Abstract
Main conclusion
It has been proposed that future efforts should focus on basic studies, biotechnology studies and synthetic biology studies related to algal biofuels and various high-value bioproducts for the economically viable production of algal biof uels.
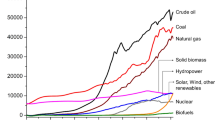
In recognition of diminishing fossil fuel reserves and the worsening environment, microalgal biofuel has been proposed as a renewable energy source with great potential. Algal biofuel thus became one of the hottest topics in renewable energy research in the new century, especially over the past decade. Between 2007 and 2017, research related to microalgal biofuels experienced a dramatic, three-stage development, rising, growing exponentially, and then declining rapidly due to overheating of the subject. However, biofuel-driven algal biotechnology and bioproducts research has been thriving since 2010. To clarify the gains (and pains) of the past decade and detail prospects for the future, this review summarizes the extensive scientific progress and substantial technical advances in algal biofuel over the past decade, covering basic biology, applied research, as well as the production of value-added natural products. Even after 10 years of hard work and billions of dollars in investments, its unacceptably high cost remains the ultimate bottleneck for the industrialization of algal biofuel. To maximize the total research benefits, both economically and socially, it has been proposed that future efforts should focus on basic studies to characterize oilgae, on biotechnology studies into various high-value bioproducts. Moreover, the development of synthetic biology provides new possibilities for the economically viable production of biofuels via the directional manufacture of microalgal bioproducts in algal cell factories.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Imamaki A, Hirano M (2002) Removal of nitrate, nitrite, ammonium and phosphate ions from water by the aerial microalga Trentepohlia aurea. J Appl Phycol 14:129–134. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019599216554
Abu GO, Ogbonda KH, Aminigo RE (2007) Optimization studies of biomass production and protein biosynthesis in a Spirulina sp isolated from an oil-polluted flame pit in the Niger Delta. Afr J Biotechnol 6:2550–2554
Ad VDW, Angermayr SA, Puthan VV, Osnato A, Hellingwerf KJ (2014) Carbon sink removal: Increased photosynthetic production of lactic acid by Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 in a glycogen storage mutant. J Biotechnol 184:100–102
Adesanya VO, Cadena E, Scott SA, Smith AG (2014) Life cycle assessment on microalgal biodiesel production using a hybrid cultivation system. Bioresour Technol 163:343–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.04.051
Ajjawi I et al (2017) Lipid production in Nannochloropsis gaditana is doubled by decreasing expression of a single transcriptional regulator. Nat Biotechnol 35:647. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3865
Alipanah L, Rohloff J, Winge P, Bones AM, Brembu T (2015) Whole-cell response to nitrogen deprivation in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Exp Bot 66:6281–6296. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv340
Alkhamis Y, Qin JG (2016) Comparison of pigment and proximate compositions of Tisochrysis lutea in phototrophic and mixotrophic cultures. J Appl Phycol 28:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0599-0
Alric J, Lavergne J, Rappaport F (2010) Redox and ATP control of photosynthetic cyclic electron flow in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (I) aerobic conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenergy 1797:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.07.009
Amaro HM, Guedes AC, Malcata FX (2011) Advances and perspectives in using microalgae to produce biodiesel. Appl Energy 88:3402–3410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.12.014
Anandarajah K, Mahendraperumal G, Sommerfeld M, Hu Q (2012) Characterization of microalga Nannochloropsis sp mutants for improved production of biofuels. Appl Energy 96:371–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.02.057
Anila N, Chandrashekar A, Ravishankar GA, Sarada R (2011) Establishment of Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation in Dunaliella bardawil. Eur J Phycol 46:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2010.550386
Baek K et al (2016) DNA-free two-gene knockout in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii via CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Sci Rep 6:30620. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30620
Barsanti L, Passarelli V, Evangelista V, Frassanito AM, Gualtieri P (2011) Chemistry, physico–chemistry and applications linked to biological activities of beta-glucans. Nat Prod Rep 28:457–466. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0np00018c
Beach ES, Eckelman MJ, Cui Z, Brentner L, Zimmerman JB (2012) Preferential technological and life cycle environmental performance of chitosan flocculation for harvesting of the green algae Neochloris oleoabundans. Bioresour Technol 121:445–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.012
Becker EW (2007) Micro-algae as a source of protein. Biotechnol Adv 25:207–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.11.002
Bentley FK, Melis A (2012) Diffusion-based process for carbon dioxide uptake and isoprene emission in gaseous/aqueous two-phase photobioreactors by photosynthetic microorganisms. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23298
Bentley FK et al (2013) Paradigm of Monoterpene (beta-phellandrene) Hydrocarbons Production via; Photosynthesis in Cyanobacteria. Bioenergy Res. 6:917–929
Bentley FK, Zurbriggen A, Melis A (2014) Heterologous expression of the mevalonic acid pathway in cyanobacteria enhances endogenous carbon partitioning to isoprene. Mol Plant 7:71–86. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst134
Berla BM, Saha R, Immethun CM, Maranas CD, Moon TS, Pakrasi HB (2013) Synthetic biology of cyanobacteria: unique challenges and opportunities. Front Microbiol 4:246. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00246
Bigelow TA, Xu J, Stessman DJ, Yao LX, Spalding MH, Wang T (2014) Lysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by high-intensity focused ultrasound as a function of exposure time. Ultrason Sonochem 21:1258–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.11.014
Blanc G et al (2010) The Chlorella variabilis NC64A genome reveals adaptation to photosymbiosis, coevolution with viruses, and cryptic sex. Plant Cell 22:2943–2955. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.076406
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Keyzers RA, Munro MHG, Prinsep MR (2017) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep. 34:235–294. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6np00124f
Bohutskyi P, Kula T, Kessler B, Hong Y, Bouwer EJ, Betenbaugh MJ, Allnutt FCT (2014) Mixed Trophic State Production Process for Microalgal Biomass with High Lipid Content for Generating Biodiesel and Biogas. Bioenerg Res 7:1174–1185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-014-9453-5
Brennan L, Owende P (2010) Biofuels from microalgae: a review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:557–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.10.009
Ceron-Garcia Mdel C, Campos-Perez I, Macias-Sanchez MD, Bermejo-Roman R, Fernandez-Sevilla JM, Molina-Grima E (2010) Stability of carotenoids in Scenedesmus almeriensis biomass and extracts under various storage conditions. J Agric Food Chem 58:6944–6950. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf100020s
Cha SH, Ko SC, Kim D, Jeon YJ (2011) Screening of marine algae for potential tyrosinase inhibitor: those inhibitors reduced tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in zebrafish. J Dermatol 38:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1346-8138.2010.00983.x
Chaves JE, Melis A (2018) Biotechnology of cyanobacterial isoprene production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:6451–6458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9093-3
Chaves JE, Romero PR, Kirst H, Melis A (2016) Role of isopentenyl-diphosphate isomerase in heterologous cyanobacterial (Synechocystis) isoprene production. Photosynth Res 130:517–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-016-0293-3
Chen CY, Yeh KL, Aisyah R, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2011a) Cultivation, photobioreactor design and harvesting of microalgae for biodiesel production: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 102:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.159
Chen H, Lao YM, Jiang JG (2011b) Effects of salinities on the gene expression of a (NAD+)-dependent glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in Dunaliella salina. Sci Total Environ 409:1291–1297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.12.038
Chen Y, Wang JF, Zhang W, Chen L, Gao LL, Liu TZ (2013) Forced light/dark circulation operation of open pond for microalgae cultivation. Biomass Bioenergy 56:464–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.05.034
Chen H, Zhang Y, He C, Wang Q (2014) Ca2+ signal transduction related to neutral lipid synthesis in an oil-producing green alga Chlorella sp. C2. Plant Cell Physiol 55:634–644. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu015
Chen CY et al (2015a) Improving protein production of indigenous microalga Chlorella vulgaris FSP-E by photobioreactor design and cultivation strategies. Biotechnol J 10:905–914. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201400594
Chen GY, Zhao L, Qi Y (2015b) Enhancing the productivity of microalgae cultivated in wastewater toward biofuel production: a critical review. Appl Energy 137:282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.10.032
Chen H et al (2015c) Ca(2+)-regulated cyclic electron flow supplies ATP for nitrogen starvation-induced lipid biosynthesis in green alga. Sci Rep 5:15117. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15117
Chen H, Qiu T, Rong JF, He CL, Wang Q (2015d) Microalgal biofuel revisited: an informatics-based analysis of developments to date and future prospects. Appl Energy 155:585–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.06.055
Chen W, Zhang S, Rong J, Li X, Chen H, He C, Wang Q (2016) Effective biological DeNOx of industrial flue gas by the mixotrophic cultivation of an oil-producing green alga Chlorella sp. C2. Environ Sci Technol 50:1620–1627. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04696
Chen H, Zheng YL, Zhan J, He CL, Wang Q (2017) Comparative metabolic profiling of the lipid-producing green microalga Chlorella reveals that nitrogen and carbon metabolic pathways contribute to lipid metabolism. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0839-4
Chen H, Wang J, Zheng Y, Zhan J, He C, Wang Q (2018) Algal biofuel production coupled bioremediation of biomass power plant wastes based on Chlorella sp. C2 cultivation. Appl Energy 211:296–305
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.02.001
Choi YE, Hwang H, Kim HS, Ahn JW, Jeong WJ, Yang JW (2013) Comparative proteomics using lipid over-producing or less-producing mutants unravels lipid metabolisms in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bioresour Technol 145:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.142
Chojnacka K, Marquez-Rocha FJ (2004) Kinetic and stoichiometric relationships of the energy and carbon metabolism in the culture of microalgae. Biotechnology 3:21–34
Choudhary P, Prajapati SK, Malik A (2016) Screening native microalgal consortia for biomass production and nutrient removal from rural wastewaters for bioenergy applications. Ecol Eng 91:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.11.056
Chung BYW, Deery MJ, Groen AJ, Howard J, Baulcombe DC (2017a) mRNA turnover through CDS-targeting is the primary role of miRNA in the green alga Chlamydomonas. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/088807
Chung YS, Lee JW, Chung CH (2017b) Molecular challenges in microalgae towards cost-effective production of quality biodiesel. Renew Sust Energy Rev 74:139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.02.048
Coons JE, Kalb DM, Dale T, Marrone BL (2014) Getting to low-cost algal biofuels: a monograph on conventional and cutting-edge harvesting and extraction technologies. Algal Res 6:250–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2014.08.005
Couso I, Vila M, Rodriguez H, Vargas MA, Leon R (2015) Overexpression of an exogenous phytoene synthase gene in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii leads to an increase in the content of carotenoids. Biotechnol Prog 27:54–60
da Silva FV, Sant’Anna C (2017) Impact of culture conditions on the chlorophyll content of microalgae for biotechnological applications. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2181-6
Daboussi F et al (2014) Genome engineering empowers the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum for biotechnology. Nat Commun 5:3831. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4831
Daddy S, Zhan J, Jantaro S, He C, He Q, Wang Q (2015) A novel high light-inducible carotenoid-binding protein complex in the thylakoid membranes of Synechocystis PCC 6803. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09480
Davies FK, Work VH, Beliaev AS, Posewitz MC (2014) Engineering limonene and bisabolene production in wild type and a glycogen-deficient mutant of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2014.00021
Deamer D (2005) A giant step towards artificial life? Trends Biotechnol 23:336–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.05.008
Del Campo JA, Garcia-Gonzalez M, Guerrero MG (2007) Outdoor cultivation of microalgae for carotenoid production: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:1163–1174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0844-9
Demirbas A (2009) Progress and recent trends in biodiesel fuels. Energy Convers Manag 50:14–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2008.09.001
Deng MD, Coleman JR (1999) Ethanol synthesis by genetic engineering in cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:523–528
Derelle E et al (2006) Genome analysis of the smallest free-living eukaryote Ostreococcus tauri unveils many unique features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:11647–11652. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604795103
Dexter J, Fu PC (2009) Metabolic engineering of cyanobacteria for ethanol production. Energy Environ Sci 2:857–864. https://doi.org/10.1039/b811937f
Doucha J, Livansky K (2008) Influence of processing parameters on disintegration of Chlorella cells in various types of homogenizers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:431–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1660-6
Douglas SE, Penny SL (1999) The plastid genome of the cryptophyte alga, Guillardia theta: Complete sequence and conserved synteny groups confirm its common ancestry with red algae. J Mol Evol 48:236–244
Durmaz Y, Monteiro M, Bandarra N, Gokpinar S, Isik O (2007) The effect of low temperature on fatty acid composition and tocopherols of the red microalga, Porphyridium cruentum. J Appl Phycol 19:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-006-9127-6
Emanuel SL, Francisco OC, Aurora G, Emilio F, Amaury DM (2016) Characterization of a Mutant Deficient for Ammonium and Nitric Oxide Signalling in the Model System Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plos One 11:e0155128
Englund E, Shabestary K, Hudson EP, Lindberg P (2018) Systematic overexpression study to find target enzymes enhancing production of terpenes in Synechocystis PCC 6803, using isoprene as a model compound. Metab Eng 49:164–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.07.004
Faried M, Samer M, Abdelsalam E, Yousef RS, Attia YA, Ali AS (2017) Biodiesel production from microalgae: processes, technologies and recent advancements. Renew Sust Energy Rev 79:893–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.199
Formighieri C, Melis A (2014) Regulation of beta-phellandrene synthase gene expression, recombinant protein accumulation, and monoterpene hydrocarbons production in Synechocystis transformants. Planta 240:309–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2080-8
Formighieri C, Melis A (2015) A phycocyanin·phellandrene synthase fusion enhances recombinant protein expression and beta-phellandrene (monoterpene) hydrocarbons production in Synechocystis (cyanobacteria). Metab Eng 32:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.09.010
Formighieri C, Melis A (2016) Sustainable heterologous production of terpene hydrocarbons in cyanobacteria. Photosynth Res 130:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-016-0233-2
Formighieri C, Melis A (2018) Cyanobacterial production of plant essential oils. Planta 248:933–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2948-0
Fu W et al (2014) Effects of abiotic stressors on lutein production in the green microalga Dunaliella salina. Microb Cell Fact 13:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-13-3
Ganuza E, Benitez-Santana T, Atalah E, Vega-Orellana O, Ganga R, Izquierdo MS (2008) Crypthecodinium cohnii and Schizochytrium sp as potential substitutes to fisheries-derived oils from seabream (Sparus aurata) microdiets. Aquaculture 277:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.02.005
Gao ZX, Zhao H, Li ZM, Tan XM, Lu XF (2012) Photosynthetic production of ethanol from carbon dioxide in genetically engineered cyanobacteria. Energy Environ Sci 5:9857–9865. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee22675h
Gao X, Gao F, Liu D, Zhang H, Nie XQ, Yang C (2016) Engineering the methylerythritol phosphate pathway in cyanobacteria for photosynthetic isoprene production from CO2. Energ Environ Sci 9:1400–1411. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ee03102h
Ghosh A et al (2016) Progress toward isolation of strains and genetically engineered strains of microalgae for production of biofuel and other value added chemicals: a review. Energy Convers Manag 113:104–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.01.050
Giordano M, Wang Q (2018) Microalgae for Industrial Purposes. In: Vaz S Jr (ed) Biomass and Green Chemistry: building a renewable pathway. Springer, Cham, pp 133–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66736-2_6
Glass JB, Wolfe-Simon F, Anbar AD (2009) Coevolution of metal availability and nitrogen assimilation in cyanobacteria and algae. Geobiology 7:100–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4669.2009.00190.x
Gnansounou E, Raman JK (2016) Life cycle assessment of algae biodiesel and its co-products. Appl Energy 161:300–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.043
Gobler CJ et al (2011) Niche of harmful alga Aureococcus anophagefferens revealed through ecogenomics. P Natl Acad Sci USA 108:4352–4357. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1016106108
Goncalves EC, Wilkie AC, Kirst M, Rathinasabapathi B (2016) Metabolic regulation of triacylglycerol accumulation in the green algae: identification of potential targets for engineering to improve oil yield. Plant Biotechnol J 14:1649–1660. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12523
Grzesik M, Romanowska-Duda Z, Kalaji HM (2017) Effectiveness of cyanobacteria and green algae in enhancing the photosynthetic performance and growth of willow (Salix viminalis L.) plants under limited synthetic fertilizers application. Photosynthetica 55:510–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-017-0716-1
Guarnieri MT, Nag A, Smolinski SL, Darzins A, Seibert M, Pienkos PT (2011) Examination of triacylglycerol biosynthetic pathways via de novo transcriptomic and proteomic analyses in an unsequenced microalga. Plos One 6:e25851. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025851
Guo SL et al (2013) Establishment of an efficient genetic transformation system in Scenedesmus obliquus. J Biotechnol 163:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.10.020
Guschina IA, Harwood JL (2006) Lipids and lipid metabolism in eukaryotic algae. Prog Lipid Res 45:160–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2006.01.001
Gwak Y et al (2014) Comparative analyses of lipidomes and transcriptomes reveal a concerted action of multiple defensive systems against photooxidative stress in Haematococcus pluvialis. J Exp Bot 65:4317–4334. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru206
Hamilton ML, Haslam RP, Napier JA, Sayanova O (2014) Metabolic engineering of Phaeodactylum tricornutum for the enhanced accumulation of omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Metab Eng 22:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.12.003
He Y, Qiu C, Guo Z, Huang J, Wang M, Chen B (2017) Production of new human milk fat substitutes by enzymatic acidolysis of microalgae oils from Nannochloropsis oculata and Isochrysis galbana. Bioresour Technol 238:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.041
Heimann K (2016) Novel approaches to microalgal and cyanobacterial cultivation for bioenergy and biofuel production. Curr Opin Biotech 38:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.02.024
Hempel N, Petrick I, Behrendt F (2012) Biomass productivity and productivity of fatty acids and amino acids of microalgae strains as key characteristics of suitability for biodiesel production. J Appl Phycol 24:1407–1418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9795-3
Ho DP, Ngo HH, Guo W (2014) A mini review on renewable sources for biofuel. Bioresour Technol 169:742–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.07.022
Hockin NL, Mock T, Mulholland F, Kopriva S, Malin G (2012) the response of diatom central carbon metabolism to nitrogen starvation is different from that of green algae and higher plants. Plant Physiol 158:299–312. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.184333
Holbrook GP, Davidson Z, Tatara RA, Ziemer NL, Rosentrater KA, Grayburn WS (2014) Use of the microalga Monoraphidium sp grown in wastewater as a feedstock for biodiesel: cultivation and fuel characteristics. Appl Energy 131:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.06.043
Hu Q, Sommerfeld M, Jarvis E, Ghirardi M, Posewitz M, Seibert M, Darzins A (2008) Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances. Plant J 54:621–639. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03492.x
Hu J, Li T, Xu W, Zhan J, Chen H, He C, Wang Q (2017) Small antisense RNA RblR positively regulates RuBisCo in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Front Microbiol 8:231
Huang JJ, Cheung PC (2011) +UVA treatment increases the degree of unsaturation in microalgal fatty acids and total carotenoid content in Nitzschia closterium (Bacillariophyceae) and Isochrysis zhangjiangensis (Chrysophyceae). Food Chem 129:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.05.021
Huang CH, Shen CR, Li H, Sung LY, Wu MY, Hu YC (2016) CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) for gene regulation and succinate production in cyanobacterium S. elongatus PCC 7942. Microb Cell Fact 15:196. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0595-3
Iwai M, Ikeda K, Shimojima M, Ohta H (2014) Enhancement of extraplastidic oil synthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using a type-2 diacylglycerol acyltransferase with a phosphorus starvation-inducible promoter. Plant Biotechnol J 12:808–819. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12210
Jiang X, Han Q, Gao X, Gao G (2016) Conditions optimising on the yield of biomass, total lipid, and valuable fatty acids in two strains of Skeletonema menzelii. Food Chem 194:723–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.073
Jinkerson RE, Jonikas MC (2015) Molecular techniques to interrogate and edit the Chlamydomonas nuclear genome. Plant J 82:393–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12801
Kanda H, Li P, Yoshimura T, Okada S (2013) Wet extraction of hydrocarbons from Botryococcus braunii by dimethyl ether as compared with dry extraction by hexane. Fuel 105:535–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.08.032
Kilian O, Benemann CS, Niyogi KK, Vick B (2011) High-efficiency homologous recombination in the oil-producing alga Nannochloropsis sp. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:21265–21269. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1105861108
Kiyota H, Okuda Y, Ito M, Hirai MY, Ikeuchi M (2014) Engineering of cyanobacteria for the photosynthetic production of limonene from CO2. J Biotechnol 185:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.05.025
Knies JM (2017) Algae and algal products as novel foods. Ernahrungs Umschau 64:M84–M93. https://doi.org/10.4455/eu.2017.008
Kumar A et al (2010) Enhanced CO(2) fixation and biofuel production via microalgae: recent developments and future directions. Trends Biotechnol 28:371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.04.004
Lam MK, Lee KT (2012) Microalgae biofuels: a critical review of issues, problems and the way forward. Biotechnol Adv 30:673–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.11.008
Lauersen KJ et al (2016) Efficient phototrophic production of a high-value sesquiterpenoid from the eukaryotic microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metab Eng 38:331–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.07.013
Laurens LML et al (2017) Development of algae biorefinery concepts for biofuels and bioproducts; a perspective on process-compatible products and their impact on cost-reduction. Energy Environ Sci 10:1716–1738. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ee01306j
Lee Chang KJ, Nichols CM, Blackburn SI, Dunstan GA, Koutoulis A, Nichols PD (2014) Comparison of Thraustochytrids Aurantiochytrium sp., Schizochytrium sp., Thraustochytrium sp., and Ulkenia sp. for production of biodiesel, long-chain omega-3 oils, and exopolysaccharide. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 16:396–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-014-9560-5
Lee WNP, Wahjudi PN, Xu J, Go VL (2010) Tracer-based metabolomics: concepts and practices. Clin Biochem 43:1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2010.07.027
Lee YC et al (2013) Harvesting of oleaginous Chlorella sp. by organoclays. Bioresour Technol 132:440–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.102
Leite GB, Paranjape K, Abdelaziz AE, Hallenbeck PC (2015) Utilization of biodiesel-derived glycerol or xylose for increased growth and lipid production by indigenous microalgae. Bioresour Technol 184:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.117
Leon R, Vila M, Hernanz D, Vilchez C (2005) Production of phytoene by herbicide-treated microalgae Dunaliella bardawil in two-phase systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:695–701. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20660
Li Y, Han D, Hu G, Dauvillee D, Sommerfeld M, Ball S, Hu Q (2010) Chlamydomonas starchless mutant defective in ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase hyper-accumulates triacylglycerol. Metab Eng 12:387–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2010.02.002
Li J, Zhu D, Niu J, Shen S, Wang G (2011) An economic assessment of astaxanthin production by large scale cultivation of Haematococcus pluvialis. Biotechnol Adv 29:568–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.04.001
Li T, Xu G, Rong J, Chen H, He C, Giordano M, Wang Q (2016) The acclimation of Chlorella to high-level nitrite for potential application in biological NOx removal from industrial flue gases. J Plant Physiol 195:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2016.03.006
Lin PC, Saha R, Zhang F, Pakrasi HB (2017) Metabolic engineering of the pentose phosphate pathway for enhanced limonene production in the cyanobacterium Synechocysti s sp. PCC 6803. Sci Rep 7:17503. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17831-y
Lindberg P, Park S, Melis A (2010) Engineering a platform for photosynthetic isoprene production in cyanobacteria, using Synechocystis as the model organism. Metab Eng 12:70–79
Liu J, Hu Q (2013) Chlorella: industrial production of cell mass and chemicals. In: Handbook of Microalgal Culture: Applied Phycology and Biotechnology, Second Edition, Wiley, Hoboken
Liu BF, Ma C, Xiao RN, Xing DF, Ren HY, Ren NQ (2015) The screening of microalgae mutant strain Scenedesmus sp Z-4 with a rich lipid content obtained by Co-60 gamma-ray mutation. RSC Adv 5:52057–52061. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra07263h
Lodi A, Binaghi L, De Faveri D, Carvalho JCM, Converti A, Del Borghi M (2005) Fed-batch mixotrophic cultivation of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis (Cyanophyceae) with carbon source pulse feeding. Ann Microbiol 55:181–185
Lohr M, Schwender J, Polle JEW (2012) Isoprenoid biosynthesis in eukaryotic phototrophs: a spotlight on algae. Plant Sci 185:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.07.018
Lu YM, Xiang WZ, Wen YH (2011) Spirulina (Arthrospira) industry in Inner Mongolia of China: current status and prospects. J Appl Phycol 23:265–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9552-4
Lu L, Wang J, Yang GP, Zhu BH, Pan KH (2017) Heterotrophic growth and nutrient productivities of Tetraselmis chuii using glucose as a carbon source under different C/N ratios. J Appl Phycol 29:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0919-z
Lv H, Qu G, Qi X, Lu L, Tian C, Ma Y (2013) Transcriptome analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii during the process of lipid accumulation. Genomics 101:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.01.004
Ma YH et al (2014) Antisense knockdown of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase promotes the neutral lipid accumulation in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Microb Cell Fact 13:100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-014-0100-9
Ma F et al (2017) Dynamic changes of IsiA-containing complexes during long-term iron deficiency in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Mol Plant 10:143–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.10.009
Machado IM, Atsumi S (2012) Cyanobacterial biofuel production. J Biotechnol 162:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.03.005
Marcus Y, Altman-Gueta H, Wolff Y, Gurevitz M (2011) Rubisco mutagenesis provides new insight into limitations on photosynthesis and growth in Synechocystis PCC6803. J Exp Bot 62:4173–4182. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err116
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew Sust Energy Rev 14:217–232
Maurya R et al (2015) Lipid extracted microalgal biomass residue as a fertilizer substitute for Zea mays L. Front Plant Sci 6:1266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01266
McMillan JR, Watson IA, Ali M, Jaafar W (2013) Evaluation and comparison of algal cell disruption methods: Microwave, waterbath, blender, ultrasonic and laser treatment. Appl Energy 103:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.09.020
Miandoab LZ, Bagheriehnajjar MB, Hejazi MA, Chaparzadeh N (2015) The psy transcript level and cell composition of Dunaliella salina under salinity. Int J Biosci 6:34–43
Milke LM, Bricelj VM, Parrish CC (2008) Biochemical characterization and nutritional value of three Pavlova spp. in unialgal and mixed diets with Chaetoceros muelleri for postlarval sea scallops, Placopecten magellanicus. Aquaculture 276:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.01.040
Mo R et al (2015) Acetylome analysis reveals the involvement of lysine acetylation in photosynthesis and carbon metabolism in the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J Proteome Res 14:1275–1286. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr501275a
Mouahid A, Crampon C, Toudji SAA, Badens E (2013) Supercritical CO2 extraction of neutral lipids from microalgae: experiments and modelling. J Supercrit Fluid 77:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2013.01.024
Nascimento IA et al (2013) Screening microalgae strains for biodiesel production: lipid productivity and estimation of fuel quality based on fatty acids profiles as selective criteria. Bioenergy Res 6:1–13
Niehaus TD et al (2012) Functional identification of triterpene methyltransferases from Botryococcus braunii race B. J Biol Chem 287:8163–8173. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.316059
Norambuena F, Hermon K, Skrzypczyk V, Emery JA, Sharon Y, Beard A, Turchini GM (2015) Algae in fish feed: performances and fatty acid metabolism in juvenile Atlantic Salmon. Plos One 10:e0124042. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124042
Olasehinde TA, Olaniran AO, Okoh AI (2017) Therapeutic potentials of microalgae in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 22:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030480
Osbourn AE, O’Maille PE, Rosser SJ, Lindsey K (2012) Synthetic biology. 4th New Phytologist Workshop, Bristol, UK, June 2012. New Phytol 196:671–677. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04374.x
Oudot-Le Secq MP, Grimwood J, Shapiro H, Armbrust EV, Bowler C, Green BR (2007) Chloroplast genomes of the diatoms Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Thalassiosira pseudonana: comparison with other plastid genomes of the red lineage. Mol Genet Genom 277:427–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0199-4
Pade N et al (2016) Insights into isoprene production using the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0503-4
Palenik B et al (2007) The tiny eukaryote Ostreococcus provides genomic insights into the paradox of plankton speciation. P Natl Acad Sci USA 104:7705–7710. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611046104
Park JJ et al (2015) The response of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to nitrogen deprivation: a systems biology analysis. Plant J 81:611–624. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12747
Pasquet V, Ulmann L, Mimouni V, Guiheneuf F, Jacquette B, Morant-Manceau A, Tremblin G (2014) Fatty acids profile and temperature in the cultured marine diatom Odontella aurita. J Appl Phycol 26:2265–2271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0252-3
Pratheesh PT, Vineetha M, Kurup GM (2014) An efficient protocol for the Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Biotechnol 56:507–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9720-2
Puerta MVS, Bachvaroff TR, Delwiche CF (2004) The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the haptophyte Emiliania huxleyi and its relation to heterokonts. DNA Res 11:1–10
Qiao HJ, Cong C, Sun CX, Li BS, Wang JY, Zhang LM (2016) Effect of culture conditions on growth, fatty acid composition and DHA/EPA ratio of Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Aquaculture 452:311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.11.011
Ramazanov A, Ramazanov Z (2006) Isolation and characterization of a starchless mutant of Chlorella pyrenoidosa STL-PI with a high growth rate, and high protein and polyunsaturated fatty acid content. Phycol Res 54:255–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1835.2006.00416.x
Raven JA, Beardall J, Giordano M (2014) Energy costs of carbon dioxide concentrating mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Photosynth Res 121:111–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9962-7
Rawat I, Kumar RR, Mutanda T, Bux F (2013) Biodiesel from microalgae: a critical evaluation from laboratory to large scale production. Appl Energy 103:444–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.10.004
Reinsvold RE, Jinkerson RE, Radakovits R, Posewitz MC, Basu C (2011) The production of the sesquiterpene beta-caryophyllene in a transgenic strain of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis. J Plant Physiol 168:848–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.11.006
Rengasamy KR, Kulkarni MG, Stirk WA, Van Staden J (2014) Advances in algal drug research with emphasis on enzyme inhibitors. Biotechnol Adv 32:1364–1381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.08.005
Richardson JW, Johnson MD, Outlaw JL (2012) Economic comparison of open pond raceways to photo bio-reactors for profitable production of algae for transportation fuels in the Southwest. Algal Res 1:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2012.04.001
Run CL, Fang L, Fan JH, Fan CM, Luo YC, Hu ZM, Li YG (2016) Stable nuclear transformation of the industrial alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Algal Res 17:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.05.002
Saeid A, Chojnacka K, Korczynski M, Korniewicz D, Dobrzanski Z (2013) Biomass of Spirulina maxima enriched by biosorption process as a new feed supplement for swine. J Appl Phycol 25:667–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9901-6
Samarasinghe N, Fernando S, Lacey R, Faulkner WB (2012) Algal cell rupture using high pressure homogenization as a prelude to oil extraction. Renew Energy 48:300–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2012.04.039
Savakis P, Hellingwerf KJ (2015) Engineering cyanobacteria for direct biofuel production from CO2. Curr Opin Biotech 33:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.09.007
Scott SA, Davey MP, Dennis JS, Horst I, Howe CJ, Lea-Smith DJ, Smith AG (2010) Biodiesel from algae: challenges and prospects. Curr Opin Biotech 21:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2010.03.005
Sheng J, Vannela R, Rittmann BE (2011) Evaluation of cell-disruption effects of pulsed-electric-field treatment of Synechocystis PCC 6803. Environ Sci Technol 45:3795–3802. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103339x
Singh RN, Sharma S (2012) Development of suitable photobioreactor for algae production: a review. Renew Sust Energy Rev 16:2347–2353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.01.026
Sizova I, Greiner A, Awasthi M, Kateriya S, Hegemann P (2013) Nuclear gene targeting in Chlamydomonas using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. Plant J 73:873–882. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12066
Soratana K, Landis AE (2011) Evaluating industrial symbiosis and algae cultivation from a life cycle perspective. Bioresour Technol 102:6892–6901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.018
Spolaore P, Joannis-Cassan C, Duran E, Isambert A (2006) Commercial applications of microalgae. J Biosci Bioeng 101:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.101.87
Tamayo-Ordonez YJ, Ayil-Gutierrez BA, Sanchez-Teyer FL, De la Cruz-Arguijo EA, Tamayo-Ordonez FA, Cordova-Quiroz AV, Tamayo-Ordonez MC (2017) Advances in culture and genetic modification approaches to lipid biosynthesis for biofuel production and in silico analysis of enzymatic dominions in proteins related to lipid biosynthesis in algae. Phycol Res 65:14–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/pre.12162
Temina M, Rezankova H, Rezanka T, Dembitsky VM (2007) Diversity of the fatty acids of the Nostoc species and their statistical analysis. Microbiol Res 162:308–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2006.01.010
Thapa HR, Naik MT, Okada S, Takada K, Molnar I, Xu YQ, Devarenne TP (2016) A squalene synthase-like enzyme initiates production of tetraterpenoid hydrocarbons in Botryococcus brauniiRace L. Nat Commun 7:ARTN 11198. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11198
Tibbetts SM, Yasumaru F, Lemos D (2017) In vitro prediction of digestible protein content of marine microalgae (Nannochloropsis granulata) meals for Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Algal Res 21:76–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.11.010
Torres-Duran PV, Ferreira-Hermosillo A, Juarez-Oropeza MA (2007) Antihyperlipemic and antihypertensive effects of Spirulina maxima in an open sample of Mexican population: a preliminary report. Lipids Health Dis 6:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-6-33
Tran M, Van C, Barrera DJ, Pettersson PL, Peinado CD, Bui J, Mayfield SP (2013) Production of unique immunotoxin cancer therapeutics in algal chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E15–22. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1214638110
Trentacoste EM, Martinez AM, Zenk T (2015) The place of algae in agriculture: policies for algal biomass production. Photosynth Res 123:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-014-9985-8
Uchida H, Sumimoto K, Oki T, Nishii I, Mizohata E, Matsunaga S, Okada S (2018) Isolation and characterization of 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase gene from Botryococcus braunii, race B. J Plant Res 131:839–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-018-1039-4
Vidyashankar S, VenuGopal KS, Chauhan VS, Muthukumar SP, Sarada R (2015) Characterisation of defatted Scenedesmus dimorphus algal biomass as animal feed. J Appl Phycol 27:1871–1879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0498-9
Wan C et al (2015) Current progress and future prospect of microalgal biomass harvest using various flocculation technologies. Bioresour Technol 184:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.081
Wang B, Pugh S, Nielsen DR, Zhang W, Meldrum DR (2013) Engineering cyanobacteria for photosynthetic production of 3-hydroxybutyrate directly from CO2. Metab Eng 16:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.01.001
Wang Q, Lu Y, Xin Y, Wei L, Huang S, Xu J (2016a) Genome editing of model oleaginous microalgae Nannochloropsis spp. by CRISPR/Cas9. Plant J 88:1071–1081. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13307
Wang X et al (2016b) Enhanced limonene production in cyanobacteria reveals photosynthesis limitations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:14225–14230. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1613340113
Wang Y, Sun T, Gao X, Shi M, Wu L, Chen L, Zhang W (2016c) Biosynthesis of platform chemical 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) directly from CO2 in cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Metab Eng 34:60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.10.008
Wannathong T, Waterhouse JC, Young RE, Economou CK, Purton S (2016) New tools for chloroplast genetic engineering allow the synthesis of human growth hormone in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:5467–5477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7354-6
Weeks DP (2011) Homologous recombination in Nannochloropsis: a powerful tool in an industrially relevant alga. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:20859–20860. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1118670109
Wells ML et al (2017) Algae as nutritional and functional food sources: revisiting our understanding. J Appl Phycol 29:949–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0974-5
Weyman PD et al (2015) Inactivation of Phaeodactylum tricornutum urease gene using transcription activator-like effector nuclease-based targeted mutagenesis. Plant Biotechnol J 13:460–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12254
Wichmann J, Baier T, Wentnagel E, Lauersen KJ, Kruse O (2018) Tailored carbon partitioning for phototrophic production of (E)-alpha-bisabolene from the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metab Eng 45:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.12.010
Worden AZ et al (2009) Green evolution and dynamic adaptations revealed by genomes of the marine picoeukaryotes. Micromonas Sci 324:268–272. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1167222
Wuang SC, Khin MC, Qiang P, Chua D, Luo YD (2016) Use of Spirulina biomass produced from treatment of aquaculture wastewater as agricultural fertilizers. Algal Res 15:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.02.009
Xiong W, Morgan JA, Ungerer J, Wang B, Maness PC, Yu J (2015) The plasticity of cyanobacterial metabolism supports direct CO2 conversion to ethylene. Nat Plants 1:15053
Xu J, Hu H (2013) Screening high oleaginous Chlorella strains from different climate zones. Bioresour Technol 144:637–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.029
Xu W, Chen H, He CL, Wang Q (2014) Deep sequencing-based identification of small regulatory RNAs in Synechocystis sp PCC 6803. Plos One 9:e92711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092711
Xue Y, Zhang Y, Cheng D, Daddy S, He Q (2014) Genetically engineering Synechocystis sp. Pasteur Culture Collection 6803 for the sustainable production of the plant secondary metabolite p-coumaric acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:9449–9454. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1323725111
Yang MK et al (2014) Proteogenomic analysis and global discovery of posttranslational modifications in prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E5633–5642. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1412722111
Yang J, Pan YF, Bowler C, Zhang LX, Hu HH (2016) Knockdown of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase increases carbon flux to lipid synthesis in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Algal Res 15:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.02.004
Yu Y, Wang HY, Yang Y, Pei GF, Qin Z, Ji JJ (2016) Study on preparation of nutritional nostoc spheroids jelly amino acids and biotic resources. Amino Acids Biotic Res 38:30–35
Zhan J, Rong JF, Wang Q (2017) Mixotrophic cultivation, a preferable microalgae cultivation mode for biomass/bioenergy production, and bioremediation, advances and prospect. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:8505–8517
Zhang C, Hu H (2014) High-efficiency nuclear transformation of the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum by electroporation. Mar Genom 16:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2013.10.003
Zhang YM, Chen H, He CL, Wang Q (2013) Nitrogen starvation induced oxidative stress in an oil-producing green alga Chlorella sorokiniana C3. Plos One 8:e69225. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069225
Zhang X, Chen H, Chen W, Qiao Y, He C, Wang Q (2014a) Evaluation of an oil-producing green alga Chlorella sp. C2 for biological DeNOx of industrial flue gases. Environ Sci Technol 48:10497–10504. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5013824
Zhang X, Rong J, Chen H, He C, Wang Q (2014b) Current status and outlook in the application of microalgae in biodiesel production and environmental protection. Front Energy Res 2:32
Zhao C, Li Z, Li T, Zhang Y, Bryant DA, Zhao J (2015) High-yield production of extracellular type-I cellulose by the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Cell Discov 1:15004. https://doi.org/10.1038/celldisc.2015.4
Zhou J, Li Y (2010) Engineering cyanobacteria for fuels and chemicals production. Protein cell 1:207–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-010-0043-9
Zhu LD (2015) Biorefinery as a promising approach to promote microalgae industry: an innovative framework. Renew Sust Energy Rev 41:1376–1384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.040
Acknowledgements
This work was supported jointly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870041, 31770128, 31700107), Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2017CFA021), and the State Key Laboratory of Freshwater Ecology and Biotechnology (2016FB11). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Funding
All authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Li, T. & Wang, Q. Ten years of algal biofuel and bioproducts: gains and pains. Planta 249, 195–219 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-3066-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-3066-8