Abstract
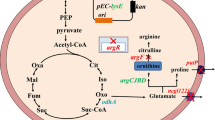
Recently, Corynebacterium glutamicum has been shown to exhibit gluconate bypass activity, with two key enzymes, glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) and gluconate kinase, that provides an alternate route to 6-phosphogluconate formation. In this study, gene disruption analysis was used to examine possible metabolic functions of three proteins encoded by open reading frames having significant sequence similarity to GDH of Bacillus subtilis. Chromosomal in-frame deletion of three genes (NCgl0281, NCgl2582, and NCgl2053) encoding putative NADP+-dependent oxidoreductases led to the absence of GDH activity and correlated with increased specific glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase activities. This finding suggested that enhanced carbon flux from glucose was directed toward the oxidative pentose phosphate (PP) pathway, when the mutant was cultivated with 6 % glucose. Consequently, the mutant showed 72.4 % increased intracellular NADPH and 66.3 % increased extracellular l-ornithine production. The enhanced activities of the oxidative PP pathway in the mutant explain both the increased intracellular NADPH and the high extracellular concentration of l-ornithine. Thus, the observed metabolic changes in this work corroborate the importance of NADPH in l-ornithine production from C. glutamicum.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson WB, Nordlie RC (1968) Glucose dehydrogenase activity of yeast glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. I. Selective stimulation by bicarbonate, phosphate, and sulfate. Biochemistry 7:1479–1485
Bartek T, Blombach B, Zönnchen E, Makus P, Lang S, Eikmanns BJ, Oldiges M (2010) Importance of NADPH supply for improved l-valine formation in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol Prog 26:361–371
Becker J, Klopprogge C, Herold A, Zelder O, Bolten CJ, Wittmann C (2007) Metabolic flux engineering of l-lysine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum–over expression and modification of G6P dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 132:99–109
Becker J, Klopprogge C, Zelder O, Heinzle E, Wittmann C (2005) Amplified expression of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase in Corynebacterium glutamicum increase in vivo flux through the pentose phosphate pathway and lysine production on different carbon sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8587–8596
Frunzke J, Engels V, Hasenbein S, Gätgens C, Bott M (2008) Co-ordinated regulation of gluconate catabolism and glucose uptake in Corynebacterium glutamicum by two functionally equivalent transcriptional regulators, GntR1 and GntR2. Mol Microbiol 67:305–322
Georgi T, Rittmann D, Wendisch VF (2005) Lysine and glutamate production by Corynebacterium glutamicum on glucose, fructose and sucrose: roles of malic enzyme and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Metab Eng 7:291–301
Hwang J-H, Hwang G-H, Cho J-Y (2008) Effect of increased glutamate availability on l-ornithine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:704–710
Hwang G-H, Cho J-Y (2012) Implication of gluconate kinase activity in l-ornithine biosynthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:1869–1874
Kabus A, Georgi T, Wendisch VF, Bott M (2007) Expression of the Escherichia coli pntAB genes encoding a membrane-bound transhydrogenase in Corynebacterium glutamicum improves l-lysine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:47–53
Lessie TG, Phibbs PV Jr (1984) Alternative pathways of carbohydrate utilization in pseudomonads. Ann Rev Microbiol 38:359–387
Lindner SN, Knebl S, Pallerla SR, Schoberth SM, Wendisch VF (2010) Cg2091 encodes a polyphosphate/ATP-dependent glucokinase of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:703–713
Lindner S, Seibold GM, Henrich A, Krämer R, Wendisch VF (2011) Phosphotransferase system-independent glucose utilization in Corynebacterium glutamicum by inositol permeases and glucokinases. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3571–3581
Marx A, Striegel K, de Graaf AA, Sahm H, Eggeling L (1997) Response of the central metabolism of Corynebacterium glutamicum to different flux burdens. Biotechnol Bioeng 56:168–180
Marx A, Eikmanns BJ, Sahm H, de Graaf AA, Eggeling L (1999) Response of the central metabolism in Corynebacterium glutamicum to the use of an NADH-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase. Metab Eng 1:35–48
Marx A, Hans S, Möckel B, Bathe B, de Graaf AA, McCormack AC, Stapleton C, Burke K, O’Donohue M, Dunican LK (2003) Metabolic phenotype of phosphoglucose isomerase mutants of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 104:185–197
Mortiz B, Striegel K, de Graaf AA, Sahm H (2000) Kinetic properties of the glucose 6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases from Corynebacterium glutamicum and their application for predicting pentose phosphate pathway flux in vivo. Eur J Biochem 267:3442–3452
Mortiz B, Striegel K, de Graaf AA, Sahm H (2002) Changes of pentose phosphate pathway flux in vivo in Corynebacterium glutamicum during leucine-limited batch cultivation as determined from intracellular metabolite concentration measurements. Metab Eng 4:295–305
Nachlas MM, Davidson MB, Goldberg JD, Seligman AM (1963) Colorimetric method for the measurement of isocitric dehydrogenase activity. J Lab Clin Med 62:148–158
Ohnishi J, Katahira R, Mitsuhashi S, Kakita S, Ikeda M (2005) A novel gnd mutation leading to increased l-lysine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 242:265–274
Otani M, Ihara N, Umezawa C, Sano K (1986) Predominance of gluconate formation from glucose during germination of Bacillus megaterium QM B1551 spores. J Bacteriol 167:148–152
Schäfer A, Tauch A, Jäger W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Pühler A (1994) Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined selections in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145:69–73
Siedler S, Lindner SN, Bringer S, Wendisch VF, Bott M (2013) Reductive whole-cell biotransformation with Corynebacterium glutamicum: improvement of NADPH generation from glucose by a cyclized pentose phosphate pathway using pfkA and gapA deletion mutants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:143–152
Takeno S, Murata R, Kobayashi R, Mitsuhashi S, Ikeda M (2010) Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum with an NADPH-generating glycolytic pathway for l-lysine production. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7154–7160
Yoon K-H, Cho J-Y (2007) Transcriptional analysis of the gum gene cluster from Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae. Biotechnol Lett 29:95–103
Zamboni N, Fischer E, Laudert D, Aymerich S, Hohmann H-P, Sauer U (2004) The Bacillus subtilis yqjI gene encodes the NADP+-dependent 6-P-gluconate dehydrogenase in the pentose phosphate pathway. J Bacteriol 186:4528–4534
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Advanced R&D supporting business between industry and university, funded by the Small and Medium Business Administration in 2012, Republic of Korea, and, in part, by the Sangji University Research Fund 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, GH., Cho, JY. Enhancement of l-ornithine production by disruption of three genes encoding putative oxidoreductases in Corynebacterium glutamicum . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 573–578 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1398-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1398-8