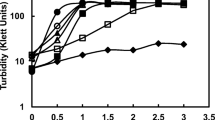
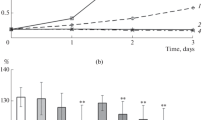
Abstract
This study examined the influence of prior salt adaptation on the survival rate of (hyper)-thermophilic bacteria and archaea after desiccation and UV or ionizing irradiation treatment. Survival rates after desiccation of Hydrogenothermus marinus and Archaeoglobus fulgidus increased considerably when the cells were cultivated at higher salt concentrations before drying. By doubling the concentration of NaCl, a 30 times higher survival rate of H. marinus after desiccation was observed. Under salt stress, the compatible solute diglycerol phosphate in A. fulgidus and glucosylglycerate in H. marinus accumulated in the cytoplasm. Several different compatible solutes were added as protectants to A. fulgidus and H. marinus before desiccation treatment. Some of these had similar effects as intracellularly produced compatible solutes. The survival rates of H. marinus and A. fulgidus after exposure to UV-C (254 nm) or ionizing X-ray/gamma radiation were irrespective of the salt-induced synthesis or the addition of compatible solutes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MB (1959) Studies with Cyanidium caldarium, an anomalously pigmented chlorophyte. Archiv für Mikrobiologie 32(3):270–277
Beblo K, Rabbow E, Rachel R, Huber H, Rettberg P (2009) Tolerance of thermophilic and hyperthermophilic microorganisms to desiccation. Extremophiles 13:521–531
Beblo K, Douki T, Schmalz G, Rachel R, Wirth R, Huber H, Reitz G, Rettberg P (2011) Survival of thermophilic and hyperthermophilic microorganisms after exposure to UV-C, ionizing radiation and desiccation. Arch Microbiol 193:797–809
Bieger-Dose A, Dose K, Meffert R, Mehler M, Risi S (1992) Extreme dryness and DNA-protein cross-links. Adv Space Res 12:265–270
Billi D, Potts M (2002) Life and death of dried prokaryotes. Res Microbiol 153:7–12
Borges N, Matsumi R, Imanaka T, Atomi H, Santos H (2010) Thermococcus kodakarensis mutants deficient in di-myo-inositol phosphate use aspartate to cope with heat stress. J Bacteriol 192:191–197
Borges N, Jorge CD, Gonçalves LG, Gonçalves S, Matias PM, Santos H (2014) Mannosylglycerate: structural analysis of biosynthesis and evolutionary history. Extremophiles 18:835–852
Brock TD, Brock KM, Belly RT, Weiss RL (1972) Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and High temperature. Arch Microbiol 84:54–68
Bünger J, Driller H (2004) Ectoin: an effective natural substance to prevent UVA-induced premature photoaging. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 17:232–237
Campos F, Cuevas-Velazquez C, Fares MA, Reyes JL, Covarrubias AA (2013) Group 1 LEA proteins, an ancestral plant protein group, are also present in other eukaryotes, and in the archeae and bacteria domains. Mol Genet Genomics 288:503–517
Costa J, Empadinhas N, Gonçalves L, Lamosa P, Santos H, da Costa MS (2006) Characterization of the biosynthetic pathway of glucosylglycerate in the archaeon Methanococcoides burtonii. J Bacteriol 188:1022–1030
Cox CS (1993) Roles of water molecules in bacteria and viruses. Orig Life Evol Biosph 23:29–36
Crowe JH, Oliver AE, Tablin F (2002) Is there a single biochemical adaptation to anhydrobiosis? Integr Comp Biol 42:497–503
Den Besten HMW, van der Mark EJ, Hensen L, Abee T, Zwietering MH (2010) Quantification of the effect of culturing temperature on salt-induced heat resistance of bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4286–4292
Dwivedi M, Backers H, Harishchandra RK, Galla HJ (2014) Biophysical investigations of the structure and function of the tear fluid lipid layer and the effect of ectoine. Part A: natural meibomian lipid films. BBA-Biomembr 1838:2708–2715
Empadinhas N, da Costa MS (2006) Diversity and biosynthesis of compatible solutes in hyper/thermophiles. Int Microbiol 9:199–206
Empadinhas N, da Costa MS (2008a) To be or not to be a compatible solute: bioversatility of mannosylglycerate and glucosylglycerate. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:159–168
Empadinhas N, da Costa MS (2008b) Osmoadaptation mechanisms in prokaryotes: distribution of compatible solutes. Int Microbiol 11:151–161
Empadinhas N, Marugg JD, Borges N, Santos H, da Costa MS (2001) Pathway for the synthesis of mannosylglycerate in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii. Biochemical and genetic characterization of key enzymes. J Biol Chem 276:43580–43588
Empadinhas N, Mendes V, Simoes C, Santos MS, Mingote A, Lamosa P, Santos H, da Costa MS (2007) Organic solutes in Rubrobacter xylanophilus: the first example of di-myo-inositol-phosphate in a thermophile. Extremophiles 11:667–673
Esteves AM, Chandrayan SK, McTernan PM, Borges N, Adams MW, Santos H (2014) Mannosylglycerate and di-myo-inositol phosphate have interchangeable roles during adaptation of Pyrococcus furiosus to heat stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:4226–4233
Fiala G, Stetter KO (1986) Pyrococcus furiosus sp. nov. represents a novel genus of marine heterotrophic archaebacteria growing optimally at 100°C. Arch Microbiol 145:56–61
Fiala G, Stetter KO, Jannasch HW, Langworthy TA, Madon J (1986) Staphylothermus marinus sp. nov. represents a novel genus of extremely thermophilic submarine heterotrophic archaebacteria growing up to 98°C. Syst Appl Microbiol 8:106–113
Franson MAH (ed) (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. In: American Public Health Association, 16th edn. Washington DC
Galinski EA, Herzog RM (1990) The role of trehalose as a substitute for nitrogen-containing compatible solutes (Ectothiorhodospira halochloris). Arch Microbiol 153:607–613
Galinski EA, Trüper HG (1994) Microbial behaviour in salt-stressed ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:95–108
Gonçalves LG, Huber R, da Costa MS, Santos H (2003) A variant of the hyperthermophile Archaeoglobus fulgidus adapted to grow at high salinity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 218:239–244
Gonçalves LG, Lamosa P, Huber R, Santos H (2008) Di-myo-inositol phosphate and novel UDP-sugars accumulate in the extreme hyperthermophile Pyrolobus fumarii. Extremophiles 12:383–389
Goude R, Renaud S, Bonnassie S, Bernard T, Blanco C (2004) Glutamine, glutamate, and alpha-glucosylglycerate are the major osmotic solutes accumulated by Erwinia chrysanthemi strain 3937. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6535–6541
Goyal K, Walton LJ, Tunnacliffe A (2005) LEA proteins prevent protein aggregation due to water stress. Biochem J 388:151–157
Graf R, Anzali S, Bünger J, Pflücker F, Driller H (2008) The multifunctional role of ectoine as a natural cell protectant. Clin Dermatol 26:326–333
Harishchandra RK, Sachan AK, Kerth A, Lentzen G, Neuhaus T, Galla HJ (2011) Compatible solutes: ectoine and hydroxyectoine improve functional nanostructures in artificial lung surfactants. BBA-Biomembr 1808:2830–2840
Harm W (1980) Biological effects of ultraviolet radiation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hensel R, König H (1988) Thermoadaptation of methanogenic Bacteria by intracellular ion concentration. FEMS Microbiol Lett 49:75–79
Hincha DK, Hagemann M (2004) Stabilization of model membranes during drying by compatible solutes involved in the stress tolerance of plants and microorganisms. Biochem J 383:277–283
Hirai T, Murata K, Mitsuoka K, Kimura Y, Fujiyoshi Y (1999) Trehalose embedding technique for high-resolution electron crystallography: application to structural study on bacteriorhoposin. J Electron Microsc 48:653–658
Huber H, Thomm M, König H, Thies G, Stetter KO (1982) Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus, a novel thermophilic lithotrophic methanogen. Arch Microbiol 132:47–50
Huber R, Wilharm T, Huber D, Trincone A, Burggraf S, König H, Rachel R, Rockinger I, Fricke H, Stetter KO (1992) Aquifex pyrophilus gen. nov. sp. nov., represents a novel group of marine hyperthermophilic hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:340–351
Jebbar M, Talibart R, Gloux K, Bernard T, Blanco C (1992) Osmoprotection of Escherichia coli by ectoine: uptake and accumulation characteristics. J Bacteriol 174:5027–5035
Kempf B, Bremer E (1998) Uptake and synthesis of compatible solutes as microbial stress responses to high-osmolality environments. Arch Microbiol 170:319–330
Kets E, Teunissen P, de Bont J (1996) Effect of compatible solutes on survival of lactic acid bacteria subjected to drying. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:259–261
Klähn S, Hagemann M (2011) Compatible solute biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Environ Microbiol 13:551–562
Klähn S, Steglich C, Hess WR, Hagemann M (2010) Glucosylglycerate: a secondary compatible solute common to marine cyanobacteria from nitrogen-poor environments. Environ Microbiol 12:83–94
Kraegeloh A, Kunte HJ (2002) Novel insights into the role of potassium for osmoregulation in Halomonas elongata. Extremophiles 6:453–462
Kunte HJ, Lentzen G, Galinski EA (2014) Industrial production of the cell protectant ectoine: protection mechanisms, processes, and products. Curr Biotechnol 3:10–25
Kurz M (2008) Compatible solute influence on nucleic acids: many questions but few answers. Saline Syst 4:6
Lamosa P, Martins LO, da Costa MS, Santos H (1998) Effects of temperature, salinity, and medium composition on compatible solute accumulation by Thermococcus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3591–3598
Lamosa P, Burke A, Peist R, Huber R, Liu MY, Silva G, Rodrigues-Pousada C, Le Gall J, Maycock C, Santos H (2000) Thermostabilization of proteins by diglycerol phosphate, a new compatible solute from the hyperthermophile Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1974–1979
Lamosa P, Gonçalves LG, Rodrigues MV, Martins LO, Raven NDH, Santos H (2006) Occurrence of 1-glyceryl-1-myo-inosityl phosphate in hyperthermophiles. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6169–6173
Lentzen G, Schwarz T (2006) Extremolytes: natural compounds from extremophiles for versatile applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:623–634
Leslie SB, Israeli E, Lighthart B, Crowe JH, Crowe LM (1995) Trehalose and sucrose protect both membranes and proteins in intact bacteria during drying. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3592–3597
Lippert K, Galinski EA (1992) Enzyme stabilization by ectoine-type compatible solutes: protection against heating, freezing and drying. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37:61–65
Martins LO, Santos H (1995) Accumulation of mannosylglycerate and di-myo-inositol-phosphate by Pyrococcus furiosus in response to salinity and temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3299–3303
Martins LO, Carreto LS, da Costa MS, Santos H (1996) New compatible solutes related to di-myo-inositol-phosphate in members of the order Thermotogales. J Bacteriol 178:5644–5651
Martins LO, Huber R, Huber H, Stetter KO, da Costa MS, Santos H (1997) Organic solutes in hyperthermophilic Archaea. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:896–902
Múčka V, Bláha P, Cuba V, Červenák J (2013) Influence of various scavengers of ·OH radicals on the radiation sensitivity of yeast and Bacteria. Int J Radiat Biol 89:1045–1052
Müller V, Spanheimer R, Santos H (2005) Stress response by solute accumulation in archaea. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:729–736
Norville JE, Kelly DF, Knight TF Jr, Belcher AM, Walz T (2007) 7 Å projection map of the S-layer protein sbpA obtained with trehalose-embedded monolayer crystals. J Struct Biol 160:313–323
Oren A (2008) Microbial life at high salt concentrations: phylogenetic and metabolic diversity. Saline Syst 4:2
Pastor JM, Salvador M, Argandoña M, Bernal V, Reina-Bueno M, Csonka LN, Iborra JL, Vargas C, Nieto JJ, Cánovas M (2010) Ectoines in cell stress protection: uses and biotechnological production. Biotechnol Adv 28:782–801
Peters P, Galinski EA, Trüper HG (1990) The biosynthesis of ectoine. FEMS Microbiol Lett 71:157–162
Pospíšil S, Halada P, Petříček M, Sedmera P (2007) Glucosylglycerate is an osmotic solute and an extracellular metabolite produced by Streptomyces caelestis. Folia Microbiol 52:451–456
Prestrelski SJ, Tedeschi N, Arakawa T, Carpenter JF (1993) Dehydration-induced conformational transitions in proteins and their inhibition by stabilizers. Biophys J 65:661–671
Ramos A, Raven N, Sharp RJ, Bartolucci S, Rossi M, Cannio R, Lebbink J, Van Der Oost J, De Vos WM, Santos H (1997) Stabilization of enzymes against thermal stress and freeze-drying by mannosylglycerate. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4020–4025
Riley PA (1994) Free radicals in biology: oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 65:27–33
Robertson DE, Lai M, Gunsalus RP, Roberts MF (1992) Composition, variation, and dynamics of major osmotic solutes in Methanohalophilus strain FDF1. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2438–2443
Santacruz-Calvo L, González-López J, Manzanera M (2013) Arthrobacter siccitolerans sp. nov., a highly desiccation-tolerant, xeroprotectant-producing strain isolated from dry soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4174–4180
Santos H, da Costa MS (2002) Compatible solutes of organisms that live in hot saline environments. Environ Microbiol 4:501–509
Sawangwan T, Goedl C, Nidetzky B (2010) Glucosylglycerol and glucosylglycerate as enzyme stabilizers. Biotechnol J 5:187–191
Scholz S, Sonnenbichler J, Schäfer W, Hensel R (1992) Di-myo-insitol-1,1′-phosphate: a new inositol phosphate isolated from Pyrococcus woesei. FEBS Lett 306:239–242
Schwarz T (2009) Use of compatible solutes as substances having free radical scavenging properties. US Patent application. Pub. no.: US 2009/0227523 A1
Sterner R, Liebl W (2001) Thermophilic adaptation of proteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 36:39–106
Stetter KO (1988) Archaeoglobus fulgidus gen. nov., sp. nov.: a new taxon of extremely thermophilic archaebacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 10:172–173
Stöhr R, Waberski A, Völker H, Tindall B, Thomm M (2001) Hydrogenothermus marinus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel thermophilic hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium, recognition of Calderobacterium hydrogenophilum as a member of the genus Hydrogenobacter and proposal of the reclassification of Hydrogenobacter acidophilus as Hydrogenobaculum acidophilum gen. nov., comb. nov., in the phylum ‘Hydrogenobacter/Aquifex’. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1853–1862
Tanne C, Golovina EA, Hoekstra FA, Meffert A, Galinski EA (2014) Glass-forming property of hydroxyectoine is the cause of its superior function as a desiccation protectant. Front Microbiol 5:150
Vriezen JAC, de Bruijn FJ, Nüsslein K (2007) Responses of Rhizobia to desiccation in relation to osmotic stress, oxygen, and temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3451–3459
Webb KM, DiRuggiero J (2012) Role of Mn2+ and compatible solutes in the radiation resistance of thermophilic Bacteria and Archaea. Archaea 2012:845756
Welsh DT, Herbert RA (1999) Osmotically induced intracellular trehalose, but not glycine betaine accumulation promotes desiccation tolerance in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 174:57–63
Zillig W, Stetter KO, Schäfer W, Janekovic D, Wunderl S, Holz J, Palm P (1981) Thermoproteales: a novel type of extremely thermoacidophilic anaerobic archaebacteria isolated from icelandic solfataras. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg I Abt C 2:205–227
ZoBell CE (1941) Studies on marine bacteria. The cultural requirements of heterotrophic aerobes. J Mar Res 4:42–75
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Birgit Amendt (Institute of Microbiology and Biotechnology, University Bonn) for carrying out the HPLC analysis, Dr. Stefan Kehraus (Institute of Pharmaceutical Biology, University Bonn) for performing the NMR experiments, Denise Bachmann for doing the desiccation experiments with added compatible solutes, and Dipl. Ing. Thomas Hader (Institute for Microbiology and Archaea Center, University Regensburg) for technical assistance during cultivation of the cells in fermenters.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Michael Rother.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beblo-Vranesevic, K., Galinski, E.A., Rachel, R. et al. Influence of osmotic stress on desiccation and irradiation tolerance of (hyper)-thermophilic microorganisms. Arch Microbiol 199, 17–28 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1269-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1269-6