Abstract
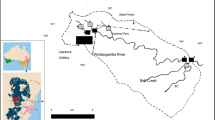
This work focuses on the characterization of a typical coastal karst watershed by addressing its physico-chemical parameters. The concentrations of the main ions clearly indicate the dominance of Ca2+ and HCO3− with a carbonate weathering rate equivalent to 230t/Km2/year; that is a typical weathering of karst watersheds. The spatio-temporal variability of dissolved organic matter (DOM) is also assessed in the watershed. Many samples were collected under different hydrological conditions from three representative sites. The evolution of OM composition along an urbanization gradient from upstream to downstream Kadisha watershed reveals the very strong impact of urban discharges on the receiving waters. Substantial differences in DOC results are highlighted in relation to the urban or natural origin of the DOM. Upstream OM flux is quantified and compared to downstream OM flux showing that, during the low flow period, the downstream flux is 29 times higher than the upstream. Also, a large fraction of non-humic substances, including hydrophilic organic matter HPI, is detected in the downstream section impacted by urban discharges. The higher values of SUVA noticed for DOM at upstream compared to downstream, reflects the low aromaticity and non-humic character of DOM in downstream. These outcomes show the impact of the Tripoli urban discharges on the quality and quantity of OM in the receiving waters downstream of the Kadisha catchment. This is typical at low water period when the dilution factor of urban discharges in the receiving waters is the least.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information file).
References
Aiken GR, McKnight DM, Thorn KA, Thurman EM (1992) Isolation of hydrophilic organic acids from water using nonionic macroporous resins. Org Geochem 18(4):567–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6380(92)90119-I
APHA-AWWA-WEF (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Assaker A (2016) Hydrologie et biogéochimie du bassin versant du fleuve Ibrahim : un observatoire du fonctionnement de la zone critique au Liban. (Hydrology and biogeochemistry of the Ibrahim River Basin: an observatory of the critical zone functioning in Lebanon). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toulouse. INP Toulouse. 1–278
Awad M, Darwich TK (2009a) Evaluating sea water quality in the coastal zone of North Lebanon using Telemac-2 DTM. Leban Sci J 10(1):35
Awad MM, Darwich T (2009b) Evaluating sea water quality in the coastalz one of north lebanon uSing. Leban Sci J 10(1):35–43
Azzi V, Kazpard V, Lartiges B, Kobeissi A, Kanso A, El Samrani AG (2017) Trace metals in phosphate fertilizers used in eastern mediterranean countries. Clean Soil Air Water. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201500988
Barlow PM, Reichard EG (2010) L’intrusion d’eau salée dans les régions côtières d’Amérique du Nord. Hydrogeol J 18(1):247–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-009-0514-3
Bonacci O, Ljubenkov I, Roje-Bonacci T (2006) Karst flash floods: An example from the Dinaric karst (Croatia). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 6(2):195–203. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-6-195-2006
Brinkmann R, Parise M (2012) Karst environments: problems, management, human impacts, and sustainability an introduction to the special issue. J Cave Karst Stud 74(2):135–136. https://doi.org/10.4311/2011JCKS0253
Buffle J (1988) Complexation reactions in aquatic systems: an analytical approach. Ellis Horwood, New York
Buffle J, Altmann RS, Filella M, Tessier A (1990) Complexation by natural heterogeneous compounds: site occupation distribution functions, a normalized description of metal complexation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54(6):1535–1553. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(90)90389-3
Butturini A, Guarch A, Romaní AM, Freixa A, Amalfitano S, Fazi S, Ejarque E (2016) Hydrological conditions control in situ DOM retention and release along a Mediterranean river. Water Res 99:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.04.036
Buzier R, Tusseau-Vuillemin MH, Meriadec CM, Rousselot O, Mouchel JM (2006) Trace metal speciation and fluxes within a major French wastewater treatment plant: Impact of the successive treatments stages. Chemosphere 65(11):2419–2426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.059
Carrasco F, Sánchez D, Vadillo I, Andreo B, Martínez C, Fernández L (2008) Application of the European water framework directive in a Western Mediterranean basin (Málaga, Spain). Environ Geol 54(3):575–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0852-1
Catalán N, Obrador B, Alomar C, Pretus JL (2013) Seasonality and landscape factors drive dissolved organic matter properties in Mediterranean ephemeral washes. Biogeochemistry 112(1–3):261–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-012-9723-2
Chávez-Mejía AC, Navarro-González I, Magaña-López R, Uscanga-Roldán D, Zaragoza-Sánchez PI, Jiménez-Cisneros BE (2019) Presence and natural treatment of organic micropollutants and their risks after 100 years of incidental water reuse in agricultural irrigation. Water (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102148
Cheshire MV, Russell JD, Fraser AR, Bracewell JM, Robertsons GW, Benzing-Purdie LM, Goodman BA (1992) Nature of soil carbohydrate and its association with soil humic substances. J Soil Sci 43(2):359–373
Chln Y, Alken G, Loughlins EO (1994) Molecular weight, polydispersity, and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 28(11):1853–1858. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00060a015
Constantino C, Comber SDW, Scrimshaw MD (2017) The effect of wastewater effluent derived ligands on copper and zinc complexation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(9):8363–8374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8332-3
Croué JP (2004) Isolation of humic and non-humic NOM fractions: structural characterizations. Environ Monit Assess 92:193–207
Dotson A, Westerhoff P, Krasner SW (2009) Nitrogen enriched dissolved organic matter (DOM) isolates and their affinity to form emerging disinfection by-products. Water Sci Technol 60(1):135–143. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2009.333
Duan S, Amon RMW, Brinkmeyer RL (2014) Tracing sources of organic matter in adjacent urban streams having different degrees of channel modification. Sci Total Environ 485–486(1):252–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.066
Edzwald JK (1993) Coagulation in drinking water treatment: particles, organics and coagulants. Water Sci Technol 27:21–35
El Samrani AG, Lartiges BS, Montargès-Pelletier E, Kazpard V, Barrès O, Ghanbaja J (2004) Clarification of municipal sewage with ferric chloride: the nature of coagulant species. Water Res 38(3):756–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.10.002
Farré MJ, Day S, Neale PA, Stalter D, Tang JYM, Escher BI (2013) Bioanalytical and chemical assessment of the disinfection by-product formation potential: role of organic matter. Water Res 47(14):5409–5421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.06.017
Gogu RC, Dassargues A (2000) Current trends and future challenges in groundwater vulnerability assessment using overlay and index methods. Environ Geology 39(6):549–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050466
Goldman JH, Rounds SA, Keith MK, Sobieszczyk S (2014) Investigating organic matter in Fanno Creek, Oregon, Part 3 of 3: identifying and quantifying sources of organic matter to an urban stream. J Hydrol 519:3028–3041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.07.033
Goudie A (2018) The human impact on the natural environment. Wiley, Hoboken
Hanna N, Lartiges B, Kazpard V, Maatouk E, Amacha N, Sassine S, El A, Hanna N, Lartiges B, Kazpard V, Maatouk E, Amacha N (2019) Hydrogeochemical processes in a small eastern mediterranean karst watershed ( Nahr Ibrahim, Lebanon ) To cite this version : HAL Id : hal-02265626 Hydrogeochemical processes in a small eastern mediterranean. Aquatic Geochem 24(5):325–344
Hoikkala L, Tammert H, Lignell R, Eronen-Rasimus E, Spilling K, Kisand V (2016) Autochthonous dissolved organic matter drives bacterial community composition during a bloom of filamentous cyanobacteria. Front Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2016.00111
Hosen JD, McDonough OT, Febria CM, Palmer MA (2014) Dissolved organic matter quality and bioavailability changes across an urbanization gradient in headwater streams. Environ Sci Technol 48(14):7817–7824. https://doi.org/10.1021/es501422z
Inamdar S, Singh S, Dutta S, Levia D, Mitchell M, Scott D, Bais H, Mchale P (2011) Fluorescence characteristics and sources of dissolved organic matter for stream water during storm events in a forested mid - Atlantic watershed. J Geophys Res Biogeosci. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JG001735
Jabali Y, Millet M, El-Hoz M (2020) Spatio-temporal distribution and ecological risk assessment of pesticides in the water resources of Abou Ali River, Northern Lebanon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(15):17997–18012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08089-5
Kabbara N, Benkhelil J, Awad M, Barale V (2008) Monitoring water quality in the coastal area of Tripoli (Lebanon) using high-resolution satellite data. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 63(5):488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2008.01.004
Kalscheur KN, Penskar RR, Daley AD, Pechauer SM, Kelly JJ, Peterson CG, Gray KA (2012) Effects of anthropogenic inputs on the organic quality of urbanized streams. Water Res 46(8):2515–2524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.043
Kazpard V (2008) Tracing sources of pollution in groundwater using hydrochemical and isotopic methods: beirut and its suburbs. J Environ Hydrol. 21:537
Khatib RE, Lartiges BS, Samrani AE, Faure P, Houhou J, Ghanbaja J (2012) Speciation of organic matter and heavy metals in urban wastewaters from an emerging country. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(8):4695–4708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1226-1
Khatri N, Tyagi S (2015) Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front Life Sci 8(1):23–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/21553769.2014.933716
Langmuir D (1997) Aqueous Environmental Geochemistry. Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ, New Jersey
Li S, Lu XX, He M, Zhou Y, Bei R, Li L, Ziegler AD (2011) Major element chemistry in the upper Yangtze River: a case study of the Longchuanjiang River. Geomorphology 129(1–2):29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.01.010
Louis Y, Pernet-Coudrier B, Varrault G (2014) Implications of effluent organic matter and its hydrophilic fraction on zinc(II) complexation in rivers under strong urban pressure: Aromaticity as an inaccurate indicator of DOM-metal binding. Sci Total Environ 490:830–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.123
Ly QV, Maqbool T, Hur J (2017) Unique characteristics of algal dissolved organic matter and their association with membrane fouling behavior: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(12):11192–11205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8683-4
Ma H, Allen HE, Yin Y (2001) Characterization of isolated fractions of dissolved organic matter from natural waters and a wastewater effluent. Water Res 35(4):985–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00350-X
Maatouk E (2014) Caractérisation des eaux usées au Liban: Impact sur le fonctionnement des stations d’épuration. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris-Est, France
MacCarthy P (2001) The principles of humic substances. Soil Sci 166(11):738–751. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200111000-00003
Malcolm RL, MacCarthy P (1992) Quantitative evaluation of XAD-8 and XAD-4 resins used in tandem for removing organic solutes from water. Environ Int 18(6):597–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-4120(92)90027-2
Manzano MG, Návar J (2000) Processes of desertification by goats overgrazing in the Tamaulipan thornscrub (matorral) in north-eastern Mexico. J Arid Environ 44(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.1999.0577
Massoud MA, El-Fadel M, Scrimshaw M, Lester J (2004) Land use impact on the spatial and seasonal variation of the contaminant loads to Abou Ali River and its coastal zone in North Lebanon. Agric Eng Int CIGRE J 6:1–18
Massoud MA, El-Fadel M, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2006) Factors influencing development of management strategies for the Abou Ali River in Lebanon II: seasonal and annual variation. Sci Total Environ 362(1–3):31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.09.056
Matar Z, Soares Pereira C, Chebbo G, Uher E, Troupel M, Boudahmane L, Saad M, Gourlay-France C, Rocher V, Varrault G (2015) Influence of effluent organic matter on copper speciation and bioavailability in rivers under strong urban pressure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(24):19461–19472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5110-6
Matar Z (2012) Influence de la matière organique dissoute d’origine urbaine sur la spéciation et la biodisponibilité des métaux dans les milieux récepteurs anthropisés. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris-Est, France
Merhabi F, Amine H, Halwani J (2019) Evaluation de la qualité des eaux de surface de la rivière Kadicha. J Sci Libanais 20(1):10–34
Mulholland PJ (2003) Large-scale patterns in dissolved organic carbon concentration, flux, and sources. Aquatic Ecosyst. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012256371-3/50007-x
Muresan B, Pernet-Coudrier B, Cossa D, Varrault G (2011) Measurement and modeling of mercury complexation by dissolved organic matter isolates from freshwater and effluents of a major wastewater treatment plant. Appl Geochem 26(12):2057–2063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.07.003
Mustapha H, Cherifa H, Abdelkrim H, Abdellah G, Abdelali T (2014) Assessment of water pollution in the semi-arid region: case watershed Wadi Saida (Northwest of Algeria). Desalin Water Treat 52(31–33):5995–6008. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.812984
Parise M, Closson D, Gutiérrez F, Stevanović Z (2015) Anticipating and managing engineering problems in the complex karst environment. Environ Earth Sci 74(12):7823–7835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4647-5
Park MH, Lee TH, Lee BM, Hur J, Park DH (2010) Spectroscopic and chromatographic characterization of wastewater organic matter from a biological treatment plant. Sensors 10(1):254–265. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100100254
Pernet-Coudrier B, Clouzot L, Varrault G, Tusseau-Vuillemin MH, Verger A, Mouchel JM (2008) Dissolved organic matter from treated effluent of a major wastewater treatment plant: characterization and influence on copper toxicity. Chemosphere 73(4):593–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.05.064
Pernet-Coudrier B, Varrault G, Saad M, Croue JP, Dignac MF, Mouchel JM (2011) Characterisation of dissolved organic matter in Parisian urban aquatic systems: predominance of hydrophilic and proteinaceous structures. Biogeochemistry 106(1):89–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-010-9480-z
Pernet-Coudrier B (2008) Influence de la matière organique dissoute sur la spéciation et la biodisponibilité des métaux: cas de la Seine, un milieu sous forte pression urbaine. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris-Est, France
Petrone KC, Richards JS, Grierson PF (2009) Bioavailability and composition of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in a near coastal catchment of South-Western Australia. Biogeochemistry 92(1–2):27–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-008-9238-z
Reasoner DJ (2004) Heterotrophic plate count methodology in the United States. Int J Food Microbiol 92(3):307–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2003.08.008
Rodríguez-Murillo JC, Filella M (2015) Temporal evolution of organic carbon concentrations in Swiss lakes: trends of allochthonous and autochthonous organic carbon. Sci Total Environ 520:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.085
Sarathy V, Allen HE (2005) Copper complexation by dissolved organic matter from surface water and wastewater effluent. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 61(3):337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.01.006
Seidl M (1997) Caractérisation des rejets urbains de temps de pluie et de leurs impacts sur l’oxygénation de la Seine. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées. France
Sirivedhin T, Gray KA (2005) Part I. Identifying anthropogenic markers in surface waters influenced by treated effluents: a tool in potable water reuse. Water Res 39(6):1154–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.11.032
Soares-Pereira C (2016) Influence de la matière organique dissoute d’origine urbaine sur la spéciation des micropolluants : de la station d’épuration au milieu récepteur. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris-Est. France
Stackpoole SM, Stets EG, Clow DW, Burns DA, Aiken GR, Aulenbach BT, Creed IF, Hirsch RM, Laudon H, Pellerin BA, Striegl RG (2017) Spatial and temporal patterns of dissolved organic matter quantity and quality in the Mississippi River Basin, 1997–2013. Hydrol Process 31(4):902–915. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11072
Stevenson F-J (1994) Humus chemistry: Genesis, composition, reaction, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Tessier A, Turner DR (1995) Metal speciation and bioavailability in aquatic systems. Wiley, Chichester
Thornton DCO (2014) Dissolved organic matter (DOM) release by phytoplankton in the contemporary and future ocean. Eur J Phycol 49(1):20–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2013.875596
Truchot MC et al (1994) La pollution due aux rejets urbains par temps de pluie : impacts sur les milieux récepteurs. La Houille Blanche 1–2:97–105
Tzortziou M, Zeri C, Dimitriou E, Ding Y, Jaffe R, Anagnostou E, Pitta E, Mentzafou A (2015) Colored dissolved organic matter dynamics and anthropogenic influences in a major transboundary river and its coastal wetland. Limnol Oceanogr 60(4):1222–1240. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10092
Varrault G, Parlanti E, Matar Z, Garnier J, Nguyen PT, Derenne S, Rocher V, Muresan B, Louis Y, Soares-Pereira C, Goffin A, Benedetti MF, Bressy A, Gelabert A, Guo Y, Cordier MA (2019) Aquatic Organic Matter in the Seine Basin: Sources, Spatio-Temporal Variability, Impact of Urban Discharges and Influence on Micro-pollutant. Springer, Berlin
Violleau D (1999) Intérêt du fractionnement et de l’extraction des matières organiques naturelles d’eaux de surface pour l’étude de leurs propriétés structurales et de leur pouvoir complexant vis-à-vis du cuivre. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Poitiers, France
Wang T, Wang L, Chen Q, Kalogerakis N, Ji R, Ma Y (2020) Interactions between microplastics and organic pollutants: Effects on toxicity, bioaccumulation, degradation, and transport. Sci Total Environ 748:142427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142427
Weishaar JL, Aiken GR, Bergamaschi BA, Fram MS, Fujii R, Mopper K (2003) Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37:4702–4708
Wu W, Yang J, Xu S, Yin H (2008) Applied Geochemistry Geochemistry of the headwaters of the Yangtze River, Tongtian He and Jinsha Jiang : Silicate weathering and CO 2 consumption. Appl Geochem 23(12):3712–3727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.09.005
Xue S, Zhao Q, Ma X, Li F, Wang J, Wei L (2011) Comparison of dissolved organic matter fractions in a secondary effluent and a natural water. Environ Monit Assess 180(1–4):371–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1793-9
Zheng X, Khan MT, Croué JP (2014) Contribution of effluent organic matter (EfOM) to ultrafiltration (UF) membrane fouling: Isolation, characterization, and fouling effect of EfOM fractions. Water Res 65:414–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.039
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the research grant programs of the Lebanese University (le projet est soutenu par le programme de subvention de la recherche scientifique à l’Université Libanaise). The funding source was not involved in the study design, writing of the report, and decision to submit the article for publication. We thank the research assistants of the Research and Analysis Platform for Environmental Sciences (PRASE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maatouk, E., Samrani, A.E., Sawan, R. et al. Influence of Diverse Urban Pressures on Water Characteristics in a Small Eastern Mediterranean Watershed. Aquat Geochem 28, 111–133 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-022-09405-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-022-09405-w