Abstract
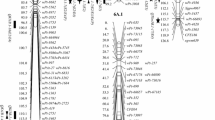
Kernel size and weight are important agronomic traits, as well as crucial traits that influence grain yield in maize. In the present study, 150 F7 recombinant inbred lines derived from a cross 178×K12 were evaluated for kernel length (KL), kernel width (KW), kernel thickness (KT), and 100-kernel weight (HKW) across seven environments. Natural variations in KL, KW, KT, and HKW were observed in the population. A set of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for the kernel-related traits were identified by inclusive composite interval mapping method. For the four kernel traits from seven environments and the best linear unbiased prediction data, a total of 52 QTLs were detected, which distributed on all chromosomes except chromosome 6. The LOD values ranged from 2.52 to 8.91, the additive effect from − 2.22 to 1.37, and the range of individually explaining phenotypic variation was from 5.8 to 23.49%. Amongst these QTLs, most were detected only in one or two environments. Three stable QTLs, qKL4-1 at bin 4.07/4.08, qKW4-2 at bin 4.06 and qKT2-1 at bin 2.02/2.03, were identified across at least three environments. Besides, several overlapping QTLs associated with multiple traits were identified. For example, qKW3-1 for KW and qHKW3-1 for HKW were located in the same marker interval at Bin 3.01/3.02. These stable QTLs and overlapping QTLs found in this study will contribute to the understanding of genetic components of grain yield and provide the foundation for molecular marker-assisted breeding in maize.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- KL:
-
Kernel length
- KW:
-
Kernel width
- KT:
-
Kernel thickness
- HKW:
-
100-Kernel weight
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- QTLs:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- ICIM:
-
Inclusive composite interval mapping
- BLUP:
-
Best linear unbiased prediction
References
Agrama HA, Eizenga GC, Yan W (2007) Association mapping of yield and its components in rice cultivars. Mol Breeding 19:341–356
Austin DF, Lee M (1996) Comparative mapping in F2:3 and F6:7 generations of quantitative trait loci for grain yield and yield components in maize. Theor Appl Genet 92:817–826
Blummel M, Grings E, Erenstein O (2013) Potential for dual-purpose maize varieties to meet changing maize demands: synthesis. Field Crop Res 153:107–112
Boer MP, Wright D, Feng L, Podlich DW, Luo L, Cooper M, van Eeuwijk FA (2007) A mixed-model quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis for multiple-environment trial data using environmental covariables for QTL-by-environment interactions, with an example in maize. Genetics 177:1801–1813
Chen J, Zhang L, Liu S, Li Z, Huang R, Li Y, Cheng H, Li X, Zhou B, Wu S (2016) The genetic basis of natural variation in kernel size and related traits using a four-way cross population in maize. PLoS ONE 11:e0153428
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kumar N (2006) Genetic and molecular basis of grain size and grain number and its relevance to grain productivity in higher plants. Genome 49:565–571
Han Y, Li D, Zhu D, Li H, Li X, Teng W, Li W (2012) QTL analysis of soybean seed weight across multi-genetic backgrounds and environments. Theor Appl Genet 125:671–683
He KH, Chang LG, Cui TT, Qu JZ, Guo DW, Xu ST, Zhang XH, Zhang RH, Xue JQ, Liu JC (2016) Mapping QTL for plant height and ear height in maize under multi-environments. Sci Agric Sin 49:1443–1452
Ho J, McCouch S, Smith M (2002) Improvement of hybrid yield by advanced backcross QTL analysis in elite maize. Theor Appl Genet 105:440–448
Huang R, Jiang L, Zheng J, Wang T, Wang H, Huang Y, Hong Z (2013) Genetic bases of rice grain shape: so many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci 18:218–226
Jiang L, Ge M, Zhao H, Zhang T (2015) Analysis of heterosis and quantitative trait loci for kernel shape related traits using triple testcross population in maize. PLoS ONE 10:e0124779
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis 1. Crop Sci 25:192–194
Li C, Li Y, Sun B, Peng B, Liu C, Liu Z, Yang Z, Li Q, Tan W, Zhang Y (2013) Quantitative trait loci mapping for yield components and kernel-related traits in multiple connected RIL populations in maize. Euphytica 193:303–316
Li H, Ye G, Wang J (2007a) A modified algorithm for the improvement of composite interval mapping. Genetics 175:361–374
Li Y, Wang Y, Shi Y, Song Y, Wang T, Li Y (2009) Correlation analysis and QTL mapping for traits of kernel structure and yield components in maize. Sci Agric Sin 42:408–418
Li YL, Niu SZ, Dong YB, Cui DQ, Wang YZ, Liu YY, Wei MG (2007b) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci for grain yield components from a dent corn inbred line in an advanced backcross BC2F2 population and comparison with its F2: 3 population in popcorn. Theor Appl Genet 115:129–140
Liu J, Huang J, Guo H, Lan L, Wang H, Xu Y, Yang X, Li W, Tong H, Xiao Y (2017) The conserved and unique genetic architecture of kernel size and weight in maize and rice. Plant Physiol 175:774–785
Liu Y, Wang L, Sun C, Zhang Z, Zheng Y, Qiu F (2014) Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 127:1019–1037
Liu ZH, Ji HQ, Cui ZT, Wu X, Duan LJ, Feng XX, Tang JH (2011) QTL detected for grain-filling rate in maize using a RIL population. Mol Breeding 27:25–36
Lu GH, Tang JH, Yan JB, Ma XQ, Li JS, Chen SJ, Ma JC, Liu ZX, Zhang YR, Dai JR (2006) Quantitative trait loci mapping of maize yield and its components under different water treatments at flowering time. J Integr Plant Biol 48:1233–1243
Lu M, Xie C-X, Li X-H, Hao Z-F, Li M-S, Weng J-F, Zhang D-G, Bai L, Zhang S-H (2011) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for kernel row number in maize across seven environments. Mol Breeding 28:143–152
Messmer R, Fracheboud Y, Bänziger M, Vargas M, Stamp P, Ribaut J-M (2009) Drought stress and tropical maize: QTL-by-environment interactions and stability of QTLs across environments for yield components and secondary traits. Theor Appl Genet 119:913–930
Peng B, Li Y, Wang Y, Liu C, Liu Z, Tan W, Zhang Y, Wang D, Shi Y, Sun B (2011) QTL analysis for yield components and kernel-related traits in maize across multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 122:1305–1320
Prado SA, López CG, Senior ML, Borrás L (2014) The genetic architecture of maize (Zea mays L.) kernel weight determination. G3 Genes Genomes Genet 4:1611–1621
Qin H, Cai Y, Liu Z, Wang G, Wang J, Guo Y, Wang H (2012) Identification of QTL for zinc and iron concentration in maize kernel and cob. Euphytica 187:345–358
Raihan MS, Liu J, Huang J, Guo H, Pan Q, Yan J (2016) Multi-environment QTL analysis of grain morphology traits and fine mapping of a kernel-width QTL in Zheng58× SK maize population. Theor Appl Genet 129:1465–1477
Ramya P, Chaubal A, Kulkarni K, Gupta L, Kadoo N, Dhaliwal HS, Chhuneja P, Lagu M, Gupt V (2010) QTL mapping of 1000-kernel weight, kernel length, and kernel width in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Appl Genet 51:421–429
Revilla P, Butrón A, Malvar RA, Ordás RA (1999) Relationship among kernel weight, early vigor, and growth in maize. Crop Sci 39:654–658
Ribaut JM, Jiang C, Gonzalez-de-Leon D, Edmeades GO, Hoisington DA (1997) Identification of quantitative trait loci under drought conditions in tropical maize. 2. Yield components and marker-assisted selection strategies. Theor Appl Genet 94:887–896
Shi Z, Song W, Xing J, Duan M, Wang F, Tian H, Xu L, Wang S, Su A, Li C (2017) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for three kernel-related traits in maize using a double haploid population. Mol Breeding 37:108
Sun X-Y, Wu K, Zhao Y, Kong F-M, Han G-Z, Jiang H-M, Huang X-J, Li R-J, Wang H-G, Li S-S (2009) QTL analysis of kernel shape and weight using recombinant inbred lines in wheat. Euphytica 165:615
Utz HF (2001) PLABSTAT: a computer program for statistical analysis of plant breeding experiments. Seed Science and Population Genetics, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Institute for Plant Breeding
Veldboom LR, Lee M (1996) Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci in maize in stress and nonstress environments: I. Grain yield and yield components. Crop Sci 36:1310–1319
Wang Y, Liu C, Wang TY, Shi YS, Song YC, Li Y (2007) QTL analysis of yield components in maize under different water regimes. J Plant Genet Resour 2:010
Xu Y (2010) Molecular plant breeding. CAB International, Wallingford
Xu Y, Li H-N, Li G-J, Wang X, Cheng L-G, Zhang Y-M (2011) Mapping quantitative trait loci for seed size traits in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Theor Appl Genet 122:581–594
Yang C, Zhang L, Jia A, Rong T (2016) Identification of QTL for maize grain yield and kernel-related traits. J Genet 95:239–247
Yang G, Dong Y, Li Y, Wang Q, Shi Q, Zhou Q (2013) Verification of QTL for grain starch content and its genetic correlation with oil content using two connected RIL populations in high-oil maize. PLoS ONE 8:e53770
Zhang C, Zhou Z, Yong H, Zhang X, Hao Z, Zhang F, Li M, Zhang D, Li X, Wang Z (2017) Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize ear and grain morphological traits by combined linkage and association mapping. Theor Appl Genet 130:1011–1029
Zhang H, Jin T, Huang Y, Chen J, Zhu L, Zhao Y, Guo J (2015) Identification of quantitative trait loci underlying the protein, oil and starch contents of maize in multiple environments. Euphytica 205:169–183
Zhang Z, Liu Z, Hu Y, Li W, Fu Z, Ding D, Li H, Qiao M, Tang J (2014) QTL analysis of kernel-related traits in maize using an immortalized F2 population. PLoS ONE 9:e89645
Acknowledgements
This study was supported financially by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 31301830), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2014JQ3108), and Special Fund for Basic Research in Northwest A&F University (No. QN2012001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, T., He, K., Chang, L. et al. QTL mapping and genetic analysis for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Euphytica 214, 119 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2189-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2189-0