Abstract
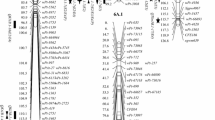
Kernel size and morphology influence the market value and milling yield of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). The objective of this study was to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling kernel traits in hexaploid wheat. We recorded 1000-kernel weight, kernel length, and kernel width for 185 recombinant inbred lines from the cross Rye Selection 111 × Chinese Spring grown in 2 agro-climatic regions in India for many years. Composite interval mapping (CIM) was employed for QTL detection using a linkage map with 169 simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. For 1000-kernel weight, 10 QTLs were identified on wheat chromosomes 1A, 1D, 2B, 2D, 4B, 5B, and 6B, whereas 6 QTLs for kernel length were detected on 1A, 2B, 2D, 5A, 5B and 5D. Chromosomes 1D, 2B, 2D, 4B, 5B and 5D had 9 QTLs for kernel width. Chromosomal regions with QTLs detected consistently for multiple year-location combinations were identified for each trait. Pleiotropic QTLs were found on chromosomes 2B, 2D, 4B, and 5B. The identified genomic regions controlling wheat kernel size and shape can be targeted during further studies for their genetic dissection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammiraju JSS, Dholakia BB, Santra DK, Singh H, Lagu MD, Tamhankar SA et al. 2001. Identification of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers associated with seed size in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 102: 726–732.
Ammiraju JSS, Dholakia BB, Jawdekar G, Santra DK, Singh H, Lagu MD, et al. 2002. Inheritance and identification of DNA markers associated with yellow berry tolerance in wheat (T. aestivum L.). Euphytica 123: 229–233.
Ammiraju JSS, Dholakia BB, Jawdekar G, Santra DK, Röder MS, Singh H, et al. 2004. Identification of chromosomal regions governing grain size and shape in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Genet & Breed 58: 91–100.
Ayoub M, Symons SJ, Edney MJ, Mather DE, 2002. QTLs affecting kernel size and shape in a two-rowed by six-rowed barley cross. Theor Appl Genet 105:237–247.
Baker S, Herrman TJ, Loughin T, 1999. Segregating hard red winter wheat into dough factor groups using single kernel measurements and whole grain protein analysis. Cereal Chem 76, 884–889.
Baril CP, 1992. Factor regression for interpreting genotype-environment interaction in bread-wheat trials. Theor Appl Genet 83: 1022–1026.
Berman M, Bason ML, Ellison R, Peden G, Wrigley CW, 1996. Image analysis of the whole grains to screen for flour-milling yield in wheat breeding. Cereal Chem 73: 323–327.
Börner A, Schumann E, Fürste A, Cöster H, Leithold B, Röder MS, Weber WE, 2002. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for agronomic important characters in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 105: 921–936.
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME, 2006. Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 177: 1165–1177.
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME, 2007. QTL analysis of kernel size and shape in two hexaploid wheat mapping populations. Field Crop Res 101: 172–179.
Campbell KG, Bergman CJ, Gualberto DG, Anderson JA, Giroux MJ, Hareland G, et al. 1999. Quantitative trait loci associated with kernel traits in soft × hard wheat cross. Crop Sci 39: 1184–1195.
Churchill GA, Doerge RW, 1994. Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138: 963–971.
Dholakia BB, Ammiraju JSS, Singh H, Lagu MD, Röder MS, Rao VS et al. 2003. Molecular marker analysis of kernel size and shape in bread wheat. Plant Breeding 122: 392–395.
Doerge RW, Churchill GA, 1996. Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142: 285–294.
Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q, 2006.Gs3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112: 1164–1171.
Giura A, Saulescu NN, 1996. Chromosomal location of genes controlling grain size in a large grained selection of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 89: 77–80.
Groh S, Kianian SF, Philips RL, Rines HW, Stuthman DD, Wesenberg DM, Fulcher RG, 2001. Analysis of factors influencing milling yield and their association to other traits by QTL analysis in two hexaploid oat populations. Theor Appl Genet 103:9–18.
Groos C, Robert N, Bervas E, Charmet G, 2003. Genetic analysis of grain protein content, grain yield and thousand-kernel weight in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 106: 1032–1040.
Huang XQ, Cloutier S, Lycar L, Radovanovic N, Humphreys DG, Noll JS, et al. 2006. Molecular detection of QTLs for agronomic and quality traits in a doubled haploid population derived from two Canadian wheats (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 113: 753–766.
Jiang C, Zeng Z-B, 1995. Multiple trait analysis of genetic mapping for quantitative trait loci. Genetics 140: 1111–1127
Kosambi DD, 1944. The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12: 172–175.
Kumar N, Kulwal PL, Gaur A, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP, Khurana P, et al. 2006. QTL analysis for grain weight in common wheat. Euphytica 151: 135–144.
Marshall DR, Mares DJ, Moss HJ, Ellison FW, 1986. Effects of grain shape and size on milling yields in wheat. II. Experimental studies. Aust J Agr Res 37:331–342.
McIntosh RA, Yamazaki Y, Devos KM, Dubcovsky J, Rogers WJ, Appels R, 2003. Catalog of gene symbols for wheat. Tenth International Wheat Genetics Symposium, Paestum, Italy, 1–6 September 2003.
Morgan BC, Dexter JE, Preston KR, 2000. Relationship of kernel size to flour water absorption for Canada Western Red Spring Wheat. Cereal Chem 77, 286–292.
Novaro P, Colucci F, Venora G, D’Egidio MG, 2001. Image analysis of whole grains: A noninvasive method to predictsemolina yield in durum wheat. Cereal Chem 78: 217–221.
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW, 1998. A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149: 2007–2023.
Röder MS, Huang XQ, Börner A, 2008. Fine mapping of the region on wheat chromosome 7D controlling grain weight. Funct Integr Genomics 8: 79–86.
Sanguinetti CJ, Dias Neto E, Simpson AJG, 1994. Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 17: 915–919.
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K, 2004. A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109: 1105–1114.
Song J-X, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu Z-M, Lin X-H, 2007. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nature Genet 39: 623–630
Sourdille P, Singh S, Cadalen T, Brown-Guedira GL, Gay G, Qi L et al. 2004. Microsatellite-based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic-physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct Integr Genomics 4: 12–25
Stein N, Herren G, Keller B, 2001. A new DNA extraction method for high-throughput marker analysis in a large-genome species such asTriticum aestivum. Plant Breeding 120: 354–356.
VanOoijen JW, 2006. JoinMap®4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen, Netherlands.
Varshney RK, Prasad M, Roy JK, Kumar N, Singh H, Dhaliwal HS, et al. 2000. Identification of eight chromosomes and a microsatellite marker on1 AS associated with QTLs for grain weight in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100: 1290–1294.
Voorrips, RE, 2002. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93: 77–78.
Wang RX, Hai L, Zhang XY, You GX, Yan CS, Xiao SH, 2009. QTL mapping for grain filling rate and yield-related traits in RILs of the Chinese winter wheat population Heshangmai × Yu8679. Theor Appl Genet 118: 313–325.
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB, 2007. WindowsQTLCartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. (http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm).
Wiersma JJ, Busch RH, Fulcher GG, Hareland G, 2001. Recurrent selection for kernel weight in spring wheat. Crop Sci 41: 999–1005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramya, P., Chaubal, A., Kulkarni, K. et al. QTL mapping of 1000-kernel weight, kernel length, and kernel width in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Appl Genet 51, 421–429 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03208872
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03208872