Abstract
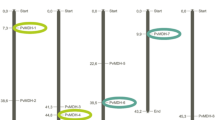
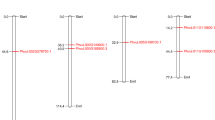
In higher plants, formate dehydrogenase (FDH, EC1.2.1.2.) catalyzes the NAD-linked oxidation of formate to CO2, and FDH transcript accumulation has been reported after various abiotic stresses. By sequencing a Phaseolus vulgaris BAC clone encompassing a CC-NBS-LRR gene rich region of the B4 resistance gene cluster, we identified three FDH-encoding genes. FDH is present as a single copy gene in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome, and public database searches confirm that FDH is a low copy gene in plant genomes, since only 33 FDH homologs were identified from 27 plant species. Three independent prediction programs (Predotar, TargetP and Mitoprot) used on this large subset of 33 plant FDHs, revealed that mitochondrial localization of FDH might be the rule in higher plants. A phylogenetic analysis suggests a scenario of local FDH gene duplication in an ancestor of the Phaseoleae followed by another more recent duplication event after bean/soybean divergence. The expression levels of two common bean FDH genes under different treatments were investigated by quantitative RT-PCR analysis. FDH genes are differentially up-regulated after biotic and abiotic stresses (infection with the fungus Colletotrichum lindemuthianum, and dark treatment, respectively). The present study provides the first report of FDH transcript accumulation after biotic stress, suggesting the involvement of FDH in the pathogen resistance process.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAC:
-
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- FDH:
-
Formate dehydrogenase
- Mya:
-
Million years ago
References
Agarwal PK, Agarwal P, Reddy MK, Sopory SK (2006) Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Rep 25:1263–1274
Allen E, Xie ZX, Gustafson AM, Sung GH, Spatafora JW, Carrington JC (2004) Evolution of microRNA genes by inverted duplication of target gene sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 36:1282–1290
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Ambard-Bretteville F, Small I, Grandjean O, Colas des Francs-Small C (2003a) Discrete mutations in the presequence of potato formate dehydrogenase inhibit the in vivo targeting of GFP fusions into mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:966–971
Ambard-Bretteville F, Sorin C, Rebeille F, Hourton-Cabassa C, Colas des Francs-Small C (2003b) Repression of formate dehydrogenase in Solanum tuberosum increases steady-state levels of formate and accelerates the accumulation of proline in response to osmotic stress. Plant Mol Biol 52:1153–1168
Bateman A, Coin L, Durbin R, Finn RD, Hollich V, Griffiths Jones S, Khanna A, Marshall M, Moxon S, Sonnhammer ELL, Studholme DJ, Yeats C, Eddy SR (2004) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D138–D141
Belkhadir Y, Subramaniam R, Dangl JL (2004) Plant disease resistance protein signaling: NBS-LRR proteins and their partners. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:391–399
Burset M, Guigo R (1996) Evaluation of gene structure prediction programs. Genomics 34:353–367
Bykova NV, Stensballe A, Egsgaard H, Jensen ON, Moller IM (2003) Phosphorylation of formate dehydrogenase in potato tuber mitochondria. J Biol Chem 278:26021–26030
Cannon SB, Sterck L, Rombauts S, Sato S, Cheung F, Gouzy J, Wang XH, Mudge J, Vasdewani J, Scheix T, Spannagl M, Monaghan E, Nicholson C, Humphray SJ, Schoof H, Mayer KFX, Rogers J, Quetier F, Oldroyd GE, Debelle F, Cook DR, Retzel EF, Roe BA, Town CD, Tabata S, Van de Peer Y, Young ND (2006) Legume genome evolution viewed through the Medicago truncatula and Lotus japonicus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14959–14964
Cao YF, Song FM, Goodman RM, Zheng Z (2006) Molecular characterization of four rice genes encoding ethylene-responsive transcriptional factors and their expressions in response to biotic and abiotic stress. J Plant Physiol 163:1167–1178
Chini A, Grant JJ, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Loake GJ (2004) Drought tolerance established by enhanced expression of the CC-NBS-LRR gene, ADR1, requires salicylic acid, EDS1 and ABI1. Plant J 38:810–822
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ (2006) Host–microbe interactions: Shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124:803–814
Claros MG, Vincens P (1996) Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur J Biochem 241:779–786
Colas des Francs-Small C, Ambard-Bretteville F, Small ID, Remy R (1993) Identification of a major soluble-protein in mitochondria from nonphotosynthetic tissues as NAD-dependent formate dehydrogenase. Plant Physiol 102:1171–1177
Cronk Q, Ojeda I, Pennington RT (2006) Legume comparative genomics: progress in phylogenetics and phylogenomics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:99–103
D’Ovidio R, Raiola A, Capodicasa C, Devoto A, Pontiggia D, Roberti S, Galletti R, Conti E, O’Sullivan D, De Lorenzo G (2004) Characterization of the complex locus of bean encoding polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins reveals subfunctionalization for defense against fungi and insects. Plant Physiol 135:2424–2435
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
David P, Sévignac M, Thareau V, Catillon Y, Kami J, Gepts P, Langin T, Geffroy V (2008) BAC end sequences corresponding to the B4 resistance gene cluster in common bean: a resource for markers and synteny analyses. Mol Genet Genomics 280:521–533
Davison D (1949) The distribution of formic and alcohol dehydrogenases in the higher plants, with particular reference to their variation in the pea plant during its life cycle. Proc Linn Soc NSW 74:26–36
Desveaux D, Singer AU, Dangl JL (2006) Type III effector proteins: doppelgangers of bacterial virulence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:376–382
Dong QF, Schlueter SD, Brendel V (2004) PlantGDB, plant genome database and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D354–D359
Doyle JJ, Luckow MA (2003) The rest of the iceberg. Legume diversity and evolution in a phylogenetic context. Plant Physiol 131:900–910
Dufresne M, Perfect S, Pellier AL, Bailey JA, Langin I (2000) A GAL4-like protein is involved in the switch between biotrophic and necrotrophic phases of the infection process of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum on common bean. Plant Cell 12:1579–1589
Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2007) Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc 2:953–971
Farinelli MP, Fry DW, Richardson KE (1983) Isolation, purification and partial characterization of formate dehydrogenase from soybean seed. Plant Physiol 73:858–859
Ferrier Cana E, Geffroy V, Macadre C, Creusot F, Imbert Bollore P, Sevignac M, Langin T (2003) Characterization of expressed NBS-LRR resistance gene candidates from common bean. Theor Appl Genet 106:251–261
Ferrier Cana E, Macadre C, Sevignac M, David P, Langin T, Geffroy V (2005) Distinct post-transcriptional modifications result into seven alternative transcripts of the CC-NBS-LRR gene JA1tr of Phaseolus vulgaris. Theor Appl Genet 110:895–905
Flor HH (1955) Host–parasite interaction in flax rust. Its genetics and other implications. Phytopathol 45:680–685
Florea L, Hartzell G, Zhang Z, Rubin GM, Miller W (1998) A computer program for aligning a cDNA sequence with a genomic DNA sequence. Genome Res 8:967–974
Friso G, Giacomelli L, Ytterberg AJ, Peltier JB, Rudella A, Sun Q, van Wijk KJ (2004) In-depth analysis of the thylakoid membrane proteome of Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts: New proteins, new functions, and a plastid proteome database. Plant Cell 16:478–499
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Noutoshi Y, Takahashi F, Narusaka Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses: a current view from the points of convergence in the stress signaling networks. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:436–442
Geffroy V, Sicard D, de Oliveira JCF, Sevignac M, Cohen S, Gepts P, Neema C, Langin T, Dron M (1999) Identification of an ancestral resistance gene cluster involved in the coevolution process between Phaseolus vulgaris and its fungal pathogen Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:774–784
Geffroy V, Sevignac M, De Oliveira JCF, Fouilloux G, Skroch P, Thoquet P, Gepts P, Langin T, Dron M (2000) Inheritance of partial resistance against Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in Phaseolus vulgaris and co-localization of quantitative trait loci with genes involved in specific resistance. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:287–296
Geffroy V, Sevignac M, Billant P, Dron M, Langin T (2008) Resistance to Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in Phaseolus vulgaris: a case study for mapping two independent genes. Theor Appl Genet 116:407–415
Geffroy V, Macadre C, David P, Pedrosa-Harand A, Sevignac M, Dauga C, Langin T (2009) Molecular analysis of a large subtelomeric NBS-LRR family in two representative genotypes of the major gene pools of Phaseolus vulgaris. Genetics 181:405–419
Grant JJ, Chini A, Basu D, Loake GJ (2003) Targeted activation tagging of the Arabidopsis NBS-LRR gene, ADR1, conveys resistance to virulent pathogens. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:669–680
Grant SR, Fisher EJ, Chang JH, Mole BM, Dangl JL (2006) Subterfuge and manipulation: Type III effector proteins of phytopathogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 60:425–449
Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JDG (1996) Resistance gene-dependent plant defense responses. Plant Cell 8:1773–1791
Hammond-Kosack KE, Parker JE (2003) Deciphering plant–pathogen communication: fresh perspectives for molecular resistance breeding. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:177–193
Hartl F-U, Pfanner N, Nicholson DW, Neupert W (1989) Mitochondrial protein import. Biochim Biophys Acta 988:1–45
Heazlewood JL, Verboom RE, Tonti-Filippini J, Small I, Millar AH (2007) SUBA: the Arabidopsis subcellular database. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D213–D218
Herman PL, Ramberg H, Baack RD, Markwell J, Osterman JC (2002) Formate dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis thaliana: overexpression and subcellular localization in leaves. Plant Sci 163:1137–1145
Hourton-Cabassa C, Ambard-Bretteville F, Moreau F, de Virville JD, Remy R, Colas des Francs-Small C (1998) Stress induction of mitochondrial formate dehydrogenase in potato leaves. Plant Physiol 116:627–635
Huang XQ, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Hurt EC, Muller U, Schatz G (1985) The 1st 12 amino-acids of a yeast mitochondrial outer-membrane protein can direct a nuclear-encoded cytochrome-oxidase subunit to the mitochondrial inner membrane. EMBO J 4:3509–3518
Igamberdiev AU, Bykova NV, Kleczkowski LA (1999) Origins and metabolism of formate in higher plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 37:503–513
Innes RW, Ameline-Torregrosa C, Ashfield T, Cannon E, Cannon S, Chacko B, Chen NWG, Couloux A, Dalwani A, Denny R, Deshpande S, Egan AN, Glover N, Hans CS, Howell S, Ilut D, Jackson S, Lai H, Mammadov J, Martin del Campo S, Metcalf M, Nguyen A, O’Bleness M, Pfeil BE, Podicheti R, Ratnaparkhe MB, Samain S, Sanders I, Segurens B, Sevignac M, Sherman-Broyles S, Thareau V, Tucker DM, Walling J, Wawrzynski A, Yi J, Doyle JJ, Geffroy V, Roe BA, Saghai Maroof MA, Young ND (2008) Differential accumulation of retroelements and diversification of NB-LRR disease resistance genes in duplicated regions following polyploidy in the ancestor of soybean. Plant Physiol 148:1740–1759
Jiang SY, Ramamoorthy R, Bhalla R, Luan HF, Venkatesh PN, Cai M, Ramachandran S (2008) Genome-wide survey of the RIP domain family in Oryza sativa and their expression profiles under various abiotic and biotic stresses. Plant Mol Biol 67:603–614
Kami J, Poncet V, Geffroy V, Gepts P (2006) Development of four phylogenetically-arrayed BAC libraries and sequence of the APA locus in Phaseolus vulgaris. Theor Appl Genet 112:987–998
Kleffmann T, Russenberger D, von Zychlinski A, Christopher W, Sjolander K, Gruissem W, Baginsky S (2004) The Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplast proteome reveals pathway abundance and novel protein functions. Curr Biol 14:354–362
Langlois-Meurinne M, Gachon CMM, Saindrenan P (2005) Pathogen-responsive expression of glycosyltransferase genes UGT73B3 and UGT73B5 is necessary for resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:1890–1901
Lavin M, Herendeen PS, Wojciechowski MF (2005) Evolutionary rates analysis of Leguminosae implicates a rapid diversification of lineages during the tertiary. Syst Biol 54:575–594
Li R, Ziola B, King J (2000) Purification and characterization of formate dehydrogenase from Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 157:161–167
Li R, Bonham-Smith PC, King J (2001) Molecular characterization and regulation of formate dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Can J Bot 79:796–804
Li R, Moore M, Bonham-Smith PC, King J (2002) Overexpression of formate dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis thaliana resulted in plants tolerant to high concentrations of formate. J Plant Physiol 159:1069–1076
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lopez CE, Acosta IF, Jara C, Pedraza F, Gaitan-Solis E, Gallego G, Beebe S, Tohme J (2003) Identifying resistance gene analogs associated with resistances to different pathogens in common bean. Phytopathology 93:88–95
Lukashin AV, Borodovsky M (1998) GeneMark.hmm: new solutions for gene finding. Nucleic Acids Res 26:1107–1115
Martin GB, Bogdanove AJ, Sessa G (2003) Understanding the functions of plant disease resistance proteins. Ann Rev Plant Biol 54:23–61
McHale L, Tan XP, Koehl P, Michelmore RW (2006) Plant NBS-LRR proteins: adaptable guards. Genome Biol 7:212
Melotto M, Coelho MF, Pedrosa Harand A, Kelly JD, Camargo LEA (2004) The anthracnose resistance locus Co-4 of common bean is located on chromosome 3 and contains putative disease resistance-related genes. Theor Appl Genet 109:690–699
Nicholls P (1975) Formate as an inhibitor of cytochrome-C oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 67:610–616
Olson B, Skavdahl M, Ramberg H, Osterman JC, Markwell J (2000) Formate dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis thaliana: characterization and possible targeting to the chloroplast. Plant Sci 159:205–212
Popov VO, Lamzin VS (1994) NAD(+)-Dependent formate dehydrogenase. Biochem J 301:625–643
Radwan O, Gandhi S, Heesacker A, Whitaker B, Taylor C, Plocik A, Kesseli R, Kozik A, Michelmore RW, Knapp SJ (2008) Genetic diversity and genomic distribution of homologs encoding NBS-LRR disease resistance proteins in sunflower. Mol Genet Genomics 280:111–125
Rairdan G, Moffett P (2007) Brothers in arms? Common and contrasting themes in pathogen perception by plant NB-LRR and animal NACHT-LRR proteins. Microbes Infect 9:677–686
Ramirez M, Graham MA, Blanco-Lopez L, Silvente S, Medrano-Soto A, Blair MW, Hernandez G, Vance CP, Lara M (2005) Sequencing and analysis of common bean ESTs. Building a foundation for functional genomics. Plant Physiol 137:1211–1227
Robert-Seilaniantz A, Navarro L, Bari R, Jones JD (2007) Pathological hormone imbalances. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:372–379
Rossi M, Araujo PG, Paulet F, Garsmeur O, Dias VM, Chen H, Van Sluys MA, D’Hont A (2003) Genomic distribution and characterization of EST-derived resistance gene analogs (RGAs) in sugarcane. Mol Genet Genomics 269:406–419
Rutherford K, Parkhill J, Crook J, Horsnell T, Rice P, Rajandream MA, Barrell B (2000) Artemis: sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics 16:944–945
Sato S, Nakamura Y, Kaneko T, Asamizu E, Kato T, Nakao M, Sasamoto S, Watanabe A, Ono A, Kawashima K, Fujishiro T, Katoh M, Kohara M, Kishida Y, Minami C, Nakayama S, Nakazaki N, Shimizu Y, Shinpo S, Takahashi C, Wada T, Yamada M, Ohmido N, Hayashi M, Fukui K, Baba T, Nakamichi T, Mori H, Tabata S (2008) Genome structure of the legume, Lotus japonicus. DNA Res 15:227–239
Sessa G, Yang XQ, Rat V, Eyal Y, Fluhr R (1995) Dark induction and subcellular-localization of the pathogenesis-related PRB1-1b protein. Plant Mol Biol 28:537–547
Shoemaker RC, Schlueter J, Doyle JJ (2006) Paleopolyploidy and gene duplication in soybean and other legumes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:104–109
Small I, Peeters N, Legeai F, Lurin C (2004) Predotar: A tool for rapidly screening proteomes for N-terminal targeting sequences. Proteomics 4:1581–1590
Sudo E, Itouga M, Yoshida-Hatanaka K, Ono Y, Sakakibara H (2008) Gene expression and sensitivity in response to copper stress in rice leaves. J Exp Bot 59:3465–3474
Suzuki K, Itai R, Suzuki K, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa NK, Yoshimura E, Mori S (1998) Formate dehydrogenase, an enzyme of anaerobic metabolism, is induced by iron deficiency in barley roots. Plant Physiol 116:725–732
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Thunberg T (1921) Sur la presence de certains ferments oxydants dans les grains de Phaseolus vulgaris. Arch Int Physiol 18:601–606
Uotila L, Koivusalo M (1979) Purification of formaldehyde and formate dehydrogenases from pea seeds by affinity chromatography and S-formylglutathione as the intermediate of formaldehyde metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys 196:33–45
van Dijken JP, Oostra-Demkes GT, Otto R, Harder W (1976) S-formylglutathione: the substrate for formate dehydrogenase in methanol-utilizing yeasts. Arch Microbiol 111:77–83
van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CMJ (2006) Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:135–162
von Heijne G (1986) Mitochondrial targeting sequences may form amphiphilic helices. EMBO J 5:1335–1342
Young ND, Cannon SB, Sato S, Kim D, Cook DR, Town CD, Roe BA, Tabata S (2005) Sequencing the genespaces of Medicago truncatula and Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol 137:1174–1181
Yurimoto H, Lee B, Yano T, Sakai Y, Kato N (2003) Physiological role of S-formylglutathione hydrolase in C-1 metabolism of the methylotrophic yeast Candida boidinii. Microbiology Sgm 149:1971–1979
Zhu HY, Cannon SB, Young ND, Cook DR (2002) Phylogeny and genomic organization of the TIR and non-TIR NBS-LRR resistance gene family in Medicago truncatula. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:529–539
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Steven B. Cannon for critical reading of the manuscript. They also thank Mathilde Langlois-Meurinne and Claire Gachon for helpful discussions and Jim Kami and Paul Gepts for providing us the Phaseolus vulgaris BAT93 FY-N24 BAC clone. Special thanks to Georgina Hernández for sharing ESTs data prior to publication. The research was supported by INRA-DGAP, CNRS and the French Ministère de la Recherche.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. T. Nguyen.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2010_1293_MOESM3_ESM.ppt
Multiple alignment performed on 36 FDH deduced amino acid sequences using the Clustal X software and edited in GENEDOC for manual adjustments. Details concerning the origin of the 36 FDH sequences are given in Supplementary Table 1. Peptide signal, as defined on the potato Z21493 sequence (Colas des Francs et al. 2003), is indicated. The multiple alignment used for phylogenetic analyses is based on the region between the two black arrows (PPT 233 kb)
122_2010_1293_MOESM4_ESM.ppt
Analysis of the flanking sequences of the three FDH genes. Hatched areas designate regions presenting > 38% nucleotide identity. Size in base pair of each considered region is indicated in brackets (PPT 165 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
David, P., Colas des Francs-Small, C., Sévignac, M. et al. Three highly similar formate dehydrogenase genes located in the vicinity of the B4 resistance gene cluster are differentially expressed under biotic and abiotic stresses in Phaseolus vulgaris . Theor Appl Genet 121, 87–103 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1293-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1293-x