Abstract
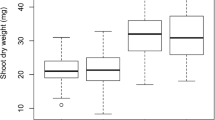
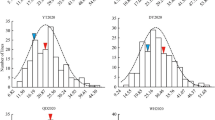
Boron (B) and phosphorus (P) are two essential nutrients for plants. To unravel the genetic basis of B and P efficiency in Brassica napus, quantitative trait locus (QTL) and epistatic interaction analysis for yield and yield-related traits under contrast B and P conditions were performed using two mapping populations across various environments. Main effect QTLs were detected by QTLNetwork and QTL Icimapping (ICIM), and were compared with our previously reported main effect QTLs identified by QTLCartographer. Epistatic QTLs were identified by QTLNetwork, ICIM and Genotype matrix mapping (GMM), and multiple comparisons of main effect QTLs and epistatic QTLs were conducted. For the two mapping populations, 51 main effect QTLs were identified by QTLNetwork, 106 by ICIM. Among them, 35 main effect QTLs were simultaneously identified by three programs. Moreover, 578, 18 and 62 epistatic QTLs were identified by GMM, QTLNetwork and ICIM, respectively. Interestingly, a total of 235 epistatic QTLs identified by GMM were associated with 50 main effect QTLs identified by three programs. However, only nine epistatic QTLs identified by QTLNetwork and ICIM were involved in main effect QTLs. Twenty-two main effect QTLs in the BERIL population overlapped with 20 main effect QTLs for the same traits in the BQDH population, but no main effect QTLs were detected both under P and B stress environments, indicating the genetic differences in B and P homeostasis in B. napus. By in silico mapping, 29 candidate genes were located in the consensus QTL intervals. This study suggested the availability of dissecting genetic basis for complex traits under B/P deficiency by analyzing main effect QTLs and epistatic QTLs using multiple programs across different environments. The robust main effect QTLs and epistatic QTLs associated could be useful in breeding B and P efficient cultivars of B. napus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basunanda P, Radoev M, Ecke W, Friedt W, Becker HC, Snowdon RJ (2010) Comparative mapping of quantitative trait loci involved in heterosis for seedling and yield traits in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 120:271–281
Carlborg O, Haley CS (2004) Epistasis: too often neglected in complex trait studies? Nat Rev Genet 5:618–625
Cooper M, van Eeuwijk FA, Hammer GL, Podlich DW, Messina C (2009) Modeling QTL for complex traits: detection and context for plant breeding. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:231–240
Coque M, Gallais A (2006) Genomic regions involved in response to grain yield selection at high and low nitrogen fertilization in maize. Theor Appl Genet 112:1205–1220
Cordell HJ (2009) Detecting gene–gene interactions that underlie human diseases. Nat Rev Genet 10:392–404
Ding GD, Zhao ZK, Liao Y, Hu YF, Shi L, Long Y, Xu FS (2012) Quantitative trait loci for seed yield and yield-related traits, and their responses to reduced phosphorus supply in Brassica napus. Ann Bot 109:747–759
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1996) Less-than-additive epistatic interactions of quantitative trait loci in tomato. Genetics 143:1807–1817
Fageria NK, Baligar VC, Li YC (2008) The role of nutrient efficient plants in improving crop yields in the twenty first century. J Plant Nutr 31:1121–1157
Fan C, Cai G, Qin J, Li Q, Yang M, Wu J, Fu T, Liu K, Zhou Y (2010) Mapping of quantitative trait loci and development of allele-specific markers for seed weight in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 121:1289–1301
Gamuyao R, Chin JH, Pariasca-Tanaka J, Pesaresi P, Catausan S, Dalid C, Slamet-Loedin I, Tecson-Mendoza EM, Wissuwa M, Heuer S (2012) The protein kinase Pstol1 from traditional rice confers tolerance of phosphorus deficiency. Nature 488:535–539
Gautami B, Pandey MK, Vadez V, Niqam SN, Ratnakumar P, Krishnamurthy L, Radhakrishnan T, Gowda MV, Narasu ML, Hoisinqton DA, Knapp SJ, Varshney RK (2012) Quantitative trait locus analysis and construction of consensus genetic map for drought tolerance traits based on three recombinant inbred line populations in cultivated groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Mol Breeding 30:757–772
Günes A, Alpaslan M (2000) Boron uptake and toxicity in maize genotypes in relation to boron and phosphorus supply. J Plant Nutri 23:541–550
Huang X, Effgen S, Meyer RC, Theres K, Koornneef M (2012) Epistatic natural allelic variation reveals a function of AGAMOUS-LIKE6 in axillary bud formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:2364–2379
Isobe S, Nakaya A, Tabata S (2007) Genotype Matrix Mapping: searching for quantitative trait loci interactions in genetic variation in complex traits. DNA Res 14:217–225
Jannink J (2007) Identifying quantitative trait locus by genetic background interactions in association studies. Genetics 176:553–561
Kaya C, Tuna AL, Dikilitas M, Ashraf M, Koskeroglu S, Guneri M (2009) Supplementary phosphorus can alleviate boron toxicity in tomato. Sci Hortic 121:284–288
Kobayashi T, Nishizawa NK (2012) Iron uptake, translocation, and regulation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:131–152
Kochian LV, Hoekenga OA, Pineros MA (2004) How do crop plants tolerate acid soils? Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance and phosphorous efficiency. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:459–493
Li HH, Ye GY, Wang JK (2007) A modified algorithm for the improvement of composite interval mapping. Genetics 175:361–374
Li HH, Ribaut JM, Li ZL, Wang JK (2008) Inclusive composite interval mapping (ICIM) for digenic epistasis of quantitative traits in biparental populations. Theor Appl Genet 116:243–260
Loudet O, Chaillou S, Merigout P, Talbotec J, Daniel-Vedele F (2003) Quantitative trait loci analysis of nitrogen use efficiency in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 131:345–358
Ma XQ, Tang JH, Teng WT, Teng WT, Yan JB, Meng YJ, Li JS (2007) Epistatic interaction is an important genetic basis of grain yield and its components in maize. Mol Breed 20:41–51
Mackay I, Powell W (2007) Methods for linkage disequilibrium mapping in crops. Trends Plant Sci 12:57–63
Malmberg RL, Held S, Waits A, Mauricio R (2005) Epistasis for fitness-related quantitative traits in Arabidopsis thaliana grown in the field and in the greenhouse. Genetics 171:2013–2027
Marschner P (1995) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, vol 2. Academic Press, London
Meyer M (2009) Rapeseed oil fuel-the crisis-proof home-made eco-fuel. Agrarforschung 16:262–267
Quarrie S, Pekic Quarrie S, Radosevic R, Rancic D, Kaminska A, Barnes JD, Leverington M, Ceoloni C, Dodig D (2006) Dissecting a wheat QTL for yield present in a range of environments: from the QTL to candidate genes. J Exp Bot 57:2627–2637
Radoev M, Becker HC, Ecke W (2008) Genetic analysis of heterosis for yield and yield components in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by quantitative trait locus mapping. Genetics 179:1547–1558
Ravi K, Vadez V, Isobe S, Mir RR, Guo Y, Nigam SN, Gowda MVC, Radhakrishnan T, Bertioli DJ, Knapp SJ, Varshney RK (2011) Identification of several small main-effect QTLs and a large number of epistatic QTLs for drought tolerance related traits in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 122:1119–1132
Schachtman DP, Reid RJ, Ayling S (1998) Phosphorus uptake by plants: from soil to cell. Plant Physiol 116:447–453
Shi JQ, Li RY, Qiu D, Jiang CC, Long Y, Morgan C, Bancroft I, Zhao JY, Meng JL (2009) Unraveling the complex trait of crop yield with quantitative trait loci mapping in Brassica napus. Genetics 182:851–861
Shi JQ, Li RY, Zou J, Long Y, Meng JL (2011) A dynamic and complex network regulates the heterosis of yield-correlated traits in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). PLoS ONE 6:e21645
Shi TX, Li RY, Zhao ZK, Ding GD, Long Y, Meng JL, Xu FS, Shi L (2013) QTL for yield traits and their association with functional genes in response to phosphorus deficiency in Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 8:e54559
Shorrocks VM (1997) The occurrence and correction of boron deficiency. Plant Soil 193:121–148
Sosnowski O, Charcosset A, Joets J (2012) BioMercator V3: an upgrade of genetic map compilation and QTL meta-analysis algorithms. Bioinformatics 28:2082–2083
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447
Wang SC, Bastern J, Zeng ZB (2011) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Wang ZF, Chen ZW, Cheng JP, Lai YY, Wang JF, Bao YM, Huang J, Zhang HS (2012) QTL analysis of Na+ and K+ concentrations in roots and shoots under different levels of NaCl stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS ONE 7:e51202
Xing GN, Zhou B, Wang YF, Zhao TJ, Yu DY, Chen SY, Gai JY (2012) Genetic components and major QTL confer resistance to bean pyralid (Lamprosema indicata Fabricius) under multiple environments in four RIL populations of soybean. Theor Appl Genet 125:859–875
Xu FS, Wang YH, Meng JL (2001) Mapping boron efficiency gene(s) in Brassica napus using RFLP and AFLP markers. Plant Breed 120:319–324
Yan XL, Wu P, Ling HQ, Xu GH, Xu FS, Zhang QF (2006) Plant nutriomics in China: an overview. Ann Bot 98:473–482
Yang J, Zhu J, Williams RW (2007) Mapping the genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 23:1527–1536
Yang M, Ding GD, Shi L, Feng J, Xu FS, Meng JL (2010) Quantitative trait loci for root morphology in response to low phosphorus stress in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 121:181–193
Zhao ZK, Wu LK, Nian FZ, Ding GD, Shi TS, Zhang DD, Shi L, Xu FS, Meng JL (2012) Dissecting quantitative trait loci for boron efficiency across multiple environments in Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 7:e45215
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31201672 and 30971861), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (2011PY150 and 2013JC012), and the Specialized Research Found for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, Ministry of Education of China (20120146120024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guangda Ding and Zunkang Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, G., Zhao, Z., Wang, L. et al. Identification and multiple comparisons of QTL and epistatic interaction conferring high yield under boron and phosphorus deprivation in Brassica napus . Euphytica 198, 337–351 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1110-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1110-8