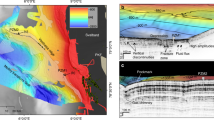
Abstract
New data from surveys of gas-bearing mud areas in the Gdansk Deep (southeastern Baltic Sea) were collected during four research cruises in 2009–2011. These revealed the presence of seven large pockmarks apart from the three already known, and enabled significant improvement of the existing digital map of gassy mud distribution. Based on geochemical sediment analyses, calculated diffusive methane fluxes from the upper (0–5 cm) seabed layer into near-bottom waters were highest—3.3 mmol/(m2 day)—in pockmark mud, contrasting strongly with the minimum value of 0.004 mmol/(m2 day) observed in typical, background mud. However, fluxes of less than 0.1 mmol/(m2 day) were observed in all sediment types, including pockmarks. In a newer attempt to roughly estimate budgets at a more regional scale, diffusive methane venting amounts to 280 × 106 mmol/day for southeastern Baltic Sea muddy sediments. Elongated pockforms in the southern Gotland Deep, known since the end of the 1980s as pockmarks, had methane concentrations that were similar to those of gassy mud from the Gdansk Basin, and there was no geo-acoustic evidence of considerably increased gas levels.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blazhchishin A (1998) Paleogeography and evolution of late quaternary sedimentation in the Baltic Sea (in Russian). Yantarnyi skaz, Kaliningrad
Blazhchishin A, Eger V (1990) Pockmarks at the Baltic bottom – the indicators of hydrocarbon migration process from the deep layers (in Russian). In: Geodekyan AA, Trotcuk VY, Blazhchishin A (eds) Combined geoacoustic, gasometric and lithogeochemical investigations in the Baltic Sea. Institute of Oceanology RAS, Moscow, pp 93–127
Brothers LL, Kelley JT, Belknap DF, Barnhardt WA, Andrews BD, Landon Maynard M (2011) More than a century of bathymetric observations and present-day shallow sediment characterization in Belfast Bay, Maine, USA: implications for pockmark field longevity. Geo-Mar Lett 31(4):237–248. doi:10.1007/s00367-011-0228-0
Clark JF, Washburn L, Schwager Emery K (2010) Variability of gas composition and flux intensity in natural marine hydrocarbon seeps. Geo-Mar Lett 30(3/4):379–388. doi:10.1007/s00367-009-0167-1
Dando PR, Hughes JA, Leahy Y, Niven SJ, Taylor LJ, Smith C (1995) Gas venting from submarine hydrothermal areas around the island of Milos, Hellenic Volcanic Arc. Cont Shelf Res 15:913–929. doi:10.1016/0278-4343(95)80002-4
Diez R, García-Gil S, Durán R, Vilas F (2007) Gas-charged sediments in the Ría de Arousa: short- to long-term fluctuations? Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 71:467–479. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2006.08.027
Dodonov AE, Namestnikov YG, Yakushova AF (1976) Neotectonics of the southeastern part of the Baltic syncline (in Russian). Moscow State University, Moscow
Egorov AV, Rozhkov AN (1997) Scales of the methane diffusive dispersion in the sediments of the Baltic Sea above the geoacoustical anomalies (in Russian). In: Geodekyan AA, Romankevich EA, Trotcuk VY (eds) Geochemistry of the water and sediments of the Baltic Sea in the area of gas craters and geoacoustical anomalies development. Institute of Oceanology RAS, Moscow, pp 135–147
Emelyanov EM (2002) Geology of the Gdansk Basin, Baltic Sea (in Russian). Yantarnyi skaz, Kaliningrad
Fleischer P, Orsi TH, Richardson MD, Anderson AL (2001) Distribution of free gas in marine sediments: a global overview. Geo-Mar Lett 21(2):103–122. doi:10.1007/s003670100072
Floodgate GD, Judd AG (1992) The origins of shallow gas. Cont Shelf Res 10:1145–1156. doi:10.1016/0278-4343(92)90075-U
Foucher J-P, Dupré S, Scalabrin C, Feseker T, Harmegnies F, Nouzé H (2010) Changes in seabed morphology, mud temperature and free gas venting at the Håkon Mosby mud volcano, offshore northern Norway, over the time period 2003–2006. Geo-Mar Lett 30(3/4):157–167. doi:10.1007/s00367-010-0193-z
Frenzel P, Rothfuss F, Conrad R (1992) Oxygen profiles and methane turnover in a flooded rice microcosm. Biol Fertil Soils 14:84–89. doi:10.1007/BF00336255
Geodekyan AA, Trotcuk VY (1990) Pockmarks at the Baltic bottom – the indicators of hydrocarbon migration process from the deep layers (in Russian). In: Geodekyan AA, Trotcuk VY, Blazhchishin A (eds) Combined geoacoustic, gasometric and lithogeochemical investigations in the Baltic Sea. Institute of Oceanology RAS, Moscow, pp 6–11
Gülzow W, Rehder G, Schneider B, Schneider v. Deimling J, Sadkowiak B (2011) A new method for continuous measurement of methane and carbon dioxide in surface waters using off-axis integrated cavity output spectroscopy (ICOS): an example from the Baltic Sea. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 9:176–184
Gülzow W, Rehder G, Schneider v. Deimling J, Seifert T, Tóth Z (2012) One year of continuous measurements constraining methane emissions from the Baltic Sea to the atmosphere using a ship of opportunity. Biogeosci Discuss 9:9897–9944
Iglesias J, Ercilla G, García-Gil S, Judd AG (2010) Pockforms: an evaluation of pockmark-like seabed features on the Landes Plateau, Bay of Biscay. Geo-Mar Lett 30(3/4):207–219. doi:10.1007/s00367-009-0182-2
Iversen N, Jørgensen BB (1993) Diffusion-coefficients of sulfate and methane in marine sediments – influence of porosity. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57(3):571–578. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(93)90368-7
Judd AG, Hovland M (2007) Seabed fluid flow: the impact on geology, biology and the marine environment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kostecki R, Janczak-Kostecka B (2012) Holocene environmental changes in the south-western Baltic Sea reflected by the geochemical data and diatoms of the sediment cores. J Mar Syst. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2012.06.005
Leipe T, Tauber F, Vallius H, Virtasalo J, Uścinowicz S, Kowalski N, Hille S, Lindgren S, Myllyvirta T (2011) Particulate organic carbon (POC) in surface sediments of the Baltic Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 31(3):175–188. doi:10.1007/s00367-010-0223-x
Marinaro G, Etiope G, Lo Bue N, Favali P, Papatheodorou G, Christodoulou D, Furlan F, Gasparoni F, Ferentinos G, Masson M, Rolin J-F (2006) Monitoring of a methane-seeping pockmark by cabled benthic observatory (Patras Gulf, Greece). Geo-Mar Lett 26(5):297–302. doi:10.1007/s00367-006-0040-4
Mojski JE (1995) Structural conditions of Pleistocene ice-sheet development. Geological atlas of the Southern Baltic, 1:500 000. Sopot, Warsaw, pp 20–22
Müller H, von Dobeneck T, Nehmiz W, Hamer K (2011) Near-surface electromagnetic, rock magnetic, and geochemical fingerprinting of submarine freshwater seepage at Eckernförde Bay (SW Baltic Sea). Geo-Mar Lett 31(2):123–140. doi:10.1007/s00367-010-0220-0
Newman KR, Cornier M-H, Weissel JK, Driscoll NW, Kastner M, Solomon EA, Robertson G, Hill JC, Singh H, Camilli R, Eustice R (2007) Active methane venting observed at giant pockmarks along the U.S. mid-Atlantic shelf break. Earth Planet Sci Lett 267:341–352. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.11.053
Pimenov NV, Ulyanova MO, Kanapatsky TA, Veslopolova EF, Sigalevich PA, Sivkov VV (2010) Microbially mediated methane and sulfur cycling in pockmark sediments of the Gdansk Basin, Baltic Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 30(3/4):439–448. doi:10.1007/s00367-010-0200-4
Sakagami H, Takahashi N, Hachikubo A, Minami H, Yamashita S, Shoji H, Khlystov O, Kalmychkov G, Grachev M, De Batist M (2012) Molecular and isotopic composition of hydrate-bound and dissolved gases in the southern basin of Lake Baikal, based on an improved headspace gas method. Geo-Mar Lett. doi:10.1007/s00367-012-0294-y
Schmale O, Schneider von Deimling J, Gülzow W, Nausch G, Waniek JJ, Rehder G (2010) Distribution of methane in the water column of the Baltic Sea. Geophys Res Lett 37:L12604. doi:10.1029/2010GL043115
Schulz HD (2000) Quantification of early diagenesis: dissolved constituents in marine pore water. In: Schulz HD, Zabel M (eds) Marine geochemistry. Springer, Berlin, pp 85–128
Sivkov V, Gorbatskiy V, Kuleshov A, Zhurov Y (2002) Muddy contourites in the Baltic Sea. In: Stow D, Pudsey C, Howe J, Faugères J-C, Viana AR (eds) Deep-water contourite systems: modern drifts and ancient series, seismic and sedimentary characteristics. Geol Soc Lond Mem 22:121–136
Sviridov NI (1990) Geological and physical nature of geoacoustical anomalies in the upper part of the sedimentary cover of the Baltic Sea (in Russian). In: Geodekyan AA, Trotcuk VY, Blazhchishin A (eds) Combined geoacoustic, gasometric and lithogeochemical investigations in the Baltic Sea. Institute of Oceanology RAS, Moscow, pp 47–56
Thießen O, Schmidt M, Theilen F, Schmitt M, Klein G (2006) Methane formation and distribution of acoustic turbidity in organic-rich surface sediments in the Arkona Basin, Baltic Sea. Cont Shelf Res 26:2469–2483. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.020
Vardaro MF, MacDonald IR, Bender LC, Guinasso NL Jr (2006) Dynamic processes observed at a gas hydrate outcropping on the continental slope of the Gulf of Mexico. Geo-Mar Lett 26(1):6–15. doi:10.1007/s00367-005-0010-2
Wever TF, Luhder R, Voss H, Knispel U (2006) Potential environmental control of free shallow gas in the seafloor of Eckernförde Bay, Germany. Mar Geol 225:1–4. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2005.08.005
Whiticar MJ (2002) Diagenetic relationships of methanogenesis, nutrients, acoustic turbidity, pockmarks and fresh water seepages in Eckernförde Bay. Mar Geol 182:29–53. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00227-4
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the RFBR 11-05-01093-а and 08-04-92422-BONUS_а. We are grateful to Prof. Bo Barker Jørgensen and Dr. José Mogollón for their assistance in diffusive flux calculations, to Alexander Krek for his help, and to the crews of R/V Professor Shtokman and Shelf for their support during the cruises. Also acknowledged are constructive assessments and comments by Dr. T. Missiaen, an anonymous reviewer, and the editors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible guest editors: M. De Batist and O. Khlystov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulyanova, M., Sivkov, V., Kanapatskij, T. et al. Methane fluxes in the southeastern Baltic Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 32, 535–544 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-012-0304-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-012-0304-0