Abstract
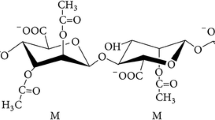
Streptomyces caelestis DSM 40084produces two osmolytes,viz. 2-O-(α-d-glucopyranosyl)-ζ-glyceric acid (GG) and trehalose. Both compounds were isolated and identified by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. A very sensitive regulation of the cell osmolytes was demonstrated in exponentially growing cultures. The intracellular levels of GG and trehalose increased 2× in response to a step change of medium osmolarity caused by 0.3 % NaCl.1H NMR analysis of the cell extracts did not confirm the presence of additional osmolytes. GG is aS. caelestis metabolite commonly released from the cells; its concentration reached 3 g/L during the cultivation in a yeast extract-(NH4)2SO4-glycerol medium. This is the first report on the occurrence of the ionic osmolyte GG in the genusStreptomyces and on its free excretion to the medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1D-TOCSY:
-
one-dimensional total-correlated spectroscopy
- CD:
-
chemically defined (medium)
- ESI MS:
-
electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- GG:
-
2-O-(α-d-glucopyranosyl)-ξ-glyceric acid
- HMBC:
-
heteronuclear multiple bond correlation
- MS:
-
mass spectrometry
- NMR:
-
NMR spectroscopy
- YEA:
-
complex (medium)
References
Alarico S., Empadinhas N., Simöes C., Silva Z., Henne A., Mingote A., Santos H., da Costa M.S.: Distribution of genes for the synthesis of trehalose and mannosylglycerate inThermus spp. and direct correlation with halotolerance.Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 71, 2460–2466 (2005).
Argoudelis A.D., Brodasky T.F.: Studies withStreptomyces caelestis. I. New celesticetins.J.Antibiot. 25, 194–196 (1972).
Cánovas D., Borges N., Vargas C., Ventosa A., Nieto J.J., Santos H.: Role ofN-γ-acetyldiaminobutyrate as an enzyme stabilizer and an intermediate in the biosynthesis of hydroxyectoine.Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 65, 3774–3779 (1999).
Costa J., Empadinhas N., Goncalves L., Lamosa P., Santos H., da Costa M.S.: Characterization of the biosynthetic pathway of glucosylglycerate in the archaeonMethanococcoides burtonii.J.Bacteriol. 188, 1022–1030 (2006).
da Costa M.S., Santos H., Galinski E.A.: An overview of the role and diversity of compatible solutes inBacteria andArchaea.Adv.Biochem.Eng.Biotechnol. 61, 117–153 (1998).
Duus J.Ø., Gotfredsen C.H., Bock K.: Carbohydrate structural determination by NMR spectroscopy. Modern methods and limitations.Chem.Rev. 100, 4589–4614 (2000).
Elbein A.D., Pan Y.T., Pastuszak I., Carroll D.: New insights on trehalose: a multifunctional molecule.Glycobiology 13, 17R-27R (2003).
Goude R., Renaud S., Bonnassie S., Bernard T., Blanco C.: Glutamine, glutamate, and α-glucosylglycerate are the major osmotic solutes accumulated byErwinia chrysanthemi strain 3937.Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 70, 6535–6541 (2004).
Killham K., Firestone M.K.: Salt stress control of intracellular solutes in streptomycetes indigenous to saline soils.Appl.Environ.Microbiol 47, 301–306 (1984).
Kollman V.H., Hanners J.L., London R.E., Adame E.G., Walker T.E.: Photosynthetic preparation and characterization of13C-labeled carbohydrates inAgmenellum quadruplicatum.Carbohydr.Res. 73, 193–202 (1979).
Křen V., Sedmera P., Havlíęk V., Fišerová A.: Enzymatic galactosylation of ergot alkaloids.Tetrahedron Lett. 33, 7233–7236 (1992).
Malin G., Lapidot A.: Induction of synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidine derivatives inStreptomyces strains and their effect onEscherichia coli in response to osmotic and heat stress.J.Bacteriol. 178, 385–395 (1996).
Poolman B., Blount P., Folgering J.H.A., Friesen R.H.E., Moe P.C., van der Heide T.: How do membrane proteins sense water stress?Mol.Microbiol. 44, 889–902 (2002).
Pospíšil S., Sedmera P., Halada P., Spížek J.: Oxidation of lincomycin by hydrogen peroxide restricts its potential biotransformation with haloperoxidases.Folia Microbiol. 46, 376–378 (2001).
Pospíšil S., Sedmera P., Halada P., Petříček M.: Extracellular carbohydrate metabolites fromStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2).J.Nat.Prod. 70, 768–771 (2007).
Robertson D.E., Lai M., Gunsalus R.P., Roberts M.F.: Composition, variation, and dynamics of major osmotic solutes inMethanohalophilus strain FDF1.Appl.Environ.Microbiol. 58, 2438–2443 (1992).
Roder A., Hoffmann E., Hagemann M., Berg G.: Synthesis of the compatible solutes glucosylglycerol and trehalose by salt-stressed cells ofStenotrophomonas strains.FEMS Microbiol.Lett. 243, 219–226 (2005).
Uhrín D., Barlow P.N.: Gradient-enhanced one-dimensional proton chemical-shift correlation with full sensitivity.J.Magnet.Reson. 126, 248–255 (1997).
Zhang J., Reddy J., Buckland B., Greasham R.: Toward consistent and productive complex media for industrial fermentations: studies on yeast extract for a recombinant yeast fermentation process.Biotechnol.Bioeng. 82, 640–652 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by theInstitutional Research Concept AV 0Z 5020 0510 and, in part, by theGrant Agency of the Czech Academy of Sciences (research grant IAA 600 660 607).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pospíšil, S., Halada, P., Petříček, M. et al. Glucosylglycerate is an osmotic solute and an extracellular metabolite produced byStreptomyces caelestis . Folia Microbiol 52, 451–456 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932103
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932103