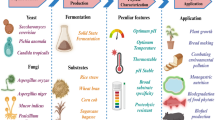
Abstract
Objective
The application of phytases helps in releasing bound phosphorus and other nutrients in cattle feed eventually reducing the need for supplementations. However, high production cost owing to the unavailability of cheaper sources of phytases has limited their usage in developing countries. Herein, firstly isolation, identification of a phytase from fungal isolate, Aspergillus niger NT7 was carried out followed by optimizing of all production parameters, through solid-state fermentation (SSF). Secondly, crude phytase was characterized and potential applicability of crude phytase was evaluated for dephytinization of wheat bran.
Results
The highest phytase production (208.30 ± 0.22 U/gds) was achieved using wheat bran as cheap agro-industrial substrate for SSF. The various physiological parameters were optimized including inoculum age and level (3-day old inoculum and 15 × 107 spores/ml), temperature (35 °C), a moistening agent (distilled water), medium pH (5), and supplementation of various biochemicals like sugar (Mannitol), nitrogen (ammonium sulphate) and detergent (Tween 80). Process optimization through one variable at a time (OVAT) approach increased the difference in productivity to more than 200%. The crude phytase of A. niger NT7 was thermostable, with optimal activity at 60 °C and also displayed optimal activity over a broad range of acidic pH. Further, enhancement in phytase activity was found specifically in the presence of Ca2+, Zn2+, and Co2+ ions, while other metal ions including Fe2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Mg2+and Cu2+ inhibited its activity. Finally, the phytase showed efficient and sustained release of inorganic phosphate, proteins, and reducing sugars (> 60 h) from livestock feed.
Conclusion
Overall, our report highlights the production of an efficient and thermotolerant phytase with potential as a low-cost animal feed supplement.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data and related materials are with the authors wherever it is needed the same may be provided.
References
Ajith S, Ghosh J, Shet D, ShreeVidhya S, Punith BD, Elangovan AV (2019) Partial purification and characterization of phytase from Aspergillus foetidus MTCC 11682. AMB Express 9(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0725-x
Anwar Z, Gulfraz M, Irshad M (2014) Agro-industrial lignocellulosic biomass a key to unlock the future bio-energy: a brief review. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:163–173
Arora S, Dubey M, Singh P, Rani R, Ghosh S (2017) Effect of mixing events on the production of a thermo-tolerant and acid-stable phytase in a novel solid-state fermentation bioreactor. Process Biochem 61:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.06.009
Awad GEA, Helal MMI, Danial EN, Esawy MA (2014) Optimization of phytase production by Penicillium purpurogenum GE1 under solid state fermentation by using Box-Behnken design. Saudi J Biol Sci 21:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.06.004
Bae HD, Yanke LJ, Cheng K-J, Selinger LB (1999) A novel staining method for detecting phytase activity. J Microbiol Methods 39:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(99)00096-2
Bhavsar K, Ravi Kumar V, Khire JM (2011) High level phytase production by Aspergillus niger NCIM 563 in solid state culture: response surface optimization, up-scaling, and its partial characterization. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:1407–1417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0926-z
Bhavsar K, Buddhiwant P, Soni SK, Depan D, Sarkar S, Khire JM (2013) Phytase isozymes from Aspergillus niger NCIM 563 under solid state fermentation: biochemical characterization and their correlation with submerged phytases. Process Biochem 48(11):1618–1625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.08.001
Bogar B, Szakacs G, Linden JC, Pandey A, Tengerdy RP (2003a) Optimization of phytase production by solid substrate fermentation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30(3):183–189
Bogar B, Szakacs G, Pandey A, Abdulhameed S, Linden JC, Tengerdy RP (2003b) Production of Phytase by Mucor racemosus in solid-state fermentation. Biotechnol Prog 19(2):312–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp020126v
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Cao L, Wang WM, Yang C, Yang Y, Diana J, Yakupitiyage A, Luo Z, Li D (2007) Application of microbial phytase in fish feed. Enzym Microb Technol 40(4):497–507
Chadha BS, Harmeet G, Mandeep M, Saini HS, Singh N (2004) Phytase production by the thermophilic fungus Rhizomucor pusillus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(1):105–109. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WIBI.0000013319.13348.0a
Chantasartrasamee K, Na Ayuthaya DI, Intarareugsorn S, Dharmsthiti S (2005) Phytase activity from Aspergillus oryzae AK9 cultivated on solid state soybean meal medium. Process Biochem 40(7):2285–2289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.03.019
Chen J, Zhu Y, Nout MJR, Sarkar PK (2013) Solid state fermentation for foods and beverages. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Chugh P, Soni R, Soni SK (2016) Deoiled Rice Bran: a substrate for co-production of a consortium of hydrolytic enzymes by Aspergillus niger P-19. Waste Biomass Valoriz 7(3):513–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9477-x
Consulting AR (2019) Phytase market global size worth over $1 billion by 2025: Acumen research and consulting. In: Globe News wire News Room. Accessed 21 Jan 2020
Das A, Raychaudhuri U, Chakraborty R (2012) Cereal based functional food of Indian subcontinent: a review. J Food Sci Technol 49(6):665–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0474-1
De Castro RJS, Sato HH (2015) Enzyme production by solid state fermentation: general aspects and an analysis of the physicochemical characteristics of substrates for agro-industrial wastes valorization. Waste Biomass Valoriz 6(6):1085–1093
El-Shishtawy RM, Mohamed SA, Asiri AM, Abu-bakr MG, Ibrahim IH, Al-Talhi HA (2014) Solid fermentation of wheat bran for hydrolytic enzymes production and saccharification content by a local isolate Bacillus megatherium. BMC Biotechnol 14(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-14-29
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y (1925) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66(2):375–400
Fu S, Sun J, Qian L (2008) Effect of Ca2+ on beta-propeller phytases. Protein Pept Lett 15(1):39–42. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986608783330404
Gaind S, Singh S (2015) Production, purification and characterization of neutral phytase from thermotolerant Aspergillus flavus ITCC 6720. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 99:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.12.013
Gautam P, Sabu A, Pandey A, Szakacs G, Soccol CR (2002) Microbial production of extra-cellular phytase using polystyrene as inert solid support. Bioresour Technol 83(3):229–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00215-2
Guerrand D (2018) Chapter 26—economics of food and feed enzymes: status and prospectives. In: Nunes CS, Kumar V (eds) Enzymes in human and animal nutrition. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 487–514
Gulati H, Chadha B, Saini H (2007) Production, purification and characterization of thermostable phytase from thermophilic fungus Thermomyces lanuginosus TL-7. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 54(2):121–138. https://doi.org/10.1556/AMicr.54.2007.2.3
Gunashree BS, Venkateswaran G (2015) Extracellular phytase from Aspergillus niger CFR 335: purification and characterization. J Food Sci Technol 52(7):4558–4564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1304-z
Gupta RK, Gangoliya SS, Singh NK (2014) Isolation of thermotolerant phytase producing fungi and optimisation of phytase production by Aspergillus niger NRF9 in solid state fermentation using response surface methodology. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 19(6):996–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0175-5
Jatuwong K, Suwannarach N, Kumla J, Penkhrue W, Kakumyan P, Lumyong S (2020) Bioprocess for production, characteristics, and biotechnological applications of fungal phytases. Front Microbiol 11:188. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00188
Krishna C (2005) Solid-state fermentation systems—an overview. Crit Rev Biotechnol 25:1–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550590925383
Kumar V, Sinha AK (2018) Chapter 3—general aspects of phytases. In: Nunes CS, Kumar V (eds) Enzymes in human and animal nutrition. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 53–72
Kumar V, Sinha AK, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2010) Dietary roles of phytate and phytase in human nutrition: a review. Food Chem 120(4):945–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.052
Linderberg JE, and B Ogle (2002) Digestive physiology of pigs. In: Proceedings of the 8th Symposium. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition 86: 55–56. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0396.2002.0347b.x
Makolomakwa M, Puri AK, Permaul K, Singh S (2017) Thermo-acid-stable phytase-mediated enhancement of bioethanol production using Colocasia esculenta. Bioresour Technol 235:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.157
McClenny N (2005) Laboratory detection and identification of Aspergillus species by microscopic observation and culture: the traditional approach. Med Mycol 43(Supplement_1):125–128. https://doi.org/10.1080/13693780500052222
McCoy M (1998) Enzymes emerge as big as feed supplement. Chem Eng News 76(18):29–30
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Monteiro PS, Guimarães VM, de Melo RR, de Rezende ST (2015) Isolation of a thermostable acid phytase from Aspergillus niger UFV-1 with strong proteolysis resistance. Braz J Microbiol 46(1):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838220120037
Neira-Vielma AA, Aguilar CN, Ilyina A, Contreras-Esquivel JC, das Graça Carneiro-da-Cunha M, Michelena-Alvarez G, Martínez-Hernandez JL (2018) Purification and biochemical characterization of an Aspergillus niger phytase produced by solid-state fermentation using triticale residues as substrate. Biotechnol Rep 17:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.12.004
Pandey A (2003) Solid-state fermentation. Biochem Eng J 13:81–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-703X(02)00121-3
Pandey A, Szakacs G, Soccol CR, Rodriguez-Leon JA, Soccol VT (2001) Production, purification and properties of microbial phytases. Bioresour Technol 77(3):203–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(00)00139-5
Peng M, Aguilar-Pontes MV, de Vries RP, Makela MR (2018) In silico analysis of putative sugar transporter genes in Aspergillus niger using phylogeny and comparative transcriptomics. Front Microbiol 9:1045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01045
Raboy V (2001) Seeds for a better future: ‘low phytate’ grains help to overcome malnutrition and reduce pollution. Trends Plant Sci 6(10):458–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(01)02104-5
Ramachandran S, Roopesh K, Nampoothiri KM, Szakacs G, Pandey A (2005) Mixed substrate fermentation for the production of phytase by Rhizopus spp. using oilcakes as substrates. Process Biochem 40(5):1749–1754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.06.040
Rani R, Ghosh S (2011) Production of phytase under solid-state fermentation using Rhizopus oryzae: novel strain improvement approach and studies on purification and characterization. Bioresour Technol 102(22):10641–10649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.075
Ranjan A, Sahu NP, Deo AD, Kumar S (2019) Solid state fermentation of de-oiled rice bran: effect on in vitro protein digestibility, fatty acid profile and anti-nutritional factors. Food Res Int 119:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.01.054
Rodríguez-Fernández DE, Parada JL, Medeiros AB, de Carvalho JC, Lacerda LG, Rodríguez-León JA, Soccol CR (2013) Concentration by ultrafiltration and stabilization of phytase produced by solid-state fermentation. Process Biochem 48(2):374–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.12.021
Roopesh K, Ramachandran S, Nampoothiri KM, Szakacs G, Pandey A (2006) Comparison of phytase production on wheat bran and oilcakes in solid-state fermentation by Mucor racemosus. Bioresour Technol 97(3):506–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.046
Sabino R, Pinheiro AC (2016) Chapter 26—molecular approaches to detect and identify fungal agents in various environmental settings. In: Viegas C, Pinheiro AC, Sabino R et al (eds) Environmental mycology in public health. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 421–428
Sabu A, Sarita S, Pandey A, Bogar B, Szakacs G, Soccol CR (2002) Solid-state fermentation for production of phytase by Rhizopus oligosporus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 102(1–6):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:102-103:1-6:251
Salmon DN, Piva LC, Binati RL, Rodrigues C, de Souza Vandenberghe LP, Soccol CR, Spier MR (2012) A bioprocess for the production of phytase from Schizophyllum commune: studies of its optimization, profile of fermentation parameters, characterization and stability. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35(7):1067–1079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0692-6
Sapna SB (2014) Phytase production by Aspergillus oryzae in solid-state fermentation and its applicability in dephytinization of wheat ban. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:1885–1895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0974-3
Sapna SB (2017) Purification and characterization of a protease-resistant phytase of Aspergillus oryzae SBS50 whose properties make it exceptionally useful as a feed supplement. Int J Biol Macromol 103:458–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.077
Sharma N, Angural S, Rana M, Puri N, Kondepudi KK, Gupta N (2020) Phytase producing lactic acid bacteria: cell factories for enhancing micronutrient bioavailability of phytate rich foods. Trends Food Sci Technol 96:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.12.001
Shivanna GB, Venkateswaran G (2014) Phytase production by Aspergillus niger CFR 335 and Aspergillus ficuum SGA 01 through submerged and solid-state fermentation. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/392615
Singh B, Satyanarayana T (2006) Phytase production by thermophilic mold sporotrichum thermophile in solid-state fermentation and its application in dephytinization of sesame oil cake. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 133:239–250. https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:133:3:239
Singh B, Satyanarayana T (2009) Characterization of a HAP–phytase from a thermophilic mould Sporotrichum thermophile. Bioresour Technol 100:2046–2051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.10.025
Singh P, Yadav SK (2018) Feed enzymes: source and applications. In: Kuddus M (ed) Enzymes in food technology: improvements and innovations. Springer, Singapore, pp 347–358
Singh B, Singh D, Sharma KK (2013) Microbial phytases in skirmishing and management of environmental phosphorus pollution. Biotechnology for environmental management and resource recovery. Springer, Cham, pp 239–260
Soni SK, Magdum A, Khire JM (2010) Purification and characterization of two distinct acidic phytases with broad pH stability from Aspergillus niger NCIM 563. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:2009–2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0385-8
Suresh S, Radha KV (2016) Statistical optimization and mutagenesis for high level of phytase production by Rhizopus oligosporus MTCC 556 under solid state fermentation. J Environ Biol 2:253
Tian M, Yuan Q (2016) Optimization of phytase production from potato waste using Aspergillus ficuum. 3 Biotech 6:256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0573-9
Tripathi P, A JL, Kapoor M (2018) Phytase from Citrobacter koseri PM-7: enhanced production using statistical method and application in ameliorating mineral bioaccessibility and protein digestibility of high-phytate food. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 48(1):84–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2017.1405024
Vashishth A, Ram S, Beniwal V (2017) Cereal phytases and their importance in improvement of micronutrients bioavailability. 3 Biotech 7(1):42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0698-5
Vasudevan UM, Jaiswal AK, Krishna S, Pandey A (2019) Thermostable phytase in feed and fuel industries. Bioresour Technol 278:400–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.065
Wieser H, Koehler P, Scherf KA (2020) Chapter 5—wheat-based raw materials. In: Wieser H, Koehler P, Scherf KA (eds) Wheat—an exceptional crop. Woodhead Publishing, New York, pp 103–131
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. V. K. Garlapati, Jaypee University of Information Technology Waknaghat, Solan, India and Dr. Ankit Shrivastava, LPVD, Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID, NIH, Hamilton, MT, 59840, USA, for his valuable inputs during the current studies.
Supporting information
Table S1—Characteristics of Wheat bran.
Table S2—Diameter of zone of hydrolysis and phytase activity (secondary screening) of isolates.
Fig. S1—Primary screening of isolate X6. X6 showing zone of hydrolysis on PSM.
Fig. S2—Morphological features of isolate X6.
Fig. S3—Selection of quantity of wheat bran for phytase production by A. niger NT7.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the Jaypee University of Information Technology Waknaghat, India, for providing infrastructure and financial support for carrying out the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish the manuscript in the said journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, N., Bansal, S. Production and characterization of a novel, thermotolerant fungal phytase from agro-industrial byproducts for cattle feed. Biotechnol Lett 43, 865–879 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03069-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03069-8