Abstract
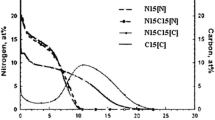
In the early 1970s, Professor Dayananda developed a technique for the direct integration of fluxes from the concentration profiles in vapor-solid diffusion couples to determine diffusion coefficients and atomic mobilities. As part of a project to control and optimize the industrial carburization process in mild- and low-alloyed steels, a modified integration analysis was applied to determine the mass transfer coefficient in the gas boundary layer and carbon diffusivity in austenite. Because carbon flux and surface carbon content vary with time during single-stage carburizing even with a fixed carbon potential in the atmosphere, a mass balance at the gas-solid interface must serve as a boundary condition. This article discusses the numerical modeling of gas carburizing, and focuses on calculating the mass transfer and carbon diffusivity parameters using the simulated concentration profiles. This approach validates the proposed method by comparing the calculated parameters with those used in simulation. The results were compared with previous determinations and predictions reported in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Wells and R.F. Mehl, Rate of Diffusion of Carbon in Austenite in Plain Carbon, in Nickel and in Manganese Steels, American Institute Mining Metallurgical Engineers, Technical Publication, 1940, p 1180
K.E. Blazek and P.R. Cost, Carbon Diffusivity in Iron-Chromium Alloys,Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1976,17(10), p 630–636
W. Batz and R.F. Mehl, Diffusion Coefficient of Carbon in Austenite,Trans. AIME, 1950,188, p 553–560
P. Stolar and B. Prenosil, Kinetics of Transfer of Carbon from Carburising and Carbonitriding Atmospheres,Metall. Mater., 1984,22(5), p 348–353
B.A. Moiseev, Y.M. Brunzel’, and L.A. Shvartsman, Kinetics of Carburizing in an Endothermal Atmosphere,Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 1979,21(5–6), p 437–442
H.W. Walton, Mathematical Modeling of the Carburising Process for Microprocessor Control,Heat Treat. Met., 1983,10(1), p 23–26
E.L. Gyulikhandanov and A.D. Khaidorov, Carburizing Low-Carbon Heat-Resistant Steels Containing Molybdenum and Titanium,Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 1991,33(5–6), p 344–348
M. Yan, Z. Liu, and G. Zu, The Mathematical Model of Surface Carbon Concentration Growth during Gas Carburization,Mater. Sci. Prog., 1992,6(3), p 223–225 (in Chinese)
T. Turpin, J. Dulcy, and M. Gantois, Carbon Diffusion and Phase Transformations during Gas Carburizing of High-Alloyed Stainless Steels: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling,Metall. Trans. A, 2005,36(10), p 2751–2760
A. Ruck, D. Monceau, and H.J. Grabke, Effects of Tramp Elements Cu, P, Pb, Sb and Sn on the Kinetics of Carburization of Case Hardening Steels,Steel Res., 1996,67(6), p 240–246
R. Collin, S. Gunnarson, and D. Thulin, Mathematical Model for Predicting Carbon Concentration Profiles of Gas-Carburized Steel,J. Iron Steel Inst., 1972,210, p 785–789
R.P. Smith, The Diffusivity of Carbon in Iron by Steady-State Method,Acta Metal., 1953,1, p 578–587
S.K. Bose and H.J. Grabke, Diffusion Coefficient of Carbon in Fe-Ni Austenite in the Temperature Range 950–1100 Degree C,Z. Metallkd., 1978,69(1), p 8–15
S.K. Roy, H.J. Grabke, and W. Wepner, Diffusivity of Carbon in Austenitic Fe-Si-C Alloys,Arch. Eisenhuett., 1980,51(3), p 91–96
C. Matano, On the Relation Between the Diffusion-Coefficients and Concentrations of Solid Metals,Jpn. J. Phys., 1933,8(3), p 109–113
M.A. Dayananda, Atomic Mobilities in Multicomponent Diffusion and Their Determination,Trans. AIME, 1968,242, p 1369–1372
M.A. Dayananda and C.W. Kim, Zero-Flux Planes and Flux Reversals in Cu-Ni-Zn Diffusion Couples,Metall. Trans. A, 1979,10(9), p 1333–1339
P.T. Carlson, M.A. Dayananda, and R.E. Grace, Diffusion in Ternary Ag-Zn-Cd Solid Solutions,Metall. Trans. A, 1972,3(4), p 819–826
A.L. Hurley and M.A. Dayananda, Multiphase Diffusion in Ag-Zn Alloys,Metall. Trans. A, 1970,1(1), p 139–143
N.R. Iorio, M.A. Dayananda, and R.E. Grace, Intrinsic Diffusion and Vacancy Wind Effects in Ag-Cd Alloys,Metall. Trans. A, 1973,4(5), p 1339–1346
G.H. Cheng, M.A. Dayananda, and R.E. Grace, Diffusion Studies in Ag-Zn Alloys,Metall. Trans. A, 1975,6(1), p 21–27
J. Dulcy, P. Bilger, D. Zimmermann, and M. Gantois, Characterization and Optimization of a Carburizing Treatment in Gas Phase: Definition of a New Process,Metall. Ital., 1999,91(4), p 39–44
W.H. McAdams,Heat Transmission, New York, McGraw-Hill, 1954, p 43–50
B. Million, K. Bacilek, J. Kucera, P. Michalicka, and A. Rek, Carbon Diffusion and Thermodynamic Characteristics in Chromium Steels,Z. Metllkd., 1995,86(10), p 706–712 (Materials Research and Advanced Techniques)
J. Kucera and K. Stransky, The Dependence of Carbon Diffusion Coefficients in Austenitic Ternary Alloys on Concentration of Additive Elements,Acta Tech. CSAV, 2003,48(4), p 353–364 (Ceskoslovensk Akademie Ved)
R.P. Smith, The Diffusivity of Carbon in γ-Fe-Co Alloys,Trans. AIME, 1964,230, p 476–480
M.M. Thete, Simulation of Gas Carburising: Development of Computer Program with Systematic Analyses of Process Variables Involved,Surf. Eng., 2003,19(3), p 217–228
G.G. Tibbetts, Diffusivity of Carbon in Iron and Steels at High Temperatures,J. Appl. Phys., 1980,51(9), p 4813–4816
J.I. Goldstein and A.E. Moren, Diffusion Modeling of the Carburization Process,Metall. Trans. A, 1978,9(11), p 1515–1525
G.E. Totten and M.A.H. Howes,Steel Heat Treatment Handbook, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, 1997
L. Sproge and J. Agren, Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Gas Consumption in the Gas Carburizing Process,J. Heat Treat., 1988,6, p 9–19
J. Agren, Revised Expression for the Diffusivity of Carbon in Binary Fe-C Austenite,Scripta Metall., 1986,20(11), p 1507–1510
R.M. Asimow, Analysis of the Variation of the Diffusion Constant of Carbon in Austenite with Concentration,Trans. AIME, 1964,230(3), p 611–613
J. Crank,The Mathematics of Diffusion, 1st ed., Oxford, UK, Clarendon Press, 1956, p 42–62
K.E. Rimmer, E. Schwarz-Bergkampf, and J. Wunning, Surface Reaction Rate in Gas Carburizing,Haerterei-Technische Mitteilungen, 1975,30(3), p 152–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karabelchtchikova, O., Sisson, R.D. Carbon diffusion in steels: A numerical analysis based on direct integration of the flux. JPED 27, 598–604 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02736561
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02736561