Abstract
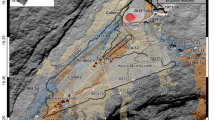
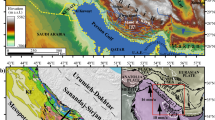
The Neka Valley nappe complex is exposed in the south of Gorgan County in the eastern Alborz fold-and-thrust belt. We use the results of a regional survey of the structural data and their patterns to interpret the mechanisms that emplaced the unmetamorphosed nappes in the foreland fold-and-thrust belt of the Alborz Mountains. Most of the strain magnitudes are low in the study area but increase slightly towards what are probably their proximal ends. Strain ellipsoid is dominantly oblate with XY aligned along and across the belt (or the nappe complex). The average kinematic vorticity number, W k = 0.6 which indicates most of the strain partitioning resulted in a general shear. Most of Flinn’s k values and α (the stretch along the shear plane) values are lower than 1. Structural indicators such as orthogonal extensional joints, pinch-and-swell structures, anastomosing cleavages, and listric normal and growth faults developed by push from the rear. Large-scale thrust complexes with opposed-dips such as triangle zones (as well as k and α-values <1) are compatible with the shear flow diverging distally and streamlines expected of the rear compression emplacement mechanism. Together with a later minor brittle deformation, these major ductile strains appears to provide a general model suitable for the emplacement of the nappes studied in a thin-skinned fold-and-thrust belt where the sedimentary cover strata shortened and imbricated in the upper crust.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad I, Gutiérrez-Alonso G, Nieto F et al (2003) The structure and the phyllosilicates (chemistry, crystallinity and texture) of Talas Ala-Tau (Tien Shan, Kyrgyz Republic): comparison with more recent subduction complexes. Tectonophysics 365:103–127
Abdelsalam MG (2010) Quantifying 3D post-accretionary tectonic strain in the Arabian-Nubian Shield: superimposition of the Oko Shear Zone on the Nakasib Suture, Red Sea Hills, Sudan. J Afr Earth Sc 56:167–178
Alavi M (1996) Tectonostratigraphic synthesis and structural style of the Alborz Mountain system in northen Iran. J Geodyn 21:1–33
Allen MB, Ghassemi MR, Shahrabi M et al (2003) Accommodation of late Cenozoic oblique shortening in the Alborz range, northern Iran. J Struct Geol 25:659–672
Allen MB, Jackson J, Walker R (2004) Late Cenozoic reorganization of the Arabia-Eurasia collision and the comparison of short-term and long-term deformation rates. Tectonics 23:1–16
Aoya M, Wallis SR (2003) Role of nappe boundaries in subduction-related regional deformation: spatial variation of meso- and microstructures in the Seba eclogite unit, the Sambagawa belt, SW Japan. J Struct Geol 25:1097–1106
Babar MD, Kaplay RD, Mukherjee S et al (2016) Evidences of deformation of dykes from Central Deccan Volcanic Province, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. In: Mukherjee S, Misra AA, Calvés G, Nemčok M (eds) Tectonics of the Deccan Large Igneous Province: an introduction. Geological Society of London, Special Publications. doi:10.1144/SP445.13
Baikpour S, Talbot CJ (2012) The Garmsar salt nappe and seasonal inversions of surrounding faults imaged by SAR interferometry, Northern Iran. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 363:563–578
Baird GB, Hudleston PJ (2007) Modelling the influence of tectonic extrusion and volume loss on the geometry, displacement, vorticity, and strain compatibility of ductile shear zones. J Struct Geol 29:1665–1678
Ballato P, Nowaczyk NR, Landgraf A et al (2008) Tectonic control on sedimentary facies pattern and sediment accumulation rates in the Miocene foreland basin of the southern Alborz mountains, northern Iran. Tectonics 27:1–20
Ballato P, Uba CE, Landgraf A et al (2011) Arabia-Eurasia continental collision: insights from the Tertiary foreland-basin evolution in the Alborz mountains, northern Iran. Geol Soc Am Bull 123:106–131
Berberian M, King GC (1981) Toward a paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Can J Earth Sci 18:210–265
Bhattacharyya P, Hudleston PJ (2001) Strain in ductile shear zones in the Caledonides of northern Sweden; a three-dimensional puzzle. J Struct Geol 23:1549–1556
Bhattacharyya K, Mitra G (2009) A new kinematic evolutionary model for the growth of a duplex—an example from the Rangit duplex, Sikkim Himalaya, India. Gondwana Res 16:697–715
Biswas T, Dutta D, Mukherjee S (2014) Tectonics of Siwalik Himalaya in Dehradun-Roorkee section, India. Geological Society of America annual meeting in Vancouver, British Columbia (19–22 October 2014). Topical session: T.23 Exploring the Development of the Himalayan-Karakoroum-Tibet Orogenic System from the Mantle to Mountain Peaks
Bose N, Mukherjee S (2015) Back structures (back-fault and back-folds) from collisional orogeny: field findings from Lesser Himalaya, Sikkim, India. 30th Himlaya-Karakoram-Tibet Workshop, Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, 06–08 Oct, Dehradun, India, pp 13–14
Brandon MT (1995) Analysis of geologic strain data in strain-magnitude space. J Struct Geol 17:1375–1385
Brun JP, Merle O (1985) Strain pattern in models of spreading-gliding nappes. Tectonics 4:705–719
Brun JP, Merle O (1988) Experiments on folding in spreading-gliding nappes. Tectonophysics 145:129–139
Burg J-P, Ricou L-E, Ivanov Z et al (1996) Syn-metamorphic nappe complex in the Rhodope Massif. Structure and kinematics. Terra Nova 8:6–15
Capponi G, Carosi R, Meccheri M et al (2003) Strain analysis in the Millen Range of Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Geol Jahrb B 85:225–251
Carosi R, Iacopini D, Montomoli C (2004) Asymmetric fold development in the Variscan Nappes. CR Geosci 336:939–949
Carosi R, Frassi C, Montomoli C et al (2005) Structural evolution of the Tuscan Nappe in the southeastern sector of the Apuan Alps metamorphic dome (Northern Apennines, Italy). Geol J 40:103–119
Carosi R, Addario E, Mammoliti E et al (2016) Geology of the northwestern portion of the Ferriere-Mollieres Shear Zone, Argentera Massif, Italy. J Maps. doi:10.1080/17445647.2016.1243491
Cello G, Nur A (1988) Emplacement of foreland thrust systems. Tectonics 7:261–271
Chapple WM (1978) Mechanics of thin-skinned fold-and-thrust belts. Geol Soc Am Bull 93:1189–1198
Coward MP (1976) Strain within ductile shear zones. Tectonophysics 34:181–197
Coward MP (1980) The Caledonian thrust and shear zones of N.W. Scotland. J Struct Geol 2:11–17
Coward MP, Kim JH (1981) Strain within thrust sheets. In: McClay KR, Price NJ (eds) Thrust and nappe tectonics. Geological Society of London, Special Publications 9, pp 275–292
Czeck DM, Hudleston PJ (2003) Testing models for obliquely plunging lineation in transpression: a natural example and theoretical discussion. J Struct Geol 25:959–982
Dahlen FA, Suppe J, Davis D (1984) Mechanics of fold-and-thrust belts and accretionary wedges: cohesive Coulomb theory. J Geophys Res 89:1189–1198
Davis DM, Engelder T (1985) The role of salt in fold-and-thrust belts. Tectonophysics 119:67–88
Davis DM, Lillie RJ (1994) Changing mechanical response during continental collision: active examples from the foreland thrust belts of Pakistan. J Struct Geol 16:21–34
Dias R, Mateus A, Ribeiro A (2003) Strain partitioning in transpressive shears zones in the southern branch of the Variscan Ibero-Armorican arc. Geodin Acta 16:119–129
Djamour Y, Vernant P, Bayer R et al (2010) GPS and gravity constraints on continental deformation in the Alborz mountain range, Iran. Geophys J Int 183:1287–1301
Dubey AK (2014) Understanding an orogenic belt: structural evolution of the Himalaya. Springer, New York
Elliott D (1976) The motion of thrusts sheets. J Geophys Res 81:949–963
Epard J-L, Escher A (1996) Transition from basement to cover: a geometric model. J Struct Geol 18:533–548
Escher A, Masson H, Steck A (1993) Nappe geometry in the Western Alps. J Struct Geol 15:501–509
Eyster EL, Bailey CM (2001) Vorticity analyses of extensional and transpressional high-strain zones; examples from the Arizona basin and range and Virginia piedmont. Geol Soc Am Abstr Prog 33(2):5
Fissler DA (2006) A quantitative analysis of strain in the Seine River Meta-conglomerates, Rainy Lake region, Northwestern Ontario, Canada. Unpublished M.S. thesis. University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
Flinn D (1956) On the deformation of the funzie conglomerate, Feltar, Shetland. J Geol 64:480–505
Flinn D (1962) On folding during three-dimensional progressive deformation. Q J Geol Soc 118:385–428
Flinn D (1979) The deformation matrix and the deformation ellipsoid. J Struct Geol 1:299–307
Fossen H (1993a) Linear fabrics in the Bergsdalen Nappes, southwest Norway: implications for deformation history and fold development. Nor Geol Tidsskr 73:95–108
Fossen H (1993b) Structural evolution of the Bergsdalen Nappes, Southwest Norway. Norsk Geol Unders Bull 424:23–49
Fossen H (2016) Structural geology, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fossen H, Holst TB (1995) Northwest-verging folds and the northwestward movement of the Caledonian Jotun Nappe, Norway. J Struct Geol 17:3–15
Fossen H, Rykkelid E (1990) Shear zone structures in the Øygarden area, West Norway. Tectonophysics 174:385–397
Fossen H, Tikoff B (1993) The deformation matrix for simultaneous simple shearing, pure shearing and volume change, and its application to transpression-transtension tectonics. J Struct Geol 15(3–5):413–422
Fowler A, El Kalioubi B (2004) Gravitational collapse origin of shear zones, foliations, and linear structures in the Neoproterozoic cover nappes, Eastern Desert, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 38:23–40
Frehner M (2011) The neutral lines in buckle folds. J Struct Geol 33(10):1501–1508
Frehner M (2016) 3D fold growth in transpression. Tectonophysics. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2016.01.002
Frehner M, Exner U (2014) Strain and foliation refraction patterns around buckle folds. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 394:21–37
Fry N (1979) Random point distribution and strain measurements. Tectonophysics 60:89–105
Gee DG (1978) Nappe emplacement in the Scandinavian Caledonides. Tectonophysics 47:393–419
Gray DR (1995) Thrust kinematics and transposition fabrics from a basal detachment zone, eastern Australia. J Struct Geol 17:1637–1654
Gray DR, Willman CE (1991) Thrust-related strain gradient and thrusting mechanisms in a chevron-folded sequence, southern Australia. J Struct Geol 13:691–710
Groshong RH Jr, Pfiffner OA, Pringle LR (1984) Strain partitioning in the Helvetic thrust belt of eastern Switzerland from the leading edge to the internal zone. J Struct Geol 6:5–18
Guest B, Guest A, Axen G (2007) Late Tertiary tectonic evolution of northern Iran: a case for simple crustal folding. Glob Plan Change 58:435–453
Guillier B (1988) Modélisation analogique des interactions compression gravite. Diplômed’Etude Approfondie, Rennes
Gutiérrez-Alonso G (1996) Strain partitioning in the footwall of the Somiedo Nappe: structural evolution of the Narcea Tectonic Window, NW Spain. J Struct Geol 18:1217–1229
Hansen EC (1971) Strain facies. Springer, New York
Harris LB, Burg J-P, Sauniac S (1983) Strain distribution within the Pardailhan Nappe (Montagne Noire, France) and structure of its basal thrust zone: implication for events associated with nappe emplacement. J Struct Geol 5:431–440
Hatcher RD Jr (2004) Properties of thrusts and the upper bounds for the size of thrust sheets. In: McClay KR (ed) Thrust tectonics and hydrocarbon systems. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir 82, pp 18–29
Hatcher RD Jr, Hooper RJ (1992) Evolution of crystalline thrust sheets in the internal parts of mountain chains. In: McClay KR (ed) Thrust tectonics. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 217–233
Henderson GGL, Dahlstom DCA (1959) First-order nappe in Canadian Rochies. Am Assoc Petrol Geol Bull 43(3):641–653
Hollinsworth J, Jackson J, Walker R et al (2008) Extrusion tectonics and subduction in the eastern South Caspian region since 10 Ma. Geology 36:763–766
Hossack J (1968) Pebble deformation and thrusting in the Bygdin area (Southern Norway). Tectonophysics 5:315–339
Hsu TC (1966) The characteristics of coaxial and non-coaxial strain paths. J Strain Anal Eng Des 1:216–222
Hsü KJ (1969) Role of cohesive strength in the mechanics of overthrust faulting and of landsliding. Geol Soc Am Bull 80:927–952
Hubbert MK, Rubey WW (1959) Role of fluid pressure in mechanics of overthrust faulting, I. Mechanics of fluid-filled porous solids and its application to overthrust faulting. Geol Soc Am Bull 70:115–166
Hudleston PJ (1976) Recumbent folding in the base of the Barnes ice cap, Baffin Island, northwest Territories, Canada. Geol Soc Am Bull 87:1684–1692
Hudleston PJ (1977) Similar folds, recumbent folds and gravity tectonics in ice and rocks. J Geol 85:113–122
Hudleston PJ (2015) Structures and fabrics in glacial ice: a review. J Struct Geol 81:1–27
Hudleston PJ, Hooke R (1980) Cumulative deformation in the Barnes ice cap and implications for the development of foliation. Tectonophysics 66:127–146
Jackson J, McKenzie D (1984) Active tectonics of the Alpine-Himalayan Belt between western Turkey and Pakistan. Geophys J Int 77:185–264
Jackson J, Priestley K, Allen MB et al (2002) Active tectonics of the South Caspian Basin. Geophys J Int 148:214–245
Javidfakhr B, Bellier O, Shabanian S et al (2011) Plio-Quaternary tectonic regime changes in the transition zone between Alborz and Kopeh Dagh mountain ranges (NE Iran). Tectonophysics 506:86–108
Jordan P (1992) Evidence for large-scale decoupling in the Triassic evaporates of Northern Switzerland: an overview. Eclogae Geol Helv 85:677–693
Kaplay RD, Babar Md, Mukherjee S et al (2016) Morphotectonic expression of geological structures in eastern part of south east Deccan volcanic province (around Nanded, Maharashtra, India). In: Mukherjee S, Misra AA, Calvés G, Nemčok M (eds) Tectonics of the Deccan Large Igneous Province: an introduction. Geological Society of London, Special Publications. doi:10.1144/SP445.12
Kaplay RD, Kumar TV, Mukherjee S et al (submitted) Strike-slip (brittle/brittle-ductile) shear from the periphery of South East Deccan Volcanic Province, Kinwat, Maharashtra, India. J Earth Syst Sci
Kassem OMK, Abd El Rahim SH (2010) Finite-strain analysis of Metavolcano-sedimentary rocks at Gabel El Mayet area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 58:321–330
Kehle RO (1970) Analysis of gravity sliding and orogenic translation. Geol Soc Am Bull 81:1641–1664
Kligfield R, Carmignani L, Owens WH (1981) Strain analysis of a Northern Apennine shear zone using deformed marble breccias. J Struct Geol 16:493–503
Lagarde JL, Michard A (1986) Stretching normal to the regional thrust displacement in a thrust-wrench shear zone, Rehamna Massif, Morocco. J Struct Geol 8:483–492
Long S, McQuarrie N, Tobgay T et al (2011) Quantifying internal strain and deformation temperature in the eastern Himalaya, Bhutan: implications for the evolution of strain in thrust sheets. J Struct Geol 33:579–608
McClay KR (1992) Glossary of thrust tectonics terms. In: McClay KR (ed) thrust tectonics. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 419–433
McClay KR, Price NJ (1981) Introduction. In: McClay KR, Price NJ (eds) Thrust and nappe tectonics. Geological Society of London, Special Publications 9, pp 1–9
Merle O (1986) Patterns of stretch trajectories and strain rate within spreading-gliding nappes. Tectonophysics 124:211–222
Merle O (1989) Strain models within spreading nappes. Tectonophysics 165:57–71
Merle O (1998) Emplacement mechanisms of nappes and thrust sheets. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Merle O, Brun J-P (1984) The curved translation path of the Parpaillon nappe (French Alps). J Struct Geol 6:711–719
Misra AA, Mukherjee S (2016) Dyke-brittle shear relationships in the Western Deccan Strike-slip Zone around Mumbai (Maharashtra, India). In: Mukherjee S, Misra AA, Calvés G, Nemčok M (eds) Tectonics of the Deccan Large Igneous Province: an introduction. Geological Society of London, Special Publications. doi:10.1144/SP445.4
Misra AA, Bhattacharya G, Mukherjee S et al (2014) Near N–S paleo-extension in the western Deccan region in India: does it link strike-slip tectonics with India-Seychelles rifting? Int J Earth Sci 103:1645–1680
Mitra G (1994) Strain variation in thrust sheets across the Sevier fold-and-thrust belt (Idaho–Utah–Wyoming): implication for section restoration and wedge taper evolution. J Struct Geol 16:585–602
Mitra G, Boyer SE (1999) Strain in the Lewis thrust sheet, NW Montana fold-and-thrust belt: implications for basin restoration and estimates of critical taper. Geol Soc Am Abstr Prog 31:237
Moriyama Y, Wallis SR (2002) Three-dimensional finite strain analysis in the high-grade part of the Sanbagawa Belt using deformed meta-conglomerate. Isl Arc 11:111–121
Mukherjee S (2005) Channel flow, ductile extrusion and exhumation of lower-mid crust in continental collisional zones. Curr Sci 89:435–436
Mukherjee S (2007) Geodynamics, deformation and mathematical analysis of metamorphic belts of the NW Himlaya. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis. Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
Mukherjee S (2010a) Applicability of channel flow as an extrusion mechanism of the Higher Himalayan Shear Zone from Sutlej, Zanskar, Dhauliganga and Goriganga Sections, Indian Himalaya. European Geosciences Union General Assembly, 2–7 May, 2010, Vienna, Austria. Geophysical Research Abstracts, vol 12, EGU2010-14
Mukherjee S (2010b) Microstructures of the Zanskar Shear Zone. Earth Sci India 3:9–27
Mukherjee S (2010c) Structures at Meso- and Micro-scales in the Sutlej section of the Higher Himalayan Shear Zone in Himalaya. E-Terra 7:1–27
Mukherjee S (2011a) Flanking microstructures from the Zanskar Shear Zone, NW Indian Himalaya. YES Netw Bull 1:21–29
Mukherjee S (2011b) Mineral fish: their morphological classification, usefulness as shear sense indicators and genesis. Int J Earth Sci 100:1303–1314
Mukherjee S (2012a) Simple shear is not so simple! Kinematics and shear senses in Newtonian viscous simple shear zones. Geol Mag 149:819–826
Mukherjee S (2012b) Tectonic implications and morphology of trapezoidal mica grains from the Sutlej section of the Higher Himalayan Shear Zone, Indian Himalaya. J Geol 120:575–590
Mukherjee S (2013a) Channel flow extrusion model to constrain dynamic viscosity and Prandtl number of the Higher Himalayan Shear Zone. Int J Earth Sci 102:1811–1835
Mukherjee S (2013b) Deformation microstructures in rocks. Springer, New York
Mukherjee S (2013c) Higher Himalaya in the Bhagirathi section (NW Himalaya, India): its structures, back-thrusts and extrusion mechanism by both channel flow and critical taper mechanisms. Int J Earth Sci 102:1851–1870
Mukherjee S (2014a) Atlas of shear zone structures in meso-scale. Springer, New York
Mukherjee S (2014b) Kinematics of ‘top-to-down’ simple shear in a Newtonian Rheology. J Indian Geophys Union 18:245–248
Mukherjee S (2014c) Mica inclusion inside Host Mica Grains from the Sutlej Section of the Higher Himalayan Crystallines, India-Morphology and Constrains in Genesis. Acta Geol Sin 88:1729–1741
Mukherjee S (2014d) Review of flanking structures in meso- and micro-scales. Geol Mag 151:957–974
Mukherjee S (2015) A review on out-of-sequence deformation in the Himalaya. In: Mukherjee S, Carosi R, van der Beek P, Mukherjee BK, Robinson D (eds) Tectonics of the Himalaya. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 412, no 1, pp 67–109
Mukherjee S (2016a) Review on symmetric structures in ductile shear zones. Int J Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s00531-016-1366-4
Mukherjee S (2016b) Shear heating by translational brittle reverse faulting along a single, sharp and straight fault plane. J Earth Syst Sci
Mukherjee S, Biswas R (2014) Kinematics of horizontal simple shear zones of concentric arcs (Taylor–Couette flow) with incompressible Newtonian rheology. Int J Earth Sci 103:597–602
Mukherjee S, Koyi HA (2010) Higher Himalayan Shear Zone, Sutlej section: structural geology and extrusion mechanism by various combinations of simple shear, pure shear and channel flow in shifting modes. Int J Earth Sci 99:1267–1303
Mukherjee S, Mulchrone KF (2013) Viscous dissipation pattern in incompressible Newtonian simple shear zones: an analytical model. Int J Earth Sci 102:1165–1170
Mukherjee S, Koyi HA, Talbot CJ (2012) Implications of channel flow analogue models in extrusion of the Higher Himalayan Shear Zone with special references to the out-of-sequence thrusting. Int J Earth Sci 101:253–272
Mukherjee S, Punekar J, Mahadani T et al (2015) A review on intrafolial folds and their morphologies from the detachments of the western Indian Higher Himalaya. In: Mulchrone K, Mukherjee S (eds) Ductile shear zones: from micro- to macro-scales. Wiley, New York, pp 182–205
Mulchrone KF, Mukherjee S (2015) Shear senses and viscous dissipation of layered ductile simple shear zones. Pure Appl Geophys 172:2635–2642
Mulchrone KF, Mukherjee S (2016) Kinematics and shear heat pattern of ductile simple shear zones with ‘slip boundary condition’. Int J Earth Sci 105:1015–1020
Nabavi ST (2012) Emplacement mechanism of fold-and-thrust nappes in Chahar-bagh area, Eastern Alborz. Unpublished M.Sc. thesis. Damghan University, Iran (in Persian with English abstract)
Nabavi ST, Khademi M, Rahimi-Chakdel A (2014) Inclined transpression deformation zone of Chahr-bagh nappe, eastern Alborz. J Tecton Struct 2:56–76 (In Persian with English abstract)
Nabavi ST, Díaz-Azpíroz M, Talbot CJ (2016a) Inclined transpression in the Neka Valley, eastern Alborz, Iran. Int J Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s00531-016-1388-y
Nabavi ST, Alavi SA, Mohammadi S, Ghassemi MR, Shirzaei M (2016b) Analysis of transpression within contractional planar fault steps using the finite-element method. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol 48, no 7. doi:10.1130/abs/2016AM-280211
Nadai A (1963) Theory of flow and fracture of solids, vol 2. McGraw-Hill, New York
O’Hara KD (1990) State of strain in mylonites from the western Blue Ridge province, south Appalachians: the role of volume loss. J Struct Geol 12:419–430
Owens WH (1984) The calculation of a best-fit ellipsoid from elliptical sections on arbitrarily oriented planes. J Struct Geol 6:571–578
Pastor-Galán D, Gutiérrez-Alonso G, Meere PA et al (2009) Factors affecting finite strain estimation in low-grade, low-strain clastic rocks. J Struct Geol 31:1586–1596
Pfiffner OA (1981) Fold-and-thrust tectonics in the Helvetic Nappes (E Switzerland). In: McClay KR, Price NJ (eds) Thrust and nappee tectonics. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 9, no 1, pp 319–327
Pfiffner OA (1985) Displacements along thrust faults. Eclogae Geol Helv 78:313–333
Pfiffner OA (1993) The structure of the Helvitic nappes and its relation to the mechanical stratigraphy. J Struct Geol 15(3–5):511–521
Pfiffner OA (2006) Thick-skinned and thin-skinned styles of continental contraction. In: Mazzoli S, Butler RWH (eds) Styles of continental contraction. Geological Society of America, Special Paper 414, pp 153–177
Plašienka D, Prokešova R (1996) Towards an evolutionary tectonic model of the Krížna cover nappe (Western Carpathians, Slovakia). Slovak Geol Mag 3–4(96):279–286
Platt JP (1986) Dynamics of orogenic wedges and the uplift of high-pressure metamorphic rocks. Geol Soc Am Bull 97:1037–1053
Prokešova R, Plašienka D, Milovský R (2012) Structural pattern and emplacement mechanisms of the Krížna cover nappe (Central Western Carpathians). Geol Carpath 63:13–32
Provost A, Buisson C, Merle O (2004) From progressive to finite deformation and back. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2001JB001734
Rahimi-Chakdel A, Raghimi M (2014) Some characteristics of mafic dykes in Gondwanan land from South of Gorgan, Northeastern Iran: implication to Petrogenesis and Paleotectonic. J Tethys 2:137–147
Ramberg H (1975a) Particle path, displacement and progressive strain applicable to rocks. Tectonophysics 28:1–37
Ramberg H (1975b) Superposition of homogeneous strain and progressive deformation in rocks. Bull Geol Inst Univ Uppsala NS 6:35–67
Ramberg H (1977) Some markers on the mechanism of nappe movement. Geol Fören Stockh Förh 99:110–117
Ramberg H (1989) A new numerical simulation method applied to spreading nappes. Tectonophysics 162:173–192
Ramberg H (1991) Numerical simulation of spreading nappes, sliding against basal friction. Tectonophysics 188:159–186
Ramsay JG (1967) Folding and fracturing of rocks. McGraw-Hill, New York
Ramsay JG (1981) Tectonics of the Helvetic Nappes. In: McClay KR, Price NJ (eds) Thrust and nappee tectonics. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 9, no 1, pp 293–309
Ramsay JG, Huber MI (1983) The techniques of modern structural geology: strain analysis, vol 1. Academic Press, London
Ramsay JG, Wood DS (1973) The geometric effects of volume change during deformation processes. Tectonophysics 16:263–277
Ring U (1998) Volume strain, strain type and flow path in a narrow shear zone. Geol Rundsch 86:786–801
Ring U, Kassem OMK (2007) The nappe rule: why does it work? J Geol Soc Lond 164:1109–1112
Ring U, Bradon MT, Ramthum A (2001) Solution mass-transfer deformation adjacent to the Glarus Thrust, with implications for the tectonic evolution of the Alpine wedge in eastern Switzerland. J Struct Geol 23:1491–1505
Ritz JF, Nazari H, Ghassemi A et al (2006) Active transtension inside Central Alborz: a new insight into northern Iran-southern Caspian geodynamics. Geology 34:477–480
Roday P, Purohit MK, Prajapati KK (2010) A compute program for the determination of finite strain using Fry method. J Geol Soc India 76:151–154
Samani B (2015) Strain analysis using structural elements and geometry of surfaces of no finite longitudinal strain. Arab J Geosci 8:8461–8468
Sanderson DJ (1982) Models of strain variation in nappes and thrust sheets: a review. Tectonophysics 88:201–233
Sanderson DJ, Marchini WRD (1984) Transpression. J Struct Geol 6:449–458
Sanderson DJ, Andrew JR, Phollips WEA et al (1980) Deformation studies in the Irish Caledonides. J Geol Soc Lond 137:289–302
Sarkarinejad K, Samani B, Faghih A et al (2010) Implication of strain and vorticity of flow analyses to interpret the kinematics of an oblique convergence event Zagros Mountains, Iran). J Asian Earth Sci 38:34–43
Sarkarinejad K, Keshavarz S, Faghih A (2015) Kinematics of the Sirjan mylonite nappe, Zagros Orogenic Belt: insights from strain and vorticity analyses. J Geosci 60:189–202
Schmalholz SM, Duretz T, Schenker FL et al (2014) Kinematics and dynamics of tectonic nappes: 2-D numerical modelling and implications for high and ultra-high pressure tectonism in the Western Alps. Tectonophysics 631:160–175
Seno S (1992) Finite strain and deformation within the Briançonnais Castelvecchio-Cerisola nappe of the Ligurian Alps, Italy. J Struct Geol 14:825–838
Seno S, Dallagiovanna G, Vanossi M (1998) From finite strain data to strain history: a model for a sector of the Ligurian Alps, Italy. J Struct Geol 20:573–585
Shahrabi M (1990) Geological map of the gorgan quadrangle, scale: 1:250,000. Geological Survey of Iran, Tehran
Siddans AWB (1983) Finite strain patterns in some Alpine nappes. J Struct Geol 5:441–448
Siddans AWB (1984) Thrust tectonics—a mechanistic view from the West and Central Alps. Tectonophysics 104:257–281
Siddans AWB, Henry B, Kligfield R et al (1984) Finite strain patterns and their significance in Permian rocks of the Alpes Maritimes (France). J Struct Geol 6:339–368
Singh S, Jain AK (1993) Deformational and strain patterns of the Jutogh Nappe along the Sutlej Valley in Jeori-Wangtu region, Himachal Pradesh, India. J Himal Geol 4:41–55
Talbot CJ (1974) Fold nappes as asymmetric mantled gneiss domes and ensialic orogeny. Tectonophysics 24:259–276
Talbot CJ (1979) Fold trains in a glacier of salt in southern Iran. J Struct Geol 1(1):5–18
Talbot CJ (2014) Lessons from the first 100 minimum strain ellipsoids constrained in gneisses deformed at high metamorphic grade. Earth Sci Rev 138:231–267
Talbot CJ, Aftabi P (2004) Geology and models of salt extrusion at Qum Kuh, central Iran. J Geol Soc Lond 161:321–334
Talbot CJ, Pohjola V (2009) Subaerial salt extrusions in Iran as analogues of ice sheets, streams and glaciers. Earth Sci Rev 97:167–195
Talbot CJ, Sokoutis D (1995) Strain ellipsoids from incompetent dykes: application to volume loss during mylonitization in the Singo gneiss zone, central Sweden. J Struct Geol 17:927–948
Thigpen JR, Law RD, Lloyd GE et al (2010) Deformation temperatures, vorticity of flow and strain in the Moine thrust zone and Moine nappe: reassessing the tectonic evolution of the Scandian foreland-hinterland transition zone. J Struct Geol 32:920–940
Tikoff B, Fossen H (1993) Simultaneous pure and shear shear: the unifying deformation matrix. Tectonophysics 217:267–283
Toriumi M (1985) Two type of ductile deformation/regional metamorphic belt. Tectonophysics 113:307–326
Toriumi M, Noda H (1986) The origin of strain patterns resulting from contemporaneous deformation and metamorphism in the Sambagawa metamorphic belt. J Metamorph Geol 4:409–420
Tripathy NR, Srivastava HB, Mamtani MA (2009) Evaluation of a regional strain gradient in mylonitic quartzites from the footwall of the Main Central Thrust Zone (Garhwal Himalaya, India): Inferences from finite strain and AMS analyses. J Asian Earth Sci 34:26–37
Twiss RJ, Moores EM (2007) Structural Geology, 2nd edn. Freeman and Company, New York
Vitale S, Mazzoli S (2008) Heterogeneous shear zone evolution: the role of shear strain hardening/softening. J Struct Geol 30:1363–1395
Vitale S, Mazzoli S (2009) Finite strain analysis of a natural ductile shear zone in limestones: Insights into 3-D coaxial vs. non-coaxial deformation partitioning. J Struct Geol 31:104–113
Vitale S, Mazzoli S (2010) Strain analysis of heterogeneous ductile shear zones based on the attitudes of planar markers. J Struct Geol 32:321–329
Vitale S, Mazzoli S (2015) From finite to incremental strain: insights into heterogeneous shear zone evolution. In: Mulchrone K, Mukherjee S (eds) Ductile shear zones: from micro- to macro-scales. Wiley, New York, pp 3–13
Wallis SR (1995) Vorticity analysis and recognition of ductile extension in the Sanbagawa belt, SW Japan. J Struct Geol 17:1077–1093
Wissing SB, Pfiffner OA (2003) Numerical models for the control of inherited basin geometries on structures and emplacement of the Klippen nappe (Swiss Prealps). J Struct Geol 25:1213–1227
Wissing SB, Ellis S, Pfiffner OA (2003) Numerical models of Alpine-type cover nappes. Tectonophysics 367:145–172
Wojtal S (1986) Deformation within foreland thrust sheets by populations of minor faults. J Struct Geol 8:341–360
Xypolias P, Kokkalas S (2006) Heterogeneous ductile deformation along a mid-crustal extruding shear zone: an example from the External Hellenides (Greece). In: Law RD, Searle MP Godin L (eds) Channel flow, ductile extrusion and exhumation in continental collision zones. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 268, no 1, pp 497–516
Yonkee WA (2005) Strain patterns within part of the Willard thrust sheet, Idaho-Wyoming-Utah thrust belt. J Struct Geol 27:1315–1343
Yonkee WA, Czeck DM, Nachbor AC et al (2013) Strain accumulation and fluid-rock interaction in a naturally deformed diamictite, Willard thrust system, Utah (USA): implications for crustal theology and strain softening. J Struct Geol 50:91–118
Zanchi A, Berra F, Mattei M et al (2006) Inversion tectonics in Central Alborz, Iran. J Struct Geol 28:2023–2037
Zanchi A, Zanchetta S, Berra F, Mattei M, Garzanti E, Molyneux S, Nawab A, Sabouri J (2009) The Eo-Cimmerian (Late? Triassic) orogeny in North Iran. In: Brunet M-F, Wilmsen M, Granath JW (eds) South caspian to central Iran basins. The Geological Society, London, Special Publications 312, no 1, pp 31–55
Zwart HJ (1974) Structure and metamorphism in the Seve-Köli nappe complex (Scandinavian Caledonides) and its implications concerning the formation of metamorphic nappes. Centenaire de la Géologique de Belgique, Géologie des Domaines Cristallins, Liege, pp 129–144
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Christopher J. Talbot for helpful and constructive reviews, English language, and geological discussions that significantly improved this manuscript. In addition, we are grateful for the field assistance provided by MSc student Ali Shafiei. This work is supported by the Vice Presidency of Research and Technology of Golestan University Grant No. 1122. We would like to express our thanks to Dr. Soumyajit Mukherjee and Prof. Wolf-Christian Dullo for their careful handling of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabavi, S.T., Rahimi-Chakdel, A. & Khademi, M. Structural pattern and emplacement mechanism of the Neka Valley nappe complex, eastern Alborz, Iran. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 106, 2387–2405 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-016-1433-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-016-1433-x