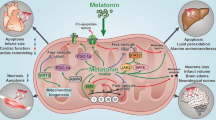
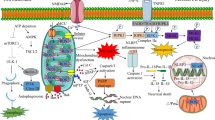
Abstract
Acute brain reperfusion stress is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction through unknown mechanisms. Accordingly, there is no effective drug to control the development and progression of brain reperfusion stress currently. The aim of our investigation is to verify whether melatonin attenuates acute brain reperfusion stress via affecting mitochondrial function. Our studies demonstrated that melatonin treatment suppressed reperfusion-induced neuron death. At the molecular levels, melatonin treatment modulated mitochondrial homeostasis via activating mitochondrial fusion. At the stage of reperfusion, MFN2 expression was downregulated, contributing to mitochondrial fusion inhibition. Interestingly, MFN2-related mitochondrial fusion was reversed by melatonin. Loss of MFN2-related mitochondrial fusion abrogated the protective actions of melatonin on mitochondrial function. Mechanistically, melatonin sustained MFN2-related mitochondrial fusion via suppressing Mst1-Hippo pathway. Overexpression of Mst1 attenuated the beneficial effects of melatonin on mitochondrial fusion, evoking mitochondrial damage and neuron death in the setting of brain reperfusion stress. Taken together, our results confirmed the protective effects of melatonin on acute brain reperfusion stress. Melatonin treatment activated MFN2-related mitochondrial fusion via suppressing Mst1-Hippo pathway, finally sustaining mitochondrial function and reducing reperfusion-mediated cerebral injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 April 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-021-01206-4
References
Bikfalvi A (2017) History and conceptual developments in vascular biology and angiogenesis research: a personal view. Angiogenesis 20:463–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9569-2
Blackburn NJR, Vulesevic B, McNeill B, Cimenci CE, Ahmadi A, Gonzalez-Gomez M, Ostojic A, Zhong Z, Brownlee M, Beisswenger PJ, Milne RW, Suuronen EJ (2017) Methylglyoxal-derived advanced glycation end products contribute to negative cardiac remodeling and dysfunction post-myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol 112:57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0646-x
Brasacchio D, Alsop AE, Noori T, Lufti M, Iyer S, Simpson KJ, Bird PI, Kluck RM, Johnstone RW, Trapani JA (2017) Epigenetic control of mitochondrial cell death through PACS1-mediated regulation of BAX/BAK oligomerization. Cell Death Differ 24:961–970. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.119
Buijs N, Oosterink JE, Jessup M, Schierbeek H, Stolz DB, Houdijk AP, Geller DA, van Leeuwen PA (2017) A new key player in VEGF-dependent angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma: dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1. Angiogenesis 20:557–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9567-4
Casadonte L, Verhoeff BJ, Piek JJ, VanBavel E, Spaan JAE, Siebes M (2017) Influence of increased heart rate and aortic pressure on resting indices of functional coronary stenosis severity. Basic Res Cardiol 112:61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0651-0
Conradi LC, Brajic A, Cantelmo AR, Bouché A, Kalucka J, Pircher A, Brüning U, Teuwen LA, Vinckier S, Ghesquière B, Dewerchin M, Carmeliet P (2017) Tumor vessel disintegration by maximum tolerable PFKFB3 blockade. Angiogenesis 20:599–613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9573-6
Cuervo H, Pereira B, Nadeem T, Lin M, Lee F, Kitajewski J, Lin CS (2017) PDGFRbeta-P2A-CreER(T2) mice: a genetic tool to target pericytes in angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 20:655–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9570-9
Das N, Mandala A, Naaz S, Giri S, Jain M, Bandyopadhyay D, Reiter RJ, Roy SS (2017) Melatonin protects against lipid-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocytes and inhibits stellate cell activation during hepatic fibrosis in mice. J Pineal Res 62. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12404
Fuhrmann DC, Brune B (2017) Mitochondrial composition and function under the control of hypoxia. Redox Biol 12:208–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.02.012
Gadicherla AK, Wang N, Bulic M, Agullo-Pascual E, Lissoni A, de Smet M, Delmar M, Bultynck G, Krysko DV, Camara A, Schlüter KD, Schulz R, Kwok WM, Leybaert L (2017) Mitochondrial Cx43 hemichannels contribute to mitochondrial calcium entry and cell death in the heart. Basic Res Cardiol 112:27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0618-1
Gao Y, Xiao X, Zhang C, Yu W, Guo W, Zhang Z, Li Z, Feng X, Hao J, Zhang K, Xiao B, Chen M, Huang W, Xiong S, Wu X, Deng W (2017) Melatonin synergizes the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer by suppressing PI3K/AKT and NF-kappaB/iNOS signaling pathways. J Pineal Res 62. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12380
Geng C, Wei J, Wu C (2018) Yap-Hippo pathway regulates cerebral hypoxia-reoxygenation injury in neuroblastoma N2a cells via inhibiting ROCK1/F-actin/mitochondrial fission pathways. Acta Neurol Belg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0944-6
Ghiroldi A, Piccoli M, Ciconte G, Pappone C, Anastasia L (2017) Regenerating the human heart: direct reprogramming strategies and their current limitations. Basic Res Cardiol 112:68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0655-9
Giatsidis G, Cheng L, Haddad A, Ji K, Succar J, Lancerotto L, Lujan-Hernandez J, Fiorina P, Matsumine H, Orgill DP (2018) Noninvasive induction of angiogenesis in tissues by external suction: sequential optimization for use in reconstructive surgery. Angiogenesis 21:61–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9586-1
Griffiths HR, Gao D, Pararasa C (2017) Redox regulation in metabolic programming and inflammation. Redox Biol 12:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.023
Guers JJ, Zhang J, Campbell SC, Oydanich M, Vatner DE, Vatner SF (2017) Disruption of adenylyl cyclase type 5 mimics exercise training. Basic Res Cardiol 112:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0648-8
Hambright WS, Fonseca RS, Chen L, Na R, Ran Q (2017) Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox Biol 12:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.021
Han L, Wang H, Li L, Li X, Ge J, Reiter RJ, Wang Q (2017) Melatonin protects against maternal obesity-associated oxidative stress and meiotic defects in oocytes via the SIRT3-SOD2-dependent pathway. J Pineal Res 63. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12431
Hassanshahi M, Hassanshahi A, Khabbazi S, Su YW, Xian CJ (2017) Bone marrow sinusoidal endothelium: damage and potential regeneration following cancer radiotherapy or chemotherapy. Angiogenesis 20:427–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9577-2
Hong H, Tao T, Chen S, Liang C, Qiu Y, Zhou Y, Zhang R (2017) MicroRNA-143 promotes cardiac ischemia-mediated mitochondrial impairment by the inhibition of protein kinase Cepsilon. Basic Res Cardiol 112:60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0649-7
Hooshdaran B, Kolpakov MA, Guo X, Miller SA, Wang T, Tilley DG, Rafiq K, Sabri A (2017) Dual inhibition of cathepsin G and chymase reduces myocyte death and improves cardiac remodeling after myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol 112:62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0652-z
Iggena D, Winter Y, Steiner B (2017) Melatonin restores hippocampal neural precursor cell proliferation and prevents cognitive deficits induced by jet lag simulation in adult mice. J Pineal Res 62:e12397. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12397
Jin Q, Li R, Hu N, Xin T, Zhu P, Hu S, Ma S, Zhu H, Ren J, Zhou H (2018) DUSP1 alleviates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing the Mff-required mitochondrial fission and Bnip3-related mitophagy via the JNK pathways. Redox Biol 14:576–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.004
Jokinen R, Pirnes-Karhu S, Pietilainen KH, Pirinen E (2017) Adipose tissue NAD(+)-homeostasis, sirtuins and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases -important players in mitochondrial metabolism and metabolic health. Redox Biol 12:246–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.02.011
Karwi QG, Bice JS, Baxter GF (2017) Pre- and postconditioning the heart with hydrogen sulfide (H2S) against ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Basic Res Cardiol 113:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0664-8
Kelly P, Denver P, Satchell SC, Ackermann M, Konerding MA, Mitchell CA (2017) Microvascular ultrastructural changes precede cognitive impairment in the murine APPswe/PS1dE9 model of Alzheimer's disease. Angiogenesis 20:567–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9568-3
Kleinbongard P, Skyschally A, Gent S, Pesch M, Heusch G (2017) STAT3 as a common signal of ischemic conditioning: a lesson on “rigor and reproducibility” in preclinical studies on cardioprotection. Basic Res Cardiol 113:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0660-z
Kozlov AV, Lancaster JR Jr, Meszaros AT, Weidinger A (2017) Mitochondria-meditated pathways of organ failure upon inflammation. Redox Biol 13:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.05.017
Lee K, Back K (2017) Overexpression of rice serotonin N-acetyltransferase 1 in transgenic rice plants confers resistance to cadmium and senescence and increases grain yield. J Pineal Res 62:e12392. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12392
Li H, He F, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Chu X, Hua C, Qu Y, Duan Y, Ming L (2017) YAP inhibits the apoptosis and migration of human rectal cancer cells via suppression of JNK-Drp1-mitochondrial fission-HtrA2/Omi pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem 44:2073–2089. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485946
Li R, Xin T, Li D, Wang C, Zhu H, Zhou H (2018) Therapeutic effect of Sirtuin 3 on ameliorating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the role of the ERK-CREB pathway and Bnip3-mediated mitophagy. Redox Biol 18:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.011
Liu D, Zeng X, Li X, Mehta JL, Wang X (2017) Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Basic Res Cardiol 113:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0663-9
Nuntaphum W, Pongkan W, Wongjaikam S, Thummasorn S, Tanajak P, Khamseekaew J, Intachai K, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N, Shinlapawittayatorn K (2018) Vagus nerve stimulation exerts cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury predominantly through its efferent vagal fibers. Basic Res Cardiol 113:22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0683-0
Peng C, Rao W, Zhang L, Gao F, Hui H, Wang K, Dai S, Yang Y, Luo P, Ma Y, Ma W, Yu X, Fei Z (2018) Mitofusin 2 exerts a protective role in ischemia reperfusion injury through increasing autophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem 46:2311–2324. https://doi.org/10.1159/000489621
Rossello X, Yellon DM (2017) The RISK pathway and beyond. Basic Res Cardiol 113:2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0662-x
Rossello X, Riquelme JA, He Z, Taferner S, Vanhaesebroeck B, Davidson SM, Yellon DM (2017) The role of PI3Kalpha isoform in cardioprotection. Basic Res Cardiol 112:66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0657-7
Tamura H, Kawamoto M, Sato S, Tamura I, Maekawa R, Taketani T, Aasada H, Takaki E, Nakai A, Reiter RJ, Sugino N (2017) Long-term melatonin treatment delays ovarian aging. J Pineal Res 62:e12381. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12381
Zhai M, Li B, Duan W, Jing L, Zhang B, Zhang M, Yu L, Liu Z, Yu B, Ren K, Gao E, Yang Y, Liang H, Jin Z, Yu S (2017) Melatonin ameliorates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through SIRT3-dependent regulation of oxidative stress and apoptosis. J Pineal Res 63:e12419. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12419
Zhang Y, Zhou H, Wu W, Shi C, Hu S, Yin T, Ma Q, Han T, Zhang Y, Tian F, Chen Y (2016) Liraglutide protects cardiac microvascular endothelial cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through the suppression of the SR-Ca(2+)-XO-ROS axis via activation of the GLP-1R/PI3K/Akt/survivin pathways. Free Radic Biol Med 95:278–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.03.035
Zhang C, Huang J, An W (2017) Hepatic stimulator substance resists hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating Drp1 translocation and activation. Hepatology 66:1989–2001. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29326
Zhao H, Luo Y, Chen L, Zhang Z, Shen C, Li Y, Xu R (2018) Sirt3 inhibits cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through normalizing Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and blocking mitochondrial fission. Cell Stress Chaperones 23:1079–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-0917-y
Zhou H, Hu S, Jin Q, Shi C, Zhang Y, Zhu P, Ma Q, Tian F, Chen Y (2017a) Mff-dependent mitochondrial fission contributes to the pathogenesis of cardiac microvasculature ischemia/reperfusion injury via induction of mROS-mediated cardiolipin oxidation and HK2/VDAC1 disassociation-involved mPTP opening. J Am Heart Assoc 6:e005328. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.005328
Zhou H, Zhang Y, Hu S, Shi C, Zhu P, Ma Q, Jin Q, Cao F, Tian F, Chen Y (2017b) Melatonin protects cardiac microvasculature against ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of mitochondrial fission-VDAC1-HK2-mPTP-mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res 63:e12413. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12413
Zhou H, Ma Q, Zhu P, Ren J, Reiter RJ, Chen Y (2018a) Protective role of melatonin in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: from pathogenesis to targeted therapy. J Pineal Res 64. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12471
Zhou H, Wang J, Hu S, Zhu H, Toanc S, Ren J (2018b) BI1 alleviates cardiac microvascular ischemia-reperfusion injury via modifying mitochondrial fission and inhibiting XO/ROS/F-actin pathways. J Cell Physiol doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27308
Zhou H, Zhu P, Wang J, Zhu H, Ren J, Chen Y (2018c) Pathogenesis of cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury is associated with CK2alpha-disturbed mitochondrial homeostasis via suppression of FUNDC1-related mitophagy. Cell Death Differ 25:1080–1093. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0086-7
Zhu H, Jin Q, Li Y, Ma Q, Wang J, Li D, Zhou H, Chen Y (2018a) Melatonin protected cardiac microvascular endothelial cells against oxidative stress injury via suppression of IP3R-[Ca(2+)]c/VDAC-[Ca(2+)]m axis by activation of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones 23:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0827-4
Zhu P, Hu S, Jin Q, Li D, Tian F, Toan S, Li Y, Zhou H, Chen Y (2018b) Ripk3 promotes ER stress-induced necroptosis in cardiac IR injury: a mechanism involving calcium overload/XO/ROS/mPTP pathway. Redox Biol 16:157–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.02.019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL, XYL, CLB, and JFL were involved in the conception and design, performance of experiments, data analysis and interpretation, and manuscript writing. CLB was involved in data analysis and interpretation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12192-021-01206-4
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, S., Liu, J., Luo, X. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Effects of melatonin on acute brain reperfusion stress: role of Hippo signaling pathway and MFN2-related mitochondrial protection. Cell Stress and Chaperones 24, 235–245 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-00960-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-00960-2