Abstract
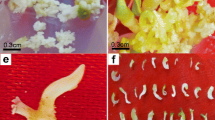
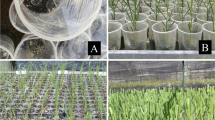
Citrus jambhiri Lush. (rough lemon) is considered a major rootstock for a number of Citrus species. Different explants were used for somatic embryogenesis: leaf, nodal, and root segments excised from in vitro seedlings, stigmas, styles, and ovaries from flower buds, nucellar tissues and cotyledons from seeds, and juice vesicles from fruits. The explants were cultured on MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP), kinetin (KN), malt extract (ME), and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) for callus induction. All explants formed callus except styles and juice vesicles. The most responsive explants were leaf and nodal segments cultured in the presence of 2,4-D, and ovary and nucellar tissues cultured in a medium with BA 4 mg/l. Callus obtained from all explants was transferred to MS medium supplemented with different concentrations and combinations of 2,4-D, BA, KN, ME, and ABA (abscisic acid) for somatic embryo induction. Only calli from ovaries and nucellar tissue were competent to form somatic embryos, mainly when they were transferred to a induction medium supplemented with BA 4 mg/l and ME 500 mg/l (89.33 and 83.50 %, respectively). The somatic embryos were shifted to MS medium containing different concentrations of sucrose with or without activated charcoal (AC) or polyethylene glycol (PEG) for somatic embryo germination. Maximum somatic embryo germination (98.85 %) was noticed from somatic embryos from ovary calli on MS medium consisting of 8 % sucrose. By increasing and decreasing the concentration of sucrose from 8 %, a corresponding decrease in somatic embryo germination was observed. The addition of AC and PEG to somatic embryo germination medium reduced the percentage of germination of somatic embryos. RAPD analysis was employed to assess the genetic fidelity of plantlets. The plantlets regenerated through somatic embryogenesis from nucellar tissues showed no variation in their RAPD profile but the plantlets raised through somatic embryogenesis from ovaries showed variation in around 20–30 % plantlets.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaf N, Khan AR, Ali L, Bhatti IA (2008) Propagation of rough lemon (Citrus jambhiri Lush.) through in vitro culture and adventitious rooting in cuttings. Electron J Environ Agric Food Chem 7:3326–3333
Azad MAK, Yokota S, Ohkubo T, Andoh Y, Yahara S, Yoshizawa N (2005) In vitro regeneration of the medicinal woody plant Phellodendron amurense Rupr. through excised leaves. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 80:43–50
Bano S, Jabeen M, Rahim F, Ilahi I (2005) Callus induction and regeneration in seed explants of rice (Oryza sativa CV. Swat-II). Pak J Bot 37(3):829–836
Beloualy N (1991) Plant regeneration from callus of three Citrus rootstocks. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 24:29–34
Bhatia R, Singh KP, Jhang T, Sharma TR (2009) Assessment of clonal fidelity of micropropagated gerbera plants by ISSR markers. Sci Hortic 119:208–211
Bitters WP, Murashige T, Rangan TS, Nauer E (1970) Investigations on established virus-free plants through tissue culture. Calif Citrus Nurs Soc 9:27–30
Button J, Bornman CH (1971) Development of nucellar plants from unpollinated and unfertilized ovules of the Washington navel orange in vitro. J S Afr Bot 37:127–134
Button J, Kochba J, Bornman CH (1977) Fine structure of embryoid 341 development from embryogenic ovular callus of ‘Shamouti’ 342 orange (Citrus sinensis Osb.). J Exp Bot 25:446–457
Calic-Dragosavac D, Zdravkovi-Kora S, Bohanec B, Radojevi L, Vinterhalter B, Stevovi S, Cingel A, Savi J (2010) Effect of activated charcoal, abscisic acid and polyethylene glycol on maturation, germination and conversion of Aesculus hippocastanum androgenic embryos. Afr J Biotechnol 9:3786–3793
Carimi F, Pasquale FD, Grescimanno FG (1995) Somatic embryogenesis in Citrus from styles culture. Plant Sci 105:81–86
Carimi F, Tortorici MC, Pasquala FD, Giulio F (1998) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from undeveloped ovules and stigma/style explant of sweet orange navel group [Citrus sinensis (L.) Qsb.]. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 54:183–189
Carimi F, De Pasquale F, Crescimanno FG (1999) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from pistil thin cell layers of Citrus. Plant Cell Rep 18:935–940
Carimi F, Caleca V, Mineo G, De Pasquale F, Crescimanno FG (2000) Rearing of Prays citri on callus derived from lemon stigma and style culture. Entomol Exp Appl 95:251–257
Cassells AC (2000) Contamination detection and elimination. In: Spier RE (ed) Encyclopedia of plant cell biology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 577–586
Cassells AC, Doyle BM, Curry RF (eds) (2000) Methods and markers for quality assurance in micropropagation. Acta Hortic 530:437
Chaturvedi HC, Mitra G (1972) Embryoids and complete plants from unpollinated ovaries and from ovules of in vivo-grown emasculated flower buds of Citrus spp. Bull Torrey Bot Club 99:184–189
D’Onghia AM, Carimi F, De Pasquale F, Djelouah K, Martelli GP (2001) Somatic embryogenesis from style culture: A new technique for the sanitation, conservation, and safe exchange of citrus germplasm. In: Proc IX International Society of Citriculture. p 12
Devarumath RM, Nandy S, Rani V, Marimuthu S, Muraleedharan N (2002) RAPD, ISSR and RFLP fingerprints as useful markers to evaluate genetic integrity of micropropagated plants of three diploid and triploid elite tea clones representing Camellia sinensis (China type) and C. assamica ssp. assamica (Assam- India type). Plant Cell Rep 21(2):166–173
Duan G, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Yu L, Yuan Q (2007) Evaluation of crude toxin and metabolite produced by Helminthosporium gramineum Rabenh for the control of rice sheath blight in paddy fields. Crop Protection 26:1036–1041
Fridborg G, Pedersen M, Landstrom LE, Eriksson T (1978) Effects of activated charcoal on tissue cultures: adsorption of metabolites in plant tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 43:104–106
Gill MIS, Singh Z, Dhillon BS, Gosal SS (1995) Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration in mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco). Sci Hortic 63:167–174
Goto S, Thakur RC, Ishii K (1998) Determination of genetic stability in long-term micropropagated shoots of Pinus thunbergii Parl. using RAPD markers. Plant Cell Rep 18:193–197
Grosser JW, Gmitter FG Jr, Chandler JL (1988) Intergeneric somatic hybrid plants of Citrus sinensis CV. Hamlin and Poncirus trifoliata CV, Flying Dragon. Plant Cell Rep 7:5–8
Hao Y-J, Deng X-X (2003) Single-cell-derived sibling lines are established as an experimental system to assess chromosome number variations in embryogenic callus cultures of sweet orange. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 73:275–280
Heinze B, Schmidt J (1995) Monitoring genetic fidelity vs somaclonal variation in Norway spruce (Picea abies) somatic embryogenesis by RAPD analysis. Euphytica 85:341–345
Ishii K, Moran GF, Bell JC, Hartney V (1987) Genetic stability examination of micropropagated radiata pine (Pinus radiata) using isozyme assays. J Jpn For Soc 69:487–488
Iyer RI, Jayaraman G, Ramesh A (2009) Direct somatic embryogenesis in Myristica malabarica Lam., an endemic, threatened medicinal species of Southern India and detection of phytochemicals of potential medicinal value. Indian J Sci Technol 7:11–17
Jayasree PK, Asokan MP, Sobha S, Ammal LS, Rekha K, Kala RG, Jayasree R, Thulaseedharan A (1999) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature anthers of Hevea brasiliensis (Muell.) Arg.x. M.P. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 33:331–338
Joshi P, Dhawan V (2007) Assessment of genetic fidelity of micropropagated Swertia chirayita plantlets by ISSR marker assay. Biol Plant 51:22–26
Karp A, Bright SWJ (1985) On the causes of origins of somaclonal variation. In: Miflin BJ (ed) Oxford surveys of plant molecular and cell biology, Oxford University Press, London, UK, 2: 199–234
Kobayashi S, Ohgawara T, Fujiwara K, Oiyama I (1991) Analysis of cytoplasmic genomes in somatic hybrids between navel orange (Citrus sinensis Osb.) and ‘Murcott’ tangor. Theor Appl Genet 82:6–10
Koltunow AM (1993) Apomixis: embryo sacs and embryos formed without meiosis or fertilization in Ovules. Plant Cell 5:1425–1437
Li XY, Huang FH, Murphy B, Junior EE (1998) Polyethylene glycol and maltose enhance somatic embryo maturation in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). In vitro Cell Dev Biol 34:22–26
Litz RE, Moore GA, Srinivasan C (1985) In vitro system for propagation and improvement of tropical fruits and palm. Hortic Rev 7:157–200
López-Pérez AJ, Carreño J, Martínez-Cutillas A, Dabauza M (2005) High embryogenic ability and plant regeneration of table grapevine cultivars (Vitis vinifera L.) induced by activated charcoal. Vitis 44(2):79–85
Madhav MS, Rao RN, Singh S, Deka PC (2002) Nucellar embryogenesis and artificial seed production in Citrus reticulata. Plant Cell Biotechnol Mol Biol 3:77–80
Maheshwari P, Rangaswamy NS (1958) Polyembryony and in vitro culture of embryos of Citrus and Mangifera. Indian J Hortic 15:275–282
Mahmood T, Nazar N, Abbasi BH, Khan MA, Ahmad M, Zafar M (2010) Detection of somaclonal variations using RAPD fingerprinting in Silybum marianum (L.). J Med Plants Res 4(17):1822–1824
Martin KP, Pachathundkandi SK, Zhang CL, Slater A (2006) RAPD analysis of a variant of Banana (Musa sp.) cv. Grande Naine and its propagation via shoot tip culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 42:188–192
Martinelli L, Gribaudo I (2001) Somatic embryogenesis in grapevine. In: Roubelakis-Angelakis K (ed) Molecular Biology and Biotechnology of the Grapevine, pp 327–351. Kluwer Academic Pub, Dordrecht, Boston, London
Miah MN, Islam S, Hadiuzzaman S (2002) Regeneration of plantlets through somatic embryogenesis from nucellus tissue of Citrus macroptera Mont. var. anammensis (‘Sat Kara’). Plant Tissue Cult 12:167–172
Misra S, Attree SM, Leal I, Fowke LC (1993) Effect of abscisic acid, osmoticum, and desiccation on synthesis of storage proteins during the development of white spruce somatic embryos. Ann Bot 71:11–22
Mo LH, Von Arnord S, Lagercrantz U (1989) Morphogenic and genetic stability in longterm embryogenic cultures and somatic embryos of Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] Karst). Plant Cell Rep 8:375–378
Moiseeva NA, Serebryakova VN, Nardi L, Lucretti S, Butenko RG (2006) Organization of initial stages of somatic embryogenesis in tissue culture of Citrus sinensis cv. Tarocco at the organismal level. Russ J Plant Physiol 53:548–555
Moore GA (1985) Factors affecting in vitro embryogenesis from undeveloped ovules of mature Citrus fruit. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 110:66–70
Motoike SY, Skirvin RM, Norton MA, Otterbacher AG (2001) Somatic embryogenesis and long term maintenance of embryogenic lines from fox grapes. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 66:121–131
Mukhtar R, Khan MM, Fatima B, Abbas M, Shahid A (2005) In vitro regeneration and multiple shoots induction in Citrus reticulata Blanco. Int J Agric Biol 7:414–416
Neto VBP, Botelho MN, Aguİar R, Silva EAM, Otoni WC (2003) Somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of annatto (Bixa orellana L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:629–634
Niedz RP, Hyndman SE, Wynn ET, Bausher MG (2002) Normalizing sweet orange (C. sinensis (L.) Osbeck) somatic embryogenesis with semi-permeable membranes. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 38:552–557
Nito N, Iwamasa M (1990) In vitro plantlet formation from juice vesicle callus of Satsuma (Citrus unshiu Marc.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 20:137–140
Ohgawara T, Kobayashi S, Ishii S, Yoshinaga K, Oiyama I (1989) Somatic hybridization in Citrus: navel orange (C. sinensis Osb.) and grapefruit (C. paradisi Macf.). Theor Appl Genet 78:609–612
P´erez RM, Mas O, Navarro L, Duran-Vila N (1999) Production and cryoconservation of embryogenic cultures of mandarin and mandarin hybrid. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 55:71–74
Patel KR, Berlyn GP (1982) Genetic instability of multiple buds of Pinus coulteri regenerated from tissue culture. Can J For Res 12:93–101
Perl A, Saad S, Sahar N, Holland D (1995) Establishment of long-term embryogenic cultures of seedless Vitis vinifera cultivars—a synergistic effect of auxins and the role of abscisic acid. Plant Sci 104:193–200
Rafalski A, Tingey S, Williams JGK (1993) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoort RMS, Verma DPS (eds) Plant molecular biology manual. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, pp 1–9
Rani V, Raina SN (2000) Genetic fidelity of organized meristem-derived micropropagated plants: a critical reappraisal. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 36:319–330
Rani V, Parida A, Raina SN (1995) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers for genetic analysis in micropropagated plants of Populus deltoids Marsh. Plant Cell Rep 14:459–462
Renfroe MH, Berlyn GP (1984) Stability of nuclear DNA content during adventitious shoot formation in Pinus taeda L. tissue culture. Am J Bot 71:268–272
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Salvi ND, George L, Eapen S (2001) Plant regeneration from leaf callus of turmeric and random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of regenerated plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 66:113–119
Savita, Singh B, Virk GS, Nagpal A (2011) Efficient micropropagation protocol for regeneration of Citrus jambhiri Lush. using cotyledon as explant. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 17:161–169
Savita, Bhagat A, Pati PK, Virk GS, Nagpal A (2012) An efficient micropropagation protocol for Citrus jambhiri Lush. and assessment of clonal fidelity employing anatomical studies and RAPD markers. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. doi:10.1007/s11627-012-9430-7
Shekhawat GS, Mathur S, Batra A (2009) Role of phytohormones and nitrogen in somatic embryogenesis induction in cell culture derived from leaflets of Azadirachta indica. Biol Plant 53:707–710
Shenoy VB, Vasil IK (1992) Biochemical and molecular analysis of plants derived from embryogenic cultures of napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum K. Schum). Theor Appl Genet 83:947–955
Shoja AM, Hassanpouraghdam MB, Khosrowshahli M, Movafeghi A (2010) Callogenesis capability and calli somaclonal variation of costmary (Tanacetum balsamita L.). Rom Biotechnol Lett 15:5120–5124
Siragusa Mirko, Carra A, Salvia L, Puglia AM, De Pasquale F, Carimi F (2007) Genetic instability in calamondin (Citrus madurensis Lour.) plants derived from somatic embryogenesis induced by diphenylurea derivatives. Plant Cell Rep 26:1289–1296
Starrantino A, Russo F (1980) Seedlings from undeveloped ovules of ripe fruits of polyembryonic citrus cultivars. Hortic Sci 15:296–297
Svobodová H, Albrechtová J, Lipasvká H, Vagner M, Vondráková Z (1999) Somatic embryogenesis in Norway spruce: anatomical study of embryo development and influence of polyethylene glycol on maturation process. Plant Physiol Biochem 37:209–221
Tremblay L, Tremblay FM (1995) Maturation of black spruce somatic embryos: sucrose hydrolysis and resulting osmotic pressure of the medium. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 42:39–46
Vardi A, Galun E (1988) Recent advances in protoplast culture of Horticultural Crops: Citrus. Sci Hortic 37:217–230
Vardi A, Epstein E, Breiman A (1986) Is the Phytophthora citrophthora culture filtrate a reliable tool for the in vitro selection of resistant Citrus variants? Theor Appl Genet 72:569–574
Varshney A, Lakshmikumaran M, Srivastava PS, Dhawan V (2001) Establishment of genetic fidelity of in vitro raised Lilium bulbets through RAPD markers. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 37:227–231
Walker DR, Parrott WA (2001) Effect of polyethylene glycol and sugar alcohols on soybean somatic embryo germination and conversion. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 64:55–62
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucl Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic marker. Nucl Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Wu J-H, Mooney P (2002) Autotetraploid tangor plant regeneration from in vitro Citrus somatic embryogenic callus treated with colchicine. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 70:99–104
Yadav CB, Jha P, Mahalakshmi V, Anjaiah V, Bhat V (2009) Somatic embryogenesis and regeneration of Cenchrus ciliaris genotypes from immature inflorescence explants. Biol Plant 53:603–609
Yang XL, Kitajima A, Hasegawa K (2000) Callus induction and embryoid regeneration from the endosperm culture of ‘Tosa-Buntan’ pummelo (Citrus grandis [L.] Osb.). Environ Control Biol 38:241–246 (in Japanese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savita, Pati, P.K., Virk, G.S. et al. An Efficient Somatic Embryogenesis Protocol for Citrus jambhiri and Assessment of Clonal Fidelity of Plantlets Using RAPD Markers. J Plant Growth Regul 34, 309–319 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-014-9465-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-014-9465-6