Abstract
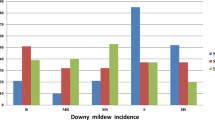
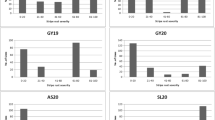
Sorghum downy mildew (SDM), caused by obligate biotrophic fungi Peronosclerospora sorghi, is an economically important disease of maize. The genetics of resistance was reported to be polygenic thereby necessitating identification of QTLs for resistance to SDM to initiate effective marker-assisted selection programs. During post-rainy and winter season of 2012, 645 F2:3 progeny families from the cross CML153 (susceptible) × CML226 (resistant) were screened for their reaction to SDM. Characterization of QTLs affecting resistance to SDM was undertaken using the genetic linkage map with 319 polymorphic SSR and SNP marker loci and the phenotypic data of F2:3 families. Three QTLs conferring resistance to SDM were consistently identified on chromosomes 2, 3 and 6 in both seasons. The resistant parent CML226 contributed all the QTL alleles conferring resistance to SDM. The major QTL located on chromosome 2 explained 38.68% of total phenotypic variation in the combined analysis with a LOD score of 9.12. All the three QTL showed partially dominant gene effects in combined analysis. The detection of more than one QTL supports the hypothesis that quantitative genes control resistance to P. sorghi. The generation was advanced to F6 using markers linked to major QTLs on chromosomes 2 and 3 to derive 33 SDM resistant maize inbred lines.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrama HA, Moussa ME (1996) Mapping QTLs in breeding for drought tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.). Euphytica 91:89–97
Agrama HA, Moussa ME, Naser ME, Tarek MA, Ibrahim AH (1999) Mapping of QTL for downy mildew resistance in maize. Theor Appl Genet 99:519–523
Beavis WD, Keim P (1996) Identification of quantitative trait loci that are affected by environment. In: Kang MS, Gauch Jr HG (eds) Genotype by environment interaction. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 123–149
Beavis WD, Grant D, Albertsen MC, Fincher RR (1991) Quantitative trait loci for plant height in four maize populations and their associations with qualitative genetic loci. Theor Appl Genet 83(2):141–145
Bohn M, Khairallah MM, Gonzalez-de-Leon D, Hoisington D, Utz HF, Deutsch JA, Jewell DC, Mihm JA, Melchinger AE (1996) QTL mapping in tropical maize: I. Genomic regions affecting leaf feeding resistance to sugarcane borer and other traits. Crop Sci 36:1352–1361
Bohn M, Khairallah MM, Jiang CZ, Gonzalez de Leon D, Hoisington D, Utz HF, Deutsch JA, Jewell DC, Mihm JA, Melchinger AE (1997) QTL mapping in tropical maize. 2. Comparison of genomic regions for resistance to Diatraea spp. Crop Sci 37(6):1892–1902
Bohn M, Schulz B, Kreps R, Klein D, Melchinger AE (2000) QTL mapping for resistance against the European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis H.) in early maturing European dent germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 101(5-6):907–917
Borges F, Orange L (1987) Diallel analysis of maize resistance to sorghum downy mildew. Crop Sci 27:178–180
Cooper CS, MacDonald PW (1970) Energetics of early seedling growth in corn (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci 10:136–138
Craig J, Bockholdt AJ, Frederiksen RA, Zuber MS (1977) Reaction of important corn inbred lines to Sclerospora sorghi. Plant Dis Rep 61:563–564
Davis GL, McMullen MD, Baysdorfer C, Musket T, Grant D, Staebell M, Xu G, Polacco M, Koster L, Melia-Hancock S, Houchins K, Chao S, Coe EH Jr (1999) A maize map standard with sequenced core markers, grass genome reference points and 932 expressed sequence tagged sites (ESTs) in a 1736-locus map. Genetics 152(3):1137–1172
De Leon C, Anuja VP, Capio ER, Mukhergee BK (1993) Genetics of resistance to Philippine downy mildew in three maize populations. Indian J Genet 53:406–410
Deleens E, Gregory N, Bourdu R (1984) Transition between seed reserve use and photosynthetic supply during development of maize seedlings. Plant Sci Lett 37:35–39
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation Tests for Multiple Loci Affecting a Quantitative Epidemic in Pennsylvania and Maryland. Genetics 78(1):579–585
Edwards MD, Stuber CW, Wendel JF (1987) Molecular marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize. I. Numbers, genomic distribution and types of gene action. Genetics 116:113–125
Geetha K, Jayaraman N (2002) Inheritance of sorghum downy resistance in maize. Indian J Agric Res 36(4):234–240
George MLC, Prasanna BM, Rathore RS, Setty TAS, Kasim F, Azrai M, Vasal S, Balla O, Hautea D, Canama A, Regalado E, Vargas M, Khairallah M, Jeffers D (2003) Identification of QTLs conferring resistance to downy mildews of maize in Asia. Theor Appl Genet 107:544–551
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Haldane JBS (1919) The combination of linkage values and the calculation of distance between the loci of linked factors. J Genet 8:299–309
Hallauer AR, Miranda JB (1981) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. Iowa State University Press, Ames
Hoisington D, Khairallah M, Gonzalez-de-Leon D (1994) Laboratory Protocols, 2nd edn. CIMMYT applied molecular genetics laboratory. Mexico, D.F., CIMMYT
Isakeit T, Odvody G, Jahn R, Decanini L (2003) Peronosclerospora sorghi resistant to metalaxyl treatment of sorghum seed in Texas. Phytopathol 93:S39
Jampatong C, Jampatong S, Jompuk C, Tanee S, Pichet G, Chatpong B, Nathinee P (2013) Mapping of QTL affecting resistance against sorghum downy mildew (Peronosclerospora sorghi) in maize (Zea mays L.). Maydica 58:119–126
Jeffers D, Cordova H, Vasal S, Srinivasan G, Beck D, Barandiaran M (2000) Status in breeding for resistance to maize diseases at CIMMYT. In: Vasal SK, Gonzalez Ceniceros F, Fan XM (eds) Proceedings of 7th Asian Regional Maize Workshop. PCARRD, Los Banos, pp. 257–266
Jones E, Chu WC, Ayele M, Ho J, Bruggeman E, Yourstone K, Rafalski A, Smith OS, McMullen MD, Bezawada C, Warren J, Babayev J, Basu S, Smith S (2009) Development of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers for use in commercial maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Breed. 24:165–176
Kaneko K, Aday BA (1980) Inheritance of Philippine downy mildew of maize. Crop Sci 20:590–594
Kearsey MJ, Pooni HS (1996) The genetical analysis of quantitative traits. Chapman and Hall, London
Krishnappa M, Naidu BS, Seetharam A (1995) Inheritance of host resistance to downy mildew in maize. Crop Improv 22:33–37
Lebreton C, Lazic-Jancic V, Steed A, Pekic S, Quarrie SA (1995) Identification of QTL for drought responses in maize and their use in testing causal relationships between traits. J Expt. Bot 46:853–865
Lin YR, Schertz KF, Paterson AH (1995) Comparative analysis of QTLs affecting plant height and maturity across the Poaceae, in reference to an interspecific sorghum population. Genetics 141:391–411
Little TM, Hills FJ (1978) Agricultural experimentation design and analysis. Wiley, New York
McMullen MD, Simcox KD (1995) Genomic organization of disease and insect resistance genes in maize. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:811–815
Nair SK, Prasanna BM, Rathore RS, Setty TAS, Kumar R, Singh NN (2004) Genetic analysis of resistance to sorghum downy mildew and Rajasthan downy mildew in maize. Field Crops Res 89:379–387
Nair SK, Prasanna BM, Garg A, Rathore RS, Setty TAS, Singh NN (2005) Identification and validation of QTLs conferring resistance to sorghum downy mildew and Rajasthan downy mildew in maize. Theor Appl Genet 110:1384–1392
Nallathambi P, Sundaram KM, Arumugachamy S (2010) Inheritance of resistance to sorghum dowmy mildew (Peronosclerospora sorghi) in maize (Zea mays L.). International J Agric Environ Biotech 3(3):285–293
Narong SB, Renfro BL (1982) Heritability of resistance in maize to sorgum downy mildew. Crop protection 1(3):323–332
Orange L, Borges F (1987) Diallel Analysis of maize resistance to sorghum downy mildew. Crop Sci 27:178–180
Phumichai C, Chalermpol C, Julapark J, Sansern G, Pichet P, Taweesak D, Weerasak W, Arunee K, Nongluck (2012) Detection and integration of gene mapping of downy mildew resistance in maize inbred lines though linkage and association. Euphytica 187(3):369–379
Pingali PL (2001) World maize facts and trends. Meeting world maize needs: technological opportunities and priorities for the public sector. CIMMYT 1999-2000, Mexico, DF
Premalatha N, Mohana SK, Arumugachamy S (2010) Inheritance of Resistance to Sorghum Downy mildew (Pernosclerospera sorghi) in Maize (Zea mays L.). Int J Agric Environ Biotech 3(3):285–293
Rao BM, Prakash HS, Shetty HS (1984) Relationship of cultivars with sporulation and morphology of asexual propagation of Perenosclerospora sorghi on maize. Int J Trop Plant Dis 2(2):175–180
Raymundo AD (2000) Downy mildew of maize in Asia: new perspectives in resistance breeding. In: Vasal SK, Gonzalez CF, Xingming F (eds) Proc. 7th Asian Regional Maize Workshop. PCARRD, Los Banos, Philippines, pp. 277–284
Sabry A, Jeffers D, Vasal SK, Frederiksen R, Magill C (2006) A region of maize chromosome 2 affects response to downy mildew pathogens. Theor Appl Genet 113:321–330
Searle SR (1971) Linear models. Wiley, New York
Singhburaudom N, Renfro BL (1982) Heritability of resistance in maize to sorghum downy mildew (Peronosclerospora sorghi (Weston and Uppal) CG Shaw). Crop Protect 1:323–332
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1967) Statistical methods, 6th edn. Oxford ans IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, p 593
Stuber CW, Edwards MD, Wendel JF (1987) Molecular marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize. II. Factors influencing yield and its component traits. Crop Sci 27:639–648
Tuberosa R, Sanguineti MC, Landi P, Giuliani MM, Salvi S, Conti S (2002a) Identification of QTLs for root characteristics in maize grown in hydroponics and analysis of their overlap with QTLs for grain yield in the field at two water regimes. Plant Mol Biol 48:697–712
Tuberosa R, Salvi S, Sanguineti MC, Landi P, Giuliani MM, Conti S (2002b) Mapping QTLs Regulating Morpho-physiological Traits and Yield: Case Studies, Shortcomings and Perspectives in Drought-stressed Maize. Ann Bot 89(7):941–963
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2010) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, NC State University, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.html
Weston WH, Uppal BN (1932) The basis of Sclerospora sorghi as a species. Phytopathol 22:273–583
Yen TTO, Rathore RS, Setty TAS, Kumar R, Singh NN, Vasal SK, Prasanna BM (2004) Inheritance of resistance to sorghum downy mildew (Peronosclerospora sorghi) and Rajasthan downy mildew (P. heteropogoni) in maize in India. Maize Genetics Cooperation Newsl 75:48–49
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Zhang Y, Xu L, Fan X, Tan J, Chen W, Xu M (2012) QTL mapping of resistance to gray leaf spot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 125:1797–1808
Zwonitzer JC, Coles ND, Krakowsky MD, Arellano C, Holland JB, McMullen MD, Pratt RC, Balint-Kurti PJ (2010) Mapping resistance quantitative trait loci for three foliar diseases in a maize recombinant inbred line population – evidence for multiple disease resistance? Phytopathol 100:72–79
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India and Pioneer Hi-Bred Pvt. Ltd. for their financial help. The first author is highly indebted to Pioneer Hi-Bred Pvt. Ltd. for providing him with Pioneer Hi-Bred Research International Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical standards
The experiments were performed following standard protocols.
Additional information
Key message
A high-density genetic linkage map of maize was constructed and identified QTLs for resistance to sorghum downy mildew. Marker-assisted selection was practised using markers linked to major QTLs on chromosomes 2 and 3, to derive 33 resistant inbreds.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagabhushan, Lohithaswa, H.C. & Pandravada, A.S. Construction of high-density linkage map and identification of QTLs for resistance to sorghum downy mildew in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Breeding 37, 2 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0601-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0601-9