Abstract
Background
l-Ornithine is a non-protein amino acid with extensive applications in medicine and the food industry. Currently, l-ornithine production is based on microbial fermentation, and few microbes are used for producing l-ornithine owing to unsatisfactory production titer.
Results
In this study, Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114, a high glutamate-producing strain, was developed for l-ornithine production by pathway engineering. First, argF was deleted to block l-ornithine to citrulline conversion. To improve l-ornithine production, ncgl1221 encoding glutamate transporter, argR encoding arginine repressor, and putP encoding proline transporter were disrupted. This base strain was further engineered by attenuating oxoglutarate dehydrogenase to increase l-ornithine production. Plasmid-based overexpression of argCJBD operon and lysine/arginine transport protein LysE was tested to strengthen l-ornithine synthesis and transportation. This resulted in efficient l-ornithine production at a titer of 18.4 g/L.
Conclusion
These results demonstrate the potential of Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114 for efficient l-ornithine production and provide new targets for strain development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Corynebacterium glutamicum, an aerobic gram-positive actinomycete capable of secreting glutamate under biotin limitation or in the presence of penicillin, has long-term applications in the industrial production of various valuable metabolites, including amino acids besides glutamate such as arginine, lysine, ornithine, and alanine [1,2,3,4]; diamines such as putrescine [5, 6] and cadaverine [7]; dicarboxylic acids such as succinate [8,9,10]; diols such as 1,3-propanediol [11] and 1,2-propanediol [12]; and terpenes such as pinene and carotenoid [13]. Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114, a subspecies of C. glutamicum derived from Brevibacterium tianjinese T6–13 [14], has been widely used for glutamate fermentation in China. Its genome sequence was published in 2011, highlighting its importance in glutamate fermentation. Compared to other strains of C. glutamicum, strain S9114 shows high glutamate production (about 80 g/L), resistance to high sugar levels, and much faster growth, and can be referred to as an ideal host for producing glutamate-related compounds [15].
l-Ornithine, a non-protein amino acid, is universally used in treating liver disease and trauma; it plays an efficient role in liver protection [16] and is useful in strengthening the heart [17]. l-Ornithine is an important constituent of the urea cycle and can be further converted to l-citrulline and l-arginine. In this pathway, l-glutamate is converted to l-ornithine by ArgC, ArgJ, ArgB, and ArgD, which are expressed as an operon and are regulated by the arginine repressor, ArgR. Recently, several reports have described the progress in the development of microorganisms used for l-ornithine production. As a potential industrial strain, C. glutamicum was proven to be a superior l-ornithine producer. Jiang et al. [18] reported an engineered C. glutamicum ATCC 13032 derived strain with inactivated argF, proB, and speE, and overexpression of NADH-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis, which produced 14.8 g/L of l-ornithine in a shake flask. In another study from the same group, 24.1 g/L of l-ornithine was obtained by adaptive evolution of C. glutamicum [19]. In addition, Hwang and Cho [20] reported a recombinant strain with inactivation of three putative glucose dehydrogenase genes to increase the NADPH supplement, which improved l-ornithine production to 14 g/L. Jensen et al. also constructed a mutant strain with feedback alleviation of N-acetylglutamate kinase, lowering expression of pgi, tuning of the promoter of gdh, which improved l-ornithine production of 71% as compared to the parental ΔargFRG strain [21]. Kim et al. [22] reported the construction of a recombinant C. glutamicum by disrupting proB, argR and argF, and overexpressing the operon of argCJDB from C. glutamicum ATCC 21831. Fed-batch culture of the engineered strain in a 6.6-L fermenter yielded 51.5 g/L of l-ornithine production titer from glucose.
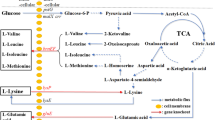
In this study, we systematically developed a new strain, C. glutamicum S9114, for l-ornithine production (Fig. 1). Compared with the model stain C. glutamicum ATCC 13032, the engineered C. glutamicum S9114 produced more l-ornithine after system pathway modification including inactivation of ArgF, Ncgl1221, ArgR, and PutP, attenuation of OdhA, and overexpression of LysE. This is the first report to explore the deletion of Ncgl1221 and PutP, along with attenuation of OdhA and overexpression of LysE as efficient strategies for improving l-ornithine production in C. glutamicum. Among these, deletion of Ncgl1221, attenuation of OdhA, and overexpression of LysE were confirmed to promote l-ornithine production, which provides crucial guidance for exploiting and developing industrial l-ornithine-producing strains.
Metabolic pathway abbreviated drawing for l-ornithine biosynthesis in C. glutamicum. Glc, glucose; G6P, glucose-6-P; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; Qxa, oxaloacetate; Mal, malate; Fum, fumarate; Suc, succiate; Suc-CoA, succinyl-coA; Oxo, 2-oxoglutarate; Iso, isocitrate; Cit, citrate; argF, encoding ornithine carbamoyltransferase; odhA, a subunit of ketoglutarate dehydrogenase; argCJBD, an operon involved in arginine synthesis; argR, a repressor for argCJBD; ncgl1221, encoding glutamate transporter; lysE, encoding lysine/arginine transporter; putP, encoding l-proline transporter. The red fonts represent gene deletion, green font means gene overexpression, and blue font means gene attenuation
Methods
Strains, medium, and culture conditions
The microorganisms and recombinant plasmids used in this study are presented in Table 1. E. coli DH5α was used as the clone host for construction of the recombinant plasmid. Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114 was used as the original strain for the development of mutants. Luria–Bertani (LB) medium was used to propagate E. coli and C. glutamicum. For the l-ornithine fermentation assay, a single clone of the mutants was activated on LB agar plate for two cycles of 12 h. Subsequently, a ring of bacteria was inoculated into 10 mL of seed medium in a 100-mL normal shake flask. The seed medium consisted of (per liter) 25 g glucose, 10 g yeast extract, 10 g corn steep liquor, 15 g (NH4)2SO4, 2.5 g MgSO4·7H2O, 1 g KH2PO4, 0.5 g K2HPO4, 0.5 g Na2HPO4, and 10 g CaCO3. After 11 h of cultivation at 32 °C and 220 rpm, the appropriate amount of culture was transferred to 24 mL of fermentation medium in a 250-mL baffle shake flask. Initial OD600 of the fermentation culture was adjusted to one. The fermentation medium consisted of (per liter) 100.0 g glucose, 20.0 g corn steep liquor, 50.0 g (NH4)2SO4, 2.5 g MgSO4·7H2O, 1.0 g KH2PO4, 0.5 g K2HPO4, 0.5 g Na2HPO4, 0.02 g FeSO4·7H2O, 0.02 g MnSO4·4H2O, and 10 g CaCO3. The initial pH was adjusted to 7.0. All cultures were grown at 32 °C and 250 rpm, and 200-µL samples were collected every 12 h to measure l-ornithine concentration, cell density, and residual glucose concentration. If necessary, 50 mg/L kanamycin was used to cultivate E. coli and 12.5 mg/L kanamycin was used to cultivate C. glutamicum.
Plasmid construction and gene knockout
The C. glutamicum S9114 derived mutant strains and plasmids constructed in this work are listed in Table 1. Genomic DNA of C. glutamicum S9114 isolated according to a previous report was used as the template for the amplification of specific genes. The suicide vector pK18mobsacB with the sucrose screening marker sacB from Bacillus subtilis was used for markerless gene deletion, insertion, and ribosome-binding site (RBS) replacement by double crossover recombination, as described previously [23]. The E. coli/C. glutamicum shuttle expression vector, pEC-XK99E, was used for overexpressing argCJBD.
For gene deletion in C. glutamicum S9114, the upstream and downstream fragments (approximately1000 bp) of argF, ncgl1221, argR, and putP were amplified and fused by PCR. Subsequently, the overlapped fragments were inserted into the HindIII/XbaI site of pK18mobsacB by Gibson assembly, thus generating the recombinant plasmids pK18-∆argF, pK18-∆ncgl1221, pK18-∆argR, and pK18-∆putP. In addition, for chromosome RBS change of OdhA, the RBS sequence listed in Additional file 1: Table S2 with the gradient translation start strength designed by the RBS calculator (https://www.denovodna.com/software/doLogin) was inserted into the overlap region between the upstream and downstream fragments of odhA, using rationally designed primers. After standardized molecular cloning operations, the plasmids pK18-odhA200, pK18-odhA400, and pK18-odhA800 were constructed. Moreover, argCJBD along with its native promoter was amplified from the genomic DNA of C. glutamicum CICC 20190 and C. crenatum MT-M4, and then inserted into expression plasmid pEC-XK99E via a BamHI/SalI site, thus generating the plasmids pEC-argCJBD1 and pEC-argCJBD2. All recombinant plasmids were transformed into C. glutamicum S9114 and the derived engineered strains by electroporation. Correct mutants obtained after two rounds of homologous recombination were confirmed by colony PCR. All the primers used in this study are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1.
Measurement of ODHC specific activity
For ODHC specific activity determination, cells were collected at 12 h, which is late exponential phase. Next, disposition of samples and enzymatic reaction system were conducted according to a previously described method with minor modification [24,25,26]. According to the previous work, cells collected by centrifugation (at 5000 rpm, 4 °C, and 10 min) and washed twice with 0.2% KCl solution. Following the pure cells were incubated in 5 mL of 0.1 M N-tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid (TES)·NaOH buffer (pH 7.7) containing 30% (v/v) glycerol and 10 mg/mL lysozyme at 37 °C for 3 h and then disrupted by sonication. After removing cell debris by centrifugation, the supernatant was collected as crude enzyme, and the protein concentration was determined by bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay using bovine serum albumin as the standard. ODHC specific activity assay was performed by adding 8 μL of crude enzyme to 200 μL of reaction mixture. The reaction mixture contained 100 mM TES·NaOH buffer (pH 7.7), 3 mM cysteine, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM coenzyme A, 0.3 mM thiamine pyrophosphate and 1 mM 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide (APAD+). The reaction was initiated by adding 1 mM α-oxoglutarate to the mixture, and then the absorbance of APADH at 365 nm was consecutively measured at 31.5 °C for 5 min with 30 s intervals. ODHC specific activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to generate 1 µmol APADH per minute.
Analytical procedures
Cell growth was monitored by measuring the OD600 using a microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA) after dissolving CaCO3 by 0.125 mol/L HCl. The fermentation supernatant was processed using a 0.22-µm filter and analyzed for glucose, glutamate, and lactate levels, using a SBA-40C biosensor (developed by Biology Institute of Shandong Academy of Sciences). l-Ornithine concentrations were determined by colorimetry using ninhydrin, as described previously [18].
Results
Deletion of argF results in efficient accumulation of l-ornithine
Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114 as an industrial strain was reported to accumulate large amounts of glutamate under appropriate fermentation conditions. Because l-ornithine is an intermediate metabolite of l-arginine synthesis derived from l-glutamate, C. glutamicum S9114 was considered a favorable host for the development of l-ornithine-producing strains. As shown in Fig. 1, l-ornithine can be converted to citrulline by carbamoyltransferase, which is encoded by argF in C. glutamicum. Therefore, argF was disrupted to accumulate l-ornithine in C. glutamicum S9114, resulting in strain Sorn1. As shown in Fig. 2, analysis of samples from the shake flask fermentation assay indicates that although growth was reduced by the deprived l-arginine synthesis pathway, the mutant strain Sorn1 produced 7.97 g/L of l-ornithine at 72 h, which is 16-fold higher than that produced by C. glutamicum S9114 (0.46 g/L). Moreover, our data also indicated that Sorn1 produced 6.5 g/L of glutamate in the fermentation supernatant (see Fig. 3). In conclusion, inactivation of ArgF resulted in a high l-ornithine production titer in C. glutamicum S9114.
Improvement of l-ornithine production by reducing glutamate transportation
Glutamate is the precursor of l-ornithine synthesis and therefore, extracellular secretion of glutamate is unfavorable attribute to the problems of downstream separation and wastage of materials. According to a previous report, deleting ncgl1221, which encodes a glutamate transport protein, caused intracellular accumulation of l-glutamate by damaging the transportation system and showed no influence on growth [26]. Thus, ncgl1221 was disrupted to reduce glutamate secretion and provide more precursors for l-ornithine production in strain Sorn1, thus generating the strain Sorn2. The results from the shake flask test shown in Fig. 4 suggest that 9.8 g/L of l-ornithine was produced by stain Sorn2 after 72 h of cultivation, which was 22.7% higher than that obtained with strain Sorn1. The growth, glucose consumption, and lactate production of Sorn2 were consistent with those of Sorn1 (Fig. 3). These preliminary results demonstrate an efficient strategy to improve l-ornithine production by deleting ncgl1221. In addition, the glutamate concentration in the fermentation supernatant of Sorn2 was decreased to 0.5 g/L, which was just about 7.6% of that in the control strain Sorn1. Consequently, glutamate production was reduced by a titer of 6 g/L whereas l-ornithine production was only increased by a titer of 1.83 g/L, which illustrated that further enhancement of l-ornithine production was limited by the conversion efficiency of glutamate to ornithine in strain Sorn2.
Optimization of l-ornithine production by inactivation of argR and putP
l-Ornithine is synthesized via a four-step enzyme reaction and the genes encoding these enzymes are expressed as a gene cluster, argCJBD. Deletion of argR, an arginine negative regulatory protein, can significantly increase the expression level of the argCJBDFR gene cluster [27]. Therefore, to enhance the metabolic flux from l-glutamate to l-ornithine, argR was deleted to remove the feedback repression in Sorn2, thus generating the mutant strain, Sorn3. According to Fig. 5, the l-ornithine production titer of Sorn3 in the shake flask reached 13.2 g/L after 72 h of incubation, which was 34.6% higher than that of Sorn2. In addition, the growth, glucose consumption, and lactate production was not affected by deletion of argR. However, l-proline was considered a competing metabolic by-product owing to the consumption of glutamate as a common precursor. For further saving carbon metabolism, putP that encodes l-proline transport protein, was inactivated to reduce l-proline synthesis by biological robustness, and generate the strain Sorn4. The l-ornithine production titer of Sorn4 was equal to that of Sorn3, indicating that l-proline production in Sorn3 has no significant impact on the production of l-ornithine.
Attenuation of odhA exerts a positive effect on l-ornithine production
l-Ornithine is a derivative product of glutamate, which suggests that increased metabolic flux from 2-oxoglutarate to glutamate is a reasonable strategy for enhancing l-ornithine production. Therefore, odhA was selected as a target for attenuation in the strain Sorn4 via the RBS modification method. The RBS strength of the original odhA in the chromosome of Sorn4 as predicted by the RBS Calculator (https://www.denovodna.com/software/doLogin) was 1613 au. Afterwards, three kinds of RBS with predicted translation initiation intensity of 217, 373 and 837 au were designed and used to replace the natural RBS of the strain Sorn4 and the start codon ATG of odhA was simultaneously replaced with GTG, thus generating strains Sorn5, Sorn6, and Sorn7. The results of the shake flask test illustrated that without influencing growth, the recombinant strains Sorn5, Sorn6, Sorn7 produced 14.1, 14.2, and 16 g/L of l-ornithine at 72 h, respectively (see in Table 2). The production titer of Sorn7 was 16.7% higher than that of the control strain Sorn4. Compared with the parent strain Sorn4, the relative ODHC specific activity of strains Sorn5, Sorn6, Sorn7 reduced to 15, 22 and 40% (see in Table 2). This result illustrated that attenuation of odhA promotes l-ornithine production in C. glutamicum S9114.
Heterologous expression of argCJBD causes no further improvement in l-ornithine production
To examine whether the expression level of argCJBD is a rate-limiting step for further enhancing l-ornithine production, the argCJBD operon under its native promoter from two l-arginine producing strains was amplified and introduced into the mutant strain Sorn7, via the expression plasmid pEC-XK99E, thus generating strains Sorn9 and Sorn10. Shake flask fermentation was performed to evaluate the effect of these modifications on l-ornithine production. As illustrated in Table 2, strains Sorn9 and Sorn10 produced 15.1 and 15.28 g/L of l-ornithine respectively, which is the same titer as 15.1 g/L obtained with Sorn8. The growth of those strains was also not changed. This result suggests that after eliminating the feedback control by inactivation of argR, expression of argCJBD is not a rate-limiting step for l-ornithine production.
Overexpression of LysE to enhance l-ornithine production
LysE, a broad amino acid transporter, possessed the ability to transport l-lysine, l-arginine and l-citrulline [28]. Hence, to investigate whether overexpression of LysE could further improve l-ornithine production based on the strain Sorn7, we constructed a mutant strain Sorn11. As shown in Fig. 6, the Sorn11 strain consumed 74.9 ± 1 g/L glucose and produced 18.4 ± 0.49 g/L l-ornithine with a yield of 0.25 g/g glucose. These data represent an increase of 21.8% in l-ornithine production as compared to that of the strain Sorn8. However, compared with the strain Sorn8, Sorn11 did not show any obvious differences in cell growth, but its glucose consumption was slightly increased. It was thus concluded that overexpression of LysE caused further improved l-ornithine production in Sorn7. The result obtained in this section demonstrates the remarkable application of LysE in constructing an l-ornithine-producing strain.
Effect of lysE overexpression on l-ornithine production. a The glucose concentration and growth curve of Sorn8 and Sorn11. The solid line represents the glucose concentration curve; the dotted line represents growth curve. b l-Ornithine production curves of Sorn8 and Sorn11. Results of standard deviations present in three individual experiments
Discussion
Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114, an industrial glutamate producer, was systematically engineered for l-ornithine production for the first time. Inactivation of argF, encoding a carbamoyltransferase that converts ornithine to citrulline in C. glutamicum S9114, led to l-ornithine production of 7.97 g/L, which is 2.74-fold higher than the 2.13 g/L obtained by disrupting argF in C. glutamicum ATCC 13032 [29]. Compared with the model strain C. glutamicum ATCC 13032, C. glutamicum S9114 possesses a tremendous advantage in the precursor supplement. To improve l-ornithine production, ncgl1221 encoding the known transport protein of glutamate was also disrupted to avoid glutamate as a by-product secreted to the medium, which was reported to effectively improve the production titer of l-arginine in C. glutamicum [30]. To our knowledge, this is the first study confirming that elimination of ncgl1221 significantly contributes to l-ornithine synthesis. We speculated that deletion of ncgl1221 leads to intracellular accumulation of glutamate and then stimulates the downstream metabolic pathways to improve l-ornithine production. A second step to improve l-ornithine yield was to remove the feedback control by inactivating argR, which was reported to effectively improve the transcription level of the arginine operon. The result of increased l-ornithine production by ArgR inactivation was consistent with that of a previous study, which revealed that disrupting argR improved the transcription of arginine operon [27] and enhanced l-arginine and l-ornithine production in C. glutamicum [31]. However, deletion of putP did not exert a positive effect on l-ornithine production, which suggested that production of l-proline was controlled by other unknown mechanisms and did not compete for the precursor glutamate.
Decreased specific activity of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase was proven as an important target for glutamate [25] and arginine production [32]. In this study, we attempted to decrease the expression of odhA to enhance the metabolic flux from TCA cycle to l-ornithine by RBS modification and initiation codon replacement. The highest yield of l-ornithine was observed for strain Sorn7 with RBS of 837 au in upstream region of odhA. This is consistent with previous result obtained in engineered C. crenatum possessing gene odhA with RBS of 800 au [32]. Two strains with weaker RBS of 217 au or 373 au in upstream region of odhA displayed slow growth, and producing the lower amount of l-ornithine. Based on this, we continued to strengthen the l-ornithine synthesis pathway by overexpressing the argCJBD operon from two arginine-producing strains. However, this was not consistent with previous research which revealed that overexpression of argCJBD genes from C. glutamicum ATCC 21831 in the model strain C. glutamicum ATCC 13032 significantly increased l-ornithine production [22]. The different strains may account for these diverse outcomes. It is speculated that the expression of argCJBD is not the rate-limiting step for l-ornithine synthesis after deletion of the arginine repressor ArgR. There may be other reasons that limit the further improvement of l-ornithine production.
LysE, a lysine transporter [33], is also reported to transport l-arginine [34]. In previous work, overexpression of LysE in C. glutamicum could significantly increase l-arginine and l-citrulline yield [28]. In this study, overexpression of LysE under its native promoter in the mutant strain Sorn7 (with argF, ncgl1221, argR, putP, and odhA800 modifications) contributed to a 21.8% increase in l-ornithine production compared with that by the base strain. These data demonstrate the significant effect of LysE on l-ornithine production. Moreover, overexpression of LysE also significantly promotes the utilization of glucose, which was illustrated for the first time. Some correlations may thus exist between improvement of glucose consumption and l-ornithine production. However, Bellmann [34] reported that LysE is not able to transport l-ornithine in C. glutamicum ATCC 13032 in short time fermentation. We speculated that the difference of species or other unknown mechanism except enhancing transport system might contribute to those controversial results. In our next project, further experiments such as gene deletion and anaplerosis experiments were needed to explore the insight of why LysE present those effects.
While further improvement and optimization of metabolic pathways as well as process engineering remain to be investigated, this work demonstrates the enormous potential of C. glutamicum S9114 to produce l-ornithine from glucose. As l-ornithine is an intermediate of l-citrulline and l-arginine biosynthesis, successful overproduction of this compound by pathway engineering indicates that this organism has superduper potential to overproduce not only l-ornithine but also l-citrulline, l-arginine and other glutamate relative compound.
Conclusions
In this study, we achieved the goal of development of a high glutamate-producing strain, Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114, for l-ornithine production by deletion of argF, ncgl1221, argR, putP, attenuating oxoglutarate dehydrogenase and overexpression of LysE, which produced 18.4 g/L of l-ornithine. The development of metabolically engineered C. glutamicum S9114 strains provides a new strain and some useful strategies for enhanced fermentative production of l-ornithine from renewable resources such as glucose. Through further genetic engineering and fermentation condition optimization, the yield of l-ornithine is capable for further improvement.
References
Wieschalka S, Blombach B, Bott M, Eikmanns BJ. Bio-based production of organic acids with Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb Biotechnol. 2013;6:87–102.
Lee J-H, Wendisch VF. Production of amino acids-Genetic and metabolic engineering approaches. Bioresourc Technol. 2017. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.065.
Jorge JM, Pérez-García F, Wendisch VF. A new metabolic route for the fermentative production of 5-aminovalerate from glucose and alternative carbon sources. Bioresourc Technol. 2017. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.108.
Anusree M, Wendisch VF, Nampoothiri KM. Co-expression of endoglucanase and β-glucosidase in Corynebacterium glutamicum DM1729 towards direct lysine fermentation from cellulose. Bioresourc Technol. 2016;213:239–44.
Nguyen AQ, Schneider J, Reddy GK, Wendisch VF. Fermentative production of the diamine putrescine: system metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Metabolites. 2015;5:211–31.
Meiswinkel TM, Rittmann D, Lindner SN, Wendisch VF. Crude glycerol-based production of amino acids and putrescine by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Bioresourc Technol. 2013;145:254–8.
Leßmeier L, Pfeifenschneider J, Carnicer M, Heux S, Portais J-C, Wendisch VF. Production of carbon-13-labeled cadaverine by engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum using carbon-13-labeled methanol as co-substrate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99:10163–76.
Chung S-C, Park J-S, Yun J, Park JH. Improvement of succinate production by release of end-product inhibition in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Metab Eng. 2017;40:157–64.
Shi X, Chen Y, Ren H, Liu D, Zhao T, Zhao N, Ying H. Economically enhanced succinic acid fermentation from cassava bagasse hydrolysate using Corynebacterium glutamicum immobilized in porous polyurethane filler. Bioresourc Technol. 2014;174:190–7.
Chen T, Zhu N, Xia H. Aerobic production of succinate from arabinose by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. Bioresourc Technol. 2014;151:411–4.
Huang J, Wu Y, Wu W, Zhang Y, Liu D, Chen Z. Cofactor recycling for co-production of 1, 3-propanediol and glutamate by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42246.
Siebert D, Wendisch VF. Metabolic pathway engineering for production of 1, 2-propanediol and 1-propanol by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015;8:91.
Kang M-K, Eom J-H, Kim Y, Um Y, Woo HM. Biosynthesis of pinene from glucose using metabolically-engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol Lett. 2014;36:2069–77.
Mei J, Xu N, Ye C, Liu L, Wu J. Reconstruction and analysis of a genome-scale metabolic network of Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114. Gene. 2016;575:615–22.
Zhang C, Shi Z, Gao P, Duan Z, Mao Z. On-line prediction of products concentrations in glutamate fermentation using metabolic network model and linear programming. Biochem Eng J. 2005;25:99–108.
Salvatore F, Cimino F, d’Ayello-Caracciolo M, Cittadini D. Mechanism of the protection by l-ornithine-l-aspartate mixture and by l-arginine in ammonia intoxication. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964;107:499–503.
Shi HP, Fishel RS, Efron DT, Williams JZ, Fishel MH, Barbul A. Effect of supplemental ornithine on wound healing. J Surg Res. 2002;106:299–302.
Jiang L-Y, Zhang Y-Y, Li Z, Liu J-Z. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for increasing the production of l-ornithine by increasing NADPH availability. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;40:1143–51.
Jiang L-Y, Chen S-G, Zhang Y-Y, Liu J-Z. Metabolic evolution of Corynebacterium glutamicum for increased production of l-ornithine. BMC Biotechnol. 2013;13:47.
Hwang G-H, Cho J-Y. Enhancement of l-ornithine production by disruption of three genes encoding putative oxidoreductases in Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;41:573–8.
Jensen JV, Eberhardt D, Wendisch VF. Modular pathway engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for production of the glutamate-derived compounds ornithine, proline, putrescine, citrulline, and arginine. J Biotechnol. 2015;214:85–94.
Kim SY, Lee J, Lee SY. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of l-ornithine. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2015;112:416–21.
Zhang B, Wan F, Qiu YL, Chen XL, Tang L, Chen JC, Xiong YH. Increased l-arginine production by site-directed mutagenesis of N-acetyl-l-glutamate kinase and proB gene deletion in Corynebacterium crenatum. Biomed Environ Sci. 2015;28(12):864–74.
Shiio I, Ujigawa-Takeda K. Presence and regulation of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in a glutamate-producing bacterium, Brevibacterium flavum. Agric Biolog Chem. 1980;44:1897–904.
Kim J, Hirasawa T, Sato Y, Nagahisa K, Furusawa C, Shimizu H. Effect of odhA overexpression and odhA antisense RNA expression on Tween-40-triggered glutamate production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microb Biotech. 2009;81:1097.
Chen M, Chen X, Wan F, Zhang B, Chen J, Xiong Y. Effect of Tween 40 and DtsR1 on l-arginine overproduction in Corynebacterium crenatum. Microb Cell Fact. 2015;14:119.
Yim S-H, Jung S, Lee S-K, Cheon C-I, Song E, Lee S-S, Shin J, Lee M-S. Purification and characterization of an arginine regulatory protein, ArgR, in Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;38:1911–20.
Lubitz D, Jorge JM, Perez-Garcia F, Taniguchi H, Wendisch VF. Roles of export genes cgmA and lysE for the production of l-arginine and l-citrulline by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:8465–74.
Dongmei L, Jianzhong L, Zongwan M. Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum to enhance l-ornithine production by gene knockout and comparative proteomic analysis. Chin J Chem Eng. 2012;20:731–9.
Park SH, Kim HU, Kim TY, Park JS, Kim S-S, Lee SY. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for l-arginine production. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4618.
Schneider J, Niermann K, Wendisch VF. Production of the amino acids l-glutamate, l-lysine, l-ornithine and l-arginine from arabinose by recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol. 2011;154:191–8.
Man Z, Xu M, Rao Z, Guo J, Yang T, Zhang X, Xu Z. Systems pathway engineering of Corynebacterium crenatum for improved l-arginine production. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28629.
Vrljic M, Sahm H, Eggeling L. A new type of transporter with a new type of cellular function: l-lysine export from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mol Microbiol. 1996;22:815–26.
Bellmann A, Vrljić M, Patek M, Sahm H, Krämer R, Eggeling L. Expression control and specificity of the basic amino acid exporter LysE of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microbiology. 2001;147:1765–74.
Schafer A, Tauch A, Jager W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Puhler A. Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene. 1994;145:69–73.
Authors’ contributions
BZ planned and conducted the experiments, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote the manuscript; MY and YZ participated in the research; YL and BCY supervised the research and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Xue-Lan Chen for providing pk18mobsacB. We thank Dr. Zhong-Gui Mao and Dr. Li-Ming Liu for providing strains Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
Gene sequences used in this project are from Genbank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and the material and data supporting their findings can be found in the main paper and the Additional file.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31730004 and 21575089).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Yu, M., Zhou, Y. et al. Systematic pathway engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114 for l-ornithine production. Microb Cell Fact 16, 158 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0776-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0776-8