Abstract
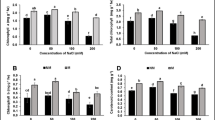
Kallar grass (Leptochloa fusca) is a perennial C4 halophytic species with high salt tolerant. The present research was made to investigate the physio-biochemical characters and transcriptional changes of L. fusca under varying salinity levels (0–600 mM NaCl). The Na+ level in shoots and roots increased significantly, whereas the K+ content was maintained high in 300 mM NaCl and then declined with increasing salinity in both tissues. The content of proline in seedlings exposed to extreme salinity level was 15.5-fold higher than control. Photosynthetic pigments, total soluble proteins, PAL activity, and total phenolic compounds in salt-stressed plants increased gradually up to 450 mM and declined at 600 mM NaCl. High salt concentration led to oxidative stress that was manifested by increased MDA level. To tackle with oxidative damages, L. fusca enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX). Moreover, under NaCl stress, the mRNA levels of SOS1, PM H+-ATPase, and NHX1 were up-regulated in both tissues, but higher in roots than in shoots. Our results demonstrate that L. fusca could use an osmotic adjustment, antioxidant defense system, and regulating the ion homeostasis as the most effective salt tolerance mechanisms for better plant growth under saline conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- PM:
-
Plasma membrane
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- TBA:
-
Tribromoarsenazo
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- PVP:
-
Polyvinylpyrrolidone
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- NBT:
-
Nitro blue tetrazolium
- REST:
-
Relative expression software tool
References
Acosta-Motos JR, Díaz-Vivancos P, Alvarez S, Fernández-García N, Sánchez-blanco MJ, Hernandez JA (2015) Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of the ornamental Eugenia myrtifolia L. plants for coping with NaCl stress and recovery. Planta 242:829–846
Acosta-Motos JR, Ortuño MF, Bernal-Vicente A, Diaz-Vivancos P, Sanchez-Blanco MJ, Hernandez JA (2017) Plant responses to salt stress: adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy 7:18
Adabnejad H, Kavousi HR, Hamidi Ravari H, Tavassolian I (2015) Assessment of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter (NHX1) transcriptional changes in Leptochloa fusca L. in response to salt and cadmium stresses. Mol Biol Res Commun 4(3):133–142
Aghaleh M, Niknam V, Ebrahimzadeh H, Razavi K (2009) Salt stress effects on growth, pigments, proteins and lipid peroxidation in Salicornia persica and S. europaea. Biol Plant 53:243–248
Ali A, Iqbal N, Ali F, Afzal B (2012) Alternantera bettzickiana (Regel) G. Nicholson, a potential halophytic ornamental plant: growth and physiological adaptations. Flora 207(4):318–321
Almeida DM, Oliveira MM, Saibo NJM (2017) Regulation of Na+ and K+ homeostasis in plants: towards improved salt stress tolerance in crop plants. Genet Mol Biol 40:326–345
Amtmann A, Leigh R (2010) Ion homeostasis. In: Pareek J, Sopory A, Bohnert SK, Govindjee HJ (eds) Abiotic stress adaptation in plants: physiological, molecular and genomic foundation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 245–262
Apse MP, Blumwald E (2007) Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett 581:2247–2254
Apse MP, Sottosanto JB, Blumwald E (2003) Vacuolar cation/H+ exchange, ion homeostasis, and leaf development are altered in a T-DNA insertional mutant of AtNHX1, the Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter. Plant J 36:229–239
Ashraf M, Harris PJC (2013) Photosynthesis under stressful environments: an overview. Photosynthetica 51:163–190
Bassi R, Sandonà D, Croce R (1997) Novel aspects of chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins. Physiol Plant 100:769–779
Bates L, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Beer RF Jr, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195:133–140
Ben Amor N, Jiménez A, Megdiche W, Lundqvist M, Sevilla F, Abdelly C (2006) Response of antioxidant systems to NaCl stress in the halophyte Cakile maritima. Physiol Plant 126:446–457
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:140–151
Boşcaiu M, Lull C, Llinares JV, Vicente O, Boira H (2012) Proline as a biochemical marker in relation to the ecology of two halophytic Juncus species. J Plant Ecol 6:177–186
Bose J, Rodrigo-Moreno A, Shabala S (2014) ROS homeostasis in halophytes in the context of salinity stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 65:1241–1257
Boudet AM (2007) Evolution and current status of research in phenolic compounds. Phytochemistry 68:2722–2735
Bradford MM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cahill DM, McComb JA (1992) A comparison of changes in phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity, lignin and phenolic synthesis in the roots of Eucalyptus calophylla (field resistant) and E. marginata (susceptible) when infected with Phytophthora cinnamomi. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 40:315–332
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2017) Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J 90:856–867
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Throne TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–110
Falleh H, Jalleli I, Ksouri R, Boulaaba M, Guyot S, Magne M, Abdely C (2012) Effect of salt treatment on phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of two Mesembryanthemum edule provenances. Plant Physiol Biochem 52:1–8
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2008) Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:945–963
Guo Q, Wang P, Ma Q, Zhang JL, Bao AK, Wang SM (2012) Selective transport capacity for K+ over Na+ is linked to the expression levels of PtSOS1 in halophyte Puccinellia tenuiflora. Funct Plant Biol 39:1047–1057
Hayat S, Hayat Q, Alyemeni MN, Wani AS, Pichtel J, Ahmad A (2012) Role of proline under changing environments. Plant Signal Behav 7(11):1456–1466
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Stn Circ 347:1–32
Huang BK, Sikes HD (2014) Quantifying intracellular hydrogen peroxide perturbations in terms of concentration. Redox Biol 2:955–962
Jannesar M, Razavi K, Saboora A (2014) Effects of salinity on expression of the salt overly sensitive genes in Aeluropus lagopoides. Aust J Crop Sci 8(1):1–8
Kaya C, Tuna AL, Yokas I (2009) The role of plant hormones in plants under salinity stress. In: Ashraf M, Ozturk M, Athar HR (eds) Salinity and water stress. Springer, Berlin, pp 45–50
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382
Lu Y, Lei JQ, Zeng FJ, Zhang B, Liu GJ, Liu B, Li XY (2017) Effect of NaCl-induced changes in growth, photosynthetic characteristics, water status and enzymatic antioxidant system of Calligonum caput-medusae seedlings. Photosynthetica 55:99–106
Miao L, Clair DK (2009) Regulation of superoxide dismutase fenes: implications in diseases. Free Radic Biol Med 47(4):344–356
Mishra A, Tanna B (2017) Halophytes: potential resources for salt stress rolerance genes and promoters. Front Plant Sci 8:829
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Palliyath S, Puthur JT (2018) The modulation of various physiochemical changes in Bruguiera cylindrica (L.) Blume affected by high concentrations of NaCl. Acta Physiol Plant 40:160
Rabhi M, Giuntini D, Castagna A, Remorini D, Baldan B, Smaoui A, Abdelly C, Ranieri A (2010) Sesuvium portulacastrum maintains adequate gas exchange, pigment composition, and thylakoid proteins under moderate and high salinity. J Plant Physiol 167:1336–1341
Rabhi M, Castagna A, Remorini D, Scattino C, Smaoui A, Ranieri A, Abdelly C (2012) Photosynthetic responses to salinity in two obligate halophytes: Sesuvium portulacastrum and Tecticornia indica. S Afr J Bot 79:39–47
Rauf M, Shahzad K, Ali R, Ahmad M, Habib I, Mansoor S, Berkowitz GA, Saeed NA (2014) Cloning and characterization of Na+/H+ antiporter (LfNHX1) gene from a halophyte grass Leptochloa fusca for drought and salt tolerance. Mol Biol Rep 41:1669–1682
Reginato MA, Castagna A, Furlán A, Castro S, Ranieri A, Luna V (2014) Physiological responses of a halophytic shrub to salt stress by Na2SO4 and NaCl: oxidative damage and the role of polyphenols in antioxidant protection. AoB Plants 6:plu042
Sanadhya P, Agarwal P, Agarwal PK (2015) Ion homeostasis in a salt-secreting halophtic grass. AoB Plants 7:plv055
Sekmen AH, Turkan I, Tanyolac ZO, Ozfidan C, Dinc A (2012) Different antioxidant defense responses to salt stress during germination and vegetative stages of endemic halophyte Gypsophila oblanceolata Bark. Environ Exp Bot 77:63–76
Shabala S (2013) Learning from halophytes: physiological basis and strategies to improve stress tolerance in crops. Ann Bot 112:1209–1221
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6896–6901
Shi H, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Zhu JK (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Slinkard K, Singleton VL (1977) Total phenol analyses: automation and comparison with manual methods. Am J Enol Vitic 28:49–55
Sobhanian H, Motamed N, Jazii FR, Razavi K, Niknam V, Komatsu S (2010) Salt stress responses of a halophytic grass Aeluropus lagopoides and subsequent recovery. Russ J Plant Physiol 57:784–791
Strzalka A, Kostecka-Gugala A, Latowski D (2003) Carotenoids and environmental stress in plants: significance of carotenoid-mediated modulation of membrane physical properties. Russ J Plant Physiol 50:168–172
Sun CQ, Chen FD, Teng NJ, Liu ZL, Fang WM, Hou XL (2010) Interspecific hybrids between Chrysanthemum grandiflorum (Ramat.) Kitamura and C. indicum (L.) Des Moul. and their drought tolerance evaluation. Euphytica 174:51–60
Taherinia B, Kavousi HR, Dehghan S (2015) Isolation and characterization of plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter (SOS1) gene during salinity stress in Kallar grass (Leptochloa fusca). Eurasia J Biosci 9:12–20
Talbi Zribi O, Hessini K, Trabelsi N, Zribi F, Hamdi A, Ksouri R, Abdelly C (2017) Aeluropus littoralis maintains adequate gas exchange, pigment composition and phenolic contents under combined effects of salinity and phosphorus deficiency. Aust J Bot 65:453–462
Theerawitaya C, Tisarum R, Samphumphuang T, Singh HP, Suriyan CU, Kirdmanee C, Takabe T (2015) Physio-biochemical and morphological characters of halophyte legume shrub, Acacia ampliceps seedlings in response to salt stress under greenhouse. Front Plant Sci 6:630
Tuna AL, Kaya C, Ashraf M, Altunlu H, Yokas I, Yagmur B (2007) The effects of calcium sulfate on growth, membrane stability and nutrient uptake of tomato plants grown under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 59:173–178
Yang Y, Guo Y (2018) Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 60:796–804
Yang Y, Wei X, Shi R, Fan Q, An L (2010) Salinity-induced physiological modification in the callus from halophyte Nitraria tangutorum Bobr. J Plant Growth Regul 29:465–476
Yin D, Zhang J, Jing R, Qu Q, Guan H, Zhang L, Dong L (2018) Effect of salinity on ion homeostasis in three halophyte species, Limonium bicolor, Vitex trifolia Linn. var. simplicifolia Cham and Apocynaceae venetum. Acta Physiol Plant 40:40
Zhang X, Liu CJ (2015) Multifaceted regulations of gateway enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids. Mol Plant 8:17–27
Zhang JS, Xie C, Li ZY, Chen SY (1999) Expression of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase gene in response to salt stress in a rice salt-tolerant mutant and its original variety. Theor Appl Genet 99:1006–1011
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran for financially supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Wojtaszek.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, F., Kavousi, H.R. & Mansouri, M. Effects of salt stress on physio-biochemical characters and gene expressions in halophyte grass Leptochloa fusca (L.) Kunth. Acta Physiol Plant 41, 143 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2935-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2935-5