Abstract
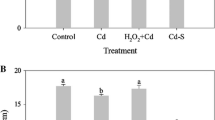
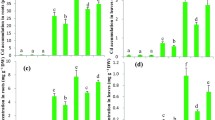
Greenhouse hydroponic experiments were conducted to evaluate the ameliorative effects of NaHS, a donor of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), on different levels of cadmium (Cd) stress in barley seedlings. The results showed that Cd stress dramatically reduced plant biomass, chlorophyll and soluble protein contents. Exogenous application of H2S significantly alleviated Cd-induced growth inhibition and reductions in chlorophyll content, and dramatically depressed leaf malondialdehyde (MDA) accumulation. Addition of H2S markedly reduced Cd concentration in plants and increased leaf soluble protein contents compared with the corresponding Cd-only treatments. Supplemental H2S counteracted Cd-induced alterations of certain antioxidant enzymes, e.g. elevated depressed superoxide dismutase in leaves and roots and depressed Cd-induced increase in leaf catalase and ascorbate peroxidase activities. Pretreatment with 200 μM NaHS markedly reduced the accumulation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide ions (O ⋅−2 ) in roots tissues treated with 5 and 25 μM Cd, which was consistent with the result of histochemical staining of roots. Compared with non-pretreated plants, exogenous H2S significantly increased reduced glutathione contents and ascorbate contents in barley given the 25 μM Cd treatment. These results indicate that the mitigated Cd toxicity by H2S is involved in the reduced Cd uptake/translocation and decreased MDA, H2O2 and O ⋅−2 accumulation, and increased chlorophyll.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cai Y, Cao FB, Wei K, Zhang GP, Wu FB (2011) Genotypic dependent effect of exogenous glutathione on Cd-induced changes in proteins, ultrastructure and antioxidant defense enzymes in rice seedlings. J Hazard Mater 192:1056–1066
Cao FB, Chen F, Sun HY, Zhang GP, Chen ZH, Wu FB (2014a) Genome-wide transcriptome and functional analysis of two contrasting genotypes reveals key genes for cadmium tolerance in barley. BMC Genomics 15:611
Cao FB, Wang RF, Cheng WD, Zeng FR, Ahmed IM, Hu XN, Zhang GP, Wu FB (2014b) Genotypic and environmental variation in cadmium, chromium, lead and copper in rice and approaches for reducing the accumulation. Sci Total Environ 496:275–281
Chen F, Wang F, Sun HY, Cai Y, Mao WH, Zhang GP, Vincze E, Wu FB (2010a) Genotype-dependent effect of exogenous nitric oxide on cd-induced changes in antioxidative metabolism, ultrastructure, and photosynthetic performance in barley seedlings (Hordeum vulgare). J Plant Growth Regul 29:394–408
Chen F, Wang F, Wu FB, Mao WH, Zhang GP, Zhou MX (2010b) Modulation of exogenous glutathione in antioxidant defense system against Cd stress in the two barley genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:663–672
Chen J, Wu FH, Wang WH, Zheng CJ, Lin GH, Dong XJ, He JX, Pei ZM, Zheng HL (2011) Hydrogen sulphide enhances photosynthesis through promoting chloroplast biogenesis, photosynthetic enzyme expression, and thiol redox modification in Spinacia oleracea seedlings. J Exp Bot 62:4481–4493
Chen J, Wang WH, Wu FH, You CY, Liu TW, Dong XJ, He JX, Zheng HL (2012) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in barley seedlings. Plant Soil 362:301–318
Christou A, Manganaris GA, Papadopoulos I, Fotopoulos V (2013) Hydrogen sulfide induces systemic tolerance to salinity and non-ionic osmotic stress in strawberry plants through modification of reactive species biosynthesis and transcriptional regulation of multiple defence pathways. J Exp Bot 64:1953–1966
Cuypers A, Plusquin M, Remans T, Jozefczak M, Keunen E, Gielen H, Opdenakker K, Nair AR, Munters E, Artois TJ, Nawrot T, Vangronsveld J, Smeets K (2010) Cadmium stress: an oxidative challenge. Biometals 23:927–940
Davis RD (1984) Cadmium in sludges used as fertilizer. Experientia 40:117–126
Dawood M, Cao F, Jahangir MM, Zhang G, Wu F (2012) Alleviation of aluminum toxicity by hydrogen sulfide is related to elevated ATPase, and suppressed aluminum uptake and oxidative stress in barley. J Hazard Mater 209–210:121–128
Fang T, Cao Z, Li J, Shen W, Huang L (2014) Auxin-induced hydrogen sulfide generation is involved in lateral root formation in tomato. Plant Physiol Biochem 76:44–51
Hasan SA, Fariduddin Q, Ali B, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2009) Cadmium: toxicity and tolerance in plants. J Environ Biol 30:165–174
Herren T, Feller U (1997) Transport of cadmium via xylem and phloem in maturing wheat shoots: comparison with the translocation of zinc, strontium and rubidium. Ann Bot 80:623–628
Hou Z, Wang L, Liu J, Hou L, Liu X (2013) Hydrogen sulfide regulates ethylene-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Integr Plant Biol 55:277–289
Jin Z, Xue S, Luo Y, Tian B, Fang H, Li H, Pei Y (2013) Hydrogen sulfide interacting with abscisic acid in stomatal regulation responses to drought stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 62:41–46
Li L, Wang Y, Shen W (2012) Roles of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in the alleviation of cadmium-induced oxidative damage in alfalfa seedling roots. Biometals 25:617–631
Lin L, Zhou WH, Dai HX, Cao FB, Zhang GP, Wu FB (2012) Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. J Hazard Mater 235:343–351
Lisjak M, Srivastava N, Teklic T, Civale L, Lewandowski K, Wilson I, Wood ME, Whiteman M, Hancock JT (2010) A novel hydrogen sulfide donor causes stomatal opening and reduces nitric oxide accumulation. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:931–935
Mostofa MG, Hossain MA, Fujita M, Tran LSP (2015a) Physiological and biochemical mechanisms associated with trehalose-induced copper-stress tolerance in rice. Sci Rep 5:11433
Mostofa MG, Rahman A, Ansary MM, Watanabe A, Fujita M, Tran LS (2015b) Hydrogen sulfide modulates cadmium-induced physiological and biochemical responses to alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice. Sci Rep 5:14078
Ryan JA, Pahren HR, Lucas JB (1982) Controlling cadmium in the human food-chain—a review and rationale based on health-effects. Environ Res 28:251–302
Sanita di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Savvides A, Ali S, Tester M, Fotopoulos V (2016) Chemical priming of plants against multiple abiotic stresses: mission possible? Trends Plant Sci 21:329–340
Singh PK, Tewari RK (2003) Cadmium toxicity induced changes in plant water relations and oxidative metabolism of Brassica juncea L. plants. J Environ Biol 24:107–112
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal-ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–336
Sun HY, Zhang XH, He XY, Ahmed IM, Cao FB, Zhang GP, Wu FB (2014) N-acetyl-cysteine alleviates Cd toxicity and reduces Cd uptake in the two barley genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Plant Growth Regul 74:93–105
Sun HY, Chen ZH, Chen F, Xie LP, Zhang GP, Vincze E, Wu FB (2015) DNA microarray revealed and RNAi plants confirmed key genes conferring low Cd accumulation in barley grains. BMC Plant Biol 15:259
Tang QY, Zhang CX (2013) Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci 20:254–260
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants—protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151:59–66
Vieira LR, Correa ES, Moraes BS, Rossato MV, Vestena S (2015) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Rev Electron Gest Ed 19:1574–1588
Wang TT, Shi ZQ, Hu LB, Xu XF, Han FXX, Zhou LG, Chen J (2017) Thymol ameliorates cadmium-induced phytotoxicity in the root of rice (Oryza sativa) seedling by decreasing endogenous nitric oxide generation. J Agric Food Chem 65:7396–7405
Wu FB, Zhang GP, Dominy P (2003) Four barley genotypes respond differently to cadmium: lipid peroxidation and activities of antioxidant capacity. Environ Exp Bot 50(1):67–78
Yu Y, Zhou XY, Zhu ZH, Zhou KJ (2019) Sodium Hydrosulfide Mitigates Cadmium Toxicity by Promoting Cadmium Retention and Inhibiting Its Translocation from Roots to Shoots in Brassica napus. J Agric Food Chem 67:433–440
Zhang H, Hu LY, Hu KD, He YD, Wang SH, Luo JP (2008) Hydrogen sulfide promotes wheat seed germination and alleviates oxidative damage against copper stress. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1518–1529
Zhang H, Ye YK, Wang SH, Luo JP, Tang J, Ma DF (2009) Hydrogen sulfide counteracts chlorophyll loss in sweetpotato seedling leaves and alleviates oxidative damage against osmotic stress. Plant Growth Regul 58:243–250
Zhang H, Tan ZQ, Hu LY, Wang SH, Luo JP, Jones RL (2010) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in germinating wheat seedlings. J Integr Plant Biol 52:556–567
Zhang H, Hu SL, Zhang ZJ, Hu LY, Jiang CX, Wei ZJ, Liu J, Wang HL, Jiang ST (2011) Hydrogen sulfide acts as a regulator of flower senescence in plants. Postharvest Biol Technol 60:251–257
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from the Key Research Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province of China (2016C02050-9-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, MM., Dawood, M., Wang, NH. et al. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide reduces cadmium uptake and alleviates cadmium toxicity in barley. Plant Growth Regul 89, 227–237 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-019-00529-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-019-00529-8