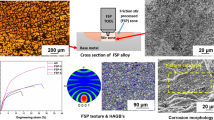
Abstract
An effort to obtain superior impact properties for Al-7Si-0.35 Mg alloy is presented, where modification with 0.02 wt% Sr and 0.1 wt% La as well as solution treatment was jointly employed. The samples were solution treated at 535 °C for 15 min to 12 h. The microstructure, fracture mechanism, and their correlation with the impact properties of the alloy were studied in detail mainly through optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and oscillography impact test. The results show that the addition of Sr and La refined the eutectic Si particles significantly from ~ 2.05 μm (modified with Sr alone) to ~ 0.75 μm in as-cast microstructure, leading to a very homogeneous distribution of spheroidized Si particles in the alloy solution treated at 535 °C for 8 h. The alloy exhibits excellent impact toughness up to 75 J·cm−2, which is much higher than the maximum impact toughness of the alloys modified by Sr alone (~ 46 J·cm−2). The major reason for this remarkable increase in the impact property is the dramatic increase in crack initiation energy. The dispersoid-free zones (DFZs) near the eutectic regions mainly consist of the ductile Al-matrix, which exhibits excellent ductility. The ductile Al-matrix of the DFZs hinders the crack propagation, resulting in a significant increase in crack propagation energy.
Graphical abstract

摘要
为了提升铸造铝合金的冲击韧性,本文对铸造Al-Si-Mg合金进行Sr和La变质,并对变质后的合金进行固溶处理。通过光学显微镜(OP)、扫描电镜(SEM)和示波冲击试验等手段,研究了合金的微观结构、断裂机理和冲击性能的相关性。结果表明,添加Sr和La可以大幅细化铸态合金中的共晶Si颗粒,颗粒尺寸从~2.05 μm(单独用Sr改性)大幅细化到 ~0.75 μm。Sr和La变质的合金经过535 ℃固溶处理8小时后具有相对最佳的共晶Si形貌。该合金表现出优异的冲击韧性,最高可达 75 J·cm-2,远高于Sr单独变质合金的最大冲击韧性(~46 J·cm-2)。冲击韧性的提高主要原因是裂纹形成能的显著增加,而裂纹形成能的增加与共晶Si颗粒的形貌有关。同时,固溶过程中形成的无弥散相区(DFZ)主要由韧性的Al基体组成,而韧性的DFZ可以进一步阻碍裂纹的扩展,导致裂纹扩展能显著增加。这项工作表明Sr和La变质及固溶处理的联合使用可以有效提高铸造Al-Si-Mg合金的冲击性能。













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang T, Zhao X, Liu J, Zhang R, Wang X, Yuan Y, Li Z, Han Z. The microstructure, fracture mechanism and their correlation with the mechanical properties of as-cast Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy under the effect of cooling rate. Mater Sci Eng A. 2021;801:140382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140382.
Wang F, Meng W, Zhang H, Han Z. Effects of under-aging treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of squeeze-cast Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2018;28:1920. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64837-X.
Hu XP, Wang Q, Hu H, Li RX, Zhao Y, Wang ZM, Zhang BR. Nano-yttrium-containing precipitates of T6 heat-treated A356.2 alloy when trace yttrium (Y less than 0.100 wt%) added. Rare Met. 2021;40(11):3279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01671-3.
Cai Q, Mendis CL, Chang ITH, Fan Z. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of new die-cast Al-Si-Mg-Mn alloys. Mater Des. 2020;187:108394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108394.
Su DY, Jin HJ, Wu SJ. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 2219 aluminum alloy VPTIG welds during cyclic thermal treatment. Rare Met. 2022;41(10):3539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0642-y.
Singh LK, Joseph P, Srinivasan A, Pillai UTS, Pai BC. Microstructure and mechanical properties of gadolinium- and misch metal-added Mg-Al alloy. Rare Met. 2022;41(9):3205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0928-3.
Su B, Ma Q, Han Z. Modeling of austenite decomposition during continuous cooling process in heat treatment of hypoeutectoid steel with cellular automaton method. Steel Res Int. 2017;88:1600490. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201600490.
Shang S, Guo Z, Han Z. On the kinetics of dendritic sidebranching: a three dimensional phase field study. J Appl Phys Am Inst Phys. 2016;119:164305. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4947450.
Shang S, Han Z, Sun W, Luo AA. A phase field model coupled with pressure-effect-embedded thermodynamic modeling for describing microstructure and microsegregation in pressurized solidification of a ternary magnesium alloy. Comput Mater Sci. 2017;136:264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2017.05.015.
Eiken J, Apel M, Liang SM, Schmid-Fetzer R. Impact of P and Sr on solidification sequence and morphology of hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys: combined thermodynamic computation and phase-field simulation. Acta Mater. 2015;98:152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.06.056.
Hekimoğlu AP, Çalış M, Ayata G. Effect of strontium and magnesium additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–12Si alloys. Met Mater Int. 2019;25:1488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00429-6.
Guo FB, Zhu BH, Jin LB, Wang GJ, Yan HW, Li ZH, Zhang YA, Xiong BQ. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 7A56 aluminum alloy after solution treatment. Rare Met. 2021;40(1):168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0985-7.
Tavitas-Medrano FJ, Doty H, Valtierra S, Samuel FH. On the enhancement of the impact toughness of A319 alloys: role of Mg content and melt treatment. Int J Met. 2017;11:536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0098-3.
Tang HP, Wang QD, Luo C, Lei C, Liu TW, Li ZY, Wang K, Jiang HY, Ding WJ. Effects of solution treatment on the microstructure, tensile properties, and impact toughness of an Al–5.0Mg–3.0Zn–1.0Cu cast alloy. Acta Metall Sin Engl Lett. 2021;34:98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-020-01077-1.
Ibrahim MF, Samuel E, Samuel AM, Al-Ahmari AMA, Samuel FH. Impact toughness and fractography of Al–Si–Cu–Mg base alloys. Mater Des. 2011;32:3900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.02.058.
Chen F, Lu T, Pan Y. effects of grain refinement on tensile properties and precipitation kinetics of Al-Si-Mg alloys cast in sand molds. Metall Mater Trans B. 2020;51:1933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01910-z.
Cai Q, Mendis CL, Chang ITH, Fan Z. Effect of short T6 heat treatment on the microstructure and the mechanical properties of newly developed die-cast Al–Si–Mg–Mn alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2020;788:139610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139610.
Asghar G, Peng L, Fu P, Yuan L, Liu Y. Role of Mg2Si precipitates size in determining the ductility of A357 cast alloy. Mater Des. 2020;186:108280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108280.
Yang BC, Chen SF, Song HW, Zhang SH, Chang HP, Xu SW, Zhu ZH, Li CH. Effects of microstructure coarsening and casting pores on the tensile and fatigue properties of cast A356–T6 aluminum alloy: a comparative investigation. Mater Sci Eng A. 2022;857:144106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.144106.
Zhang J, Cinkilic E, Huang X, Wang GG, Liu Y, Weiler JP, Luo AA. Optimization of T5 heat treatment in high pressure die casting of Al–Si–Mg–Mn alloys by using an improved Kampmann-Wagner numerical (KWN) model. Mater Sci Eng A. 2023;865:144604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2023.144604.
Yi W, Liu G, Lu Z, Gao J, Zhang L. Efficient alloy design of Sr-modified A356 alloys driven by computational thermodynamics and machine learning. J Mater Sci Technol. 2022;112:277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.09.061.
Lan Q, Wang X, Sun J, Chang Z, Deng Q, Sun Q, Liu Z, Yuan L, Wang J, Wu Y, Liu B, Peng L. Artificial neural network approach for mechanical properties prediction of as-cast A380 aluminum alloy. Mater Today Commun. 2022;31:103301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103301.
Cao Y, Chen X, Wang Z, Chen K, Pan S, Zhu Y, Wang Y. Synergistic influence of La and Zr on microstructure and mechanical performance of an Al-Si-Mg alloy at casting state. J Alloys Compd. 2022;902:163829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163829.
Elsebaie O, Samuel AM, Samuel FH. Effects of Sr-modification, iron-based intermetallics and aging treatment on the impact toughness of 356 Al–Si–Mg alloy. J Mater Sci. 2011;46:3027. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-5181-1.
Samuel AM, Doty HW, Valtierra S, Samuel FH. Effect of grain refining and Sr-modification interactions on the impact toughness of Al–Si–Mg cast alloys. Mater Des. 2014;1980–2015(56):264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.10.029.
Mohamed AMA, Samuel FH, Samuel AM, Doty HW. Influence of additives on the impact toughness of Al–10.8% Si near-eutectic cast alloys. Mater Des. 2009;30:4218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.04.041.
Elsharkawi EA, Abdelaziz MH, Doty HW, Valtierra S, Samuel FH. Effect of β-Al5FeSi and π-Al8Mg3FeSi6 phases on the impact toughness and fractography of Al–Si–Mg-based alloys. Int J Met. 2018;12:148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0153-8.
Chen Y, Xu J, Pan S, Li N, Ou C, Liu W, Song Y, Tan X, Liu Y. Effect of T6I6 treatment on dynamic mechanical behaviour of Al-Si-Mg-Cu cast alloy and impact resistance of its cast motor shell. J Cent South Univ. 2022;29:924. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-4964-2.
Abuhasel KhA, Ibrahim MF, Elgallad EM, Samuel FH. On the impact toughness of Al–Si cast alloys. Mater Des. 2016;91:388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.072.
Alexopoulos ND, Stylianos A. Impact mechanical behaviour of Al–7Si–Mg (A357) cast aluminum alloy. The effect of artificial aging. Mater Sci Eng A. 2011;528:6303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.04.086.
Lin YC, Luo S-C, Huang J, Yin L-X, Jiang X-Y. Effects of solution treatment on microstructures and micro-hardness of a Sr-modified Al-Si-Mg alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2018;725:530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.04.049.
Ding J, Miao S, Ma B, Xia X, Qiu C, Chen X. Effect of solution treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of A356.2 aluminum alloy treated with Al-Sr-La master alloy. Adv Eng Mater. 2018;20:1701173. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201701173.
Zheng Q, Ye Z. Effect of micro-alloying element la on solidification microstructure and mechanical properties of hypoeutectic Al-Si alloys. Acta Metall Sin. 2020;57:103. https://doi.org/10.11900/0412.1961.2020.00158.
Dang B, Liu C, Liu F, Liu Y, Li Y. Effect of as-solidified microstructure on subsequent solution-treatment process for A356 Al alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2016;26:634. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64152-3.
Chen R, Xu Q, Jia Z, Liu B. Precipitation behavior and hardening effects of Si-containing dispersoids in Al–7Si–Mg alloy during solution treatment. Mater Des. 2016;90:1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.069.
Lin YC, Luo S-C, Yin L-X, Huang J. Microstructural evolution and high temperature flow behaviors of a homogenized Sr-modified Al-Si-Mg alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2018;739:590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.278.
Muggerud AMF, Mørtsell EA, Li Y, Holmestad R. Dispersoid strengthening in AA3xxx alloys with varying Mn and Si content during annealing at low temperatures. Mater Sci Eng A. 2013;567:21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.01.004.
Wang QG. Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of aluminum casting alloys A356/357. Metall Mater Trans A. 2003;34:2887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0189-7.
Wang QG, Caceres CH, Griffiths JR. Damage by eutectic particle cracking in aluminum casting alloys A356/357. Metall Mater Trans A. 2003;34:2901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0190-1.
Caceres CH, Griffiths JR. Damage by the cracking of silicon particles in an Al-7Si-0.4Mg casting alloy. Acta Mater. 1996;44:25. https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-6454(95)00172-8.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. L223001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, XL., Li, SX., Ma, JL. et al. Improvement of impact properties of Al–Si–Mg alloy via solution treatment and joint modification with Sr and La. Rare Met. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-024-02622-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-024-02622-y