families in higher plants, caused by tandem or segmental duplication, some duplicated genes in the same group had nearly identical exon lengths [4, 20]. Combined with the finding that the lengths of the exons from the same group were diverse, it is therefore likely that the Nh. haitanensis bZIP gene family has not undergo tandem or segmental duplication in the evolutionary process. As expected, tandem duplication and segmental duplication events were not found in the Nh. haitanensis bZIP gene family. We hypothesized that the generation of some paralogous NhhbZIP genes may be caused by species-specific approaches in the evolutionary process. Additionally, motif constitution analysis showed that there were different motif constitutions among the different groups; however, most bZIP proteins in the same group harbored similar motifs (Fig. 4). For example, group N shares motifs 1 and 6, except for NhhbZIP8 and NhhbZIP18, which only contain motifs 1 and 7. Some specific motifs, such as motifs 3, 4, and 10, exist only in group I. These motifs may perform specific functions in the bZIP family of Nh. haitanensis. Further studies are clearly required to completely understand the roles of these specific motifs in Nh. haitanensis. Taken together, phylogenetic analysis of the NhhbZIP genes is basically congruent with the gene structures and motif compositions; there are similar exon/intron numbers and conserved motifs in every group, which has also been observed for several green plants, such as rape, grape, and Fagopyum talaricum [38,39,40].
To explore the evolutionary relationship of the bZIP gene family across different species, we analyzed the synteny between the Nh. haitanensis bZIP genes and their counterparts from five red algae, one brown algae, and one green algae. There were more orthologous gene pairs between Nh. haitanensis and two Bangiales algae than between Nh. haitanensis and other algae species (Fig. 6, Additional file 2: Table S2). In particular, Nh. haitanensis and Ny. yezoensis had the most orthologous gene pairs, in agreement with their closer evolutionary relationship. Within these gene pairs, 15 single collinearity gene pairs between Nh. haitanensis and Ny. yezoensis were detected, revealing that these bZIP genes seemed to be present in the genome of the last common ancestor of the two algae species. In addition, a number of bZIP genes present in Nh. haitanensis and Po. umbilicalis were not syntenic, suggesting that their genomes might have experienced multiple chromosomal rearrangements after the divergence of these two genera, in agreement with a previous study [33]. The Ka/Ks ratios for all orthologous gene pairs were far less than 1, indicating that these genes may have undergone strong purifying selection pressure during evolution.
In plants, bZIP genes are master regulators of many central physiological processes, including drought/osmotic stress response [7, 22, 35], pathogen defense [41, 42], and light and stress signaling [43]. However, little is known about the functions of bZIP genes in the regulation of the dehydration stress response in Nh. haitanensis. According to the expression data, almost all bZIP genes showed expression to some degree in at least one treatment, revealing that they may play an extensive role in Nh. haitanensis dehydration and rehydration. Comparing the expression data from samples both before and after dehydration/rehydration treatments, seven bZIP genes showed significant expression changes in response to dehydration and rehydration (Additional file 3: Table S3). Interestingly, more bZIP genes showed expression changes after severe dehydration and rehydration than after moderate dehydration; therefore, the bZIP family might play a more dominant role in regulating severe dehydration and rehydration. Taken together, these results suggest that bZIP genes contribute to strong resistance to desiccation/rehydration stress and pave the way for further research on the bZIP-mediated desiccation/rehydration stress response in Nh. haitanensis.
To gain insight into the function of these bZIP genes, gene co-expression network analysis focusing on the seven key genes was performed, followed by GO enrichment analysis of co-expression gene sets. These results indicate that the shared DEGs collectively responding to dehydration and rehydration and their corresponding network genes were mainly enriched in DNA repair, DNA metabolic process, and regulation of helicase activity. Furthermore, the two upregulated genes responding to severe dehydration and the genes in their networks were enriched in macromolecule modification, cellular catabolic process, and transmembrane transport. In addition, the three specific DEGs responding to rehydration and their co-expression gene networks were enriched in the regulation of the cell cycle process and defense response. These findings suggest that different regulatory factors and their co-expression gene networks play vital roles in specific biological functions.
Conclusions
To summarize, we first identified and analyzed the genome-wide bZIP transcription factor family in Nh. haitanensis. Nineteen NhhbZIP genes were identified in the Nh. haitanensis genome and distributed unevenly on the 11 superscaffolds. Based on phylogenetic analysis, 19 NhhbZIP genes were divided into four groups, and each group had an analogous exon/intron number and motif composition, as well as diverse exon lengths. Notably, no tandem or segmental duplication events were found in the NhhbZIP gene family, suggesting that the evolution of NhhbZIP genes is not driven by tandem or segmental duplication events. Additionally, we performed a cross-species collinearity analysis of the bZIP family genes between Nh. haitanensis and seven other algae. The findings of these analyses will contribute to future comparative gene function studies. The expression profiles of NhhbZIP genes in response to dehydration and rehydration were displayed using the RNA-seq data. The analysis of seven key DEGs and their corresponding network genes revealed that these NhhbZIP genes and their co-expression gene networks are involved in diverse biological processes. This study lays a foundation for further exploring the functions of bZIP genes in response to dehydration and rehydration in Nh. haitanensis and for improving Nh. haitanensis in southern China.
Methods
Identification of bZIP family genes and their conserved domains in Nh. haitanensis
The high-quality Nh. haitanensis genome assemblies and protein sequences were obtained from our laboratory [30]. The known Cy. merolae and Ga. sulphuraria bZIP protein sequences were downloaded from the PlnTFDB database (http://plntfdb.bio.uni-potsdam.de/v3.0/), and A. thaliana and Cl. reinhardtii bZIP protein sequences were downloaded from the Phytozome database [44]. Neoporphyra haitanensis bZIP sequences were obtained through three steps. First, the Hidden Markov Model profiles of the bZIP domain (PF07716, PF03131, PF00170) obtained from the Pfam database (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/) were used to identify the bZIP proteins in the Nh. haitanensis dataset using HMMER software 3.0 with a threshold of e-value < e− 5 [45, 46]. A BLAST search was performed to identify putative bZIPs in the Nh. haitanensis database with all Cy. merolae, Ga. sulphuraria, Cl. reinhardtii, and A. thaliana bZIPs as queries. Finally, all candidate genes were examined to confirm the existence of the bZIP domain using the online program SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/). The non-redundant and confident genes were gathered and assigned as Nh. haitanensis bZIP genes. The same process was used to obtain Ny. yezoensis bZIP family genes from its genome database [33]. Additionally, we collected sequences of the conserved domains from the identified NhhbZIP proteins. Then, the conserved domains of the NhhbZIP protein sequences were aligned using the ClustalX 1.83 program with default parameters [32]. WebLogo was used for the visualization of multiple sequence alignment of the NhhbZIP family domains [47].
Phylogenetic analyses and classification of NhhbZIP family members
Two phylogenetic trees were generated, one using only NhhbZIP protein sequences and the other using the bZIP protein sequences of Nh. haitanensis and five other plant species (Ny. yezoensis, Cy. merolae, E. siliculosus, Cl. reinhardtii, and A. thaliana). E. siliculosus bZIP protein sequences were acquired from the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Multiple alignments of protein sequences were performed by ClustalW in MEGA 7.0 with default parameters [48]. The ML method was used to construct phylogenetic trees using MEGA 7.0 [48] under the JTT + G amino acid substitution model selected based on an ML model test. The bootstrap test was carried out with 1000 replicates. The classification of all identified NhhbZIP family members refers to previous studies on Arabidopsis [8]. Finally, the phylogenetic trees were edited and visualized using the online tvBOT tool [49].
Protein properties and sequence analyses
The CDS, MW, and other properties of the identified bZIP proteins were determined using the ExPasy website (https://web.expasy.org/). The online MEME tool (https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/meme) was used to identify the conserved motifs in all NhhbZIP protein sequences with the following parameters: the maximum number of motifs was 10, and the optimum motif width was set between 6 and 200. The exon and intron constituents of the NhhbZIP members were displayed with the Gene Structure Display Server program (GSDS: http://gsds.gao-lab.org/).
Location on superscaffolds, gene duplication of NhhbZIP family members, and collinearity analysis with other species
Using MapGene2Chromosome online software (http://mg2c.iask.in/mg2c_v2.0/) and Nh. haitanensis genome data [30], we visualized the location of the bZIP genes on superscaffolds. In addition, we investigated the tandem and segmental duplication events of the bZIP gene family within the Nh. haitanensis genome using BLAST and MCScanX [50] software with default parameters.
The CDSs of all genes in Cy. merolae, Ch. crispus, Pr. purpureum, Po. umbilicalis, and E. siliculosus were downloaded from the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), and those of Ny. yezoensis and Cl. reinhardtii were obtained from our laboratory and the Ensembl database (https://www.ensembl.org/index.html), respectively. The Ch. crispus, Pr. purpureum, Po. umbilicalis, and E. siliculosus bZIP genes were acquired from accessions GCA_000350225.2, GCA_008690995.1, GCA_002049455.2, and GCA_000310025.1 (NCBI), respectively. We used LAST software (https://gitlab.com/mcfrith/last) with the default parameter to perform a pairwise comparison of the CDSs of all genes between the genomes of Nh. haitanensis and seven other algae (Cy. merolae, Ny. yezoensis, Cl. reinhardtii, Ch. crispus, Pr. purpureum, Po. umbilicalis, and E. siliculosus), and then, we identified the collinearity regions from different species according to the comparison results and gene location information using JCVI software (https://github.com/tanghaibao/jcvi) with the default parameter. Diagrams were drawn using JCVI software. The Ka and Ks nucleotide substitutions between orthologous bZIP gene pairs were obtained using ParaAT software [51].
Expression analysis of NhhbZIP genes
Using the RNA-seq data described in the previously published study [26], we explored the expression patterns of the bZIP genes in response to dehydration/rehydration treatments. Reads counts were normalized to the expected number of Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript sequence per Millions base pairs sequenced (FPKM). Using the DESeq2 package, DEGs were identified among various treatments (|log2(FoldChange)| ≥ 1 and adjusted P-value ≤ 0.05) [52]. A heatmap of the NhhbZIP expression profile was drawn using the pheatmap package in R.
Algal materials and treatments
The algal material used in this study, Nh. haitanensis PH-38, was a laboratory-cultured genetically pure line, as described in our previous study [26]. Gametophytes (thalli) of this pure line were cultured in running sterilized seawater with Provasoli’s enrichment solution medium (PES) under the following conditions: 20 ± 1 °C with 50 μmol photons · m− 2 s− 1 and a 12 h:12 h light:dark (L:D) photoperiod. Before performing the experiments, the thalli were acclimatized for 2 weeks in running sterilized seawater under the following conditions: 20 ± 1 °C with 1250 μmol photons·m− 2 s− 1 and 12 h:12 h L:D photoperiod. After acclimation, the surface water was removed from the thalli with paper towels, and then, the selected thalli were naturally exposed to air at 20 ± 1 °C and 1250 μmol photons·m− 2 s− 1. The absolute water content (AWC) of the thalli was determined according to Kim et al. [53]. Algal materials under normal growth conditions were collected as the control group (AWC100). The algal samples were collected when the total water content of the algae decreased by 30% (AWC70) and 80% (AWC20). For rehydration (AWC20_REH), severely dehydrated algae (losing 80% water content) were recovered under normal conditions for 30 min [26]. Three biological replicates were used for each treatment. All samples from each treatment were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen.
qRT-PCR validation
Total RNA was extracted from each sample using a plant RNA extraction kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA), and contaminating DNA was digested with RNase-Free DNase I (Tiangen, Beijing, China), following the manufacturer’s instructions. For the first-strand cDNA synthesis experiment, approximately 1 μg of purified total RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA in a 20 μL reaction volume using a Transcriptor First Stand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Mannheim, BW, Germany), following the supplier’s instructions. The relative transcript levels of selected genes were analyzed by real-time PCR with the TaKaRa PCR Thermal Cycler Dice Real Time System (TaKaRa Bio Inc., Otsu, Shiga, Japan). The reactions were performed in 25 μL volumes containing 12.5 μL of 2 × TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (TaKaRa Bio Inc.), 2 μL of the diluted cDNA mix, 1 μL of each primer (0.4 μM final concentration of each primer), and 8.5 μL of RNA-free water. The qRT-PCR program was 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 30 s. To verify the specificity of each amplification reaction, the melting curves for each amplicon were also analyzed. Each PCR reaction was performed in three independent biological replicates. The primers used for qRT-PCR are listed in Additional file 5: Table S5. The ubiquitin conjugating enzyme (UBC) gene was used as an internal control [54]. The relative gene expression values were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method [55].
Gene co-expression networks and gene ontology enrichment analysis
Gene co-expression networks were identified using the R package WGCNA [56]. We visualized the gene co-expression network results using Cytoscape software [57]. The previously published RNA-seq data were used for gene co-expression analysis with the following parameters: the soft threshold power was set to 18, the “minModuleSize” value was set to 30, and the “mergeCutHeight” value was set to 0.25. Only genes with FPKM values > 0 in any sample were used for analysis. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was obtained using the Pearson algorithm. The co-expression networks were constructed based on all genes with a weighted correlation.
GO enrichment analysis of gene sets were conducted using TBtools [58]. We focused on biological processes. The P-value of each GO term was generated and adjusted using the Benjamin–Hochberg method [59].
Data Availability
RNA-seq data of Nh. haitanensis in dehydration/rehydration treatments are available in NCBI under accession number PRJNA282903. All other datasets generated in this study are included as supplementary information of this article.
Abbreviations
- NhhbZIP :
-
Neoporphyra haitanensis bZIP
- AWC:
-
Absolute water content
- bZIP:
-
Basic leucine zipper
- CDS:
-
Coding sequence length
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- FPKM:
-
Expected number of Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript sequence per Millions base pairs sequenced
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- GSDS:
-
Gene Structure Display Server
- Ka:
-
Non-synonymous
- Ks:
-
Synonymous
- ML:
-
Maximum Likelihood
- MW:
-
Molecular weight
- PES:
-
Provasoli’s enrichment solution medium
- pI:
-
Isoelectric point
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- REH:
-
Rehydration
- RNA-seq:
-
RNA sequencing
- UBC:
-
Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme
- WGCNA:
-
Weighted Correlation Network Analysis
References
Godwin J, Farrona S. Plant epigenetic stress memory induced by drought: a physiological and molecular perspective. In: Spillane C, McKeown P, editors. Plant epigenetics and Epigenomics. New York: Humana; 2020. pp. 243–59.
Estravis-Barcala M, Mattera MG, Soliani C, Bellora N, Opgenoorth L, Heer K, et al. Molecular bases of responses to abiotic stress in trees. J Exp Bot. 2020;71(13):3765–79.
Bacova R, Kolackova M, Klejdus B, Adam V, Huska D. Epigenetic mechanisms leading to genetic flexibility during abiotic stress responses in microalgae: a review. Algal Res. 2020;50:101999.
Zhao J, Guo R, Guo C, Hou H, Wang X, Gao H. Evolutionary and expression analyses of the apple basic leucine zipper transcription factor family. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:376.
Nijhawan A, Jain M, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008;146(2):333–50.
Jakoby M, Weisshaar B, Dröge-Laser W, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Tiedemann J, Kroj T, et al. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002;7(3):106–11.
Liu X, Chu Z. Genome-wide evolutionary characterization and analysis of bZIP transcription factors and their expression profiles in response to multiple abiotic stresses in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):227.
Dröge-Laser W, Snoek BL, Snel B, Weiste C. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor family—an update. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018;45:36–49.
Silveira AB, Gauer L, Tomaz JP, Cardoso PR, Carmello-Guerreiro S, Vincentz M. The Arabidopsis AtbZIP9 protein fused to the VP16 transcriptional activation domain alters leaf and vascular development. Plant Sci. 2007;172(6):1148–56.
Baena-González E, Rolland F, Thevelein J, Sheen J. A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature. 2007;448(7156):938–44.
Maier AT, Stehling-Sun S, Wollmann H, Demar M, Hong RL, Haubeiß S, et al. Dual roles of the bZIP transcription factor PERIANTHIA in the control of floral architecture and homeotic gene expression. Development. 2009;136(10):1613–20.
Guan Y, Ren H, Xie H, Ma Z, Chen F. Identification and characterization of bZIP-type transcription factors involved in carrot (Daucus carota L.) somatic embryogenesis. Plant J. 2009;60(2):207–17.
Lara P, Onate-Sanchez L, Abraham Z, Ferrandiz C, Diaz I, Carbonero P, et al. Synergistic activation of seed storage protein gene expression in Arabidopsis by ABI3 and two bZIPs related to OPAQUE2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(23):21003–11.
Hsieh T-H, Li C-W, Su R-C, Cheng C-P, Sanjaya, Tsai Y-C, et al. A tomato bZIP transcription factor, SlAREB, is involved in water deficit and salt stress response. Planta. 2010;231(6):1459–73.
Zhu M, Meng X, Cai J, Li G, Dong T, Li Z. Basic leucine zipper transcription factor SlbZIP1 mediates salt and drought stress tolerance in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2018;18(1):83.
Orellana S, Yañez M, Espinoza A, Verdugo I, González E, Ruiz-Lara S, et al. The transcription factor SlAREB1 confers drought, salt stress tolerance and regulates biotic and abiotic stress-related genes in tomato. Plant Cell Environ. 2010;33(12):2191–208.
Xiang Y, Tang N, Du H, Ye H, Xiong L. Characterization of OsbZIP23 as a key player of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family for conferring abscisic acid sensitivity and salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008;148(4):1938–52.
Lu G, Gao C, Zheng X, Han B. Identification of OsbZIP72 as a positive regulator of ABA response and drought tolerance in rice. Planta. 2009;229(3):605–15.
Yang Y, Yu T-F, Ma J, Chen J, Zhou Y-B, Chen M, et al. The soybean bZIP transcription factor gene GmbZIP2 confers drought and salt resistances in transgenic plants. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):670.
Zhang M, Liu Y, Shi H, Guo M, Chai M, He Q, et al. Evolutionary and expression analyses of soybean basic leucine zipper transcription factor family. BMC Genomics. 2018;19:159.
Hwang I, Jung HJ, Park JI, Yang TJ, Nou IS. Transcriptome analysis of newly classified bZIP transcription factors of Brassica rapa in cold stress response. Genomics. 2014;104(3):194–202.
Zhao K, Chen S, Yao W, Cheng Z, Zhou B, Jiang T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP gene family in poplar. BMC Plant Biol. 2021;21:122.
Guo Y, Gu X, Jiang Y, Zhu W, Yao L, Liu Z, et al. Antagonistic effect of laver, Pyropia Yezonensis and P. Haitanensis, on subchronic lead poisoning in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018;181(2):296–303.
Blouin NA, Brodie JA, Grossman AC, Xu P, Brawley SH. Porphyra: a marine crop shaped by stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2011;16(1):29–37.
Sun P, Mao Y, Li G, Cao M, Kong F, Wang L et al. Comparative transcriptome profiling of Pyropia yezoensis (Ueda) M.S. Hwang & H.G. Choi in response to temperature stresses. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):463.
Wang L, Mao Y, Kong F, Cao M, Sun P. Genome-wide expression profiles of Pyropia haitanensis in response to osmotic stress by using deep sequencing technology. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:1012.
Chen J, Li M, Yang R, Luo Q, Xu J, Ye Y, et al. Profiling lipidome changes of Pyropia haitanensis in short-term response to high-temperature stress. J Appl Phycol. 2016;28(3):1903–13.
Wang D, You W, Chen N, Cao M, Tang X, Guan X, et al. Comparative quantitative proteomics reveals the desiccation stress responses of the intertidal seaweed Neoporphyra Haitanensis. J Phycol. 2020;56(6):1664–75.
Huang L, Peng L, Yan X. Multi-omics responses of red algae Pyropia haitanensis to intertidal desiccation during low tides. Algal Res. 2021;58:102376.
Cao M, Xu K, Yu X, Bi G, Liu Y, Kong F, et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of Pyropia haitanensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Mol Ecol Resour. 2020;20(1):216–27.
Chen H, Chu JS-C, Chen J, Luo Q, Wang H, Lu R, et al. Insights into the ancient adaptation to intertidal environments by red algae based on a genomic and multiomics investigation of Neoporphyra haitanensis. Mol Biol Evol. 2021;39(1):msab315.
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25(24):4876–82.
Wang D, Yu X, Xu K, Bi G, Cao M, Zelzion E, et al. Pyropia yezoensis genome reveals diverse mechanisms of carbon acquisition in the intertidal environment. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4028.
Zhang Y, Xu Z, Ji A, Luo H, Song J. Genomic survey of bZIP transcription factor genes related to tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018;8(2):295–305.
Wang J, Zhou J, Zhang B, Vanitha J, Ramachandran S, Jiang S-Y. Genome-wide expansion and expression divergence of the basic leucine zipper transcription factors in higher plants with an emphasis on sorghum. J Integr Plant Biol. 2011;53(3):212–31.
Wang L, Yin X, Cheng C, Wang H, Guo R, Xu X, et al. Evolutionary and expression analysis of a MADS-box gene superfamily involved in ovule development of seeded and seedless grapevines. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015;290(3):825–46.
Xu G, Guo C, Shan H, Kong H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(4):1187–92.
Zhou Y, Xu DX, Jia LD, Huang XH, Ma GQ, Wang SX, et al. Genome-wide identification and structural analysis of bZIP transcription factor genes in Brassica napus. Genes. 2017;8(10):288–312.
Gao M, Zhang HJ, Guo CL, Cheng CX, Guo RR, Mao LY, et al. Evolutionary and expression analyses of basic zipper transcription factors in the highly homozygous model grape PN40024 (Vitis vinifera L). Plant Mol Biol Report. 2014;32(5):1085–102.
Liu M, Wen Y, Sun W, Ma Z, Huang L, Wu Q, et al. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses of bZIP transcription factor family in tartary buckwheat. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):483.
Zhang N, Liu D, Zheng W, He H, Ji B, Han Q, et al. A bZIP transcription factor, LrbZIP1, is involved in Lilium regale Wilson defense responses against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lilii. Genes Genomics. 2014;36(6):789–98.
Li X, Fan S, Hu W, Liu G, Wei Y, He C, et al. Two cassava basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors (MebZIP3 and MebZIP5) confer Disease resistance against cassava bacterial blight. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:2110.
Hu W, Wang L, Tie W, Yan Y, Ding Z, Liu J, et al. Genome-wide analyses of the bZIP family reveal their involvement in the development, ripening and abiotic stress response in banana. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):30203.
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, et al. Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;40(D1):D1178–86.
Eddy SR. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics. 1998;14(9):755–63.
Eddy SR. Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011;7(10):e1002195.
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE. WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004;14(6):1188–90.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1870–4.
Xie J, Chen Y, Cai G, Cai R, Hu Z, Wang H. Tree visualization by one table (tvBOT): a web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(W1):W587–W92.
Wang Y, Tang H, DeBarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(7):e49.
Zhang Z, Xiao J, Wu J, Zhang H, Liu G, Wang X, et al. ParaAT: a parallel tool for constructing multiple protein-coding DNA alignments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;419(4):779–81.
Anders S, Huber W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R106.
Kim JK, Kraemer GP, Yarish C. Comparison of growth and nitrate uptake by New England Porphyra species from different tidal elevations in relation to desiccation. Phycological Res. 2009;57(2):152–7.
Luo Q, Zhu Z, Zhu Z, Yang R, Qian F, Chen H, et al. Different responses to heat shock stress revealed heteromorphic adaptation strategy of Pyropia haitanensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). PLoS ONE. 2014;9(4):e94354.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆CT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Langfelder P, Horvath S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9(1):559.
Shannon P, Markeil A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11):2498–504.
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020;13(8):1194–202.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol. 1995;57(1):289–300.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32060829), National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFD0901101), Fundamental Scientific Research Foundation of the Education Department of Liaoning Province (LJKMZ20220397), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M703033) and the Major Science and Technology Program of Yazhou Bay Innovation Institute of Hainan Tropical Ocean University (2022CXYZD001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.W. collected the public dataset, analyzed the data, and performed the experiments. L.W. and Y.M. drafted the manuscript. X.Y. contributed to bioinformatics analysis. Z.M. and Y.M. supervised the research. L.W. and Y.M. conceived and designed the study. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Additional file 1: Table S1
List of the 19 Neoporphyra haitanensis basic leucine zipper (NhhbZIP) genes identified in this study. Table S1 List of the 19 Neoporphyra haitanensis basic leucine zipper (NhhbZIP) genes identified in this study
Additional file 2: Table S2 (A)
Non-synonymous (Ka), synonymous (Ks), and Ka/Ks values for syntenic gene pairs in Neoporphyra haitanensis and Neopyropia yezoensis. Table S2 (B) Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks values for syntenic gene pairs in Nh. haitanensis and Porphyra umbilicalis. Table S2 (C) Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks values for syntenic gene pairs in Nh. haitanensis and Cyanidioschyzon merolae. Table S2 (D) Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks values for syntenic gene pairs in Nh. haitanensis and Ectocarpus siliculosus. Table S2 (E) Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks values for syntenic gene pairs in Nh. haitanensis and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Table S2 (F) Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks values for syntenic gene pairs in Nh. haitanensis and Chondrus crispus. Table S2 (G) Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks values for syntenic gene pairs in Nh. haitanensis and Porphyridium purpureum
Additional file 3: Table S3 (A)
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in response to moderate dehydration. Table S3 (B) DEGs in response to severe dehydration. Table S3 (C) DEGs in response to rehydration
Additional file 4: Table S4 (A)
Co-expression gene sets of the Neoporphyra haitanensis basic leucine zipper 6 (NhhbZIP6) gene. Table S4 (B) Co-expression gene sets of NhhbZIP9. Table S4 (C) Co-expression gene sets of NhhbZIP10. Table S4 (D) Co-expression gene sets of NhhbZIP11. Table S4 (E) Co-expression gene sets of NhhbZIP14. Table S4 (F) Co-expression gene sets of NhhbZIP18. Table S4 (G) Co-expression gene sets of NhhbZIP19
Additional file 5: Table S5
Primers used in quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) for validating Neoporphyra haitanensis basic leucine zipper (NhhbZIP) genes
Additional file 6: Figure S1
. Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) responsive to moderate dehydration (AWC70), severe dehydration (AWC20), and rehydration (AWC20_REH). This Venn diagram was drawn using the number of DEGs in the three stress treatments (AWC70, AWC20, and AWC20_REH) relative to the control group (AWC100). AWC70 vs. AWC100 represents DEGs between AWC70 and AWC100, AWC20 vs. AWC100 represents DEGs between AWC20 and AWC100, AWC20_REH vs. AWC100 represents DEGs between AWC20_REH and AWC100
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Mo, Z., Yu, X. et al. Characterization of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family of Neoporphyra haitanensis and its role in acclimation to dehydration stress. BMC Plant Biol 23, 617 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04636-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04636-7