Abstract
Purpose
Xylitol is used in the food and pharmaceutical industries as a sweetener, and its consumption rate has remarkably increased over the years. Currently, xylitol is produced through a chemical reduction method. However, considering the global climate change issue, the development of eco-friendly, renewable, and sustainable substrates for the production of high-value platform chemicals such as xylitol is the need of the hour. Hence, the present study aimed to use a microbial process for xylitol production.
Methods
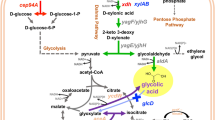
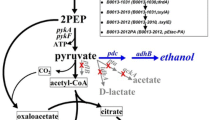
Escherichia coli M15 platform was used to overexpress the D-xylose reductase (XR) gene from a mesophilic yeast, Candida tropicalis GRA1. The 37-KDa CtXR sequence exhibited a highly conserved active site structure, where a tetrad of residues (Tyr51, Lys80, His113, and Asp46) was located at the base of the substrate-binding pocket. To mitigate the rate-limiting step of cofactor supply in the bioconversion of xylose to xylitol, overexpression of XR genes coupled with auxiliary substrates was used toward in vivo cofactor regeneration.
Results
In the presence of xylose as the only carbon source, the M15 CtXRΔ produced 2.1 g L−1 of xylitol. The xylitol titer showed a steady-state increase with the addition of auxiliary substrates glucose and glycerol to 3.4 and 6.4 g L−1, respectively. Further, M15 CtXRΔ as a whole-cell biocatalyst in alkali pretreated detoxified corncob hydrolysate produced xylitol titer of 3.7 g L−1.
Conclusion
Therefore, we successfully produced xylitol from corncob hydrolysates using the engineered E. coli M15 as whole-cell biocatalysts. Further, this process can be up scaled for the synthesis of eco-friendly high-value green chemicals.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and its supplementary information files.
References
Chattopadhyay, S., Raychaudhuri, U., Chakraborty, R.: Artificial sweeteners—a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 611–621 (2014)
Lugani, Y., Sooch, B.S.: Xylitol, an emerging prebiotic: a review. Int J. Appl. Pharm. Biol. Res. 2, 67–73 (2017)
Arcaño, Y.D., García, O.D.V., Mandelli, D., Carvalho, W.A., Pontes, L.A.M.: Xylitol: a review on the progress and challenges of its production by chemical route. Catal. Today 344, 2–14 (2020)
Ravella SR, Gallagher J, Fish S, Prakasham RS: Overview on commercial production of xylitol, economic analysis and market trends. In: d-Xylitol, pp. 291–306. Springer, New York (2012)
de Paula, R.G., Antoniêto, A.C.C., Ribeiro, L.F.C., Srivastava, N., O’Donovan, A., Mishra, P.K., Gupta, V.K., Silva, R.N.: Engineered microbial host selection for value-added bioproducts from lignocellulose. Biotechnol. Adv. 37, 107347 (2019)
Van Dyk, J.S., Pletschke, B.I.: A review of lignocellulose bioconversion using enzymatic hydrolysis and synergistic cooperation between enzymes—factors affecting enzymes, conversion and synergy. Biotechnol. Adv. 30, 1458–1480 (2012)
Granström, T.B., Izumori, K., Leisola, M.: A rare sugar xylitol. Part II: biotechnological production and future applications of xylitol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74, 273–276 (2007)
Rafiqul, I.S.M., Sakinah, A.M.M.: Processes for the production of xylitol—a review. Food Rev. Intl. 29, 127–156 (2013)
Nidetzky, B., Klimacek, M., Mayr, P.: Transient-state and steady-state kinetic studies of the mechanism of NADH-dependent aldehyde reduction catalyzed by xylose reductase from the yeast Candida tenuis. Biochemistry 40, 10371–10381 (2001)
Winkelhausen, E., Kuzmanova, S.: Microbial conversion of D-xylose to xylitol. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 86, 1–14 (1998)
Jeffries, T.W., Jin, Y.S.: Metabolic engineering for improved fermentation of pentoses by yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 63, 495–509 (2004)
Atzmüller, D., Ullmann, N., Zwirzitz, A.: Identification of genes involved in xylose metabolism of Meyerozyma guilliermondii and their genetic engineering for increased xylitol production. AMB Express 10, 1–11 (2020)
Chen, X., Jiang, Z.-H., Chen, S., Qin, W.: Microbial and bioconversion production of D-xylitol and its detection and application. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 6, 834 (2010)
Rao, L.V., Goli, J.K., Gentela, J., Koti, S.: Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass to xylitol: an overview. Biores. Technol. 213, 299–310 (2016)
Sampaio, F.C., Silveira, W.B.D., Chaves-Alves, V.M., Passos, F.M.L., Coelho, J.L.C.: Screening of filamentous fungi for production of xylitol from D-xylose. Braz. J. Microbiol. 34, 325–328 (2003)
Akinterinwa, O., Cirino, P.C.: Heterologous expression of D-xylulokinase from Pichia stipitis enables high levels of xylitol production by engineered Escherichia coli growing on xylose. Metab. Eng. 11, 48–55 (2009)
Louie, T.M., Louie, K., DenHartog, S., Gopishetty, S., Subramanian, M., Arnold, M., Das, S.: Production of bio-xylitol from d-xylose by an engineered Pichia pastoris expressing a recombinant xylose reductase did not require any auxiliary substrate as electron donor. Microb. Cell Fact. 20, 1–13 (2021)
Zhang, L., Chen, Z., Wang, J., Shen, W., Li, Q., Chen, X.: Stepwise metabolic engineering of Candida tropicalis for efficient xylitol production from xylose mother liquor. Microb. Cell Fact. 20, 1–12 (2021)
de Albuquerque, T.L., da Silva Jr, I.J., de Macedo, G.R., Rocha, M.V.P.: Biotechnological production of xylitol from lignocellulosic wastes: a review. Process Biochem. 49, 1779–1789 (2014)
Buijs, N.A., Siewers, V., Nielsen, J.: Advanced biofuel production by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 17, 480–488 (2013)
Park, J.M., Vinuselvi, P., Lee, S.K.: The mechanism of sugar-mediated catabolite repression of the propionate catabolic genes in Escherichia coli. Gene 504, 116–121 (2012)
Parachin, N.S., Bergdahl, B., van Niel, E.W.J., Gorwa-Grauslund, M.F.: Kinetic modelling reveals current limitations in the production of ethanol from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 13, 508–517 (2011)
Young, E.M., Tong, A., Bui, H., Spofford, C., Alper, H.S.: Rewiring yeast sugar transporter preference through modifying a conserved protein motif. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, 131–136 (2014)
Karhumaa, K., Fromanger, R., Hahn-Hägerdal, B., Gorwa-Grauslund, M.-F.: High activity of xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase improves xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 73, 1039–1046 (2007)
Du, J., Li, S., Zhao, H.: Discovery and characterization of novel d-xylose-specific transporters from Neurospora crassa and Pichia stipitis. Mol. BioSyst. 6, 2150–2156 (2010)
Khankal, R., Chin, J.W., Cirino, P.C.: Role of xylose transporters in xylitol production from engineered Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 134, 246–252 (2008)
Hasona, A., Kim, Y., Healy, F.G., Ingram, L.O., Shanmugam, K.T.: Pyruvate formate lyase and acetate kinase are essential for anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli on xylose. J. Bacteriol. 186, 7593–7600 (2004)
Sumiya, M., Davis, E.O., Packman, L.C., McDonald, T.P., Henderson, P.J.: Molecular genetics of a receptor protein for D-xylose, encoded by the gene xylF, in Escherichia coli. Recept. Chann. 3, 117–128 (1995)
Ahlem, C., Huisman, W., Neslund, G., Dahms, A.S.: Purification and properties of a periplasmic D-xylose-binding protein from Escherichia coli K-12. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 2926–2931 (1982)
Sofia, H.J., Burland, V., Daniels, D.L., Plunkett Iii, G., Blattner, F.R.: Analysis of the Escherichia coli genome. V. DNA sequence of the region from 76.0 to 81.5 minutes. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 2576–2586 (1994)
Ariyan, M., Uthandi, S.: Xylitol production by xylose reductase over producing recombinant Escherichia coli M15. Madras Agric. J. 106, 205–209 (2019)
Kawaguchi, H., Vertès, A.A., Okino, S., Inui, M., Yukawa, H.: Engineering of a xylose metabolic pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 3418–3428 (2006)
Wang, Y., Shi, W.-L., Liu, X.-Y., Shen, Y., Bao, X.-M., Bai, F.-W., Qu, Y.-B.: Establishment of a xylose metabolic pathway in an industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotech. Lett. 26, 885–890 (2004)
Young, E., Lee, S.-M., Alper, H.: Optimizing pentose utilization in yeast: the need for novel tools and approaches. Biotechnol. Biofuels 3, 1–12 (2010)
Zhang, M., Eddy, C., Deanda, K., Finkelstein, M., Picataggio, S.: Metabolic engineering of a pentose metabolism pathway in ethanologenic Zymomonas mobilis. Science 267, 240–243 (1995)
Cirino, P.C., Chin, J.W., Ingram, L.O.: Engineering Escherichia coli for xylitol production from glucose-xylose mixtures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 95, 1167–1176 (2006)
Qi, X., Zhang, H., Magocha, T.A., An, Y., Yun, J., Yang, M., Xue, Y., Liang, S., Sun, W., Cao, Z.: Improved xylitol production by expressing a novel D-arabitol dehydrogenase from isolated Gluconobacter sp. JX-05 and co-biotransformation of whole cells. Bioresour. Technol. 235, 50–58 (2017)
Jin, L.-Q., Yang, B., Xu, W., Chen, X.-X., Jia, D.-X., Liu, Z.-Q., Zheng, Y.-G.: Immobilization of recombinant Escherichia coli whole cells harboring xylose reductase and glucose dehydrogenase for xylitol production from xylose mother liquor. Biores. Technol. 285, 121344 (2019)
Ostergaard, S., Olsson, L., Nielsen, J.: Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64, 34–50 (2000)
Watanabe, S., Kodaki, T., Makino, K.: Complete reversal of coenzyme specificity of xylitol dehydrogenase and increase of thermostability by the introduction of structural zinc. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 10340–10349 (2005)
Watanabe, S., Saleh, A.A., Pack, S.P., Annaluru, N., Kodaki, T., Makino, K.: Ethanol production from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing protein engineered NADP+-dependent xylitol dehydrogenase. J. Biotechnol. 130, 316–319 (2007)
Yan, N.: Structural advances for the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) transporters. Trends Biochem. Sci. 38, 151–159 (2013)
Mussatto, S.I., Santos, J.C.: Roberto IeC: effect of pH and activated charcoal adsorption on hemicellulosic hydrolysate detoxification for xylitol production. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 79, 590–596 (2004)
Valliammai G: Xylan derived products by fermentation. Master Thesis 2017.
Chang, A.Y., Chau, V.W., Landas, J.A., Pang, Y.: Preparation of calcium competent Escherichia coli and heat-shock transformation. JEMI Methods 1, 22–25 (2017)
He F: Laemmli-sds-page. Bio-protocol 2011:e80–e80.
He F: Bradford protein assay. Bio-protocol 2011:e45–e45.
Waterhouse, A., Bertoni, M., Bienert, S., Studer, G., Tauriello, G., Gumienny, R., Heer, F.T., de Beer, T.A.P., Rempfer, C., Bordoli, L.: SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, W296–W303 (2018)
Tian, K., Zhao, X., Zhang, Y., Yau, S.: Comparing protein structures and inferring functions with a novel three-dimensional Yau-Hausdorff method. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 37, 4151–4160 (2019)
Smiley, K.L., Bolen, P.L.: Demonstration of D-xylose reductase and D-xylitol dehydrogenase in Pachysolen tannophilus. Biotechnol. Lett. 4, 607–610 (1982)
Veras, H.C.T., Parachin, N.S., Almeida, J.R.M.: Comparative assessment of fermentative capacity of different xylose-consuming yeasts. Microb. Cell Fact. 16, 1–8 (2017)
Rajakumari, S., Grillitsch, K., Daum, G.: Synthesis and turnover of non-polar lipids in yeast. Prog. Lipid Res. 47, 157–171 (2008)
Saloheimo, A., Rauta, J., Stasyk, V., Sibirny, A.A., Penttilä, M., Ruohonen, L.: Xylose transport studies with xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing heterologous and homologous permeases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74, 1041–1052 (2007)
Görke, B., Stülke, J.: Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: many ways to make the most out of nutrients. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 613–624 (2008)
Kim, J.-H., Block, D.E., Mills, D.A.: Simultaneous consumption of pentose and hexose sugars: an optimal microbial phenotype for efficient fermentation of lignocellulosic biomass. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 88, 1077–1085 (2010)
Yokoyama, S.-I., Suzuki, T., Kawai, K., Horitsu, H., Takamizawa, K.: Purification, characterization and structure analysis of NADPH-dependent D-xylose reductases from Candida tropicalis. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 79, 217–223 (1995)
Kostrzynska, M., Sopher, C.R., Lee, H.: Mutational analysis of the role of the conserved lysine-270 in the Pichia stipitis xylose reductase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 159, 107–112 (1998)
Petschacher, B., Leitgeb, S., Kavanagh, K.L., Wilson, D.K., Nidetzky, B.: The coenzyme specificity of Candida tenuis xylose reductase (AKR2B5) explored by site-directed mutagenesis and X-ray crystallography. Biochem. J. 385, 75–83 (2005)
Silva, S.S., Vitolo, M., Pessoa, A., Jr., Felipe, M.G.A.: Xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase activities of D-xylose-xylitol-fermenting Candida guilliermondii. J. Basic Microbiol. 36, 187–191 (1996)
Suzuki, T., Yokoyama, S.-I., Kinoshita, Y., Yamada, H., Hatsu, M., Takamizawa, K., Kawai, K.: Expression of xyrA gene encoding for D-xylose reductase of Candida tropicalis and production of xylitol in Escherichia coli. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 87, 280–284 (1999)
Zhang, J., Zhang, B., Wang, D., Gao, X., Hong, J.: Improving xylitol production at elevated temperature with engineered Kluyveromyces marxianus through over-expressing transporters. Biores. Technol. 175, 642–645 (2015)
Zhang, X., Shen, Y., Shi, W., Bao, X.: Ethanolic cofermentation with glucose and xylose by the recombinant industrial strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae NAN-127 and the effect of furfural on xylitol production. Biores. Technol. 101, 7093–7099 (2010)
Tochampa, W., Sirisansaneeyakul, S., Vanichsriratana, W., Srinophakun, P., Bakker, H.H.C., Chisti, Y.: A model of xylitol production by the yeast Candida mogii. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 28, 175–183 (2005)
Khankal, R., Luziatelli, F., Chin, J.W., Frei, C.S., Cirino, P.C.: Comparison between Escherichia coli K-12 strains W3110 and MG1655 and wild-type E. coli B as platforms for xylitol production. Biotechnol. Lett. 30, 1645–1653 (2008)
Gonzalez, R., Tao, H., Shanmugam, K.T., York, S.W., Ingram, L.O.: Global gene expression differences associated with changes in glycolytic flux and growth rate in Escherichia coli during the fermentation of glucose and xylose. Biotechnol. Prog. 18, 6–20 (2002)
Carmel-Harel, O., Storz, G.: Roles of the glutathione-and thioredoxin-dependent reduction systems in the Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae responses to oxidative stress. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 54, 439–461 (2000)
Hedeskov, C., Capito, K., Thams, P.: Cytosolic ratios of free [NADPH]/[NADP+] and [NADH]/[NAD+] in mouse pancreatic islets, and nutrient-induced insulin secretion. Biochem. J. 241, 161–167 (1987)
Arruda, P.V., Felipe, M.G.: Role of glycerol addition on xylose-to-xylitol bioconversion by Candida guilliermondii. Curr Microbiol 58, 274–278 (2009)
Ahmad, I., Shim, W.Y., Kim, J.-H.: Enhancement of xylitol production in glycerol kinase disrupted Candida tropicalis by co-expression of three genes involved in glycerol metabolic pathway. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 36, 1279–1284 (2013)
Kumar, S., Dheeran, P., Singh, S.P., Mishra, I.M., Adhikari, D.K.: Bioprocessing of bagasse hydrolysate for ethanol and xylitol production using thermotolerant yeast. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 38, 39–47 (2015)
López-Linares, J.C., Romero, I., Cara, C., Castro, E., Mussatto, S.I.: Xylitol production by Debaryomyces hansenii and Candida guilliermondii from rapeseed straw hemicellulosic hydrolysate. Biores. Technol. 247, 736–743 (2018)
Pereira, I., Madeira, A., Prista, C., Loureiro-Dias, M.C., Leandro, M.J.: Characterization of new polyol/H+ symporters in Debaryomyces hansenii. PLoS ONE 9, e88180 (2014)
Dasgupta, D., Bandhu, S., Adhikari, D.K., Ghosh, D.: Challenges and prospects of xylitol production with whole cell bio-catalysis: a review. Microbiol. Res. 197, 9–21 (2017)
Cheng, H., Wang, B., Lv, J., Jiang, M., Lin, S., Deng, Z.: Xylitol production from xylose mother liquor: a novel strategy that combines the use of recombinant Bacillus subtilis and Candida maltosa. Microb. Cell Fact. 10, 1–12 (2011)
Abd Rahman, N.H., Jahim, J.M., Munaim, M.S.A., Rahman, R.A., Fuzi, S.F.Z., Illias, R.M.: Immobilization of recombinant Escherichia coli on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for xylitol production. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 135, 109495 (2020)
Yuan, X., Tu, S., Lin, J., Yang, L., Shen, H., Wu, M.: Combination of the CRP mutation and ptsG deletion in Escherichia coli to efficiently synthesize xylitol from corncob hydrolysates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104, 2039–2050 (2020)
Reshamwala, S.M.S., Lali, A.M.: Exploiting the NADPH pool for xylitol production using recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Prog. 36, e2972 (2020)
da Silva, E.G., Borges, A.S., Maione, N.R., Castiglioni, G.L., Suarez, C.A.G., Montano, I.D.C.: Fermentation of hemicellulose liquor from Brewer’s spent grain using Scheffersomyces stipitis and Pachysolen tannophilus for production of 2G ethanol and xylitol. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 14, 127–137 (2020)
Kim, S.-Y., Oh, D.-K., Kim, J.-H.: Evaluation of xylitol production from corn cob hemicellulose hydrolysate by Candida parapsilosis. Biotech. Lett. 21, 891–895 (1999)
Li, M., Meng, X., Diao, E., Du, F.: Xylitol production by Candida tropicalis from corn cob hemicellulose hydrolysate in a two-stage fed-batch fermentation process. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 87, 387–392 (2012)
Ping, Y., Ling, H.-Z., Song, G., Ge, J.-P.: Xylitol production from non-detoxified corncob hemicellulose acid hydrolysate by Candida tropicalis. Biochem. Eng. J. 75, 86–91 (2013)
Mardawati E, Andoyo R, Syukra KA, Kresnowati M, Bindar Y: Production of xylitol from corn cob hydrolysate through acid and enzymatic hydrolysis by yeast. 2018. IOP Publishing.
Prabhu, A.A., Ledesma-Amaro, R., Lin, C.S.K., Coulon, F., Thakur, V.K., Kumar, V.: Bioproduction of succinic acid from xylose by engineered Yarrowia lipolytica without pH control. Biotechnol. Biofuels 13, 1–15 (2020)
Prabhu, A.A., Thomas, D.J., Ledesma-Amaro, R., Leeke, G.A., Medina, A., Verheecke-Vaessen, C., Coulon, F., Agrawal, D., Kumar, V.: Biovalorisation of crude glycerol and xylose into xylitol by oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Microb. Cell Fact. 19, 1–18 (2020)
Baptista, S.L., Costa, C.E., Cunha, J.T., Soares, P.O., Domingues, L.: Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of top value chemicals from biorefinery carbohydrates. Biotechnol. Adv. 47, 107697 (2021)
Yuan, X., Wang, J., Lin, J., Yang, L., Wu, M.: Efficient production of xylitol by the integration of multiple copies of xylose reductase gene and the deletion of Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway-associated genes to enhance NADPH regeneration in Escherichia coli. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 46, 1061–1069 (2019)
Shah, S.S.M., Luthfi, A.A.I., Low, K.O., Harun, S., Manaf, S.F.A., Illias, R.M., Jahim, J.M.: Preparation of kenaf stem hemicellulosic hydrolysate and its fermentability in microbial production of xylitol by Escherichia coli BL21. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–13 (2019)
Camargo, D., Sene, L., Variz, D.I.L.S.: de Almeida Felipe MdG: Xylitol bioproduction in hemicellulosic hydrolysate obtained from sorghum forage biomass. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 175, 3628–3642 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, (IISER) Kolkata, India, for providing us with the expression host E. coli M15.
Funding
This work was carried out with financial assistance from University Core Project (B27NV-CP016) and previous financial assistance to SU through Indo Russia joint collaboration supported by DBT, GoI, New Delhi (No.DBT/IC2/Indo-Russia/2014–16/04) and DBT-BIOCARe (Sanction No. BT/PR18134/BIC/101/795/2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sivakumar Uthandi: Conceptualized the research, Funding acquisition, Designed the experiments, and corrected the manuscript. Manikandan Ariyan: Performed the experiments, drafted the manuscript, editing, and software. Sugitha Thankappan: Redrafted the manuscript, Assisting with experimental data analyses, Editing, and software. Priyadarshini Ramachandran: Assisted in the experimentation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ariyan, M., Thankappan, S., Ramachandran, P. et al. Xylitol Production from Corncob Hydrolysate by an Engineered Escherichia coli M15 as Whole-Cell Biocatalysts. Waste Biomass Valor 14, 3195–3210 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01860-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01860-4