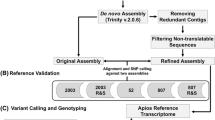
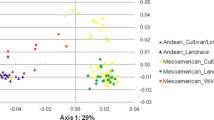
Abstract
The APA family of seed proteins consists of three subfamilies, in evolutionary order of hypothesized appearance: phytohaemagglutinins (PHA), α-amylase inhibitors (αAI), and arcelins (ARL). The APA family plays a defensive role against mammalian and insect seed predation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). The main locus (APA) for this gene family is situated on linkage group B4. In order to elucidate the pattern of duplication and diversification at this locus, we developed a BAC library in each of four different Phaseolus genotypes that represent presumptive steps in the evolutionary diversification of the APA family. Specifically, BAC libraries were established in one P. lunatus (cv. ‘Henderson: PHA+ αAI− ARL−) and three P. vulgaris accessions (presumed ancestral wild G21245 from northern Peru: PHA+ αAI + ARL−; Mesoamerican wild G02771: PHA+ αAI + ARL+; and Mesoamerican breeding line BAT93: PHA+ αAI + ARL−). The libraries were constructed after HindIII digestion of high molecular weight DNA, obtained with a novel nuclei isolation procedure. The frequency of empty or cpDNA-sequence-containing clones in all libraries is low (generally <1%). The Henderson, G21245, and G02771 libraries have a 10× genome coverage, whereas the BAT93 library has a 20× coverage to allow further, more detailed genomic analysis of the bean genome. The complete sequence of a 155 kbp-insert clone of the G02771 library revealed six sequences belonging to the APA gene family, including members of the three subfamilies, as hypothesized. The different subfamilies were interspersed with retrotransposon sequences. In addition, other sequences were identified with similarity to chloroplast DNA, a dehydrin gene, and the Arabidopsis flowering D locus. Linkage between the dehydrin gene and the D1711 RFLP marker identifies a potential syntenic region between parts of common bean linkage group B4 and cowpea linkage group 2




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Gallegos J, Quintero C, Vargas J, Toro O, Tohme J, Cardona C (1998) A new variant of arcelin in wild common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris L., from southern Mexico. Genet Res Crop Evol 45:235–242
Aravind L, Iyer LM (2002) The SWIRM domain: a conserved module found in chromosomal proteins points to novel chromatin-modifying activities. Genome Biol 3: research0039.0031–0039.0037
Broughton WJ, Hernandez G, Blair M, Beebe S, Gepts P, Vanderleyden J (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.)—model food legumes. Plant and Soil 252:55–128
Chrispeels MJ, Raikhel NV (1991) Lectins, lectin genes, and their role in plant defense. Plant Cell 3:1–9
Colucci G, Moore J, Feldman M, Chrispeels M (1999) cDNA cloning of FRIL, a lectin from Dolichos lablab, that preserves hematopoietic progenitors in suspension culture. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 96:646–650
Delgado-Salinas A, Turley T, Richman A, Lavin M (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of the cultivated and wild species of Phaseolus (Fabaceae). Syst Bot 24:438–460
Dubcovsky J, Ramakrishna W, SanMiguel PJ, Busso CS, Yan L, Shiloff BA, Bennetzen JL (2001) Comparative sequence analysis of colinear barley and rice bacterial artificial chromosomes. Plant Physiology 125:1342–1353
Ewing B, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 8:186–194
Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl M, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res 8:175–185
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:9–13
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1984)A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity (addendum). Anal Biochem 137:266–267
Ferrier-Cana E, Macadre C, Sevignac M, David P, Langin T, Geffroy V (2005) Distinct post-transcriptional modifications result into seven alternative transcripts of the CC-NBS-LRR gene JA1tr of Phaseolus vulgaris. Theor Appl Genet 110:895–905
Finardi-Filho F, Mirkov T, Chrispeels M (1996) A putative precursor protein in the evolution of the bean α-amylase inhibitor. Phytochemistry 43:57–62
Freyre R, Skroch PW, Geffroy V, Adam-Blondon A-F, Shirmohamadali A, Johnson W, Llaca V, Nodari RO, Pereira P, Tsai S-M, Tohme J, Dron M, Nienhuis J, Vallejos CE, Gepts P (1998) Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean. 4. Development of a core map and alignment of RFLP maps. Theor Appl Genet 97:847–856
Freytag GF, Debouck DG (2002) Taxonomy, distribution, and ecology of the genus Phaseolus (Leguminosae—Papilionoideae) in North America, Mexico and Central America, edn. Botanical Research Institute of Texas, Forth Worth, TX
Geffroy V, Sévignac M, De Oliveira J, Fouilloux G, Skroch P, Thoquet P, Gepts P, Langin T, Dron M (2000) Inheritance of partial resistance against Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in Phaseolus vulgaris and co-localization of QTL with genes involved in specific resistance. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:287–296
Gepts P (1998) Origin and evolution of common bean: past events and recent trends. HortScience 33:1124–1130
Gepts P (1999) Development of an integrated genetic linkage map in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and its use. In: S. Singh (ed) Bean breeding for the 21st century. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 53–91, 389–400
Gepts P, Beavis WD, Brummer EC, Shoemaker RC, Stalker HT, Weeden NF, Young ND (2005) Legumes as a model plant family. Genomics for food and feed Report of the Cross-Legume Advances through Genomics Conference. Plant Physiol 137:1228–1235
Goossens A, Geremia R, Bauw G, Van Montagu M, Angenon G (1994) Isolation and characterisation of arcelin-5 proteins and cDNAs. Eur J Biochem 225:787–795
Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P (1998) Consed: A graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res 8:195–202
Gutiérrez Salgado A, Gepts P, Debouck D (1995) Evidence for two gene pools of the lima bean, Phaseolus lunatus L., in the Americas. Genet Res Crop Evol 42:15–22
Hall AE (2004) Breeding for adaptation to drought and heat in cowpea. Eur J Agron 21:447–454
He Y, Michaels SD, Amasino RM (2003) Regulation of flowering time by histone acetylation in Arabidopsis. Science 302:1751–1754
Ho MF, Yin X, Finardi Filho F, Lajolo F, Whitaker JR (1994) Naturally occurring α-amylase inhibitors: structure/function relationships. In: Yada R, Jackman LR, Smith J (eds) Protein structure-function relationships in food Bishopbriggs. Blackie Academic and Professional, Glasgow, pp 89–119
Hoffman LM, Donaldson DD (1985) Characterization of two Phaseolus vulgaris phytohemagglutinin genes closely linked on the chromosome. EMBO J 4:883–889
Hoffman LM, Ma Y, Barker RF (1982) Molecular cloning of Phaseolus vulgaris lectin mRNA and use of cDNA as a probe to estimate lectin transcript levels in various tissues. Nucl Acids Res 10:7819–7828
Ismail AM, Hall AE, Close TJ (1999) Allelic variation of a dehydrin gene cosegregates with chilling tolerance during seedling emergence. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 96:13566–13570
John ME, Long CM (1990) Sequence analysis of arcelin 2, a lectin-like plant protein. Gene 86:171–176
Kami J, Becerra Velásquez B, Debouck DG, Gepts P (1995) Identification of presumed ancestral DNA sequences of phaseolin in Phaseolus vulgaris. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 92:1101–1104
Kelly JD, Gepts P, Miklas PN, Coyne DP (2003) Tagging and mapping of genes and QTL and molecular marker-assisted selection for traits of economic importance in bean and cowpea. Field Crops Res 82:135–154
Koinange EMK, Singh SP, Gepts P (1996) Genetic control of the domestication syndrome in common-bean. Crop Sci 36:1037–1045
Kuehl R (1964) Isolation of plant nuclei. Z Naturforsch, B: Anorg Chem, Org Chem, Biochem Biophys Biol 198:525–534
Lioi L, Sparvoli F, Galasso I, Lanave C, Bollini R (2003) Lectin-related resistance factors against bruchids evolved through a number of duplication events. Theor Appl Genet 107:814–822
Llaca V, Delgado Salinas A, Gepts P (1994) Chloroplast DNA as an evolutionary marker in the Phaseolus vulgaris complex. Theor Appl Genet 88:646–652
Llaca V, Gepts P (1996) Pulsed field gel electrophoresis analysis of the phaseolin locus region in Phaseolus vulgaris. Genome 39:722–729
Melotto M, Coelho MF, Pedrosa-Harand A, Kelly JD, Camargo LEA (2004) The anthracnose resistance locus Co-4 of common bean is located on chromosome 3 and contains putative disease resistance-related genes. Theor Appl Genet 109:690–699
Minney B, Gatehouse A, Dobie P, Dendy J, Cardona C, Gatehouse A (1990) Biochemical bases of seed resistance to Zabrotes subfasciatus (bean weevil) in Phaseolus vulgaris (common bean)—a mechanism for arcelin toxicity. J Insect Phys 36:757
Mirkov TE, Wahlstrom JM, Hagiwara K, Finardi-Filho F, Kjemtrup S, Chrispeels MJ (1994) Evolutionary relationships among proteins in the phytohemagglutinin-arcelin-alpha-amylase inhibitor family of the common bean and its relatives. Plant Mol Biol 26:1103–1113
Moreno J, Chrispeels MJ (1989) A lectin gene encodes the α-amylase inhibitor of the common bean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7885–7889
Nodari RO, Tsai SM, Gilbertson RL, Gepts P (1993) Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean. II. Development of an RFLP-based linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 85:513–520
Noutsos C, Richly E, Leister D (2005) Generation and evolutionary fate of insertions of organelle DNA in the nuclear genomes of flowering plants. Genome Res 15:616–628
Osborn TC, Alexander DC, Sun SSM, Cardona C, Bliss FA (1988) Insecticidal activity and lectin homology of arcelin seed protein. Science 240:207–210
Osborn TC, Blake T, Gepts P, Bliss FA (1986) Bean arcelin. 2. Genetic variation, inheritance and linkage relationships of a novel seed protein of Phaseolus vulgaris. Theor Appl Genet 71:847–855
Ouédraogo JT, Gowda BS, Jean M, Close TJ, Ehlers JD, Hall AE, Gillaspie AG, Roberts PA, Ismail AM, Bruening G, Gepts P, Timko MP, Belzile FJ (2002) An improved genetic linkage map for cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) combining AFLP, RFLP, RAPD, biochemical markers, and biological resistance traits. Genome 45:175–188
Peterson DG, Tomkins JP, Frisch DA, Wing RA, Paterson AH (2000) Construction of plant bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) libraries: an illustrated guide. J Agric Genomics 5: (http://www.ncgr.org/research/jag)
Pueyo JJ, Delgado-Salinas A (1997) Presence of α-amylase inhibitor in some members of the subtribe Phaseolinae (Phaseoleae: Fabaceae). Am J Bot 84:79–84
Pusztai A (1991) Plant lectins. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 263
Romero-Andreas J, Yandell BS, Bliss FA (1986) Bean arcelin. 1. Inheritance of a novel seed protein of Phaseolus vulgaris L. and its effect on seed composition. Theor Appl Genet 72:123–128
Rougé P, Barre A, Causse H, Chatelain C, Porthe G (1993) Arcelin and alpha-amylase inhibitor from the seeds of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) are truncated lectins. Biochem Syst Evol 21:696–703
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Santimone M, Koukiekolo R, Moreau Y, Le Berre V, Rougé P, Marchis-Mouren G, Desseaux V (2004) Porcine pancreatic α-amylase inhibition by the kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) inhibitor (α-AI1) and the structural changes in the α-amylase inhibitor complex. Biochim Biophys Acta 1696:181–190
Sparvoli F, Bollini R (1998) Arcelin in wild bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seeds: sequence of arcelin 6 shows it is a member of the arcelins 1 and 2 subfamily. Genet Res Crop Evol 45:383–388
Suzuki K, Ishimoto M, Kikuchi F, Kitamura K (1993) Growth inhibitory effect of an alpha-amylase inhibitor from the wild common bean resistant to the Mexican bean weevil (Zabrotes subfasciatus). Japan J Breed 43:257–265
Suzuki K, Ishimoto M, Kitamura K (1994) cDNA sequence and deduced primary structure of an α-amylase inhibitor from a bruchid resistant wild common bean. Biochim Biophys Acta 1206:289–291
Suzuki K, Ishimoto M, Iwanaga M, Kikuchi F, Kitamura K (1995) Inheritance of seed α-amylase inhibitor in the common bean and genetic relationships to arcelin. Theor Appl Genet 90:762–766
Talbot D, Adang M, Slightom J, Hall T.C. (1984) Size and organization of a multigene family encoding phaseolin, the major seed storage protein of Phaseolus vulgaris L Mol. Gen Genet 198:42–49
Toth EC, Vissi E, Kovacs I, Szoke A, Arino J, Gergely P, Dudits D, Dombradi V (2000) Protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme and its subunits from Medicago sativa. Plant Mol Biol 43:527–536
Vallejos CE, Astua-Monge G, Jones V, Plyler T, Sakiyama N, Vanhoutten W, Mackenzie S (2004) Abstract 25003: Genetic and molecular characterization of the I locus of Phaseolus vulgaris. American Society of Plant Biologists Annual Meeting July 24–28, 2004, Lake Buena Vista, FL. http://www.abstracts.aspb.org/pb2004/public/M12/7715.html
Vanhouten W, Mackenzie S (1999) Construction and characterization of a common bean bacterial artificial chromosome library. Plant Molec Biol 40:977–983
Voelker T, Sturm A, Chrispeels M (1987) Differences in expression between seed lectin alleles obtained from normal and lectin-deficient beans are maintained in transgenic tobacco. EMBO J 6:3571–3577
Young ND, Cannon SB, Sato S, Kim D, Cook DR, Town CD, Roe BA, Tabata S (2005) Sequencing the genespaces of Medicago truncatula and Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol 137:1174–1181
Zhang HB, Zhao X, Ding X, Paterson AH, Wing RA (1995) Preparation of megabase-size DNA from plant nuclei. Plant J 7:175–184
Acknowledgments
BAC sequencing was performed at the Purdue Genomics Core Facility by Phillip San Miguel and Paul Parker. The project was supported by the National Research Initiative of the USDA Cooperative State Research, Education and Extension Service, grant number #00–01972.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. J. Muehlbauer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kami, J., Poncet, V., Geffroy, V. et al. Development of four phylogenetically-arrayed BAC libraries and sequence of the APA locus in Phaseolus vulgaris . Theor Appl Genet 112, 987–998 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0201-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0201-2