Abstract
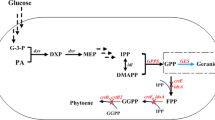
Pinene is a monoterpenes (C10) that is produced in a genetically-engineered microbial host for its industrial applications in fragrances, flavoring agents, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels. Herein, we have metabolically-engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum, to produce pinene and studied its toxicity in C. glutamicum. Geranyl diphosphate synthases (GPPS) and pinene synthases (PS), obtained from Pinus taeda and Abies grandis, were co-expressed with over-expressed native 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (Dxs) and isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase (Idi) from C. glutamicum using CoryneBrick vector. Most strains expressing PS-GPPSs produced detectable amounts of pinene, but co-expression of DXS and IDI with PS (P. taeda) and GPPS (A. grandis) resulted in 27 μg ± 7 α-pinene g−1 cell dry weight, which is the first report in C. glutamicum. Further engineering of PS and GPPS in the C. glutamicum strain may increase pinene production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajikumar PK, Xiao W-H, Tyo KEJ, Wang Y et al (2010) Isoprenoid pathway optimization for Taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli. Science 330:70–74
Alonso-Gutierrez J, Chan R, Batth TS, Adams PD et al (2013) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for limonene and perillyl alcohol production. Metab Eng 19:33–41
Alper H, Jin Y-S, Moxley JF, Stephanopoulos G (2005) Identifying gene targets for the metabolic engineering of lycopene biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 7:155–164
Bohlmann J, Steele CL, Croteau R (1997) Monoterpene synthases from Grand Fir (Abies grandis): cDNA isopation, characterization, and functional expression of myrcne synthase,(−)-(4s)-limonene synthase, and (−)-(1s, 5s)-pinene. J Biol Chem 272:21784–21792
Brennan TC, Turner CD, Krömer JO, Nielsen LK (2012) Alleviating monoterpene toxicity using a two-phase extractive fermentation for the bioproduction of jet fuel mixtures in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:2513–2522
Burke C, Croteau R (2002) Geranyl diphosphate synthase from Abies grandis: cDNA isolation, functional expression, and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys 405:130–136
Choi HS, Lee SY, Kim TY, Woo HM (2010) In silico identification of gene amplification targets for improvement of lycopene production. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3097–3105
Dusch N, Pühler A, Kalinowski J (1999) Expression of the Corynebacterium glutamicum pan D gene encoding l-aspartate-α-decarboxylase leads to pantothenate overproduction in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1530–1539
Eggeling L, Bott M (2010) Handbook of Corynebacterium glutamicum. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Foo JL, Leong SS (2013) Directed evolution of an E. coli inner membrane transporter for improved efflux of biofuel molecules. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:81
Heider SA, Peters-Wendisch P, Wendisch VF (2012) Carotenoid biosynthesis and overproduction in Corynebacterium glutamicum. BMC Microbiol 12:198
Kalinowski J, Bathe B, Bartels D, Bischoff N et al (2003) The complete Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 genome sequence and its impact on the production of l-aspartate-derived amino acids and vitamins. J Biotechnol 104:5–25
Kang M-K, Lee J, Um Y, Lee TS et al (2014) Synthetic biology platform of CoryneBrick vectors for gene expression in Corynebacterium glutamicum and its application to xylose utilization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-5714-7
Kirby J, Keasling JD (2009) Biosynthesis of plant isoprenoids: perspectives for microbial engineering. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:335–355
Lee TS, Krupa RA, Zhang F, Hajimorad M et al (2011) BglBrick vectors and datasheets: a synthetic biology platform for gene expression. J Biol Eng 5:12
Müller T, Strösser J, Buchinger S, Nolden L et al (2006) Mutation-induced metabolite pool alterations in Corynebacterium glutamicum: towards the identification of nitrogen control signals. J Biotechnol 126:440–453
Paddon CJ, Westfall PJ, Pitera DJ, Benjamin K et al (2013) High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin. Nature 25:528–532
Phillips MA, Wildung MR, Williams DC, Hyatt DC et al (2003) cDNA isolation, functional expression, and characterization of (+)-α-pinene synthase and (−)-α-pinene synthase from loblolly pine (Pinus taeda): stereocontrol in pinene biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 411:267–276
Phillips MA, León P, Boronat A, Rodríguez-Concepción M (2008) The plastidial MEP pathway: unified nomenclature and resources. Trends Plant Sci 13:619–623
Quan J, Tian J (2011) Circular polymerase extension cloning for high-throughput cloning of complex and combinatorial DNA libraries. Nat Protoc 6:242–251
Rivas da Silva AC, Lopes PM, Barros de Azevedo MM, Costa DC et al (2012) Biological activities of alpha-pinene and beta-pinene enantiomers. Molecules 17:6305–6316
Russo EB (2011) Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects. Br J Pharmacol 163:1344–1364
Sarria S, Wong B, Martín HG, Keasling JD et al (2014) Microbial Synthesis of Pinene. ACS Synth Biol. doi:10.1021/sb4001382
Uribe S, Pena A (1990) Toxicity of allelopathic monoterpene suspensions on yeast dependence on droplet size. J Chem Ecol 16:1399–1408
Van der Rest M, Lange C, Molenaar D (1999) A heat shock following electroporation induces highly efficient transformation of Corynebacterium glutamicum with xenogeneic plasmid DNA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:541–545
Woo HM, Park JB (2014) Recent progress in development of synthetic biology platforms and metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 180:43–51
Yang J, Nie Q, Ren M, Feng H et al (2013) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the biosynthesis of alpha-pinene. Biotechnol Biofuel 6:60
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Prof. Andreas Burkovski for providing the LN ΔGDH mutant and Ms. Jae Hee Jung for technical support. This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant-funded by the Korean Government (Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning) (2014, University-Institute cooperation program) and Creative Allied Program (CAP) of the Korea Research Council of Fundamental Science and Technology (KRCF)/Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) (Project No. 2E24832).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, MK., Eom, JH., Kim, Y. et al. Biosynthesis of pinene from glucose using metabolically-engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum . Biotechnol Lett 36, 2069–2077 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1578-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1578-2