Abstract
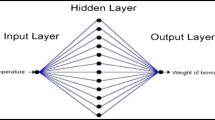
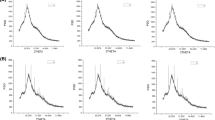
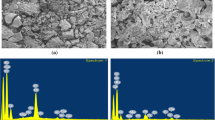
Waste materials generated from agriculture and fruit-processing industries can provide cost-effective and cost-efficient materials for the removal of contaminants from aqueous medium. This study deals with adsorption of copper ions from aqueous phase by employing orthophosphoric acid–modified biochar derived from coconut (Cocos nucifera) husk. Biochar characteristics demonstrated increased surface area (24 times) and a porous structure with functional groups such as –OH, –N-H, –CH2, C=O, and –C-N. These were responsible for active adsorption sites. Key process parameters were optimized and maximum removal efficiency was obtained at dose (0.4 g/L), time (60 min), pH (6), and initial concentration (10 mg/L). To predict the adsorptive removal, artificial neural network (ANN) modeling was performed. The mean absolute error (MAE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and coefficient of determination (R2) provided by ANN model at optimized conditions were found to be 2.63, 4.60, and 0.91, respectively. The behavior of Cu(II) adsorption was closely predicted based on a feed-forward ANN (back propagation) learning algorithm with 4–2–1 topological arrangement. The equilibrium data suggested Langmuir isotherm with a maximum monolayer adsorption capacity of 175.44 mg/g and R2 = 0.990 to be the best-suited model. Coconut husk, being an easily available agro-waste, can therefore be used efficiently as a low-cost precursor for the development of an economical adsorbent for inorganic and organic pollutants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demirbas A (2008) Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: a review. J Hazard Mater 157:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.024
Kavand M, Eslami P, Razeh L (2020) The adsorption of cadmium and lead ions from the synthesis wastewater with the activated carbon: optimization of the single and binary systems. J Water Process Eng 34:101151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101151
Peng H, Gao P, Chu G, Pan B, Peng J, Xing B (2017) Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars. Environ Pollut 229:846–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.004
Kumar U, Bandyopadhyay M (2006) Sorption of cadmium from aqueous solution using pretreated rice husk. Bioresour Technol 97:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.027
Pradhan SK, Pareek V, Panwar J, Gupta S (2019) Synthesis and characterization of ecofriendly silver nanoparticles combined with yttrium oxide (Ag-Y2O3) nanocomposite with assorted adsorption capacity for Cu(II) and Cr(VI) removal: a mechanism perspective. J Water Process Eng 32:100917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100917
Aydın H, Bulut Y, Yerlikaya C (2008) Removal of copper (II) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto low-cost adsorbents. J Environ Manag 87:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.01.005
Aman T, Ahmad A, Usman M, Bano Q (2008) Potato peels as solid waste for the removal of heavy metal copper (II) from waste water/industrial effluent. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 63:116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.11.013
Damodaran D, Vidya Shetty K, Raj Mohan B (2013) Effect of chelaters on bioaccumulation of Cd (II), Cu (II), Cr (VI), Pb (II) and Zn (II) in Galerina vittiformis from soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 85:182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.05.031
Tapiero H, Townsend DM, Tew KD (2003) Trace elements in human physiology and pathology. Copper. Biomed Pharmacother 57:386–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0753-3322(03)00012-X
Nejadshafiee V, Islami MR (2020) Intelligent-activated carbon prepared from pistachio shells precursor for effective adsorption of heavy metals from industrial waste of copper mine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:1625–1639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06732-4
Thirugnanasambandham K, Sivakumar V (2015) An eco-friendly approach for copper (II) ion adsorption onto cotton seed cake and its characterization: simulation and validation. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 50:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.12.002
Zhou N, Zu J, Feng Q, Chen H, Li J, Zhong ME, Zhou Z, Zhuang S (2019) Effect of pyrolysis condition on the adsorption mechanism of heavy metals on tobacco stem biochar in competitive mode. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:26947–26962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05917-1
Pellera F, Giannis A, Kalderis D et al (2012) Adsorption of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solutions on biochars prepared from agricultural by-products. J Environ Manag 96:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.10.010
Ben-Ali S, Jaouali I, Souissi-najar S, Ouederni A (2017) Characterization and adsorption capacity of raw pomegranate peel biosorbent for copper removal. J Clean Prod 142:3809–3821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.081
Bogusz A, Oleszczuk P, Dobrowolski R (2015) Application of laboratory prepared and commercially available biochars to adsorption of cadmium, copper and zinc ions from water. Bioresour Technol 196:540–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.006
Mohan D, Pittman CU, Bricka M et al (2007) Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J Colloid Interface Sci 310:57–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.01.020
Yadav K, Jagadevan S (2019) Influence of process parameters on synthesis of biochar by pyrolysis of biomass: an alternative source of energy. Pyrolysis. IntechOpen, In, pp 1–14
Yadav K, Tyagi M, Kumari S, Jagadevan S (2019) Influence of process parameters on optimization of biochar fuel characteristics derived from rice husk: a promising alternative solid fuel. BioEnergy Res 12:1052–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-019-10027-4
Xu X, Gao B, Jin B, Yue Q (2016) Removal of anionic pollutants from liquids by biomass materials: a review. J Mol Liq 215:565–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.12.101Review
Yadav K, Jagadevan S (2020) Effect of pyrolysis of rice husk–derived biochar on the fuel characteristics and adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution. Bioenergy Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-020-10189-6
Bedin KC, Martins AC, Cazetta AL, Pezoti O, Almeida VC (2016) KOH-activated carbon prepared from sucrose spherical carbon: adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for Methylene Blue removal. Chem Eng J 286:476–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.099
Laysandra L, Ondang IJ, Ju YH, Putro JN, Santoso SP, Soetarejo FE, Ismadji S (2019) An environment-friendly composite as an adsorbent for removal Cu (II) ions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:22979–22989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05524-0
Rehman M, Liu L, Wang Q, Saleem MH, Bashir S, Ullah S, Peng D (2019) Copper environmental toxicology, recent advances, and future outlook: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18003–18016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05073-6
Saber M, Takahashi F, Yoshikawa K (2018) Characterization and application of microalgae hydrochar as a low-cost adsorbent for Cu(II) ion removal from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:32721–32734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3106-8
Song J, He Q, Hu X, Zhang W, Wang C, Chen R, Wang H, Mosa A (2019) Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) by biochar derived from Artemisia argyi stem. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:13221–13234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04863-2
Sun K, Tang J, Gong Y, Zhang H (2015) Characterization of potassium hydroxide (KOH) modified hydrochars from different feedstocks for enhanced removal of heavy metals from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16640–16651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4849-0
Pollard SJT, Fowler GD, Sollars CJ, Perry R (1992) Low-cost adsorbents for waste and wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 116:31–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(92)90363-W
Adeniyi AG, Ighalo JO (2019) Biosorption of pollutants by plant leaves: an empirical review. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103100
Ighalo JO, Adeniyi AG (2020) Adsorption of pollutants by plant bark derived adsorbents: an empirical review. J Water Process Eng 35:101228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101228
Wu W, Li J, Niazi NK, Müller K, Chu Y, Zhang L, Yuan G, Lu K, Song Z, Wang H (2016) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on lead immobilization by chemically modified coconut fiber-derived biochars in aqueous environments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:22890–22896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7428-0
Fierro V, Muñiz G, Basta AH, el-Saied H, Celzard A (2010) Rice straw as precursor of activated carbons: activation with ortho-phosphoric acid. J Hazard Mater 181:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.062
Yakout SM, Sharaf El-Deen G (2016) Characterization of activated carbon prepared by phosphoric acid activation of olive stones. Arab J Chem 9:S1155–S1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.12.002
Ghaedi AM, Vafaei A (2017) Applications of artificial neural networks for adsorption removal of dyes from aqueous solution: a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 245:20–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2017.04.015
Ghaedi M, Shojaeipour E, Ghaedi AM, Sahraei R (2015) Isotherm and kinetics study of malachite green adsorption onto copper nanowires loaded on activated carbon: artificial neural network modeling and genetic algorithm optimization. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 142:135–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.01.086
Agarwal S, Tyagi I, Kumar V, et al (2016) Kinetics and thermodynamics of Malachite Green dye removal from aqueous phase using iron nanoparticles loaded on ash 223:1340–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.04.039
Ahmadi Azqhandi MH, Ghaedi M, Yousefi F, Jamshidi M (2017) Application of random forest, radial basis function neural networks and central composite design for modeling and/or optimization of the ultrasonic assisted adsorption of brilliant green on ZnS-NP-AC. J Colloid Interface Sci 505:278–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.05.098
Prabhakar R, Samadder SR (2020) Use of adsorption-influencing parameters for designing the batch adsorber and neural network–based prediction modelling for the aqueous arsenate removal using combustion synthesised nano-alumina. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:26367–26384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08975-y
Tanzifi M, Hosseini SH, Kiadehi AD, Olazar M, Karimipour K, Rezaiemehr R, Ali I (2017) Artificial neural network optimization for methyl orange adsorption onto polyaniline nano-adsorbent: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 244:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.122
Yadav K, Jagadevan S (2021) Influence of torrefaction and pyrolysis on engineered biochar and its applicability in defluoridation: insight into adsorption mechanism, batch adsorber design and artificial neural network modelling. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 154:105015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105015
Malik R, Dahiya S, lata S (2017) An experimental and quantum chemical study of removal of utmostly quantified heavy metals in wastewater using coconut husk: a novel approach to mechanism. Int J Biol Macromol 98:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.100
Sujana MG, Anand S (2011) Fluoride removal studies from contaminated ground water by using bauxite. Desalination 267:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.09.030
Tran HN, You SJ, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Chao HP (2017) Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water Res 120:88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014
Larous S, Meniai A, Lehocine MB (2005) Experimental study of the removal of copper from aqueous solutions by adsorption using sawdust. Desalination 185:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.03.090
Lasheen MR, Ammar NS, Ibrahim HS (2012) Adsorption /desorption of Cd (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) using chemically modified orange peel: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Solid State Sci 14:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2011.11.029
Ahmad M, Lee SS, Dou X, Mohan D, Sung JK, Yang JE, Ok YS (2012) Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soybean stover- and peanut shell-derived biochar properties and TCE adsorption in water. Bioresour Technol 118:536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.042
Intani K, Latif S, Kabir AKMR, Müller J (2016) Effect of self-purging pyrolysis on yield of biochar from maize cobs, husks and leaves. Bioresour Technol 218:541–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.114
Liu WJ, Jiang H, Yu HQ (2015) Development of biochar-based functional materials: toward a sustainable platform carbon material. Chem Rev 115:12251–12285. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00195
Arief VO, Trilestari K, Sunarso J, Indraswati N, Ismadji S (2008) Recent progress on biosorption of heavy metals from liquids using low cost biosorbents: characterization, biosorption parameters and mechanism studies. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 36:937–962. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200800167
Xu H, Liu Y (2008) Mechanisms of Cd2+, Cu2+ and Ni2+ biosorption by aerobic granules. Sep Purif Technol 58:400–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2007.05.018
Harvey OR, Herbert BE, Rhue RD, Kuo LJ (2011) Metal interactions at the biochar-water interface: energetics and structure-sorption relationships elucidated by flow adsorption microcalorimetry. Environ Sci Technol 45:5550–5556. https://doi.org/10.1021/es104401h
Wan J, Chen L, Li Q, Ye Y, Feng X, Zhou A, Long X, Xia D, Zhang TC (2020) A novel hydrogel for highly efficient adsorption of Cu(II): synthesis, characterization, and mechanisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:26621–26630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09082-8
Li AY, Deng H, Jiang YH, Ye CH, Yu BG, Zhou XL, Ma AY, (2020) Superefficient Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Mg-Loaded Biochars: Adsorption Characteristics and Removal Mechanisms. Langmuir 36 (31):9160-9174. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c01454
Vaghetti JCP, Lima EC, Royer B, da Cunha BM, Cardoso NF, Brasil JL, Dias SLP (2009) Pecan nutshell as biosorbent to remove Cu(II), Mn(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 162:270–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.039
Aksu Z, Işoǧlu IA (2005) Removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solution by biosorption onto agricultural waste sugar beet pulp. Process Biochem 40:3031–3044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.02.004
Ghasemi SM, Mohseni-Bandpei A, Ghaderpoori M et al (2017) Application of modified maize hull for removal of cu(II)ions from aqueous solutions. Environ Prot Eng 43:93–103. https://doi.org/10.5277/epe170408
Amer MW, Ahmad RA, Awwad AM (2015) Biosorption of Cu(II), Ni(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by Sophora japonica pods powder. Int J Ind Chem 6:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40090-014-0030-8
Vuković GD, Marinković AD, Škapin SD, Ristić MĐ, Aleksić R, Perić-Grujić AA, Uskoković PS (2011) Removal of lead from water by amino modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J 173:855–865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.036
Patnukao P, Pavasant P (2008) Activated carbon from Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehn bark using phosphoric acid activation. Bioresour Technol 99:8540–8543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.10.049
Mouni L, Merabet D, Bouzaza A, Belkhiri L (2011) Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions using activated carbon developed from Apricot stone. Desalination 276:148–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.03.038
Kadirvelu K, Karthika C, Vennilamani N, Pattabhi S (2005) Activated carbon from industrial solid waste as an adsorbent for the removal of Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Chemosphere 60:1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.047
Kalavathy MH, Miranda LR (2010) Moringa oleifera—a solid phase extractant for the removal of copper, nickel and zinc from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 158:188–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.12.039
Sadeghiamirshahidi M, Eslam Kish T, Doulati Ardejani F (2013) Application of artificial neural networks to predict pyrite oxidation in a coal washing refuse pile. Fuel 104:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.10.016
Tayebi HA, Ghanei M, Aghajani K, Zohrevandi M (2019) Modeling of reactive orange 16 dye removal from aqueous media by mesoporous silica/ crosslinked polymer hybrid using RBF, MLP and GMDH neural network models. J Mol Struct 1178:514–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.10.040
Hussain MA, Shafiur Rahman M, Ng CW (2002) Prediction of pores formation (porosity) in foods during drying: generic models by the use of hybrid neural network. J Food Eng 51:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0260-8774(01)00063-2
Prabhakar R, Samadder SR (2018) Low cost and easy synthesis of aluminium oxide nanoparticles for arsenite removal from groundwater: a complete batch study. J Mol Liq 250:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.173
Argun ME, Dursun S, Ozdemir C, Karatas M (2007) Heavy metal adsorption by modified oak sawdust: thermodynamics and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 141:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.095
Acheampong MA, Pereira JPC, Meulepas JW, Lens PNL (2011) Biosorption of Cu (II) onto agricultural materials from tropical regions. J Chem Technol Biotecnol 86:1184–1194. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2630
Baek M, Ijagbemi CO, Kim D (2010) Removal of Malachite Green from aqueous solution using degreased coffee bean. J Hazard Mater 176:820–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.110
Namasivayam C, Kavitha D (2002) Removal of Congo Red from water by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from coir pith, an agricultural solid waste. Dyes Pigments 54:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(02)00025-6
Romero-Cano LA, García-Rosero H, Gonzalez-Gutierrez LV, Baldenegro-Pérez LA, Carrasco-Marín F (2017) Functionalized adsorbents prepared from fruit peels: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for copper adsorption in aqueous solution. J Clean Prod 162:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.032
Izquierdo M, Marzal P, Lens PNL (2013) Effect of organic ligands on copper (II) removal from metal plating wastewater by Orange Peel-based biosorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut 224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1507-3
Basha S, Murthy ZVP, Jha B (2009) Sorption of Hg (II) onto Carica papaya : experimental studies and design of batch sorber. Chem Eng J 147:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.07.005
Kumar KV, Porkodi K (2007) Batch adsorber design for different solution volume/adsorbent mass ratios using the experimental equilibrium data with fixed solution volume/adsorbent mass ratio of malachite green onto orange peel. Dyes Pigments 74:590–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.03.024
Ramos RL, Ovalle-Turrubiartes J, Sanchez-Castillo MA (1999) Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution on aluminum-impregnated carbon. Carbon N Y 37:609–617
Sciban M, Klasnja M, Skrbic B, (2006) Modified softwood sawdust as adsorbent of heavy metal ions from water. J Hazard Mater 136 (2):266–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.009
Kalavathy MH, Miranda LR, (2010) Comparison of copper adsorption from aqueous solution using modified and unmodified Hevea brasiliensis saw dust. Desalination 255 (1–3):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.12.028
Özer A, Özer D, Özer A, (2004) The adsorption of copper(II) ions on to dehydrated wheat bran (DWB): determination of the equilibrium and thermodynamic parameters. Process Biochemistry 39 (12):2183–2191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2003.11.008
Feng N, Guo X, Liang S, (2009) Adsorption study of copper (II) by chemically modified orange peel. J Hazard Mater 164 (2–3):1286–1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.096
Benaïssa H, Elouchdi MA, (2007) Removal of copper ions from aqueous solutions by dried sunflower leaves. Chem Eng Process 46 (7):614–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2006.08.006
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge DST-FIST for the infrastructure support to the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, IIT(ISM) Dhanbad. The authors would also like to express their gratitude to CRF, IIT(ISM), and AMU, Aligarh for instrumental analysis.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was supported by FRS Scheme of IIT(ISM) (Ref No. FRS/86/2014-2015/ESE) and PhD studentship for K.Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Krishna Yadav: conceived the idea, experimental design, analysis, methodology, original draft preparation; Mohd. Raphi: experimental design, analysis, methodology; Sheeja Jagadevan: supervision, conceptualization, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 269 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, K., Raphi, M. & Jagadevan, S. Adsorption of copper(II) on chemically modified biochar: a single-stage batch adsorber design and predictive modeling through artificial neural network. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 14, 6011–6026 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01494-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01494-x