Abstract
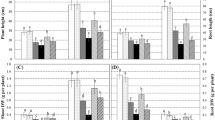
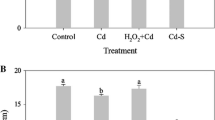
A hydroponic experiment was carried out to study the role of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in enhancing tolerance and reducing translocation of cadmium (Cd) in rice seedlings. Plant growth (length and biomass of shoot and root) was significantly repressed by Cd exposure. However, pretreatment with 100 μM H2O2 for 1d mitigated Cd stress by inducing enzyme activities for antioxidation (e.g., superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), guaiacol peroxidase (GPX), ascorbate peroxidase (APX)) and detoxification (e.g., glutathione S-transferase (GST)) as well as by elevating contents of reduced glutathione (GSH) and ascorbic acid (AsA). As a result, H2O2 and malondialdehyde (MDA) content decreased in plants and the seedling growth was less inhibited. On the other hand, H2O2 pretreatment decreased Cd concentration in shoots, thus lowered the ratio of Cd concentration in shoots and roots (S/R), indicating that H2O2 may affect Cd distribution in rice seedlings. The improved Cd tolerance is partly due to an enhanced antioxidative system that efficiently prevents the accumulation of H2O2 during Cd stress. Increased Cd sequestration in rice roots may contribute to the decline of Cd translocation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- AsA:
-
Ascorbic acid
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- CDNB:
-
1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene
- GPOX:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GPX:
-
Guaiacol peroxidase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- GSSG:
-
Oxidized glutathione
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- LSD:
-
Least-significant-differences
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NBT:
-
Nitro blue tetrazolium chloride
- NEM:
-
N-Ethylmaleimide
- OPT:
-
O-Phthalaldehyde
- PCs:
-
Phytochelatins
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- TCA:
-
Tricholoroacetic acid
References
Adam AL, Bestwick CS, Barna B, Mansfield JW (1995) Enzymes regulating the accumulation of active oxygen species during the hypersensitive reaction of bean to Pseudomonas syringae pv. Phaseolicola. Planta 197:240–249. doi:10.1007/BF00202643
Adamis PDB, Gomes DS, Pinto MLCC, Panek AD, Eleutherio ECA (2004) The role of glutathione transferases in cadmium stress. Toxicol Lett 154:81–88. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.07.003
Adamis PDB, Panek AD, Eleutherio ECA (2007) Vacuolar compartmentation of the cadmium-glutathione complex protects Saccharomyces cerevisiae from mutagenesis. Toxicol Lett 173:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.06.002
Ammar WB, Nouairi I, Zarrouk M, Jemal F (2007) Cadmium stress induces changes in the lipid composition and biosynthesis in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) leaves. Plant Growth Regul 53:75–85. doi:10.1007/s10725-007-9203-1
Azevedo Neto AD, Prisco JT, Ene’as-Filho J, Medeiros JVR, Gomes-Filho E (2005) Hydrogen peroxide pre-treatment induces salt stress acclimation in maize plants. J Plant Physiol 162:1114–1122. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2005.01.007
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Cai WM, Tang ZC (1999) Plant tolerance physiology. In: Tang ZC (ed) Experimental guide for modern plant physiology, 1st edn. Science Press, Beijing, pp 315–316
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay of catalase and perxoidase. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods in enzymology, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York-London, pp 764–775
Cho UH, Seo NH (2005) Oxidative stress in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to cadmium is due to hydrogen peroxide accumulation. Plant Sci 168:113–120. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.07.021
Davis RD (1984) Cadmium-a complex environmental problem. Part II: Cadmium in sludges used as fertilizer. Cell Mol Life Sci 40:117–126
Dixit V, Pandey V, Shyam R (2001) Differential antioxidative responses to cadmium in roots and leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L.cv.Azad). J Exp Bot 52:1101–1109. doi:10.1093/jexbot/52.358.1101
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2005) Oxidant and antioxidant signalling in plants: a re-evaluation of the concept of oxidative stress in a physiological context. Plant Cell Environ 28:1056–1071. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01327.x
Foyer CH, Lopez-Delgado H, Dat JF, Scott IM (1997) Hydrogen peroxide- and glutathione- associated mechanisms of acclamatory stress tolerance and signaling. Physiol Plant 100:241–254. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb04780.x
Ghani A, Wahid A (2007) Varietal difference for cadmium-induced seedling mortality and foliar-toxicity symptoms in mung bean (Vigna radiata). Int J Agric Biol 9:555–558
Gong M, Chen B, Li ZG, Guo LH (2001) Heat-shock-induced cross adaptation to heat, chilling, drought and salt stress in maize seedlings and involvement of H2O2. J Plant Physiol 158:1125–1130. doi:10.1078/0176-1617-00327
Guo B, Liang YC, Li ZJ, Guo W (2007a) Role of salicylic acid in alleviating cadmium toxicity in rice roots. J Plant Nutr 30:427–439. doi:10.1080/01904160601171835
Guo B, Liang YC, Zhu YG, Zhao FJ (2007b) Role of salicylic acid in alleviating oxidative damage in rice roots (Oryza sativa) subjected to cadmium stress. Environ Pollut 147:743–749. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.09.007
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hart JJ, Welch RM, Norvell WA, Sullivan LA, Kochian LV (1998) Characterization of cadmium binding, uptake, and translocation in intact seedlings of bread and durum wheat cultivars. Plant Physiol 116:1413–1420. doi:10.1104/pp.116.4.1413
He JY, Zhu C, Ren YF, Yan YP, Cheng C, Jiang DA, Sun ZX (2008) Uptake, subcellular distribution, and chemical forms of cadmium in wild-type and mutant rice. Pedosphere 18:371–377. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(08)60027-2
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplast I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 25:189–198. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1976) A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74:214–226. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90326-2
Hsu YT, Kao CH (2007) Toxicity in leaves of rice exposed to cadmium is due to hydrogen peroxide accumulation. Plant Soil 298:231–241. doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9357-7
Iannelli MA, Pietrini F, Fiore L, Petrilli L, Massacci A (2002) Antioxidant response to cadmium in Phragmites australis plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:977–982. doi:10.1016/S0981-9428(02)01455-9
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1982) Glycolate metabolism of the submerged aquatic angiosperms during aging. Aquat Bot 112:345–354. doi:10.1016/0304-3770(82)90026-2
Levine A, Tenhaken R, Dixon R, Lamb C (1994) H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell 79:583–593. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90544-4
Marrs KA (1996) The functions and regulation of glutathione S-transferase in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:127–158. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.47.1.127
Metwally A, Finkemeier I, Georgi M, Dietz KJ (2003) Salicylic acid alleviates the cadmium toxicity in barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 132:272–281. doi:10.1104/pp.102.018457
Molina AS, Nievas C, Chaca MVP, Garibotto F, Gonza’lez U, Marsá SM, Luna C, Gime’nez MS, Zirulnik F (2008) Cadmium-induced oxidative damage and antioxidative defense mechanisms in Vigna mungo L. Plant Growth Regul 56:285–295. doi:10.1007/s10725-008-9308-1
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Neill S, Desikan R, Hancock J (2002) Hydrogen peroxide signalling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:388–395. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00282-0
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:249–279. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.249
Noctor G, Gomez LA, Vanacker H, Foyer CH (2002) Interactions between biosynthesis, comparmentation and transport in the control of glutathione homeostasis and signaling. J Exp Bot 53:1283–1304. doi:10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1283
Pnueli L, Liang HJ, Rozenberg M, Mittler R (2003) Growth suppression, altered stomatal responses, and augmented induction of heat shock proteins in cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase (APX1)-deficient Arabidopsis plants. Plant J 34:187–203. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01715.x
Polidoros AN, Scandalios JG (1999) Role of hydrogen peroxide and different classes of antioxidants in the regulation of catalase and glutathione S-transferase gene expression in maize (Zea mays L.). Physiol Plant 106:112–120. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3054.1999.106116.x
Prasad TK, Anderson MD, Martin BA, Stewart CR (1994) Evidence for chilling-induced oxidative stress in maize seedlings and a regulatory role for hydrogen peroxide. Plant Cell 6:65–74
Qadir S, Qureshi MI, Javed S, Abdin MZ (2004) Genotypic variation in phytoremediation potential of Brassica juncea cultivars exposed to Cd stress. Plant Sci 167:1171. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.06.018
Rao MV, Paliyath G, Ormrod DP, Murr DP, Watkins CB (1997) Influence of salicylic acid on H2O2 production, oxidative stress, and H2O2- metabolizing enzymes. Plant Physiol 115:137–149. doi:10.1104/pp.115.1.137
Salt DE, Rauser WE (1995) MgATP dependent transport of phytochelatins across the tonoplast of oat roots. Plant Physiol 107:1293–1301
Sanità di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130. doi:10.1016/S0098-8472(98)00058-6
Shah K, Kumar RG, Verma S, Dubey RS (2001) Effect of cadmium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide anion generation and activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice seedlings. Plant Sci 161:1135–1144. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00517-9
Stewart RRC, Bewley JD (1980) Lipid peroxidation associated with accelerated aging of soybean axes. Plant Physiol 65:245–248. doi:10.1104/pp.65.2.245
Uchida A, Jagendorf AT, Hibino T, Takabe T, Takabe T (2002) Effects of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide on both salt and heat stress tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 163:515–523. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00159-0
Vázquez MD, Poschenrieder C, Barcelo J (1992) Ultrastructural effects and localization of low cadmium concentrations in bean roots. New Phytol 120:215–226. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1992.tb05657.x
Wahid A, Perveen M, Gelani S, Basra SMA (2007) Pretreatment of seed with H2O2 improves salt tolerance of wheat seedlings by alleviation of oxidative damage and expression of stress proteins. J Plant Physiol 164:283–294. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2006.01.005
Xu Q, Xu X, Zhao Y, Jiao K, Herbert SJ, Hao L (2008) Salicylic acid, hydrogen peroxide and calcium-induced saline tolerance associated with endogenous hydrogen peroxide homeostasis in naked oat seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 54:249–259. doi:10.1007/s10725-007-9247-2
Yu CW, Murphy TM, Sung WW, Lin CH (2002) H2O2 treatment induces glutathione accumulation and chilling tolerance in mung bean. Funct Plant Biol 29:1081–1087. doi:10.1071/PP01264
Acknowledgment
Financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (30700479) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (20060390288) are gratefully acknowledged. We also thank Dr. Yongguan Zhu for his helpful comments on the manuscript. Technical assistance from Junjie Zhao, Xiaojuan Bai, Fang Wang, Gaochuan Zhang and Rui Zhang are deeply appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Ge, Y., Zhang, C. et al. Cadmium toxicity and translocation in rice seedlings are reduced by hydrogen peroxide pretreatment. Plant Growth Regul 59, 51–61 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-009-9387-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-009-9387-7