Abstract
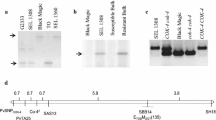
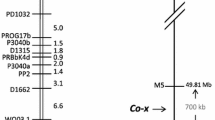
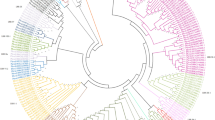
The broadest based resistance to anthracnose of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is conferred by the Co-4 locus. We sequenced a bacterial artificial chromosome clone harboring part of the Co-4 locus of the bean genotype Sprite and assembled a single contig of 106.5 kb for functional annotation. This region contained five copies of the COK-4 gene that encodes for a serine threonine kinase protein previously mapped to the Co-4 locus and 19 novel genes with no similarity to any previously identified genes of common bean. Several putative genes of the Co-4 locus seemed to be expressed as they matched perfectly with bean expressed sequence tags. The expression of the COK-4 genes was assessed by reverse transcription (RT)-PCR, and a single 850-bp cDNA fragment was sequenced and compared with the genomic sequences of the COK-4 homologs. Although the COK-4 cDNA was isolated from a different bean cultivar, it showed high similarity (95%) to the exons of genes BA17 and BA21, suggesting that they were expressed. In a phylogenetic tree including all currently available Pto-like sequences from Phaseolus species, the COK-4 homologs formed a single cluster with the Pto gene, whereas two sequences from P. coccineus and all sequences of P. vulgaris formed two closely related clusters. The Co-4 locus was physically mapped to the short arm of bean chromosome 3, which corresponds to linkage group B8. This study represents a first step in gaining an understanding of the genomic organization of an anthracnose resistance locus of common bean and provides molecular data for comparative analysis with other plant species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer A, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped blast and psi-blast: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bassett MJ (1994) Tight linkage of purple pod character and the complex C locus in common bean. J Hered 85:288–290
Bateman A, Birney E, Cerruti L, Durbin R, Etwiller L, Eddy SR, Griffiths-Jones S, Howe KL, Marshall M, Sonnhammer EL (2002) The Pfam protein family database. Nucleic Acids Res 30:276–280
Beninger CW, Bassett MJ, Owens S, Hosfield GL (2000) Chemical and morphological expression of the B and Asp seedcoat genes in Phaseolus vulgaris. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 125:52–58
Bent AF (1996) Plant disease resistance genes: function meets structure. Plant Cell 8:1757–1771
Boyes DC, Nam J, Dangl JL (1998) The Arabidopsis thaliana RPM1 disease resistance gene product is a peripheral plasma membrane protein that is degraded coincident with the hypersensitive response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15849–15854
Burge C, Karlin S (1997) Prediction of complete gene structure in human genomic DNA. J Mol Biol 268:78–94
Delgado IJ, Wang Z, Rocher A de, Keegstra K, Raikhel NV (1998) Cloning and characterization of AtRGP1, a reversibly autoglycosylated Arabidopsis protein implicated in cell wall biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 116:1339–1349
Dhugga KS, Tiwari SC, Ray PM (1997) A reversibly glycosylated polypeptide (RGP1) possibly involved in plant cell wall synthesis: purification, gene cloning and trans Golgi localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7679–7684
Dixon MS, Golstein C, Thomas CM, van der Biezen EA, Jones JDG (2000) Genetic complexity of pathogen perception by plants: The example of Rcr3, a tomato gene required specifically by Cf-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8807–8814
Ewing B, Green P (1998) Base calling of automated sequencer traces using Phred. II error probabilities. Genome Res 8:186–194
Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl M, Green P (1998) Base calling of automated sequencer traces using Phred. I accuracy assessment. Genome Res 8:175–185
Falquet L, Pagni M, Bucher P, Hulo N, Sigrist CJ, Hofmann K, Bairoch A (2002) The prosite database, its status in 2002. Nucleic Acids Res 30:235–238
Frediani M, Cremonini R, Salvi G, Caprari C, Desiderio A, D’Ovidio R, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G (1993) Cytological localization of the PGIP genes in the embryo suspensor cells of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Theor Appl Genet 87:369–373
Freyre R, Skroch PW, Geffroy V, Adam-Blondon A-F, Shirmohamadali A, Johnson WC, Llaca V, Nodari RO, Pereira PA, Tsai S-M, Tohme J, Dron M, Nienhuis J, Vallejos CE, Gepts P (1998) Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean 4. Development of a core linkage map and alignment of RFLP maps. Theor Appl Genet 97:847–856
Fujiwara H, Tanaka Y, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Nakao M, Fukui Y, Yamaguchi M, Ashikari T, Kusumi T (1998) cDNA cloning, gene expression and subcellular localization of anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase from Gentiana triflora. Plant J 16:421–431
Gantet P, Bettini P, Grisvard J, Dron M (1991) Genetic linkage between Mex2, a specific resistance gene to anthracnose, and Anp, a gene involved in pod anthocyanin accumulation in bean. Plant Dis 75:941–942
Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P (1998) consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res 8:195–202
Gough J, Karplus K, Hughey R, Chothia C (2001) Assignment of homology to genome sequences using a library of Hidden Markov Models that represent all proteins of known structure. J Mol Biol 313:903–919
Graham MA, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC (2002) Organization, expression and evolution of a disease resistance gene cluster in soybean. Genetics 162:1961–1977
Greenberg JT (1997) Programmed cell death in plant pathogen interactions. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:525–545
Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JD (1997) Plant disease resistance genes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:575–607
Heslop-Harrison JS, Schwarzacher T, Anamthawat-Jónsson K, Leitch AR, Shi M, Leitch IJ (1991) In situ hybridization with automated chromosome denaturation. Technique 3:109–115
Heslop-Harrison JS, Harrison GE, Leitch IJ (1992) Reprobing of DNA:DNA in situ hybridization preparations. Trends Genet 8:372–373
Howden R, Goldsbrough PB, Andersen CS, Cobbett CS (1995) Cadmium-sensitive, cadl mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana are phytochelatin deficient. Plant Physiol 107:1059–1066
Jia Y, MacAdams SA, Brian GT, Hershey HP, Valent B (2000) Direct interaction between resistance gene and avirulence gene products confers rice blast resistance. EMBO J 19:4004–4014
Kelly JD, Gepts P, Miklas PN, Coyne DP (2003) Tagging and mapping of genes and QTL and molecular marker-assisted selection for traits of economic importance in bean and cowpea. Field Crops Res 82:135–154
Kessmann H, Choudhary AD, Dixon RA (1990) Stress response to alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) III. Induction of medicarpin and cytochrome P450 enzyme activities in elicitor-treated cell suspension and protoplast. Plant Cell Rep 9:38–41
Llaca V, Gepts P (1996) Pulse field gel electrophoresis analysis of the phaseolin locus region in Phaseolus vulgaris. Genome 39:722–729
Martin GB, Brommonschenkel SH, Chunwongse J, Frary A, Ganal MW, Spivey R, Wu T, Earle ED, Tanksley SD (1993) Map-based cloning of a protein kinase gene conferring disease resistance in tomato. Science 262:1432–1436
McClean P, Lee R, Otto C, Gepts P, Bassett M (2002) Molecular and phenotypic mapping of genes controlling seed coat pattern and color in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Hered 93:148–152
Melotto M, Kelly JD (2001) Fine mapping of the Co-4 locus reveals a resistance gene candidate, COK-4, that encodes for a protein kinase. Theor Appl Genet 103:508–517
Melotto M, Afanador L, Kelly JD (1996) Development of a SCAR marker linked to the I gene in common bean. Genome 39:1216–1219
Melotto M, Balardin RS, Kelly JD (2000) Host-pathogen interaction and variability of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. In: Prusky D, Freeman S, Dickman MB (eds) Colletotrichum host specificity, pathology, and host-pathogen interaction. APS Press, St Paul, Minn., pp 346–361
Oh B-J, Ko MK, Kim YS, Kim KS, Kostenyuk I, Kee HK (1999) A cytochrome P450 gene is differentially expressed in compatible and incompatible interactions between pepper (Capsicum annum) and anthracnose fungus, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:1044–1052
Parniske M, Hammond-Kosaki KE, Golstein C, Thomas CM, Jones DA, Harrison K, Wulff BB, Jones JD (1997) Novel disease resistance specificities result from sequence exchange between tandemly repeated genes at the Cf4/9 locus of tomato. Cell 91:821–832
Pedrosa A, Jantsch MF, Moscone EA, Ambros PF, Schweizer D (2001) Characterization of pericentromeric and sticky intercalary heterochromatin in Ornithogalum longibracteatum (Hyacinthaceae). Chromosoma 110:203–213
Pedrosa A, Sandal N, Stougaard J, Schweizer D, Bachmair A (2002) Chromosomal map of the model legume Lotus japonicus. Genetics 161:1661–1672
Pedrosa A, Vallejos CE, Bachmair A, Schweizer D (2003) Integration of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) linkage and chromosomal maps. Theor Appl Genet 106:205–212
Ronald PC (1998) Resistance gene evolution. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:294–298
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP* Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer, Sunderland, Mass.
Temple SR, Morales FJ (1986) Linkage of dominant hypersensitive resistance to bean common mosaic virus to seed color in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Euphytica 35:331–333
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) clustalw: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Toppi LS di, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Uchiumi T, Kuwashiro R, Miyamoto J, Abe M, Higashi S (1998) Detection of the leghemoglobin gene on two chromosomes of Phaseolus vulgaris by in situ PCR linked-fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). Plant Cell Physiol 39:790–794
Vallad G, Rivkin M, Vallejos C, McClean P (2001) Cloning and homology modeling of a Pto-like protein kinase family of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 103:1046–1058
Vallejos CE, Sakiyama NS, Chase CD (1992) A molecular marker-based linkage map of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Genetics 131:733–740
Vanhouten W, MacKenzie S (1999) Construction and characterization of a common bean bacterial artificial chromosome library. Plant Mol Biol 40:977–983
Wang Y-H, Choi W, Thomas CE, Dean RA (2002) Cloning of disease-resistance homologues in end sequences of BAC clones linked to Fom-2, a gene conferring resistance to Fusarium wilt in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Genome 45:473–480
Wei F, Wing RA, Wise RP (2002) Genome dynamics and evolution of the Mla (powdery mildew) resistance locus in barley. Plant Cell 14:1903–1917
Wheeler DL, Church DM, Federhen S, Lash AE, Madden TL, Pontius JU, Schuler GD, Schrimi LM, Sequeira E, Tatusove TA, Wagner L (2003) Database resources of the national center for biotechnology. Nucleic Acids Res 31:28–33
Yang Z-N, Ye X-R, Molina J, Roose ML, Mirkov TE (2003) Sequence analysis of a 282-kilobase region surrounding the citrus tristeza virus resistance gene (Ctv) locus in Poncirus tifoliata L. Raf. Plant Physiol 131:482–492
Young RA, Melotto M, Nodari RO, Kelly JD (1998) Marker-assisted dissection of the oligogenic anthracnose resistance in the common bean cultivar, ‘G2333’. Theor Appl Genet 96:87–94
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Sally MacKenzie (University of Nebraska) for screening her BAC library with the SAS13 marker and kindly donating the four homologous BAC clones, Dr. Carlos Eduardo Vallejos (University of Florida) for providing seeds of the cultivar Calima and the RFLP clones from the University of Florida linkage map, and Dr. Dieter Schweizer (University of Vienna) for supporting the participation of A.P.-H in this project. We thank Dr. Claudia B. Monteiro-Vitorello for assisting with the assembly of the DNA contig, Dr. Jorge L.M. Rodrigues and Dr. Sheng Yang He for helpful suggestions and critical review of the manuscript, and Daniela Truffi and Maria Cristina R. Rangel for assisting with DNA sequencing. M.M. acknowledges financial support for this project from FAPESP—Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Brazil (Grant 00/09049-2). Research at L.E.A. Camargo’s lab is supported by funds from FAPESP (Grant 00/09059-8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Möllers
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melotto, M., Coelho, M.F., Pedrosa-Harand, A. et al. The anthracnose resistance locus Co-4 of common bean is located on chromosome 3 and contains putative disease resistance-related genes. Theor Appl Genet 109, 690–699 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1697-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1697-6