Abstract
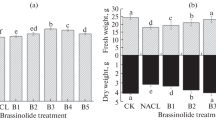
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of one of brassinosteroids (24-epibrassinolide) and clotrimazole, (an inhibitor of brassinosteroid synthesis) on plant growth parameters, parameters related to leaf gas exchange (photosynthetic and transpiration rates; stomatal conductance; water use efficiency), photosynthetic pigment content and osmolyte (sugars and proline) content in Cajanus cajan exposed to salinity. Salt stress—caused by NaCl treatment—affected values of all parameters analyzed. The effects were ameliorated by 24-epibrassinolide and intensified by clotrimazole. The hormone increased fresh mass of the plant, shoot dry mass, leaf area, water content of leaves and roots, photosynthetic pigments, sugar concentration, photosynthetic rate, and water use efficiency. The effects of hormone were less evident in the absence of salt. However, under this condition the application of clotrimazole affected the values of parameters studied, indicating the importance of brassinosteroid synthesis for the normal development of the plant.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akintayo ET, Oshodi AA, Esuoso KO (1999) Effects of NaCl, ionic strength and pH on the foaming and gelation of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) protein concentrates. Food Chem 66:51–56
Ali B, Hayat S, Fariduddin Q, Ahmad A (2008a) 24-Epibrassinolide protects against the stress generated by salinity and nickel in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 72:1387–1392
Ali Q, Athar HUR, Ashraf M (2008b) Modulation of growth, photosynthetic capacity and water relations in salt stressed wheat plants by exogenously applied 24-epibrassinolide. Plant Growth Regul 56:107–116
Amzallag GN, Vaismam J (2006) Influence of brassinosteroids on initiation of the root gravitropic response in Pisum sativum seedlings. Biol Plant 50:283–286
Ashraf M, Harris PJC (2004) Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Sci 166:3–16
Babita M, Maheswari M, Rao LM, Shanker AK, Rao DG (2010) Osmotic adjustment drought tolerance and yield in castor (Ricinus communis L.) hybrids. Environ Exp Bot 69:243–249
Bates LS, Waldren RP (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bieleski LR, Turner NA (1966) Separation and estimation of amino acids in crude plant extracts by thin-layer electrophoresis and chromatography. Anal Biochm 17:278–293
Carillo P, Mastrolonardo G, Nacca F, Fuggi A (2005) Nitrate reductase in durum wheat seedlings as affected by nitrate nutrition and salinity. Funct Plant Biol 32:209–219
Chen Z, Cuin TA, Zhou M, Twomey A, Naidu BP, Shiabala S (2007) Compatible solute accumulation and stress-mitigating effects in barley genotypes contrasting in their salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 58:4245–4255
Corzo O, Fuentes A (2004) Moisture sorption isotherms and modeling for pre-cooked flours of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajans L. millsp.) and lima bean (Canavalia ensiformis). J Food Engin 65:443–448
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
FAO (2000) Global network on integrated soil management for sustainable use of salt affected soils. http://www.fao.org/ag/AGL/agll/spush/intro.htm (accessed 22 December 2008)
Flowers TJ, Hajibagheri MA (2001) Salinity tolerance in Hordeum vulgare: ion concentrations in root cells of cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Plant Soil 231:1–9
Fujioka S, Sakurai A (1997) Brassinosteroids. Nat Prod Rep 14:1–10
Handel EV (1968) Direct microdetermination of sucrose. Anal Biochem 22:280–283
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Haubrick LL, Torsethaugen G, Assmann SM (2006) Effect of 24-epibrassinolide, alone and in concert with abscisic acid, on control of stomatal aperture and potassium currents of Vicia faba guard cell protoplasts. Physiol Plant 128:134–143
Hiscox JD, Israelstam GFA (1979) A method for the extraction of chlorophyll from leaf tissue without maceration. Can J Bot 57:1332–1334
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1938) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Sta Circ 347
Janeczko A, Gullner G, Skoczowski A, Dubert F, Barna BE (2007) Effects of brassinosteroid infiltration prior to cold treatment on ion leakage and pigment contents in rape leaves. Biol Plant 51:355–358
Kagale S, Divi UK, Krochko JE, Keller WA, Krishna P (2007) Brassinosteroid confers tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassinca napus to a range of abiotic stresses. Planta 225:353–364
Khripach VA, Zhabinskii VN, Groot AE (1999) Brassinosteroids—a new class of plant hormones. Academic Press, San Diego
Kim TW, Chang SC, Lee JS, Takatsuto S, Yokota T, Kim SK (2004) Novel biosynthetic pathway of castasterone from cholesterol in tomato. Plant Physiol 135:1231–1242
Kim YS, Joo SH, Hwang JY, Park CH, Kim SK (2006) Characterization of C29-brassinosteroids and their biosynthetic precursors in immature seeds of Phaseolus vulgaris. Bull Korean Chem Soc 27:1117–1118
Lichtenthaler BK, Welburn AR (1983) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Transact 11:591–592
Liska AJ, Shevchenko A, Pick U, Katz A (2004) Enhanced photosynthesis and redox energy production contribute to salinity tolerance in Dunaliella as revealed by homology-based proteomics. Plant Physiol 136:2806–2817
Lisso J, Altmann T, Mussig C (2006) Metabolic changes in fruits of the tomato d(x) mutant. Phytochemistry 67:2232–2238
Morillon R, Catterou M, Sangwan RS, Sangwan BS, Lassalles JP (2001) 24-epibrassinolide may control aquaporin activities in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 212:199–204
Nakajima N, Toyama S (1999). Effects of epibrassinolide on sugar transport and allocation to the epicotyl in cucumber seedlings. Plant Prod Sci 2:165–171
Ogweno JO, Song XS, Shi K, Hu WH, Mao WH, Zhou YH, Yu JQ, Nogués S (2008) Brassinosteroids alleviate heat-induced inhibition of photosynthesis by increasing carboxylation efficiency and enhancing antioxidant systems in Lycopersicum esculentum. J Plant Growth Regul 27:49–57
Ozdemir F, Bor M, Demiral T, Türkan I (2004) Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on seed germination, seedling growth, lipid peroxidation proline content and antioxidative system of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under salinity stress. Plant Growth Regul 42:203–211
Paul MJ, Foyer CH (2001) Sink regulation of photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 52:1383–1400
Reggiani R, Nebuloni M, Mattana M, Brambilla I (2000) Anaerobic accumulation of amino acids in rice roots: role of the glutamine synthetase/glutamate synthase cycle. Amino Acids 18:207–217
Sasse JM (2003) Physiological actions of brassinosteroids: an update. J Plant Growth Regul 22:276–288
Shahbaz M, Ashraf M, Athar HUR (2008) Does exogenous application of 24-epibrassinolide ameliorate salt induced growth inhibition in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)? Plant Growth Regul 55:51–64
Sharifi M, Ghorbanli M, Ebrahimzadeh H (2007) Improved growth of salinity-stressed soybean after inoculation with salt pre-treated mycorrhizal fungi. J Plant Physiol 164:1144–1151
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na + transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Xia XJ, Wang YJ, Zhou YH, Tao Y, Mao WH, Shi K, Asami T, Chen ZX, Yu JQ (2009) Reactive oxygen species are involved in brassinosteroid-induced stress tolerance in cucumber. Plant Physiol 150:801–814
Yazici I, Tuerkan I, Sekman AH, Demiral T (2007) Salinity tolerance of purslane (Portulaca oleraceae L.) is achieved by enhanced antioxidative system, lower level of lipid peroxidation and proline accumulation. Environ Exp Bot 61:49–57
Yu JQ, Huang LF, Hu WH, Zhou YH, Mão WH, Ye SF, Nogués S (2004) A role for brassinosteroid in the regulation of photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus. J Exp Bot 55:1135–1143
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo for financial support of the project (08/50165-8). Ronaldo J. D. Dalio acknowledges the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico for the grant received and we thank Dr. Elaine B. Wutke for seeds of C. cajan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. Filek.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalio, R.J.D., Pinheiro, H.P., Sodek, L. et al. The effect of 24-epibrassinolide and clotrimazole on the adaptation of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. to salinity. Acta Physiol Plant 33, 1887–1896 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0732-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0732-x