Abstract
Background
Malaria remains highly endemic in Cameroon. The rapid emergence and spread of drug resistance was responsible for the change from monotherapies to artemisinin-based combinations. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the prevalence and distribution of Plasmodium falciparum drug resistance markers within an evolving efficacy of anti-malarial drugs in Cameroon from January 1998 to August 2020.
Methods
The PRISMA-P and PRISMA statements were adopted in the inclusion of studies on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of P. falciparum anti-malarial drug resistance genes (Pfcrt, Pfmdr1, Pfdhfr, Pfdhps, Pfatp6, Pfcytb and Pfk13). The heterogeneity of the included studies was evaluated using the Cochran’s Q and I2 statistics. The random effects model was used as standard in the determination of heterogeneity between studies.
Results
Out of the 902 records screened, 48 studies were included in this aggregated meta-analysis of molecular data. A total of 18,706 SNPs of the anti-malarial drug resistance genes were genotyped from 47,382 samples which yielded a pooled prevalence of 35.4% (95% CI 29.1–42.3%). Between 1998 and 2020, there was significant decline (P < 0.0001 for all) in key mutants including Pfcrt 76 T (79.9%-43.0%), Pfmdr1 86Y (82.7%-30.5%), Pfdhfr 51I (72.2%-66.9%), Pfdhfr 59R (76.5%-67.8%), Pfdhfr 108 N (80.8%-67.6%). The only exception was Pfdhps 437G which increased over time (30.4%-46.9%, P < 0.0001) and Pfdhps 540E that remained largely unchanged (0.0%-0.4%, P = 0.201). Exploring mutant haplotypes, the study observed a significant increase in the prevalence of Pfcrt CVIET mixed quintuple haplotype from 57.1% in 1998 to 57.9% in 2020 (P < 0.0001). In addition, within the same study period, there was no significant change in the triple Pfdhfr IRN mutant haplotype (66.2% to 67.3%, P = 0.427). The Pfk13 amino acid polymorphisms associated with artemisinin resistance were not detected.
Conclusions
This review reported an overall decline in the prevalence of P. falciparum gene mutations conferring resistance to 4-aminoquinolines and amino alcohols for a period over two decades. Resistance to artemisinins measured by the presence of SNPs in the Pfk13 gene does not seem to be a problem in Cameroon.
Systematic review registration PROSPERO CRD42020162620
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Globally, malaria accounted for 228 million cases and 405,000 related deaths in 2018 [1]. Malaria remains highly endemic in Cameroon despite the adoption, implementation and deployment of different controls measures by the government and her partners [1]. In Cameroon, the rapid emergence and spread of anti-malarial drug resistance was responsible for the replacement of chloroquine (CQ) as the first-line therapy for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in 2002 and later on amodiaquine (AQ) monotherapy/sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine between 2002 and 2004 [2]. A major drug policy change occurred in 2004 following the adoption of artesunate-amodiaquine (ASAQ) and later included artemether–lumefantrine (AL) in 2006 as first-line treatments of uncomplicated malaria in line with World Health Organization (WHO) recommendations [2, 3]. The artemisinin-based combinations, ASAQ and AL, are distributed in the proportions of 75% and 25%, respectively to public, faith-based and private health facilities [4]. In the Northern Regions of Cameroon, malaria transmission is intense and seasonal when compared to the Southern Regions characterized with perennial malaria transmission. In 2016, the government of Cameroon implemented seasonal malaria chemoprevention (SMC) in the Northern Regions [5]. This prevention strategy involves the yearly administration of four doses of sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine–amodiaquine (SPAQ) to vulnerable children within the age group 3–59 months [5]. Additionally, SP is still being used as an intermittent preventive treatment in pregnant (IPTp) women from the second to the third trimester. The women receive at least 3 doses during pregnancy, with each dose (three tablets of 500 mg sulfadoxine and 25 mg pyrimethamine) given at least 1 month apart [6, 7]. Both SPAQ and SP are also subsidized by the government of Cameroon. The large-scale deployment of the SMC and IPTp strategies is a major contributory factor to drug pressure which drives the emergence of P. falciparum resistant parasites.
Furthermore, the efficacy of anti-malarial drugs is linked to the presence or absence of parasites resistant to artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) and non-ACT in the population. Thus, the regular monitoring of drug resistance markers through molecular surveillance or clinical trials can be used by malaria control programmes in endemic regions to secure the high efficacy of the different anti-malarial drugs. The use of advanced molecular biology techniques has greatly facilitated the identification of key amino acid changes in the genes of P. falciparum chloroquine resistant transporter-Pfcrt (C72S, V73K, M74I, N75E, K76T, A220S, Q271E, N326S, I356T, R371I) [8], P. falciparum multi-drug resistant 1-Pfmdr1 (N86Y, Y184F, S1034C, N1042D, D1246Y, copy number variation) [8], P. falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-Pfdhfr (A16V, C50R, N51I, C59R, S108N/T) [9,10,11] and P. falciparum dihydropteroate synthase-Pfdhps (I431V, S436A/F, A437G, K540E/N, A581G, A613S/T) [12] associated with resistance to different anti-malarial drugs. The presence of Pfcrt K76T is associated with increased risk of treatment failure after administration of chloroquine whereas, Pfmdr1 N86Y is associated with both chloroquine and amodiaquine resistance [13]. The haplotypes of the Pfcrt gene defined by the K76T codon and adjacent amino acids (numbers 72–75) have been used in the typing of malaria parasites [14]. Among the over fifteen haplotypes identified, three predominate namely: CVMNK among CQ-sensitive isolates from all geographic regions, CVIET among CQ-resistant isolates from Southeast Asia and Africa, and SVMNT among CQ-resistant isolates from South America, Africa and some countries of Asia [14,15,16]. For sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine the Pfdhfr single (S108N), triple haplotype mutants (S108N, N51I, C59R) and Pfdhfr-Pfdhps quintuple haplotype mutants (S108N, N51I, C59R, A437G, K540E) have been shown to increase the risk of treatment failure [13]. It has also been documented that increased Pfmdr1 copy number is correlated with resistance to mefloquine [17] and reduced sensitivity to lumefantrine [18,19,20]. A study on AL and ASAQ showed opposing effects for Pfcrt K76T and Pfmdr1 N86Y [21]. This was further confirmed by another study on the selection of Pfmdr1 NFD haplotype for AL and Pfmdr1 YYY haplotype for ASAQ from samples of efficacy studies conducted in Africa that led to reduced sensitivities of the two drugs [22].
In 2014, single nucleotide polymorphisms in the Pfk13 propeller domain of Cambodian parasite isolates were reported to be associated with delayed parasite clearance of artemisinins [23]. The epicentres driving the emergence and dispersal of artemisinin resistance have been identified in countries within the Greater Mekong sub-region (GMS) namely, Cambodia, China (Yunnan Province), Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam [24]. Presently, about 200 non-synonymous mutations in the K13 gene have been identified and reported [24,25,26,27]. A total of 9 Pfk13 non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (F446I, N458Y, N458Y, Y493H, R539T, I543T, P553L, R561H, C580Y) have been validated with F446I, R539T, I543T, P574L and C580Y being the most common and with the highest occurrences [24, 25, 27]. There are 11 candidate gene polymorphisms associated with delayed parasite clearance [24, 25, 27]. A number of mutations have also been reported outside the K13 propeller region notably, K189T and E252Q [25, 28,29,30]. In Africa, the Pfk13 mutation with the highest geographical distribution is A578S [25, 26, 31] and the presence of R561H mutation has recently been reported in Tanzania [32] and Rwanda [33]. Hence, there are fears that ACT resistance may spread to other regions including sub-Saharan Africa where malaria is still a major burden, similar to what happened in the past with the chloroquine, amodiaquine, and sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine. The rationale for the use of ACT relies on the rapid reduction of the parasite biomass, reduction of transmission (reducing gametocytes), protection of partner drug against resistance, and rapid fever reduction [34]. The effect of drug policy changes on the selection of P. falciparum anti-malarial drug resistant parasites in Cameroon has not been completely understood. Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the prevalence and distribution of P. falciparum drug resistance markers within an evolving efficacy of anti-malarial drugs in Cameroon from January 1998 to August 2020.
Methods
Registration of the systematic review and protocol development
In December 2019, a review protocol (#CRD42020162620) was developed and registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO: http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero). The protocol was submitted for publication to a peer review journal. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses Protocol (PRISMA-P) [35, 36] was used in the development of the protocol for this systematic review and meta-analysis.
Search strategy
An electronic systematic strategy based on the combination of key words was used to search articles from Medline via Pubmed, Google Scholar, and Science Direct databases. Both interventional and observational studies were retrieved for inclusion in the review. The following MeSH search terms were combined using the Boolean operators “OR” and “AND’’: “anti-malarial”, “drug resistance”, “Pfcrt”, “Pfmdr1”, “Pfmdr1 copy number”, “Pfdhfr”, “Pfdhps”, “Pfatp6”, “Pfcytb”, “Pfk13”, “mutations”, “gene polymorphisms”, “amino acid changes”, “Plasmodium falciparum”, “efficacy”, “artesunate-amodiaquine”, “artemether–lumefantrine”, “sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine” “Cameroon”.
Additional searches
The reference lists of published articles were searched for eligible studies. Authors were contacted when access to full length articles was restricted. Data was also obtained from the annual reports of the Cameroon National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP), Ministry of Public Health. In addition to published studies, unpublished Medical Doctor (MD), Master of Science (MSc) and Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) theses were sourced for inclusion in the study.
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria
The systematic review and meta-analysis included the following type of studies: studies published from January 1998 to August 2020; studies on human participants of all ages; original articles of studies that investigated either asymptomatic, uncomplicated or severe P. falciparum; studies that included PCR genotyping of anti-malarial drug molecular resistance markers (Pfcrt, Pfmdr1, Pfmdr1 copy number, Pfdhfr, Pfdhps, Pfcytb, Pfatp6, Pfk13); studies written in English or French; studies done within Cameroon: all multi-centric studies in which Cameroon was one of the sites, and studies in which malaria was imported from Cameroon into other countries.
Exclusion criteria
The following types of studies were not included: abstracts; studies on in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo anti-malarial drug resistance without genotyping; genetic studies on Pfcg2 gene; studies on genetic diversity and population structure of P. falciparum without drug resistance; studies on diagnostic accuracy of methods for detection of P. falciparum and studies on infections with mixed Plasmodium species.
Review process
Research articles identified from searches of the electronic databases were screened for eligibility based on their titles and abstracts. Ineligible articles and duplicates were eventually removed. Full-length articles of the selected studies were read to confirm for fulfilling of the inclusion criteria before data extraction began. Two independent reviewers (Peter Thelma Ngwa Niba-PTNN and Lesley Ngum Ngum-LNN) screened the titles and abstracts to identify potentially eligible studies and data extracted from full-length articles that fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Discrepancies were resolved by mutual consent after discussion and independent review from the third researcher (Akindeh Mbuh Nji-AMN). The whole process was supervised by Wilfred Fon Mbacham (WFM) and Michael Alifrangis (MA).
Data extraction procedure
The “Microsoft” Excel 2010 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, Washington, United States of America) was used to design the data extraction sheet. The data extraction form was produced and consisted of study identification number, author (s), study site, sample size, age group (in months and years), study design (interventional and observational), genotyping method, sequence genotyping success rate, anti-malarial drug resistance gene, total number of samples genotyped, number of samples genotyped with mutations, and prevalence of molecular markers. The database in Microsoft Excel was piloted and validated before completion of the process (Additional file 1).
Mixed genotypes were considered as mutants during data collation on frequency of mutations derived from different studies. Studies (observational or interventional) published multiple times in similar topics by the same authors were diligently screened to avoid duplication of data. These studies were differentiated based on primary variables (anti-malarial drug resistance markers and frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms) containing the datasets of interest. The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) checklist for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses was used as a guide for this study [37].
Data items
The selection and inclusion of studies was done according to the PICOS format. This approach includes: population (P), individuals infected P. falciparum parasites in Cameroon, intervention (I), use of non-artemisinin and artemisinin agents in the treatment of malaria, comparator (C), none, outcome (O), Pfcrt, Pfmdr1, Pfdhfr, Pfdhps, Pfk13 gene polymorphisms circulating in malaria endemic areas of Cameroon, study design (S), observational studies (cross-sectional, case reports, cohorts) and interventional studies such as randomized controlled trials reporting on the use of P. falciparum DNA infected samples collected before anti-malarial treatment (D0) and during follow-ups of study participants.
Data management
The Zotero Standalone software package version 5.0.56 (Corporation for Digital Scholarship, Vienna, Virginia, USA) was used to review, import full articles and delete duplicates.
Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment of individual studies included
The quality of randomized clinical trials was assessed by the revised Cochrane risk of bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2.0) [38]. The RoB 2 is structured into five bias domains namely: bias arising from the randomization process, bias due to deviations from intended interventions, bias due to missing outcome data, bias in measurement of the outcome, and bias in selection of the reported result. The overall quality of the randomized clinical trial was judged as “low risk” of bias score when all the key domains in the assessment of bias were found to be of low risk. When one of the key domains in the bias assessment was found to have some concerns, a scoring of “some concerns” was rendered. The assessment of at least one key domain of bias with a high risk in a study accorded it to be of “high risk” of bias (Additional file 2). The quality of cohort studies was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS), which included eight items related to selection, comparison, and outcome. For each item a star is awarded except for comparison that can receive up to two stars. The studies with six stars (maximum of nine) were classified as good quality (Additional file 3) [39]. Finally, the quality of included cross-sectional studies and case reports was assessed by the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Checklists for Cross-sectional [40] and Case Reports [41] which consist of eight yes/no/unclear questions. The overall quality of cross-sectional and case reports were grouped into the following categories: low risk of bias (studies that met at least 75% of the quality criteria), moderate risk of bias (studies that met between 50 and 74% of the quality criteria) and high risk of bias (studies that met less than 49% of the quality criteria) (Additional files 4 and 5) [42].
Two reviewers (Peter Thelma Ngwa Niba-PTNN and Cyrille Mbanwi Mbu'u-CMM) independently assessed the risk of bias of included studies. Disagreements between the reviewers at the different stages of the review were resolved by discussion.
Data analysis, heterogeneity assessment and data interpretation
Quantitative syntheses (meta-analyses) were done using the “metaphor” and “meta” packages in the R statistical software version 3.5.2 (supported by the R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). The conventional meta-analysis approach from pooled patient data was adopted for the synthesis. The heterogeneity of the included studies was evaluated using the Cochran’s Q and I2 statistics. The random effects model was used as standard in the determination of heterogeneity between studies [43]. The I2 values were expressed in percentages. Heterogeneity was classified as low, moderate and high, with upper limits of 25%, 50% and 75% for I2, respectively [44].
Data derived from an article published by one author or same authors in a particular year were merged before presentation on forest plots. Forest plots were used to present the data on pooled prevalence of mutations in anti-malarial drug resistance genes. Subgroup analyses were also done to show the aggregated prevalence of Pfcrt K76T, Pfmdr1 N86Y, Pfdhfr IRN haplotype, Pfdhfr-Pfdhps IRNG haplotype and Pfk13 gene mutations in cases where number of studies were greater than or equal to 5. The evolution of resistance markers and haplotypes over time was summarized on frequency tables.
The pre and post-ACT intervention periods were considered to be 1998–2004 and 2005–2020 respectively. The criterion for choosing these periods was based on 2004, the year in which the first ACT was adopted for use in Cameroon. In the analysis to compare SNPs between the two or more study periods, mixed infections with both the wild type and the mutant were all considered mutants. Haplotypes were defined as a combination of two or more wild type alleles, mutant alleles or mixed. These haplotypes included Pfcrt CVMNK, Pfcrt CVIET, Pfdhfr IRN, Pfdhfr-Pfdhps IRNG, and Pfdhfr-Pfdhps IRNGE.
The Pearson Chi square test in the International Business Machine Software Package for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS) version 20.0 software package (IBM Corporation, Armonk, New York, USA) was used to establish the evolution of drug resistance markers over time.
The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to check for normal distribution of quantitative variable data. Furthermore, the relationships between the efficacy of ACT medicines (ASAQ and AL) and anti-malarial drug resistance makers (Pfcrt 76 T and Pfmdr1 86Y) were represented on plots. The Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r) was used to assess the strength and direction of the association between the efficacy of ACT medicines (AL and ASAQ) and the prevalence of Pfcrt 76 T and Pfmdr1 86Y mutants over time. In addition, a trend analysis to explore the relationship between proportions of anti-malarial drugs (ASAQ, AL and SP) deployed in Cameroon and prevalence of drug resistance markers (Pfcrt 76 T, Pfmdr1 86Y and Pfdhfr IRN) from 2006 to 2017 was also explored using r. The standard range for r values is between -1 and + 1. The level of significance was set at p < 0.05 at 95% confidence interval and two-tailed.
Assessment of publication bias across studies
The risk of publication bias in the included articles was assessed using the asymmetry of funnel plot and Egger’s regression test with P < 0.05. The funnel plot contained the standard error on the y-axis and proportion on the x-axis (Additional file 6).
Results
Study identification, screening and selection process
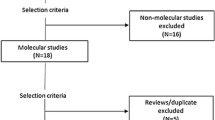
The electronic searches identified a total of 902 published articles on anti-malarial drug resistance markers in Cameroon. There were three additional unpublished citations from theses of students and one article was derived through contact with a senior researcher on malaria disease. A total of 907 studies were identified, after which 298 duplicates were removed. A total of 609 studies were screened to remove abstract and non-malaria studies, with 427 studies retained after the process. The 427 studies were checked for eligibility, with 48 studies included for both qualitative and quantitative analyses (Fig. 1).
Characteristics of studies included in the review
Participants of all age groups ranging from 0 months to 80 years and both gender were included in the study. Out of 48 studies included, 44 studies [26, 28, 30, 45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85] were obtained from published articles and 4 from unpublished data. A total of 38 (79.2%) were carried out only in Cameroon, 7 (14.6%) were studies of imported malaria cases from African countries including Cameroon, and 3 (6.3%) were multi-centric studies including Cameroon. The studies were performed in all the geo-ecological zones constituted from the 10 Regions of Cameroon, that is, Sudano-Sahelian, tropical, and equatorial. Majority of these studies (n = 25 (52.1%)) were conducted in Yaoundé. Most of the studies (n = 25 (52.1%)) were derived from observational studies while the remaining studies were randomized controlled clinical trials. The main methods used for genotyping were nested polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (nPCR-RFLP), DNA sequencing by Sanger (sequencing by dideoxy-chain termination method) and quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction. Others methods included sequence specific oligonucleotide probe, polymerase chain reaction, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (SSOP PCR ELISA), dot blot, and DNA sequencing using Illumina HiSeq platform. A total of seven P. falciparum drug resistance genes datasets were created for quantitative syntheses with the following distribution of studies: Pfcrt (n = 17), Pfmdr1 (n = 15), Pfdhfr (n = 21), Pfdhps (n = 13), Pfcytb (n = 1), Pfatp6 (n = 2) and Pf13 (n = 7) (Additional file 1).
Heterogeneity of included studies
The assessment of heterogeneity was done for all the groups containing different studies on P. falciparum single nucleotide polymorphisms that confer resistance to anti-malarial drugs. There was high heterogeneity across all the groups: pooled prevalence of all drug resistance markers (Q(df = 41) = 43,100.1, I2 = 99%, P < 0.0001), Pfcrt K76T (Q(df = 20) = 999.5, I2 = 96%, P < 0.0001), Pfcrt CVIET (Q(df = 8) = 1588.9, I2 = 94%, P < 0.0001), Pfmdr1 N86Y (Q(df = 15) = 1745.4, I2 = 97%, P < 0.0001), Pfdhfr IRN (Q(df = 25) = 4943.6, I2 = 96%, P < 0.0001), Pfdhfr-Pfdhps IRNG (Q(df = 10) = 64.4, I2 = 84%, P < 0.0001), and Pfk13 (Q(df = 6) = 72.1, I2 = 90%, P < 0.0001).
Pooled prevalence of P. falciparum anti-malarial drug resistance mutations
There were 18,706 SNPs of anti-malarial drug resistance markers genotyped from 47,382 samples which yielded a pooled prevalence of 35.4% (95% CI 29.1–42.3%). The DNA sequence genotyping success rate varied from 45.1% to 100.0% while the prevalence of mutations ranged from 0.0 to 100.0% (Additional file 1 and Fig. 2).
The key amino acid substitutions represented in the analyses were: Pfcrt (C72S, V73K, M74I, N75E, K76T, A220S, Q271E, N326S, I356T, R371I), Pfmdr1 (N86Y, Y184F, S1034C, N1042D, D1246Y, copy number variation), Pfdhfr (A16V, C50R, N51I, C59R, S108N/T) and Pfdhps (I431V, S436A/F, A437G, K540E, A581G, A613S/T). Only two studies recorded the presence of Pfdhps I431V with prevalence rates of 16.3% and 18.3% [30, 60]. One study reported the presence of Pfdhps K142N mutation with a prevalence of 8.5% not previously documented in Cameroon [30]. For Pfk13, the amino acid polymorphisms associated with artemisinin resistance in Southeast Asia were not detected in any of the 5912 P. falciparum samples genotyped and most of Pfk13 gene polymorphisms reported here have not been observed anywhere in the world. The most prevalent non-validated Pfk13 missense polymorphisms were K189T reported in 2 studies with prevalence rates of 21.2% and 35.9% [28, 30] (Additional file 1).
Subgroup analyses revealed that the aggregated prevalence of Pfcrt K76T, Pfcrt CVIET, Pfmdr1 N86Y, Pfdhfr IRN, and Pfk13 genes were 64.6% (2094/3402) [95% CI 54.2–73.8%], 42.3% (446/855) [95% CI 24.3–62.6%], 62.4% (1268/2088) [95% CI 44.7–77.4%], 71.7% (3114/4673) [95% CI 61.8–79.8%], 41.8% (348/926) [95% CI 30.3–54.2%] and 2.0% (83/5912) [95% CI 0.7–5.4%] respectively (Fig. 3a–f).
a Subgroup analysis for pooled prevalence of Pfcrt K76T mutation from 1998 to 2020. b Subgroup analysis for pooled prevalence of Pfcrt CVIET haplotype mutations from 1998–2020. c Subgroup analysis for pooled prevalence of Pfmdr1 N86Y haplotype mutations from 1998 to 2020. d Subgroup analysis for pooled prevalence of Pfdhfr IRN haplotype mutations from 1998 to 2020. e Subgroup analysis for pooled prevalence of Pfdhfr-Pfdhps IRNG haplotype mutations from 1998 to 2020. f Subgroup analysis for pooled prevalence of Pfk13 mutations from 1998 to 2020
Temporal changes of the key gene polymorphisms conferring resistance to anti-malarial drugs prior to and after adoption of artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) in Cameroon
The pre-ACT and post-ACT interventions were considered as periods before and after 2004 respectively. There was a significant decline in Pfcrt 76 T mutant alleles from 79.9% in 1998–2004 to 43.0% and 62.1% in 2005–2010 and ≥ 2017, respectively, with a slight increase of 67.5% recorded between 2011 and 2016 (P < 0.0001). Similarly, during the same study periods, the prevalence of the Pfmdr1 86Y mutant allele decreased significantly from 82.7% to 30.5% (P < 0.0001) with the exception observed between 2011 and 2016 when 90.6% was reported (Table 1).
The only Pfcrt haplotypes reported in Cameroon were: CVMNK in 10 studies, CVIET in 6 studies and SVMNT in one study. The highest frequencies recorded were: CVMNK-85.7% [66], CVIET-93.7% [48], and SVMNT-4.4% [59] (Additional file 3). There was an increase in the prevalence of the Pfcrt CVMNK wild type haplotype from 7.7% in 1998–2004 to 20.0% in 2005–2010. However, a decrease of 15.9% was observed between 2010 and 2020. Generally, there was a significant increase in the prevalence rate of the CVMNK haplotype from 7.7% in 1998 to 40.2% in 2020 (P < 0.0001). The CVIET mutant haplotype declined from 57.1% in 1998–2004 to 0.0% in 2005–2010. The prevalence rate increased to 36.7% and 57.9% respectively in 2011–2016 and 2017–2020. Similarly, there was a significant increase in the prevalent rate of Pfcrt CVIET haplotype between 1998 and 2020 (P < 0.0001) (Table 2).
Within the Pfmdr1 gene only the triple NFD haplotype was reported in 2 studies conducted in Mutengene [45, 57] with prevalence rates of 25.2% and 72.2%. The YFY and YYY triple haplotypes were not reported in any of the studies included (Additional file 3). Between the two time points 1998–2008 and 2009–2020, there was a significant drop (P < 0.0001) in the Pfdhfr (51I 72.2–66.9%, 59R 76.5–67.8%, 108 N 80.8–67.6%) mutant alleles whereas, the Pfdhps (437G 30.4–46.9%, P < 0.0001, 540E 0.0–0.4%, P = 0.201) mutant alleles increased over the two time points (Table 3).
An evaluation of gene polymorphisms of the Pfdhfr revealed that the triple IRN mutant haplotype was the most reported in 18 studies with the minimum prevalence of 4.3% [79] and a maximum prevalence of 100.0% [54, 58]. Only 10 studies reported the quadruple IRNG mutant haplotype involving Pfdhfr and Pfdhps with the highest prevalence of 95.9% [60]. Moreover, Pfdhfr/Pfdhps quintuple haplotype IRNGE was identified in 3 studies [58, 60, 79] with a maximum prevalence of 16.7% [58] (Additional file 7).
The Pfdhfr IRN and Pfdhfr/Pfdhps IRNGE haplotypes remained largely unchanged from 66.2% to 67.3 (P = 0.427) and 0.0% to 0.3% (P = 0.623), respectively, between 1998 and 2020. Conversely, a significant decrease in trend from 47.5% to 28.7% was reported for Pfdhfr-Pfdhps IRNG under the same period (P < 0.0001) (Table 4).
Distribution of antifolate haplotypes across geo-ecological zones of Cameroon
The forest and Sudano-Sahelian zones constitute the major geo-ecological zones of Cameroon. The characteristics of these geo-ecological zones are reflected in the towns of Yaoundé, Mutengene and Garoua. Different studies were conducted in Yaoundé, Mutengene and Garoua from 2004–2006 in order to understand the evolutionary origins of the antifolate haplotypes [46, 86]. The prevalence of Pfdhfr CIRN mixed haplotype in the different towns was distributed as follows: Yaounde-70.7%, Mutengene-83.2% and Garoua-21.3%. The Pfdhps SGK mixed haplotype was also common in Yaounde-36.3% and Mutengene-66.4% with the least occurrence reported in Garoua-8.3%. The SGK was associated with SP resistance at these three sites. The wild-type alleles (SAK and AAK) were mostly noticeable in Garoua, Yaoundé and Mutengene, respectively. The CIRN haplotype was highly prevalent in the Southern part when compared to the Northern part of Cameroon.
Generally, opposing trends were observed in the haplotypes SGK, AGK, AAK, SAK, CIRN, CNCS, CICN, and CNRN in malaria parasites isolated from Garoua, Yaoundé and Mutengene. Data is not available on these unique mixed haplotypes from other regions in Cameroon (Fig. 4).
Efficacy of ACTs (AL and ASAQ) and prevalence of Pfcrt 76 T and Pfmdr1 86Y mutants over time
A total of 13 (3 unpublished and 10 published) studies were used to derive the data on the efficacy (PCR-corrected cure rates) of AL and ASAQ [87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96]. The efficacy rates for AL and ASAQ were above 90.0% and remained relatively constant from 2008–2019. On the contrary, there was a general decline in the Pfcrt 76 T and Pfmdr1 86Y mutant alleles between 2008 and 2019 which were more pronounced between 2012 and 2016 for Pfmdr1 and between 2016 and 2019 for Pfcrt 76 T. The efficacy of AL showed a positive but non-significant correlation with Pfcrt 76 T mutant allele (r = 0.512, P = 0.073) while the efficacy of AL demonstrated a negative non-significant relationship with Pfmdr1 86Y mutant allele (r = −0.107, P = 0.728). However, there was a negative significant correlation between the efficacy of ASAQ and prevalence rates of Pfcrt 76 T mutant allele (r = −0.949, P < 0.0001) and Pfmdr1 86Y mutant allele (r = −0.657, P = 0.015). Generally, the prevalence of Pfcrt 76 T and Pfmdr1 86Y mutant alleles were below the efficacy rates of ASAQ and AL (Fig. 5). This showed that increase in mutant alleles corresponded with decrease in efficacy of ACTs and vice versa.
Trend analysis of proportions of anti-malarial drugs (ASAQ, AL and SP) deployed in Cameroon and prevalence of drug resistance markers from 2006 to 2017
The proportion of ASAQ, AL and SP was based on the observed frequency of each drug deployed to the different health facilities in Cameroon by the NMCP through CENAME and the Regional Funds for Health Promotions. The data was derived from annual reports published by the NMCP. Between 2006 and 2017, there was an increase in the proportion of ASAQ (6.6%-84.6%). Peak distributions for ASAQ were observed in 2010 (99.7%) and 2013 (86.5%) with corresponding prevalence of Pfcrt 76 T (65.2%, 59.0%) and Pfmdr1 86Y (57.3%, 54.7%) mutants. The proportions of AL distributed from 2006 to 2017 were low when compared with ASAQ. The maximum proportion of AL deployed was 33.1% in 2011 and this corresponded with a prevalence of 55.5% and 46.4% for Pfcrt 76 T and Pfmdr1 86Y mutants respectively. The Pearson correlation coefficients revealed negative relationships between the ACTs and anti-malarial drug resistance markers [(ASAQ versus Pfcrt 76 T, r = − 0.460, P = 0.133; ASAQ versus Pfmdr1 86Y, r = 0.464, P = − 0.129), (AL versus Pfcrt 76 T, r = − 0.584, P = 0.046; AL versus Pfmdr1 86Y, r = − 0.415, P = 0.180) (Fig. 6a).
a Proportion of ASAQ and AL deployed in Cameroon versus prevalence of Pfcrt 76 T and Pfmdr1 86Y mutants from 2006 to 2017. ASAQ: Artesunate-amodiaquine, AL, Artemether–lumefantrine; Pfcrt, Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter gene; Pfmdr1, Plasmodium falciparum, multidrug resistance 1 gene. b Proportion of SP deployed in Cameroon versus prevalence of Pfdhfr IRN mutant haplotype from 2006 to 2017. SP, Sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine, Pfcrt, Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter gene, Pfmdr1, Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance 1 gene
The proportion of SP deployed to the different Regions of Cameroon dropped from 93.4% in 2006 to 11.1% in 2017 which corresponded with the prevalence of 62.2% and 99.6% of Pfdhfr IRN triple mutant haplotype. There was a negative correlation between proportion of SP deployed and prevalence of Pfdhfr IRN triple mutant haplotype (r = − 0.423, P = 0.171).
Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis showed the frequency and geographic distribution of anti-malarial drug resistance markers over a period of three decades in Cameroon. The present study showed that the pooled prevalence of all the amino acid changes from 1998 to 2020 was 35.4%. Subgroup analyses revealed that the aggregated prevalence of Pfcrt K76T, Pfmdr1 N86Y, Pfdhfr IRN, and Pfdhfr-Pfdhps IRNG were above 40.0% with the exception of Pfk13. These analyses highlight the dominance of Pfcrt K76T, Pfmdr1 N86Y, Pfdhfr N51I, Pfdhfr C59R, Pfdhfr S108N, Pfdhps A437G and Pfk13 K189T mutations. The rates are high and further confirm that resistant parasites are still circulating in towns, such as Yaoundé, Garoua, Mutengene, and Buea. This is not surprising considering some of these towns (Yaoundé, Mutengene and Buea) are located within the high malaria transmission stratum and are urban settings with high variability and intensity in the use of anti-malarial drugs with insufficient regulation. It is also around these areas that the first cases of resistance to chloroquine were reported in the 1980s and early 2000 that eventually spread to other Regions [97,98,99,100]. The dispersal of drug resistance markers could be due to human and vector population migration within the same Region or between different Regions. The presence of drug resistance markers has been regularly reported in the Southern Regions of Cameroon where malaria transmission is perennial compared to the Northern Regions characterized by intense seasonal transmission.
Previous studies have demonstrated the association of Pfcrt 76 T and Pfmdr1 86Y mutant alleles with chloroquine and amodiaquine resistance in vivo among uncomplicated falciparum malaria patients in different transmission settings [8, 13]. These two drugs, chloroquine and amodiaquine were banned and withdrawn from the market since 2002 and 2004 respectively for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Cameroon. However, amodiaquine (AQ) continues to be used as a partner drug in the artesunate-amodiaquine (ASAQ) and sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine–amodiaquine (SPAQ) combinations. In 2004, ASAQ combination replaced AQ and SP for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in the Southern Regions while SPAQ was introduced in 2016 as chemoprophylaxis in the context of seasonal malaria chemoprevention among children 3–59 months in the North and Far north Regions of Cameroon. The most common quintuple haplotypes identified in Pfcrt gene were CVMNK and CVIET. This concords with previously published studies in other regions [101, 102]. It is important to note that one study reported the presence of Pfcrt SVMNT haplotype with a prevalence of 4.4% [59], which is lower than the 19.0% [15] and 56.9% [14] reported in the Korogwe District, Tanzania and Luanda, Angola, respectively.
Only two studies reported the triple Pfmdr1 NFD haplotype [45, 57] while the triple Pfmdr1 YYY haplotype was not documented. A number of studies carried out in malaria endemic areas have demonstrated an opposing effect in the selection of YYY for ASAQ and NFD for AL [22, 103]. This is advantageous to Cameroon since ASAQ and AL are used as multiple first-line treatments (MFTs) that can possibly slow down the emergence of drug resistance [104].
Trend analysis showed that Pfcrt 76 T, Pfcrt CVMNK quintuple wild type haplotype, and Pfmdr1 86Y mutant parasites declined from 1998–2020. This is in agreement with previous studies carried out in other malaria endemic zones confirming the re-emergence of chloroquine sensitive parasites [101, 102, 105]. However, there should be caution in the future use of chloroquine in the treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria because this may lead to reintroduction of resistant parasites population.
In Cameroon, sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine (SP) is still being deployed as intermittent preventive treatment for malaria in pregnancy (IPTp) with estimated coverage of about 32% in 2018 [106]. The antifolates are also used in combination with amodiaquine for seasonal malaria chemoprevention. The presence of mutations in Pfdhfr and Pfdhps genes conferring resistance to SP does not seem to threaten the continuous use of this drug in the future especially as there is need to scale-up deployment to pregnant women and young children as intermittent preventive treatment (IPTp and IPTi). This may also be applicable for children receiving SPAQ in the context of seasonal malaria chemoprevention in the Sahel regions of Northern Cameroon. The triple Pfdhfr IRN and quadruple Pfdhfr/Pfdhps IRNG mutant haplotypes were the most prevalent while quintuple Pfdhfr/Pfdhps IRNGE mutant haplotype was the least prevalent. There has been a gradual decline over the years in the prevalence of single antifolate gene polymorphisms associated with SP resistance in Cameroon with the exception of Pfdhps A437G and K540E. However, the rates of prevalence recorded are less than the 90% benchmark recommended by the WHO to ban the continuous use of SP. These findings corroborate with the high prevalence of Pfdhfr IRN and Pfdhfr/Pfdhps IRNG recorded in Bata District and Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea [107, 108]. There has been a gradual increase in the prevalence of the quintuple Pfdhfr/Pfdhps IRNGE mutant haplotype over the years, ascertaining the sudden emergence of the haplotype in Central Africa [107]. Other underreported Pfdhps haplotypes included SGK, AGK, SGE, AAK, and SAK. These haplotypes were extensively studied in isolates from different African countries including Cameroon by Pearce and colleagues, where they sought to investigate the evolutionary origin of the mutations flanking the Pfdhps gene [86]. The authors observed that the haplotypes in the Cameroonian samples were unique when compared to those from Central, South-eastern and West African sites [86]. The malaria parasite resistance to SP seems to be driving in opposite directions with high resistance recorded in the Southern Regions when compared to the Northern Regions. The location of these sites in different malaria transmission settings may be accountable for the variations observed.
A new mutation, I431V, recently identified in the Pfdhps gene has been reported in Yaoundé [60] and Mutengene [57] with prevalence rates of 16.3% and 18.3%, respectively. These rates are lower than that reported in Enugu Nigeria (46.0%) in 2016 [109], suggesting the possibility of different mutant haplotypes associated with SP treatment failure in Central/West Africa. This is unlike previous observations in East Africa where the quintuple Pfdhfr/Pfdhps IRNGE mutant haplotype is strongly associated is SP resistance [110].
There was the absence of key gene polymorphisms located in the Pfk13 propeller region, F446I, R539T, I543T, P574L and C580Y previously documented in the Greater Mekong sub-region which are associated with delayed parasite clearance following drug administration. Moreover, a negative or positive relationship was observed between the rate of efficacy of ASAQ/AL and the prevalence of key mutants (Pfcrt K76T and Pfmdr1 N86Y) that select for the partner drugs in ACT. These observations confirm the findings that AL and ASAQ exert opposing selective effects on single-nucleotide polymorphisms in Pfcrt and Pfmdr1 [21]. However, ASAQ and AL are still efficacious with rates of efficacy above the WHO minimum cut-off of 90%.
It has been shown that some individuals infected with drug resistant parasites are still able to clear the parasites when administered with non-ACT and ACT [111, 112]. This may be due to immune competence of such individuals. Semi-immune individuals have an enhanced ability to clear faster than non-immune people. In addition, age has also been identified as a contributory factor with children less than 5 years clearing parasites slower when compared to children greater than five years [113]. Even though immunity due to malaria infection is short-lived, certain cytokines and their receptors have been shown to be highly implicated in this process [111, 112].
Furthermore, there was a negative correlation between the proportions of anti-malarial drugs (ASAQ, AL and SP) deployed to the different public and private health establishments in Cameroon and anti-malarial drug resistance markers (Pfcrt 76T, Pfmdr1 86Y and Pfdhfr IRN). The proportion of drugs deployed may be used as a proxy for drug uptake. The decline in proportion of drugs deployed may be contributing to less drug pressure to circulating parasites. Increase in parasite fitness as a result of less drug pressure could be responsible for the decline in the prevalence of certain gene mutations associated with anti-malarial drug resistance. The two drugs, ASAQ and SP are still being subsidized by the Cameroon government. ASAQ is highly recommended for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in children less than 5 years while SP used as a preventive treatment for malaria in pregnancy. The major challenge in the fight against drug resistance in Cameroon is the inability to effectively implement the legislation on the homologation and importation of unauthorized anti-malarial therapies and insufficient pharmacovigilance. In addition, there are still issues with substandard drugs and auto-medication.
Strengths and limitations of the study
The major strength of the present review is that it has presented a picture of the prevalence and distribution of key anti-malarial drug resistance markers in Cameroon with a total of 48 studies included. The data derived from this study showed that there is little or absence of the Pfmdr1 and Pfk13 polymorphisms that select for ACT, especially ASAQ and AL. These 2 drugs are used concurrently for the management of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Cameroon.
However, despite the strengths of the study, it is not without limitations. Firstly, some studies enrolled a fewer number of participants which may not give a true representation of resistant parasite population circulating in the Cameroon. Secondly, the high heterogeneity across studies may affect the interpretation of the findings. Thirdly, some of anti-malarial drug resistance markers have been understudied in the Northern Regions of the country that border countries such as Nigeria with a high burden of malaria. Furthermore, most of the studies were conducted in symptomatic individuals and there is little or no information on the prevalence of anti-malarial drug resistance markers in asymptomatic carriers of the parasite. Asymptomatic individuals have been shown to be reservoirs for malaria parasite transmission. In addition, earlier studies mostly used nPCR-RFLP for the detection of drug resistance markers and, therefore, were not capable of identifying novel SNPs. Finally, the association between specific P. falciparum gene polymorphisms and treatment failures with ACT could not be investigated because of the non-availability of data.
Conclusions
This review reported a decline in the prevalence of single Plasmodium falciparum gene mutations (Pfcrt K76T, Pfmdr1 N86Y, Pfdhfr N51I, Pfdhfr C59R, Pfdhfr S108N) conferring resistance to 4-aminoquinolines, amino alcohols and pyrimethamine for a period over two decades pre and post adoption of ACT in Cameroon. The Pfcrt K76T and Pfmdr1 N86Y mutations still persist at moderate frequencies despite the withdrawal of chloroquine. Conversely, parasite resistance markers (Pfdhps A437G and Pfdhps K540E) linked to the sulpha drugs increased during the same study period. Resistance to artemisinins measured by the presence of SNPs in the Pfk13 gene does not seem to be a major problem in Cameroon. However, it is a wake-up call for policy makers to design and implement strategies for the regular monitoring of delayed parasite clearance after administration of artemisinin-based combination therapy. This will permit the early identification of factors driving the emergence and spread of anti-malarial drug resistance in Cameroon.
Abbreviations
- ACT:
-
Artemisinin-based combination therapy
- AL:
-
Artemether–lumefantrine
- ASAQ:
-
Artesunate-amodiaquine
- NMCP:
-
National Malaria Control Programme
- PCR:
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Pfcrt :
-
Plasmodium falciparum Chloroquine resistance transporter
- Pfmdr1 :
-
Plasmodium falciparum Multi-drug resistance 1
- Pfdhfr :
-
Plasmodium falciparum Dihydrofolate reductase
- Pfdhps :
-
Plasmodium falciparum Dihydropteroate synthase
- Pfcytb :
-
Plasmodium falciparum Cytochrome b
- Pfatp6 :
-
Plasmodium falciparum Atpase 6
- Pfk13 :
-
Plasmodium falciparum Kelch 13
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses
- PRISMA-P:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses protocol
- r:
-
Correlation coefficient
- SP:
-
Sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine
- SPAQ:
-
Sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine–amodiaquine
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
WHO. World Malaria Report 2019. Geneva, World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/world-malaria-report-2019. Accessed on 8th December, 2019.
Cameroon National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP). Annual report of activities 2006, Yaoundé, 2006.
WHO. World Malaria Report 2008. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2008. http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241563697/en/. Accessed on 10th August, 2017.
Sayang C, Gausseres M, Vernazza-Licht N, Malvy D, Bley D, Millet P. Treatment of malaria from monotherapy to artemisinin-based combination therapy by health professionals in urban health facilities in Yaoundé, central province Cameroon. Malar J. 2009;8:176.
Cameroon National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP). Annual report of activities 2016. Yaoundé, 2016.
WHO. Guidelines for the treatment of malaria. 3rd Edn. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2015. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241549127/en/. Accessed on 15th July, 2020.
Kayentao K, Garner P, van Eijk MA, Naidoo I, Roper C, Mulokozi A, et al. Intermittent preventive therapy for malaria during pregnancy using 2 vs 3 or more doses of sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine and risk of low birth weight in Africa: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2013;309:594–604.
Djimdé A, Doumbo OK, Cortese JF, Kayentao K, Doumbo S, Diourté Y, et al. A molecular marker for chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:257–63.
Cowman AF, Morry MJ, Biggs BA, Cross GA, Foote SJ. Amino acid changes linked to pyrimethamine resistance in the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:9109–13.
Foote SJ, Galatis D, Cowman AF. Amino acids in the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene of Plasmodium falciparum involved in cycloguanil resistance differ from those involved in pyrimethamine resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:3014–7.
Peterson DS, Walliker D, Wellems TE. Evidence that a point mutation in dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase confers resistance to pyrimethamine in falciparum malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:9114.
Triglia T, Menting JGT, Wilson C, Cowman AF. Mutations in dihydropteroate synthase are responsible for sulfone and sulfonamide resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:13944–9.
Picot S, Olliaro P, de Monbrison F, Bienvenu A-L, Price RN, Ringwald P. A systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence for correlation between molecular markers of parasite resistance and treatment outcome in falciparum malaria. Malar J. 2009;8:89.
Gama BE, Pereira-Carvalho GA, Kosi FJ, de Oliveira NK, Fortes F, Rosenthal PJ, et al. Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Angola show the StctVMNT haplotype in the pfcrt gene. Malar J. 2010;9:174.
Alifrangis M, Dalgaard MB, Lusingu JP, Vestergaard LS, Staalsoe T, Jensen ATR, et al. Occurrence of the Southeast Asian/South American SVMNT haplotype of the chloroquine-resistance transporter gene in Plasmodium falciparum in Tanzania. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1738–41.
Awasthi G, Satya GBK, Das A. Pfcrt haplotypes and the evolutionary history of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012;107:129–34.
Price RN, Uhlemann A-C, Brockman A, McGready R, Ashley E, Phaipun L, et al. Mefloquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum and increased pfmdr1 gene copy number. Lancet. 2004;364:438–47.
Lim P, Alker AP, Khim N, Shah NK, Incardona S, Doung S, et al. Pfmdr1 copy number and arteminisin derivatives combination therapy failure in falciparum malaria in Cambodia. Malar J. 2009;8:11.
Sidhu ABS, Uhlemann A-C, Valderramos SG, Valderramos J-C, Krishna S, Fidock DA. Decreasing pfmdr1 copy number in Plasmodium falciparum malaria heightens susceptibility to mefloquine, lumefantrine, halofantrine, quinine, and artemisinin. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:528–35.
Simpson JA, Jamsen KM, Anderson TJC, Zaloumis S, Nair S, Woodrow C, et al. Nonlinear mixed-effects modelling of in vitro drug susceptibility and molecular correlates of multidrug resistant Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e69505.
Venkatesan M, Gadalla NB, Stepniewska K, Dahal P, Nsanzabana C, Moriera C, et al. Polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter and multidrug resistance 1 genes: parasite risk factors that affect treatment outcomes for P. falciparum malaria after artemether–lumefantrine and artesunate-amodiaquine. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014;91:833–43.
Okell LC, Reiter LM, Ebbe LS, Baraka V, Bisanzio D, Watson OJ, et al. Emerging implications of policies on malaria treatment: genetic changes in the Pfmdr-1 gene affecting susceptibility to artemether–lumefantrine and artesunate-amodiaquine in Africa. BMJ Glob Health. 2018;3:e000999.
Ariey F, Witkowski B, Amaratunga C, Beghain J, Langlois A-C, Khim N, et al. A molecular marker of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature. 2014;505:50–5.
Ménard D, Khim N, Beghain J, Adegnika AA, Shafiul-Alam M, Amodu O, et al. A Worldwide Map of Plasmodium falciparum K13-Propeller Polymorphisms. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2453–64.
Ocan M, Akena D, Nsobya S, Kamya MR, Senono R, Kinengyere AA, et al. K13-propeller gene polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum parasite population in malaria affected countries: a systematic review of prevalence and risk factors. Malar J. 2019;18:60.
Kamau E, Campino S, Amenga-Etego L, Drury E, Ishengoma D, Johnson K, et al. K13-propeller polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum parasites from sub-Saharan Africa. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1352–5.
WHO. Artemisinin resistance and artemisinin-based combination therapy efficacy: status report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. https://www.who.int/malaria/areas/drug_resistance/updates/en/. Accessed on 2nd December, 2020.
Safeukui I, Fru-Cho J, Mbengue A, Suresh N, Njimoh DL, Bumah VV, et al. Investigation of polymorphisms in the P. falciparum artemisinin resistance marker kelch13 in asymptomatic infections in a rural area of Cameroon. bioRxiv. 2017;148999.
Torrentino-Madamet M, Fall B, Benoit N, Camara C, Amalvict R, Fall M, et al. Limited polymorphisms in k13 gene in Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Dakar, Senegal in 2012–2013. Malar J. 2014;13:472.
Apinjoh TO, Mugri RN, Miotto O, Chi HF, Tata RB, Anchang-Kimbi JK, et al. Molecular markers for artemisinin and partner drug resistance in natural Plasmodium falciparum populations following increased insecticide treated net coverage along the slope of mount Cameroon: cross-sectional study. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017;6:136.
Feng J, Kong X, Xu D, Yan H, Zhou H, Tu H, et al. Investigation and Evaluation of Genetic Diversity of Plasmodium falciparum Kelch 13 Polymorphisms Imported From Southeast Asia and Africa in Southern China. Front Public Health. 2019;7:95.
Bwire GM, Ngasala B, Mikomangwa WP, Kilonzi M, Kamuhabwa AAR. Detection of mutations associated with artemisinin resistance at k13-propeller gene and a near complete return of chloroquine susceptible falciparum malaria in Southeast of Tanzania. Sci Rep. 2020;10:3500.
Uwimana A, Legrand E, Stokes BH, Ndikumana JLM, Warsame M, Umulisa N, et al. Emergence and clonal expansion of in vitro artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum kelch13 R561H mutant parasites in Rwanda. Nat Med. 2020;26:1602–8.
Okell LC, Drakeley CJ, Bousema T, Whitty CJM, Ghani AC. Modelling the impact of artemisinin combination therapy and long-acting treatments on malaria transmission intensity. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e226.
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4:1.
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;350:7647.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700.
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366:l4898.
GA Wells, B Shea, D O’Connell, J Peterson, V Welch, M Losos, P Tugwell. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non-randomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed on 2nd December, 2020.
Moola S, Munn Z, Tufanaru C, Aromataris E, Sears K, Sfetcu R, Currie M, Qureshi R, Mattis P, Lisy K, Mu P-F. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z (Eds). JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI, 2020. https://synthesismanual.jbi.global. Accessed on 1st December, 2020.
Moola S, Munn Z, Tufanaru C, Aromataris E, Sears K, Sfetcu R, et al. Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z (Editors). Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer's Manual. Chapt 7. The Joanna Briggs Institute, 2017. https://reviewersmanual.joannabriggs.org/. Accessed on 1st December, 20.
Rossi-Fedele G, Kahler B, Venkateshbabu N. Limited evidence suggests benefits of single visit revascularization endodontic procedures—a systematic review. Braz Dent J. 2019;30:527–35.
Ryan R. Cochrane Consumers and Communication Review Group. Heterogeneity and subgroup analyses in Cochrane Consumers and Communication Group reviews: planning the analysis at protocol stage. http://cccrg.cochrane.org. December 2016. Accessed on 12th February, 2019.
Kontopantelis E, Springate DA, Reeves D. A re-analysis of the Cochrane Library Data: the dangers of unobserved heterogeneity in meta-analyses. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e69930.
Moyeh MN, Njimoh DL, Evehe MS, Ali IM, Nji AM, Nkafu DN, et al. Effects of drug policy changes on evolution of molecular markers of Plasmodium falciparum resistance to chloroquine, amodiaquine, and sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine in the south west Region of Cameroon. Malar Res Treat. 2018;2018:7071383–7071383.
Mbacham WF, Evehe M-SB, Netongo PM, Ateh IA, Mimche PN, Ajua A, et al. Efficacy of amodiaquine, sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine and their combination for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children in Cameroon at the time of policy change to artemisinin-based combination therapy. Malar J. 2010;9:34.
McCollum AM, Basco LK, Tahar R, Udhayakumar V, Escalante AA. Hitchhiking and selective sweeps of Plasmodium falciparum sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine resistance alleles in a population from Central Africa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:4089–97.
Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XIII. Analysis of pfcrt mutations and in vitro chloroquine resistance. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:388–91.
Basco LK, Ndounga M, Ngane VF, Soula G. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XIV. Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter (PFCRT) gene sequences of isolates before and after chloroquine treatment. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:392–5.
Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XVI. Longitudinal surveillance of in vitro pyrimethamine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;69:174–8.
Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XVII. Baseline monitoring of atovaquone-resistant Plasmodium falciparum by in vitro drug assays and cytochrome b gene sequence analysis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;69:179–83.
Tahar R, Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XXVI. Twelve-year in vitro and molecular surveillance of pyrimethamine resistance and experimental studies to modulate pyrimethamine resistance. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;77:221–7.
Tahar R, Ringwald P, Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XXVIII. In vitro activity of dihydroartemisinin against clinical isolates of Plasmodium falciparum and sequence analysis of the P. falciparum ATPase 6 gene. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;81:13–8.
Sahnouni K, Menemedengue V, Tahar R, Basco L. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XXX. Sequence analysis of Plasmodium falciparum ATPase 6, dihydrofolate reductase, and dihydropteroate synthase resistance markers in clinical isolates from children treated with an artesunate-sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine combination. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011;85:22–5.
Basco LK, Ringwald P. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Yaounde, Cameroon IV. Evolution of pyrimethamine resistance between 1994 and 1998. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;61:802–6.
Basco LK, Ringwald P. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Yaounde, Cameroon. VI. Sequence variations in the Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene and in vitro resistance to pyrimethamine and cycloguanil. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62:271–6.
Menard S, Morlais I, Tahar R, Sayang C, Mayengue P, Iriart X, et al. Molecular monitoring of Plasmodium falciparum drug susceptibility at the time of the introduction of artemisinin-based combination therapy in Yaoundé, Cameroon: Implications for the future. Malar J. 2012;11:113.
Xu C, Sun H, Wei Q, Li J, Xiao T, Kong X, et al. Mutation profile of pfdhfr and pfdhps in Plasmodium falciparum among returned Chinese migrant workers from Africa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:e01927-e2018.
Ngassa Mbenda HG, Das A. Occurrence of multiple chloroquine-resistant Pfcrt haplotypes and emergence of the S(agt)VMNT type in Cameroonian Plasmodium falciparum. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69:400–3.
Chauvin P, Menard S, Iriart X, Nsango SE, Tchioffo MT, Abate L, et al. Prevalence of Plasmodium falciparum parasites resistant to sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine in pregnant women in Yaoundé, Cameroon: emergence of highly resistant pfdhfr / pfdhps alleles. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015;70:2566–71.
Severini C, Menegon M, Sannella AR, Paglia MG, Narciso P, Matteelli A, et al. Prevalence of pfcrt point mutations and level of chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Africa. Infect Genet Evol. 2006;6:262–8.
de Monbrison F, Raynaud D, Latour-Fondanaiche C, Staal A, Favre S, Kaiser K, et al. Real-time PCR for chloroquine sensitivity assay and for pfmdr1–pfcrt single nucleotide polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum. J Microbiol Methods. 2003;54:391–401.
Ndam NT, Basco LK, Ngane VF, Ayouba A, Ngolle EM, Deloron P, et al. Reemergence of chloroquine-sensitive pfcrt K76 Plasmodium falciparum genotype in southeastern Cameroon. Malar J. 2017;16:130.
Basco LK, Tahar R, Keundjian A, Ringwald P. Sequence variations in the genes encoding dihydropteroate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase and clinical response to sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine in patients with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria. J Infect Dis. 2000;182:624–8.
Jiang J, Yu C, Tian C, Li W, Zhang T, Xu X. Surveillance of anti-malarial resistance molecular markers in imported Plasmodium falciparum malaria cases in Anhui, China, 2012–2016. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98:1132–6.
Yao Y, Wu K, Xu M, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Yang W, et al. Surveillance of genetic variations associated with anti-malarial resistance of Plasmodium falciparum isolates from returned migrant workers in Wuhan. Central China Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018;62:e02387-e2417.
Gharbi M, Flegg JA, Pradines B, Berenger A, Ndiaye M, Djimdé AA, et al. Surveillance of travellers: an additional tool for tracking anti-malarial drug resistance in endemic countries. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e77775.
Djaman JA, Olefongo D, Ako AB, Roman J, Ngane VF, Basco LK, et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Malaria in Cameroon and Côte d’Ivoire. XXXI. Kelch 13 Propeller Sequences in Plasmodium falciparum Isolates before and after Implementation of Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapy. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;97:222–4.
Youmba J-C, Ringwald P, Ngane VF, Ndounga M, Soula G, Tejiokem M, et al. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XI. Geographic distribution of Plasmodium falciparum isolates with dihydrofolate reductase gene mutations in southern and central Cameroon. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:378–82.
Zhao L, Pi L, Qin Y, Lu Y, Zeng W, Xiang Z, et al. Widespread resistance mutations to sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine in malaria parasites imported to China from Central and Western Africa. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2020;12:1–6.
Achungu CR, Nkuo-Akenji T, Apinjoh T, Wanji S. Re-emergence of chloroquine sensitive Plasmodium falciparum after several years of chloroquine withdrawal in Bamenda, North West Cameroon. EC Microbiol. 2018:831–6.
Basco LK, Tahar R, Ringwald P. Molecular basis of in vivo resistance to sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine in African adult patients infected with Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:1811–4.
Ringwald P, Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Yaounde, Cameroon I. Analysis of point mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998;58:369–73.
Ringwald P, Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Yaounde, Cameroon V. analysis of the omega repetitive region of the Plasmodium falciparum CG2 gene and chloroquine resistance. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;61:807–13.
Basco LK, Ringwald P. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. X. Evaluation of PFMDR1 mutations as genetic markers for resistance to amino alcohols and artemisinin derivatives. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;66:667–71.
Tahar R, Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XXII. Geographic mapping and distribution of Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) mutant alleles. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;75:396–401.
Menard S, Tchoufack JN, Maffo CN, Nsango SE, Iriart X, Abate L, et al. Insight into k13-propeller gene polymorphism and ex vivo DHA-response profiles from Cameroonian isolates. Malar J. 2016;15:572.
Lu F, Zhang M, Culleton RL, Xu S, Tang J, Zhou H, et al. Return of chloroquine sensitivity to Africa? Surveillance of African Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance through malaria imported to China. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:355.
Mbacham W, Evehe MS, Netongo P, Ali I, Nfor EN, Akaragwe A, et al. Mutations within folate metabolising genes of Plasmodium falciparum in Cameroon. Afr J Biotechnol. 2009;8:4749–54.
Eboumbou Moukoko CE, Huang F, Nsango SE, Kojom Foko LP, Ebong SB, Epee Eboumbou P, et al. K-13 propeller gene polymorphisms isolated between 2014 and 2017 from Cameroonian Plasmodium falciparum malaria patients. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0221895.
Witkowski B, Nicolau M-L, Soh PN, Iriart X, Menard S, Alvarez M, et al. Plasmodium falciparum isolates with increased pfmdr1 copy number circulate in West Africa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3049–51.
Basco LK, Ringwald P. Analysis of the key pfcrt point mutation and in vitro and in vivo response to chloroquine in Yaoundé Cameroon. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:1828–31.
Basco LK, Ringwald P. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Yaoundé, Cameroon. III. Analysis of chloroquine resistance and point mutations in the multidrug resistance 1 (pfmdr 1) gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998;59:577–81.
Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XII. In vitro drug assays and molecular surveillance of chloroquine and proguanil resistance. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:383–7.
Tahar R, Basco LK. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XXVII. Clinical and parasitological response to sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine treatment and Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroate synthase alleles in Cameroonian children. Acta Trop. 2007;103:81–9.
Pearce RJ, Pota H, Evehe M-SB, Bâ E-H, Mombo-Ngoma G, Malisa AL, et al. Multiple origins and regional dispersal of resistant dhps in African Plasmodium falciparum malaria. PLoS Med. 2009;6:1000055.
Kimbi HK, Nkuo-Akenji TK, Patchong AFM, Ndamukong KN, Nkwescheu A. The comparative efficacies of malartin, with and without amodiaquine, in the treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in the Buea district of Cameroon. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2007;101:95–102.
Ndiaye JLA, Faye B, Diouf AM, Kuété T, Cisse M, Seck PA, et al. Randomized, comparative study of the efficacy and safety of artesunate plus amodiaquine, administered as a single daily intake versus two daily intakes in the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Malar J. 2008;7:16.
Ndiaye JL, Randrianarivelojosia M, Sagara I, Brasseur P, Ndiaye I, Faye B, et al. Randomized, multicentre assessment of the efficacy and safety of ASAQ – a fixed-dose artesunate-amodiaquine combination therapy in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Malar J. 2009;8:125.
Sagara I, Rulisa S, Mbacham W, Adam I, Sissoko K, Maiga H, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed dose artesunate-sulphamethoxypyrazine-pyrimethamine compared to artemether–lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria across Africa: a randomized multi-centre trial. Malar J. 2009;8:63.
Whegang SY, Tahar R, Foumane VN, Soula G, Gwét H, Thalabard J-C, et al. Efficacy of non-artemisinin- and artemisinin-based combination therapies for uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Cameroon. Malar J. 2010;9:56.
Yavo W, Faye B, Kuete T, Djohan V, Oga SA, Kassi RR, et al. Multicentric assessment of the efficacy and tolerability of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine compared to artemether–lumefantrine in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Malar J. 2011;10:198.
Faye B, Kuété T, Kiki-Barro CP, Tine RC, Nkoa T, Ndiaye JLA, et al. Multicentre study evaluating the non-inferiority of the new paediatric formulation of artesunate/amodiaquine versus artemether/lumefantrine for the management of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children in Cameroon Ivory Coast and Senegal. Malar J. 2012;11:433.
Nji AM, Ali IM, Moyeh MN, Ngongang E-O, Ekollo AM, Chedjou J-P, et al. Randomized non-inferiority and safety trial of dihydroartemisin-piperaquine and artesunate-amodiaquine versus artemether–lumefantrine in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Cameroonian children. Malar J. 2015;14:27.
Tahar R, Almelli T, Debue C, Foumane Ngane V, Djaman Allico J, Whegang Youdom S, et al. Randomized trial of artesunate-amodiaquine, atovaquone-proguanil, and artesunate-atovaquone-proguanil for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in children. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:1962–71.
Apinjoh T, Anchang-Kimbi J, Ajonina M, Njonguo E, Njua-Yafi C, Ngwai A, et al. In vivo efficacy of artesunate/sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine versus artesunate/amodiaquine in the treatment of uncomplicated P falciparum malaria in children around the Slope of Mount Cameroon: a randomized controlled trial. Biomedicines. 2016;4:5.
Oduola AMJ, Moyou-Somo RS, Kyle DE, Martin SK, Gerena L, Milhous WK. Chloroquine resistant Plasmodium falciparum in indigenous residents of Cameroon. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1989;83:308–10.
Sansonetti PJ, Lebras C, Verdier F, Charmot G, Dupont B, Lapresle C. Chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in Cameroon. Lancet. 1985;325:1154–5.
Claveau S. Chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria from Cameroon. CMAJ. 1988;138:240–1.
Titanji V, Nkuo-Akenji T, Ntopi W, Djokam R. Reduced levels of chloroquine resistant Plasmodium falciparum in selected foci for the South West Province. Cameroon Cent Afr J Med. 2001;47:145–9.
Wamae K, Okanda D, Ndwiga L, Osoti V, Kimenyi KM, Abdi AI, et al. No evidence of Plasmodium falciparum k13 artemisinin resistance-conferring mutations over a 24-year analysis in Coastal Kenya but a near complete reversion to chloroquine-sensitive parasites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:e01067-e1119.
Dagnogo O, Ako AB, Ouattara L, Dago ND, Coulibaly DN, Touré AO, et al. Towards a re-emergence of chloroquine sensitivity in Côte d’Ivoire? Malar J. 2018;17:413.
Sondo P, Derra K, Diallo Nakanabo S, Tarnagda Z, Kazienga A, Zampa O, et al. Artesunate-amodiaquine and artemether–lumefantrine therapies and selection of Pfcrt and Pfmdr1 alleles in Nanoro Burkina Faso. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0151565.
Boni MF, Smith DL, Laxminarayan R. Benefits of using multiple first-line therapies against malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:14216–21.
Duah NO, Matrevi SA, de Souza DK, Binnah DD, Tamakloe MM, Opoku VS, et al. Increased pfmdr1 gene copy number and the decline in pfcrt and pfmdr1 resistance alleles in Ghanaian Plasmodium falciparum isolates after the change of anti-malarial drug treatment policy. Malar J. 2013;12:377.
Cameroon: Demographic Health Survey (DHS) 2018-Key Indicators Report. https://dhsprogram.com/publications/publication-pr116-preliminary-reports-key-indicators-reports.cfm. Accessed on 27th April, 2020.
Berzosa P, Esteban-Cantos A, García L, González V, Navarro M, Fernández T, et al. Profile of molecular mutations in pfdhfr, pfdhps, pfmdr1, and pfcrt genes of Plasmodium falciparum related to resistance to different anti-malarial drugs in the Bata District (Equatorial Guinea). Malar J. 2017;16:28.
Jiang T, Chen J, Fu H, Wu K, Yao Y, Eyi JUM, et al. High prevalence of Pfdhfr-Pfdhps quadruple mutations associated with sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Bioko Island Equatorial Guinea. Malar J. 2019;18:101.
Oguike MC, Falade CO, Shu E, Enato IG, Watila I, Baba ES, et al. Molecular determinants of sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum in Nigeria and the regional emergence of dhps 431V. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2016;6:220–9.
Matondo SI, Temba GS, Kavishe AA, Kauki JS, Kalinga A, van Zwetselaar M, et al. High levels of sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine resistance Pfdhfr-Pfdhps quintuple mutations: a cross sectional survey of six regions in Tanzania. Malar J. 2014;13:152.
Diakite M, Achidi EA, Achonduh O, Craik R, Djimde AA, Evehe M-SB, et al. Host candidate gene polymorphisms and clearance of drug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum parasites. Malar J. 2011;10:250.
Ataide R, Ashley EA, Powell R, Chan J-A, Malloy MJ, O’Flaherty K, et al. Host immunity to Plasmodium falciparum and the assessment of emerging artemisinin resistance in a multinational cohort. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:3515–20.
Djimdé AA, Doumbo OK, Traore O, Guindo AB, Kayentao K, Diourte Y, et al. Clearance of drug-resistant parasites as a model for protective immunity in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;69:558–63.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this publication are those of the author (s) and not necessarily those of AAS, NEPAD Agency, Wellcome Trust or the UK government or the WHO (Geneva).
Funding
WFM, AMN, IMA and PTNN are supported by the Malaria Research Capacity Development in West and Central Africa (MARCAD) Consortium through the Developing Excellence in Leadership, Training and Science (DELTAS) Africa Initiative [grant # DEL-15-010] to the University of Yaounde I. The DELTAS Africa Initiative is an independent funding scheme of the African Academy of Sciences (AAS)’s Alliance for Accelerating Excellence in Science in Africa (AESA) and supported by the New Partnership for Africa’s Development Planning and Coordinating Agency (NEPAD Agency) with funding from the Wellcome Trust [grant # 107741/A/15/Z] and the United Kingdom (UK) government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WFM conceived the research and coordinated the study. PTNN and LNN piloted the data extraction phase. AMN and PTNN performed the data analysis, drafted the manuscript, critically reviewed the manuscript, and wrote the final manuscript. The authors WFM, MA, MSE, IMA, PMN, RN, MNM, LNN, OEN, FAA, CMM, DAF, BAT, OAA, RDD, JPKC, JDB, CEEM, AA, EA, ET, RGFL, AT and PR proof read the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable since it is a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Summary of the studies included in the systematic review and meta-analysis on anti-malarial drug resistance markers in Cameroon.
Additional file 2.
Methodological quality assessment of interventional studies.
Additional file 3.
Methodological quality assessment of cohort studies.
Additional file 4.
Methodological quality assessment of cross-sectional studies.
Additional file 5.
Methodological quality assessment of case reports.
Additional file 6.
Assessment of publication bias using funnel plot and Egger’s regression test.
Additional file 7.
Haplotype analyses of anti-malarial drug resistance mutant allele frequencies reported in Cameroon.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Niba, P.T.N., Nji, A.M., Evehe, MS. et al. Drug resistance markers within an evolving efficacy of anti-malarial drugs in Cameroon: a systematic review and meta-analysis (1998–2020). Malar J 20, 32 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-020-03543-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-020-03543-8