Abstract
Rationale and objectives
Signal transduction involving the activation of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) to release arachidonic acid (AA) from membrane phospholipids, when coupled to dopamine D1- and D2-type receptors, can be imaged in rats having a chronic unilateral lesion of the substantia nigra. It is not known, however, if the signaling responses occur in the absence of a lesion. To determine this, we used our in vivo fatty acid method to measure signaling in response to D1 and D2 receptor agonists given acutely to unanesthetized rats.
Methods
[1-14C]AA was injected intravenously in unanesthetized rats, and incorporation coefficients k* for AA (brain radioactivity/integrated plasma radioactivity) were measured using quantitative autoradiography in 61 brain regions. The animals were administered i.v. the D2 receptor agonist, quinpirole (1 mg kg−1, i.v.), the D1 receptor agonist SKF-38393 (5 mg kg−1, i.v.), or vehicle/saline.
Results
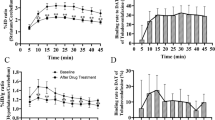
Quinpirole increased k* significantly in multiple brain regions rich in D2-type receptors, whereas SKF-38393 did not change k* significantly in any of the 61 regions examined.
Conclusions
In the intact rat brain, D2 but not D1 receptors are coupled to the activation of PLA2 and the release of AA.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- rCMRglc :
-
regional cerebral metabolic rate for glucose
- PLA2 :
-
phospholipase A2
- AA:
-
arachidonic acid
- PLC:
-
phospholipase C
- sn :
-
stereospecifically numbered
References
Barone P, Davis TA, Braun AR, Chase TN (1986) Dopaminergic mechanisms and motor function: characterization of D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptor interactions. Eur J Pharmacol 123:109–114
Basselin M, Chang L, Seemann R, Bell JM, Rapoport SI (2003) Chronic lithium administration increases cholinergic and decreases dopaminergic-agonist induced signal transduction via arachidonic acid in awake rats. Soc Neurosci Abstr 33:799.1
Bordi F, Meller E (1989) Enhanced behavioral stereotypies elicited by intrastriatal injection D1 and D2 dopamine agonists in intact rats. Brain Res 504:276–283
Bristow LJ, Cook GP, Patel S, Curtis N, Mawer I, Kulagowski JJ (1998) Discriminative stimulus properties of the putative dopamine D3 receptor agonist, (+)-PD 128907: role of presynaptic dopamine D2 autoreceptors. Neuropharmacology 37:793–802
Chang MCJ, Arai T, Freed LM, Wakabayashi S, Channing MA, Dunn BB, Der MG, Bell JM, Sasaki T, Herscovitch P, Eckelman WC, Rapoport SI (1997) Brain incorporation of [1-11C]-arachidonate in normocapnic and hypercapnic monkeys, measured with positron emission tomography. Brain Res 755:74–83
Chen YF, Jin HK, Paul R, Nagahama S (1988) Blunted pressor responsiveness to quinpirole, a specific dopamine D2 receptor agonist, in conscious deoxycorticosterone acetate/NaCl hypertensive rats is related to atrial natriuretic peptide release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:485–492
Cooper JR, Bloom FE, Roth RH (2003) The biochemical basis of neuropharmacology, 8th edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Coronas V, Krantic S, Jourdan F, Moyse E (1999) Dopamine receptor coupling to adenylyl cyclase in rat olfactory pathway: a combined pharmacological–radioautographic approach. Neuroscience 90:69–78
DeGeorge JJ, Nariai T, Yamazaki S, Williams WM, Rapoport SI (1991) Arecoline-stimulated brain incorporation of intravenously administered fatty acids in unanesthetized rats. J Neurochem 56:352–355
DeMar JC, Ma K, Bell J, Rapoport SI (2004) Brain conversion of linoleic to arachidonic acid is not a major source of the arachidonate found in brain phospholipids of adult rats. Abstr., International workshop on brain uptake and utilization of fatty acids, lipids and lipoproteins, October 7–9, 2004, Bethesda, MD
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Garau L, Govoni S, Stefanini E, Trabucchi M, Spano PF (1978) Dopamine receptors: pharmacological and anatomical evidences indicate that two distinct dopamine receptor populations are present in rat striatum. Life Sci 23:1745–1750
Gerfen CR (1992) The neostriatal mosaic: multiple levels of compartmental organization. Trends Neurosci 15:133–139
Gerfen CR, Engber TM, Mahan LC, Susel Z, Chase TN, Monsma FJ Jr, Sibley DR (1990) D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-regulated gene expression of striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons. Science 250:1429–1432
Gerfen CR, Keefe KA, Gauda EB (1995) D1 and D2 dopamine receptor function in the striatum: coactivation of D1- and D2-dopamine receptors on separate populations of neurons results in potentiated immediate early gene response in D1-containing neurons. J Neurosci 15:8167–8176
Geurts M, Hermans E, Maloteaux JM (1999) Assessment of striatal D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-G protein coupling by agonist-induced [35S]GTP gamma S binding. Life Sci 65:1633–1645
Giovacchini G, Chang MC, Channing MA, Toczek M, Mason A, Bokde AL, Connolly C, Vuong BK, Ma Y, Der MG, Doudet DJ, Herscovitch P, Eckelman WC, Rapoport SI, Carson RE (2002) Brain incorporation of [11C]arachidonic acid in young healthy humans measured with positron emission tomography. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab 22:1453–1462
Grange E, Rabin O, Bell J, Rapoport SI, Chang MCJ (1998) Manoalide, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor, inhibits arachidonate incorporation and turnover in brain phospholipids of the awake rat. Neurochem Res 23:1251–1257
Haile CN, Carey G, Varty GB, Coffin VL (2000) The dopamine D(1) receptor agonist SKF-82958 serves as a discriminative stimulus in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 388:125–131
Hayakawa T, Chang MC, Bell JM, Seemann R, Rapoport SI, Appel NM (1998) Fatty acid incorporation depicts brain activity in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 807:177–181
Hayakawa T, Chang MC, Rapoport SI, Appel NM (2001) Selective dopamine receptor stimulation differentially affects [3H]arachidonic acid incorporation, a surrogate marker for phospholipase A2-mediated neurotransmitter signal transduction, in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:1074–1084
He L, Di Monte DA, Langston JW, Quik M (2000) Autoradiographic analysis of dopamine receptor-stimulated [(35)S]GTPgammaS binding in rat striatum. Brain Res 885:133–136
Jones CR, Arai T, Bell JM, Rapoport SI (1996) Preferential in vivo incorporation of [3H]arachidonic acid from blood into rat brain synaptosomal fractions before and after cholinergic stimulation. J Neurochem 67:822–829
Kabai P, Stewart MG, Tarcali J, Csillag A (2004) Inhibiting effect of D1, but not D2 antagonist administered to the striatum on retention of passive avoidance in the chick. Neurobiol Learn Mem 81:155–158
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277:93–96
Koene P, Prinssen EP, Cools AR (1993) Involvement of the nucleus accumbens in oral behaviour in the freely moving rat. Eur J Pharmacol 233:151–156
Lawler CP, Gilmore JH, Watts VJ, Walker QD, Southerland SB, Cook LL, Mathis CA, Mailman RB (1995) Interhemispheric modulation of dopamine receptor interactions in unilateral 6-OHDA rodent model. Synapse 21:299–311
Levant B, Grigoriadis DE, DeSouza EB (1992) Characterization of [3H]quinpirole binding to D2-like dopamine receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 262:929–935
Levey AI, Hersch SM, Rye DB, Sunahara RK, Niznik HB, Kitt CA, Price DL, Maggio R, Brann MR, Ciliax BJ (1993) Localization of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in brain with subtype-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:8861–8865
Meller E, Bordi F, Bohmaker K (1988) Enhancement by the D1 dopamine agonist SKF 38393 of specific components of stereotypy elicited by the D2 agonists LY 171555 and RU 24213. Life Sci 42:2561–2567
Nilsson CL, Hellstrand M, Ekman A, Eriksson E (1998) Direct dopamine D2-receptor-mediated modulation of arachidonic acid release in transfected CHO cells without the concomitant administration of a Ca2+-mobilizing agent. Br J Pharmacol 124:1651–1658
Ong WY, Sandhya TL, Horrocks LA, Farooqui AA (1999) Distribution of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 in the normal rat brain. J Hirnforsch 39:391–400
Palacios JM, Wiederhold KH (1985) Dopamine D2 receptor agents, but not dopamine D1, modify brain glucose metabolism. Brain Res 327:390–394
Pardue S, Rapoport SI, Bosetti F (2003) Co-localization of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and cyclooxygenase-2 in rhesus monkey cerebellum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 116:106–114
Paxinos G, Watson C (1987) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3nd edn. Academic, San Diego
Piomelli D, Pilon C, Giros B, Sokoloff P, Martres MP, Schwartz JC (1991) Dopamine activation of the arachidonic acid cascade as a basis for D1/D2 receptor synergism. Nature 353:164–167
Qu Y, Chang L, Klaff J, Balbo A, Rapoport SI (2003) Imaging brain phospholipase A2 activation in awake rats in response to the 5-HT2A/2C agonist (±)2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane (DOI). Neuropsychopharmacology 28:244–252
Rapoport SI (2003) Quantifying and imaging brain arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acid metabolism in vivo. J Pediatr 143:S26–S33
Rasolonjanahary R, Gerard C, Dufour MN, Homburger V, Enjalbert A, Guillon G (2002) Evidence for a direct negative coupling between dopamine-D2 receptors and PLC by heterotrimeric Gi1/2 proteins in rat anterior pituitary cell membranes. Endocrinology 143:747–754
Rinken A, Finnman UB, Fuxe K (1999) Pharmacological characterization of dopamine-stimulated [35S]-guanosine 5′(gamma-thiotriphosphate) ([35S]GTPgammaS) binding in rat striatal membranes. Biochem Pharmacol 57:155–162
Rintala J, Seemann R, Chandrasekaran K, Rosenberger TA, Chang L, Contreras MA, Rapoport SI, Chang MC (1999) An arachidonic acid-specific 85 kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2 is a target for chronic lithium in rat brain. NeuroReport 10:3887–3890
Robinson PJ, Noronha J, DeGeorge JJ, Freed LM, Nariai T, Rapoport SI (1992) A quantitative method for measuring regional in vivo fatty-acid incorporation into and turnover within brain phospholipids: review and critical analysis. Brain Res Rev 17:187–214
Schechter MD (1995) The discriminative properties of the D1 dopamine agonist dihydrexidine in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 119:79–84
Setler PE, Sarau HM, Zirkle CL, Saunders HL (1978) The central effects of a novel dopamine agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 50:419–430
Sokoloff L (1999) Energetics of functional activation in neural tissues. Neurochem Res 24:321–329
Sokoloff L, Reivich M, Kennedy C, Des Rosiers MH, Patlak CS, Pettigrew KD, Sakurada O, Shinohara M (1977) The [14C]deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem 28:897–916
Szumlinski KK, Szechtman H (2002) D2 receptor blockade in the dorsal raphe increases quinpirole-induced locomotor excitation. NeuroReport 13:563–566
Trugman JM, Wooten GF (1987) Selective D1 and D2 dopamine agonists differentially alter basal ganglia glucose utilization in rats with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine substantia nigra lesions. J Neurosci 7:2927–2935
Trugman JM, James CL (1993) D1 dopamine agonist and antagonist effects on regional cerebral glucose utilization in rats with intact dopaminergic innervation. Brain Res 607:270–274
Tu B, Bazan NG (2003) Hippocampal kindling epileptogenesis upregulates neuronal cyclooxygenase-2 expression in neocortex. Exp Neurol 179:167–175
Vial D, Piomelli D (1995) Dopamine D2 receptors potentiate arachidonate release via activation of cytosolic, arachidonate-specific phospholipase A2. J Neurochem 64:2765–2772
Watts VJ, Lawler CP, Gonzales AJ, Zhou QY, Civelli O, Nichols DE, Mailman RB (1995) Spare receptors and intrinsic activity: studies with D1 dopamine receptor agonists. Synapse 21:177–187
Weichel O, Hilgert M, Chatterjee SS, Lehr M, Klein J (1999) Bilobalide, a constituent of Gingko biloba, inhibits NMDA-induced phospholipase A2 activation and phospholipid breakdown in rat hippocampus. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 360:609–615
Youdim KA, Martin A, Joseph JA (2000) Essential fatty acids and the brain: possible health implications. Int J Dev Neurosci 18:383–399
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharjee, A.K., Chang, L., Lee, HJ. et al. D2 but not D1 dopamine receptor stimulation augments brain signaling involving arachidonic acid in unanesthetized rats. Psychopharmacology 180, 735–742 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2208-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2208-4