Abstract
Background
The polyunsaturated fatty acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), participates in neurotransmission involving activation of calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2), which is coupled to muscarinic, cholinergic and serotonergic neuroreceptors. Drug induced activation of iPLA2 can be measured in vivo with quantitative autoradiography using 14C-DHA as a probe. The present study used this approach to address whether a DHA signal is produced following dompaminergic (D)2-like receptor activation with quinpirole in rat brain. Unanesthetized rats were infused intravenously with 14C-DHA one minute after saline or quinpirole infusion, and serial blood samples were collected over a 20-minute period to obtain plasma. The animals were euthanized with sodium pentobarbital and their brains excised, coronally dissected and subjected to quantitative autoradiography to derive the regional incorporation coefficient, k*, a marker of DHA signaling. Plasma labeled and unlabeled unesterified DHA concentrations were measured.
Results
The incorporation coefficient (k*) for DHA did not differ significantly between quinpirole-treated and control rats in any of 81 identified brain regions. Plasma labeled DHA concentration over the 20-minute collection period (input function) and unlabeled unesterified DHA concentration did not differ significantly between the two groups.
Conclusion
These findings demonstrate that D2-like receptor initiated signaling does not involve DHA as a second messenger, and likely does not involve iPLA2 activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Neurotransmission underlies cognition and behavior, and when disturbed leads to changes in these functional parameters [1]. The polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3, DHA) and arachidonic acid (20:4n-6, AA) are important second messengers in brain, where they participate in neurotransmission [2]. Agonist binding to certain neuroreceptors can release AA or DHA from the stereospecifically numbered-2 (sn-2) position of membrane phospholipids via activation of AA-selective group IVA calcium-dependent cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) or DHA-selective group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2) [3]. cPLA2 and iPLA2 are post-synaptically located [4, 5].
In the intact brain and in vitro, AA-preferring cPLA2 type IVA has been shown to be coupled to serotonergic 5-HT2A/2C receptors [6, 7], cholinergic muscarinic M1,3,5 receptors [8–10], dopaminergic (D)2-like receptors [11–14], and ionotropic N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors [15, 16]. iPLA2, which is DHA-preferring, can be activated by agonist stimulation of cholinergic muscarinic M1,3,5 and serotonergic 5-HT2A/2C receptors, but not of NMDA receptors [9, 16, 17].
The regulation of G-protein mediated activation of cPLA2 or iPLA2 depends on extracellular and intracellular calcium concentrations. cPLA2 is activated by extracellular Ca2+ entry into the cell and iPLA2 by intracellular calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum via phospholipase C (PLC) (reviewed in [18]). PLC, when activated, converts membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3). IP3 binding to IP3 receptors stimulates the release of intracellular Ca2+[19, 20] and of calcium influx factor [21] from the endoplasmic/sarcoplasmic reticulum (ER/SR). The calcium influx factor contributes to the activation of iPLA2 by dissociating calmodulin from the active site of iPLA2[22, 23]. This PLC-mediated activation of iPLA2 results in the hydrolysis of DHA from membrane phospholipid. DAG can also be further hydrolyzed to release DHA, although this pathway likely contributes minimally to DHA release.
Intracellular calcium release associated with activation of the PLC pathway regulates vesicle transport and neurotransmitter release at synaptic terminals [19, 24]. Muscarinic M1,3,5 and serotonergic 5-HT2A/2C neurotransmission is coupled to iPLA2 via the PLC pathway, as is dopaminergic neurotransmission, although the directionality of this coupling is not agreed on. Activation of D2-like receptors in isolated neurons or dissected brain structures was reported to increase [19, 20, 25, 26] or decrease [27, 28] intracellular calcium release or IP3 concentration [29]. A reduction in intracellular calcium release would not activate iPLA2, whereas an increase would activate iPLA2 and increase DHA release.
In the present study, we wished to see if activation of brain D2-like receptors in unanesthetized rats would also lead to a DHA signal, as it does an AA signal [11, 12]. Stimulation of dopaminergic receptors by the agonists quinpirole or apomorphine produced an AA signal that could be blocked by the D2 receptor antagonists raclopride or butaclamol in unanesthetized rats [11, 12, 14].
To test this, we used an established in vivo kinetic method in awake rats [16], to quantify the DHA signal in response to the D2-like receptor agonist quinpirole, compared with vehicle. With this method, radiolabeled DHA is infused to steady state levels in plasma, and brain radioactivity is measured with quantitative autoradiography to derive the regional incorporation coefficient, k*. We found that D2-like receptor activation with quinpirole did not change the DHA incorporation coefficient (k*) into brain compared to vehicle-treated controls, suggesting that D2-like receptor activation does not involve DHA release as a second messenger.
Methods
Animals and diets
Experiments were conducted following the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” (National Institutes of Health Publication No. 86–23) and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Two-month-old male Fischer CDF 344 rats (Charles River Laboratories, Wilmington, MA) were acclimated for one month in an animal facility with regulated temperature, humidity and 12-h dark/light cycle. Rats were maintained on the Rodent NIH-31 auto 18–4 diet (Zeigler Bros, Gardens, PA), which contained (as% of total fatty acid) 20.1% saturated, 22.5% monounsaturated, 47.9% linoleic, 5.1% α-linolenic, 0.02% arachidonic, 2.0% eicosapentaenoic, and 2.3% docosahexaenoic acid [30]. Water and food were provided ad libitum.
Tracer purification and drug preparation
Radiolabeled [1-14C]DHA dissolved in ethanol (53 mCi/mmol, Moravek Biochemicals, Brea, CA) was purified on 60 A° thin-layer chromatography (TLC) silica plates (~5 mg per 3 cm lane on each plate) alongside phospholipid, cholesterol, cholesteryl ester, triglyceride and unesterified fatty acid standards using diethyl ether: heptane: acetic acid (60:40:3 v/v) as a solvent. The [1-14C]DHA was purified because the stock tracer bottles used for this study had been opened in the past, a factor which was previously found to reduce tracer purity over time despite storing it in a −80°C freezer, due to loss of the preservative argon gas blanket in the stock bottle once opened. The plate was sprayed with 0.03% 6-p-toluidine-2-naphthalene-sulfonic acid in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH7.4) (w/v), and the unesterified fatty acid band containing [1-14C]DHA was identified under UV light, scraped and purified from the silica particles by the Folch method (in 30 ml 2:1 v/v chloroform/methanol and 7.5 ml 0.5 M KCl). The chloroform extract was dried under nitrogen, reconstituted twice with 10 ml ethanol, centrifuged to remove additional silica particles, and pipetted to a new 50 ml Pyrex tube. The ethanol extract was reconstituted in 5 ml of ethanol. Radioactive purity measured in a portion of the ethanol extract with HPLC using acetonitrile/water (90/10%) as a solvent (constant flow rate of 2 ml/min), confirmed that 93% of the radioactivity eluted at the same time as the unesterified DHA (unlabeled) standard. On the day of the experiment, a portion of the ethanol extract was dried under nitrogen and resuspended in HEPES buffer, pH 7.4, containing 50 mg/ml fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO).
An acute 1 mg/kg i.v. dose of (−)-quinpirole hydrochloride dissolved in 0.9% saline (Sigma-Aldrich) was chosen because it produces widespread significant increments in the incorporation coefficient, k*, for AA in the brain of unanesthetized rats, which can be blocked by the D2-like receptor antagonists, butaclamol or raclopride, without causing convulsions [12, 14, 31].
Surgical procedures and tracer infusion
A total of 16 rats were randomized to saline or quinpirole treatment (n = 8 per treatment). Rats were anesthetized with halothane (2–3% v/v in O2) and polyethylene (PE 50) catheters were surgically inserted into the right femoral artery and vein (4 rats per day, 2 saline and 2 quinpirole) [31]. The wound was closed with surgical clips and the rat was wrapped loosely, with its upper body remaining free, in a fast-setting plaster cast taped to a wooden block. Each surgery lasted 20–25 min. Rats were allowed to recover from anesthesia for 3–4 h in an environment maintained at 25°C. Rectal temperature was maintained at 36.5-37.5°C using a feedback-heating device and rectal thermometer. Arterial blood pressure and heart rate were measured with a blood pressure recorder (CyQ 103/302; Cybersense, Nicholasville, KY). One minute after an i.v. injection of quinpirole or saline, [1-14C]DHA (170 μCi/kg, 2 ml) was infused into the femoral vein for 5 min at a rate of 400 μl/min, using an infusion pump (Harvard Apparatus Model 22, Natick, MA). Blood was collected at baseline and after [1-14C]DHA infusion (time of collection: 0, 0.2, 0.35, 0.75, 1.5, 3.0, 4.0, 4.9, 5.5, 6.5, 7.5, 10.0, and 19.0 min). Twenty min after beginning tracer infusion, the rat was euthanized with an overdose of Nembutal® (90 mg/kg, i.v.) and decapitated. The brain was removed, frozen in 2-methylbutane maintained at −40°C in dry ice, and stored at −80°C until sectioned.
Chemical analysis
Blood samples, collected before, during or after [1-14C]DHA infusion, were centrifuged immediately at 18,000 g for 30 s at room temperature. Total lipids were extracted from plasma (30 μl) using a modified Folch procedure [32]. One hundred μl of the lower organic phase was used to determine the radiolabeled unesterified plasma [1-14C]DHA concentration by liquid scintillation counting.
Concentrations of unlabeled, unesterified fatty acids were determined from 100 μl of ice-thawed arterial plasma collected at 20 minutes. Unesterified heptadecanoic acid (17:0) was added as an internal standard to the plasma and total lipids were extracted with the Folch method. The total lipid extract was separated by thin layer chromatography on 60 A° silica gel plates (Whatman, Clifton, NJ) alongside phospholipid, unesterified fatty acids, triglyceride and cholesteryl ester standards using the solvent system heptane: diethylether:glacial acetic acid (60:40:3, v/v/v). The plates were sprayed with 0.03% 6-p-toluidine-2-naphthalene-sulfonic acid in 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH7.4) (w/v), and the unesterified fatty acids band was identified under UV light, scraped and methylated with 1% H2SO4 (by vol) in anhydrous methanol (3 h at 70°C) after adding 0.2 ml toluene. The fatty acid methyl esters were extracted with 3 ml heptane after terminating the reaction with 1.5 ml water [33], reconstituted in 25 μl of isooctane and quantified by gas chromatography as described [30]. The injection volume was 2 μl.
Quantitative autoradiography
Quantitative autoradiography was performed on a total of 81 brain regions from autoradiographs of coronal brain sections. The regions were identified from a stereotaxic rat brain atlas [34], and were sampled in both hemispheres. The average of bilateral measurements for each region from three consecutive brain sections was used to calculate regional radioactivity (nCi/g wet brain) by digital quantitative densitometry, using the public domain 1.62 Analysis NIH Image program. Regional brain incorporation coefficient k* (ml plasma/s/g wet brain) of [1-14C]DHA were calculated as follows [35]:
where (nCi/g wet brain wt) is brain radioactivity 20 min after infusion, (nCi/ml plasma) is arterial unesterified [1-14C]DHA concentration, and t (min) is time after beginning [1-14C]DHA infusion. Integrated plasma radioactivity (integral of c*plasma.dt), which corresponds to the input function, was determined by trapezoidal integration and used to calculate k*.
The regional rate of incorporation of unesterified DHA from plasma into brain phospholipids, Jin (nmol/s/g), was calculated as follows [30, 36, 37]:
where cplasma is the plasma concentration (nmol/ml) of unlabeled unesterified DHA. Since negligible amounts of DHA (<1%) can be synthesized de novo by the brain from its precursor, alpha-linolenic acid [30, 36], J in represents the metabolic loss of DHA by the brain [35].
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as mean ± SD. An unpaired t-test was used to assess significant changes in body weight, baseline body temperature, arterial blood pressure and heart rate, input function, the incorporation coefficient (k*) and the incorporation rate, J in . A paired t-test was applied to compare mean body temperature, blood pressure and heart rate in the same animal before and after saline or quinpirole injection. Statistical significance was accepted at p < 0.05.
Results
Physiological parameters
One control rat died after surgery and prior to infusion with saline due to unknown causes. During the brain slicing, one control and one quinpirole brains were not sectioned uniformly, resulting in a saturated, unquantifiable signal, and a sample size of 6 saline and 7 quinpirole. Physiological parameters, plasma input function and fatty acid concentrations were therefore obtained from 6 saline and 7 quinpirole treated rats.
Table 1 shows bodyweight, body temperature, arterial blood pressure, heart rate and orofacial activity, before and after saline or quinpirole treatment. Body weight did not differ significantly between the groups. Baseline body temperature was within physiological range (36.5-37.5°C) for both groups. Baseline body temperature, heart rate and systolic and diastolic blood pressure did not differ significantly (P > 0.05 by unpaired t-test).
Heart rate and systolic and diastolic blood pressures did not significantly change after saline or quinpirole injection, compared to baseline (P > 0.05 by paired t-test). Body temperature did not change also after saline injection, but was significantly reduced by 0.6°C after quinpirole injection (P < 0.01 by paired t-test; Table 1).
All quinpirole-treated rats but not controls exhibited orofacial head- and sniffing activity between 2 to 10 minutes after quinpirole injection, as reported [16]. No convulsions were observed in either group.
Plasma input function
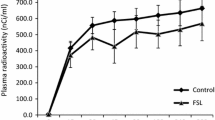
The plasma [1-14C]DHA-time curve is shown in Figure 1. Mean integral radioactivity over time, which represents the input function, did not differ significantly between saline and quinpirole treated rats (quinpirole, 183834 ± 51257 nCi/ml/s, n = 7 versus saline, 184872 ± 49596 nCi/ml/s, n = 6), consistent with our previous report [38].
14C-DHA plasma radioactivity over 20 minutes in rats administered acute 1 mg/kg i.v. dose of (−)-quinpirole hydrochloride dissolved in 0.9% saline or vehicle consisting of 0.9% saline. Solid line represents saline treated rats; dashed line represents quinpirole treated rats. Values are mean ± SD of n = 6 saline and 7 quinpirole treated rats per group.
Plasma unesterified fatty acid concentrations
Plasma unesterified fatty acid concentrations, including DHA concentration, did not differ significantly between the groups (Additional file 1: Table S1). DHA concentration was 13 ± 2 nmol/ml (n = 6) in controls, and 17 ± 4 nmol/ml (n = 7) in quinpirole treated rats (p = 0.096).
Incorporation coefficient (k*)
Mean values of DHA incorporation coefficient k* in acute saline- and quinpirole- treated rats are presented in Table 2. Regional k* values ranged between 3.4 to 15.9 ml/s/g × 10−4 in saline-treated control rats, consistent with our previous report [16]. There was no significant difference in k* between quinpirole-treated and control rats in any of the 81 brain regions examined. A representative autoradiogram comparing the DHA signal following saline or quinpirole is shown in Figure 2.
Incorporation rate (Jin)
Regional rates of unesterified DHA incorporation into the brain, calculated from the product of k* and unesterified plasma DHA concentration (2), did not differ significantly between the groups in the 81 regions examined (data not shown). Mean Jin values in vehicle and quinpirole treated rats were 58.8 ± 20.8 and 73.6 ± 22.5 nmol/s/g×10−4, respectively (P >0.05 by unpaired t-test).
Discussion and conclusions
D2-like receptor activation by acute quinpirole did not significantly change brain DHA incorporation coefficient (k*) or rate (Jin) in any of the 81 regions studied. The incorporation coefficient k* reflects the metabolic loss of DHA by the brain following its release from membrane phospholipid and Jin reflects net loss [35]. The lack of a quinpirole effect on each parameter suggests that D2-like receptor activation does not involve DHA release from membrane phospholipid.
DHA release is controlled by iPLA2[3], which is activated following displacement of bound calmodulin protein by calcium influx factor [23]. Intracellular calcium increases concurrently because it is released with the calcium influx factor from the ER/SR in response to IP3 formation following PLC stimulation [19–21]. Unlike iPLA2, cPLA2 requires extracellular calcium for activation [3], consistent with in vivo evidence of increased AA but not DHA incorporation into the brain following glutamatergic NMDA receptor activation, which allows extracellular calcium into the cell [16]. D2-like receptor stimulation also allows extracellular calcium into the cell, similar to NMDA [28]. Thus, the increase in AA [12, 38] but not DHA incorporation (Table 2) following acute quinpirole confirms the independence of iPLA2 of extracellular calcium and likely reflects selective coupling of D2-like receptors to cPLA2 but not iPLA2. Several in vitro studies reported a reduction in intracellular calcium levels following dopaminergic activation [27, 28]. The lack of effect of quinpirole on k* agrees with these observations.
This study does not rule out the possibility that intracellular calcium levels increased following D2-receptor stimulation with quinpirole, as reported in vitro [25–28]. Such elevations if present, however, were not significant enough to produce a measurable DHA signal with our method.
This study demonstrates that there is no DHA signal following activation of D2-like receptors, although there is a signal following activation of muscarinic and serotonergic receptors [9, 17]. It is likely, therefore, that iPLA2 is activated by the latter two but not D2 receptors. The difference in G-protein receptor coupling remains to be clarified, but it may be related to limited intracellular calcium release and dissociation of calmodulin from iPLA2 following dopaminergic receptor stimulation, compared to muscarinic stimulation [39–42].
In summary, this study showed that D2-like receptor activation does not involve DHA release as a second messenger. This observation, along with our previous finding that D2-like receptor activation stimulates AA release, suggest that D2 receptors are selectively coupled to AA but not DHA as a second messenger.
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Arachidonic acid
- cPLA2:
-
Ca2+-dependent cytosolic phospholipase A2
- iPLA2:
-
Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- ER/SR:
-
Endoplasmic/sarcoplasmic reticulum (ER/SR)
- IP3:
-
inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate
- PIP2:
-
phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
- PLC:
-
Phospholipase C
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- TLC:
-
Thin layer chromatography.
References
Ouyang M, Young MB, Lestini MM, Schutsky K, Thomas SA: Redundant catecholamine signaling consolidates fear memory via phospholipase C. J Neurosci. 2012, 32 (6): 1932-1941. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5231-11.2012.
Basselin M, Ramadan E, Rapoport SI: Imaging brain signal transduction and metabolism via arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acid in animals and humans. Brain Res Bull. 2012, 87 (2–3): 154-171.
Strokin M, Sergeeva M, Reiser G: Docosahexaenoic acid and arachidonic acid release in rat brain astrocytes is mediated by two separate isoforms of phospholipase A2 and is differently regulated by cyclic AMP and Ca2+. Br J Pharmacol. 2003, 139 (5): 1014-1022. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705326.
Ong WY, Yeo JF, Ling SF, Farooqui AA: Distribution of calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA 2) in monkey brain. J Neurocytol. 2005, 34 (6): 447-458. 10.1007/s11068-006-8730-4.
Ong WY, Sandhya TL, Horrocks LA, Farooqui AA: Distribution of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 in the normal rat brain. J Hirnforsch. 1999, 39 (3): 391-400.
Qu Y, Villacreses N, Murphy DL, Rapoport SI: 5-HT2A/2C receptor signaling via phospholipase A2 and arachidonic acid is attenuated in mice lacking the serotonin reuptake transporter. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005, 180: 12-20. 10.1007/s00213-005-2231-5.
Berg KA, Maayani S, Goldfarb J, Scaramellini C, Leff P, Clarke WP: Effector pathway-dependent relative efficacy at serotonin type 2A and 2C receptors: evidence for agonist-directed trafficking of receptor stimulus. Mol Pharmacol. 1998, 54 (1): 94-104.
Bayon Y, Hernandez M, Alonso A, Nunez L, Garcia-Sancho J, Leslie C, Sanchez Crespo M, Nieto ML: Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is coupled to muscarinic receptors in the human astrocytoma cell line 1321 N1: characterization of the transducing mechanism. Biochem J. 1997, 323 (Pt 1): 281-287.
DeGeorge JJ, Nariai T, Yamazaki S, Williams WM, Rapoport SI: Arecoline-stimulated brain incorporation of intravenously administered fatty acids in unanesthetized rats. J Neurochem. 1991, 56 (1): 352-355. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02603.x.
Jones CR, Arai T, Rapoport SI: Evidence for the involvement of docosahexaenoic acid in cholinergic stimulated signal transduction at the synapse. Neurochem Res. 1997, 22 (6): 663-670. 10.1023/A:1027341707837.
Bhattacharjee AK, Chang L, White L, Bazinet RP, Rapoport SI: Imaging apomorphine stimulation of brain arachidonic acid signaling via D2-like receptors in unanesthetized rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008, 197 (4): 557-566. 10.1007/s00213-008-1073-3.
Bhattacharjee AK, Chang L, Lee HJ, Bazinet RP, Seemann R, Rapoport SI: D2 but not D1 dopamine receptor stimulation augments brain signaling involving arachidonic acid in unanesthetized rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005, 180 (4): 735-742. 10.1007/s00213-005-2208-4.
Vial D, Piomelli D: Dopamine D2 receptors potentiate arachidonate release via activation of cytosolic, arachidonic-specific phospholipase A2. J Neurochem. 1995, 64: 2765-2772.
Hayakawa T, Chang MC, Rapoport SI, Appel NM: Selective dopamine receptor stimulation differentially affects [3H]arachidonic acid incorporation, a surrogate marker for phospholipase A2-mediated neurotransmitter signal transduction, in a rodent model of Parkinson's disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001, 296 (3): 1074-1084.
Basselin M, Chang L, Bell JM, Rapoport SI: Chronic lithium chloride administration attenuates brain NMDA receptor-initiated signaling via arachidonic acid in unanesthetized rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006, 31 (8): 1659-1674. 10.1038/sj.npp.1300920.
Ramadan E, Rosa AO, Chang L, Chen M, Rapoport SI, Basselin M: Extracellular-derived calcium does not initiate in vivo neurotransmission involving docosahexaenoic acid. J Lipid Res. 2010, 51 (8): 2334-2340. 10.1194/jlr.M006262.
Garcia MC, Kim HY: Mobilization of arachidonate and docosahexaenoate by stimulation of the 5-HT2A receptor in rat C6 glioma cells. Brain Res. 1997, 768 (1–2): 43-48.
Rosa AO, Rapoport SI: Intracellular- and extracellular-derived Ca(2+) influence phospholipase A(2)-mediated fatty acid release from brain phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009, 1791 (8): 697-705. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.03.009.
Fregeau MO, Carrier M, Guillemette G: Mechanism of dopamine D2 receptor-induced Ca(2+) release in PC-12 cells. Cell Signal. 2013, 25 (12): 2871-2877. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.08.021.
Tang TS, Bezprozvanny I: Dopamine receptor-mediated Ca(2+) signaling in striatal medium spiny neurons. J Biol Chem. 2004, 279 (40): 42082-42094. 10.1074/jbc.M407389200.
Smani T, Zakharov SI, Csutora P, Leno E, Trepakova ES, Bolotina VM: A novel mechanism for the store-operated calcium influx pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2004, 6 (2): 113-120. 10.1038/ncb1089.
Csutora P, Peter K, Kilic H, Park KM, Zarayskiy V, Gwozdz T, Bolotina VM: Novel role for STIM1 as a trigger for calcium influx factor production. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283 (21): 14524-14531. 10.1074/jbc.M709575200.
Bolotina VM: Orai1, STIM1, and iPLA2beta determine arterial vasoconstriction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012, 32 (5): 1066-1067. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.245449.
Ando K, Kudo Y, Aoyagi K, Ishikawa R, Igarashi M, Takahashi M: Calmodulin-dependent regulation of neurotransmitter release differs in subsets of neuronal cells. Brain Res. 2013, 1535: 1-13.
Hernandez-Lopez S, Tkatch T, Perez-Garci E, Galarraga E, Bargas J, Hamm H, Surmeier DJ: D2 dopamine receptors in striatal medium spiny neurons reduce L-type Ca2+ currents and excitability via a novel PLC[beta]1-IP3-calcineurin-signaling cascade. J Neurosci. 2000, 20 (24): 8987-8995.
Trantham-Davidson H, Neely LC, Lavin A, Seamans JK: Mechanisms underlying differential D1 versus D2 dopamine receptor regulation of inhibition in prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci. 2004, 24 (47): 10652-10659. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3179-04.2004.
Lee AK: Dopamine (D2) receptor regulation of intracellular calcium and membrane capacitance changes in rat melanotrophs. J Physiol. 1996, 495 (Pt 3): 627-640.
Ogata G, Stradleigh TW, Partida GJ, Ishida AT: Dopamine and full-field illumination activate D1 and D2-D5-type receptors in adult rat retinal ganglion cells. J Comp Neurol. 2012, 520 (17): 4032-4049. 10.1002/cne.23159.
Izquierdo-Claros RM, Boyano-Adanez MC, Larsson C, Gustavsson L, Arilla E: Acute effects of D1- and D2-receptor agonist and antagonist drugs on somatostatin binding, inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity and accumulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in the rat striatum. Mol Brain Res. 1997, 47 (1–2): 99-107.
Demar JC, Ma K, Chang L, Bell JM, Rapoport SI: Alpha-Linolenic acid does not contribute appreciably to docosahexaenoic acid within brain phospholipids of adult rats fed a diet enriched in docosahexaenoic acid. J Neurochem. 2005, 94 (4): 1063-1076. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03258.x.
Basselin M, Chang L, Bell JM, Rapoport SI: Chronic lithium chloride administration to unanesthetized rats attenuates brain dopamine D2-like receptor-initiated signaling via arachidonic acid. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005, 30: 1064-1075. 10.1038/sj.npp.1300671.
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957, 226: 497-509.
Ichihara K, Fukubayashi Y: Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters for gas–liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 2010, 51 (3): 635-640. 10.1194/jlr.D001065.
Paxinos G, Watson C: The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 1987, New York: Academic, 3
Robinson PJ, Noronha J, DeGeorge JJ, Freed LM, Nariai T, Rapoport SI: A quantitative method for measuring regional in vivo fatty-acid incorporation into and turnover within brain phospholipids: review and critical analysis. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1992, 17 (3): 187-214. 10.1016/0165-0173(92)90016-F.
Igarashi M, DeMar JC, Ma K, Chang L, Bell JM, Rapoport SI: Docosahexaenoic acid synthesis from alpha-linolenic acid by rat brain is unaffected by dietary n-3 PUFA deprivation. J Lipid Res. 2007, 48 (5): 1150-1158. 10.1194/jlr.M600549-JLR200.
DeMar JC, Lee HJ, Ma K, Chang L, Bell JM, Rapoport SI, Bazinet RP: Brain elongation of linoleic acid is a negligible source of the arachidonate in brain phospholipids of adult rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006, 1761 (9): 1050-1059. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.06.006.
Ramadan E, Basselin M, Taha AY, Cheon Y, Chang L, Chen M, Rapoport SI: Chronic valproate treatment blocks D2-like receptor-mediated brain signaling via arachidonic acid in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2011, 61 (8): 1256-1264. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.07.025.
Wang XB, Osugi T, Uchida S: Different pathways for Ca2+ influx and intracellular release of Ca2+ mediated by muscarinic receptors in ileal longitudinal smooth muscle. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1992, 58 (4): 407-415. 10.1254/jjp.58.407.
Yang CM, Chou SP, Wang YY, Hsieh JT, Ong R: Muscarinic regulation of cytosolic free calcium in canine tracheal smooth muscle cells: Ca2+ requirement for phospholipase C activation. Br J Pharmacol. 1993, 110 (3): 1239-1247. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13948.x.
Sorimachi M, Yamagami K, Nishimura S: A muscarinic receptor agonist mobilizes Ca2+ from caffeine and inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores in cat adrenal chromaffin cells. Brain Res. 1992, 571 (1): 154-158. 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90523-C.
Liao CF, Schilling WP, Birnbaumer M, Birnbaumer L: Cellular responses to stimulation of the M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor as seen in murine L cells. J Biol Chem. 1990, 265 (19): 11273-11284.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the NIA intramural research program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
AYT, ER and SIR conceived and designed the study. AYT, ER, LC and MC performed the experiments. AYT and ER analyzed the data. AYT wrote the manuscript. ER, LC, MC and SIR reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12868_2014_3806_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Additional file 1: Table S1.: Plasma unesterified fatty acid concentrations (nmol/ml) in rats treated with saline or quinpirole. (DOC 40 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Taha, A.Y., Chang, L., Chen, M. et al. D2-like receptor activation does not initiate a brain docosahexaenoic acid signal in unanesthetized rats. BMC Neurosci 15, 113 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-15-113
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-15-113