Abstract
Background
Gastric cancer peritoneal carcinomatosis is a common clinical problem, but there are no suitable large animal models to study this problem. This study was to establish a stable rabbit peritoneal carcinomatosis model of gastric cancer using VX2 tumor, and analyze the clinico-pathological features.
Methods
VX2 tumor was implanted into 36 New Zealand rabbits by 3 methods: laparotomic orthotopic injection of cancer cells into the submucosal layer of the stomach (Group A), laparotomic implantation of tumor tissue into the greater omentum immediately beneath the gastric antrum (Group B), and percutaneous injection of tumor cells directly into the peritoneal cavity (Group C), 12 rabbits in each group. The animals were closely observed and detailed clinico-pathological studies were conducted.
Results
The success rates of peritoneal carcinomatosis formation were 100% (12/12), 91.7% (11/12) and 58.3% (7/12), respectively, for Groups A, B and C (P = 0.019, A versus C; P = 0.077, B versus C; P = 0.500, A versus B, Fisher's exact test). Two weeks after submucosal cancer cells injection in Group A, ulcerative gastric cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis showed typical VX2 tumor pathology, with widespread intraperitoneal metastatic nodules, bloody ascites and perspicuous pulmonary metastases. The clinico-pathological progression pattern was very similar to patients of advanced gastric cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis. Groups B and C showed similar pattern of cancer progression, but less aggressive.
Conclusions
First large animal model of peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastric cancer has been established by laparotomic orthotopic injection of VX2 cancer cells into the submucosal layer of the stomach, providing a more suitable model for surgical interventional studies. The clinico-pathological features of this model resemble human peritoneal carcinomatosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The loco-regional progression of gastrointestinal and gynecological cancers frequently results in peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC), which is characterized by the presence of tumor nodules of various size, number and distribution on the peritoneal surface, with very poor prognosis and a median survival of less than 6 months [1, 2]. Current treatments for such PC are systemic chemotherapy, best support care and palliative therapy, with no hope of cure. In order to tackle this problem, a new treatment modality called cytoreductive surgery (CRS) plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) has been developed over the past two decades, taking advantages of surgery to reduce visible tumor burden, and regional hyperthermic chemotherapy to eradicate micrometastases [3–6].
While clinical studies have made progresses, some experimental animal PC models have also been developed, including mice models and rat models to evaluate the efficacy and adverse effects of experimental HIPEC protocols [7–10]. Although such small animal models are useful in experimental studies, it is technically difficult to perform operations on small animals because of the little body size and delicate hemodynamic conditions. Large animal such as pig has also been used to test the pharmacokinetics of HIPEC, but the animals used were healthy pigs rather than pigs with PC [11]. Therefore, a large animal PC model more suitable for surgical interventional studies is desirable. Here we report on a rabbit PC model from gastric cancer, with clinico-pathological features mimic patients with advanced gastric cancer.
Methods
Animals
Thirty six New Zealand white rabbits, 18 males and 18 females, body weight between 2.5~3.0 kg, were obtained from Animal Biosafety Level 3 Laboratory at the Animal Experimental Center of Wuhan University (Animal Study Certificate SCXK 2003-0004). The animals were individually housed and allowed free access to standard laboratory food and water as well as 12 h of light and dark cycle per day. The animal study protocol was approved by the Animal Welfare Committee of the Center.
Tumor strain and tumor cell preparation
Rabbit VX2 carcinoma was used to establish gastric cancer with PC in this study. The VX2 tumor is a transplantable rabbit squamous cell carcinoma, characterized by rapid tumor growth and early metastasis, established from a virus-induced papilloma by Rous and coworkers [12]. The tumor was maintained by successive in vivo transplantation into the hind leg of 2 carrier rabbits used for every passage.
When the VX2 tumor grew to about 1 cm in diameter on the carrier rabbit, the animal was anesthetized by ear vein injection of 3% pentobarbital sodium (30 mg/kg). After skin preparation and disinfection, the tumor was excised from the carrier rabbit and placed in icy cold 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Tumor tissue was minced into approximately 1.0~2.0 mm3 fragments and suspended in 2 mL of normal saline, then drawn into a 2 mL injector. Other tumor tissues about 3.0~5.0 mm3 were placed into the homogenizer embedded in ice bath, to which 3 mL of icy cold normal saline was added, and the tumor cells suspension was made, with the tumor cells concentration adjusted to 5×1010 vial cells/L.
Construction of gastric cancer with PC
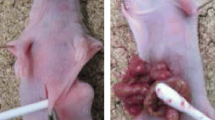
All rabbits had overnight fasting before experiment, but water was given ad libitum. After randomization, the animals were anesthetized by ear vein injection of 3% pentobarbital sodium (30 mg/kg). The abdominal skin was cleaned and disinfected. Three approaches were adopted to construct rabbit models of PC, 12 animals for each group. Group A of submucosal tumor cell inoculation: A midline incision of 3 cm long was made beginning 2 cm below the xyphoid and the upper abdomen was open. The stomach was exposed, 0.1 mL of tumor cells (5×1010 vial cells/L) was injected into the submucosal layer of the stomach (Figure 1), through the serosal layer and the muscle layer, the injection site was pressed for 1 min to keep the injected tumor cells in place, and the abdomen was closed with a double layer 3-O vicryl interrupted suture. Group B of tumor tissue implantation: The incision was the same as in Group A. When the stomach was exposed, a small piece of fresh tumor tissue about 1.0 mm3 was implanted into the greater omentum immediately beneath the gastric antrum, and the wound was closed. Group C of percutaneous injection of tumor cells: After skin preparation, 0.1 mL of tumor cells (5×1010 vial cells/L) was directly injected into the upper abdominal cavity, and the injection site was pressed for 1 min. After tumor inoculation, penicillin G at the dose of 100,000 IU/d was intramuscularly injected to each animal for 3 days. All the animals were give intravenous fluid rehydration with 100 mL of 0.9% normal saline solution.
Construction of rabbit peritoneal carcinomatosis model from gastric cancer. When the rabbit stomach was exposed under general anesthesia, a 16 G needle was inserted through the serosal and muscle layers into the submucosal layer of the stomach, and 0.1 mL of tumor cells (5×1010 vial cells/L) were injected, and injection site was pressed for 1 min to keep the tumor cells in place (See the text for detailed description).
Animal observation and pathological studies
After operation, daily observation was made on each rabbit to check food intake, activities, and any abnormalities such as diarrhea and dehydration. The body weight was measured every 3 days and the natural history of the disease progression was recorded. In order to obtain a detailed description of the progressive development of gastric cancer PC, euthanasia was performed on 3 rabbits in Group A at the end of weeks 1, 2, 3 and 4, by overdose injection of 3% pentobarbital sodium through the ear vein. For animals in Groups B and C, euthanasia was also performed when the animals showed obvious signs of distress and waste, in keeping with UKCCCR guidelines for the welfare of animals in experimental neoplasia [13]. Post mortem pathological examinations included gross pathology such as tumor size and distributions; local tumor features of gastric cancer including ulcer formation, obstruction and perforation; special features of peritoneal carcinomatosis such as bloody ascites, discrete or confluent tumor nodules on the peritoneum, cancerous changes in the greater omentum and intestinal obstructions; metastases to major organs such as the liver, adrenal glands, pancreas and the lungs. All the suspected organ tissues were sampled for routine histopathology study with sections stained by hematoxylin and eosin (HE stain).
Statistical analysis
The body weight and tumor weight were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (M ± SD). The intra-abdominal metastases and bloody ascites were recorded as ranges and medians. The SPSS statistical software package version 10.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago Il, USA) was used for analysis, with two-sided test, and P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
Success of PC model construction
Of 36 animals used for PC model construction, the operation was successful in 33 rabbits and 3 animals died 3 days after operation. Of the 3 deaths, 1 rabbit in Group C died of diffused peritonitis on day 3 because the percutaneous injection was mistakenly into the small intestine; and 1 rabbit each in Groups B and C died of congestive heart failure on day 2 because of fast fluid rehydration. Another 3 rabbits in Group C did not develop PC for unknown reasons. The success rates were 100% (12/12) in Group A, 91.7% (11/12) in Group B and 58.3% (7/12) in Group C (P = 0.019, A versus C; P = 0.077, B versus C; P = 0.500, A versus B, Fisher's exact test).
Tumor growth and its impact on the animal
After cancer cells injection into the gastric submucosa in Group A, the tumor demonstrated accelerated growth. The tumor sizes were (0.028 ± 0.012) cm3, (1.183 ± 0.148) cm3 and (7.706 ± 1.629) cm3, respectively, at the end of weeks 1, 2, and 3. The animals showed progressive decrease in body weight, from (2.48 ± 0.21) kg before operation to (2.45 ± 0.21) kg on week 1, (2.24 ± 0.19) kg on week 2, (2.02 ± 0.18) kg on week 3 and (1.81 ± 0.1) kg on week 4. Along with body weight changes, the feeding and general health status of the animals deteriorated progressively.
Growth characteristics of peritoneal carcinomatosis in animal model
Tumor characteristics in Group A were carefully recorded. One week after submucosa injection of cancer cells, many small, hard and transparent nodules began to develop on the greater omentum and the antrum of the stomach. No ascites was observed. Two weeks later, nodules on the greater omentum began to merge into confluent masses without discernable demarcations with the stomach. The mass on the gastric wall grew bigger and protruded into the stomach cavity to form typical ulcerative cancer (Figure 2). There was about 5 mL of bloody ascites in the abdominal cavity. Three weeks later, many nodules began to form in the mesentery and the retroperitoneum. The confluent mass on the greater omentum began to invade the liver and encase the stomach (Figure 3). Often the stomach mass and the greater omentum mass merged into one big tumor block. Bloody ascites could reach as much as 100 mL. There was also some fluid accumulation in the pericardium. Many nodules were seen on the abdominal wall. No nodules were observed in the lungs. Four weeks later, numerous tumor nodules were observed in the lungs, the liver, adrenal glands, small intestine, transverse colon and the bladder. The abdominal wall was totally invaded by the tumor. Tumors in Groups B and C showed similar growth characteristics.
Histopathological characteristics of VX2 rabbit PC
All investigated tumor specimens showed extensive invasive growth and tissue destruction. The tumors, on the greater curvature of the gastric antrum, penetrated the mucosal layer to form ulcers. Microscopic view could find cancer nests penetrating the whole stomach wall, with typical invasion into the muscle layer and the gastric glands (Figure 4A). The tumor cells are round, oval or atypical morphology with many pathological mitotic figures (Figure 4B). There were also conspicuous lymphocytes, plasma cells and other inflammatory cells infiltration.
Major features of this rabbit model of PC from gastric cancer could be summarized in Table 1.
Discussion
PC represents a serious clinical challenge in the treatment of gastrointestinal and gynecological cancers. In gastric cancer, PC is a frequent event with 15% to 50% or more patients having PC at the surgical exploration, especially when there is serosal involvement by the tumor [14–16]. Even after curative resection of gastric cancer, PC remains a major problem of postoperative recurrence. A Korean study in 500 gastric cancer patients treated by standardized radical gastrectomy and lymphadectomy, found that within 5 years post gastrectomy, PC is the most frequent pattern (51.7%) of cancer recurrence [17]. Another randomized prospective study in Japan also found peritoneal recurrence is the most frequent event (15.8%) at 3 years in 530 patients treated with highly standardized curative gastrectomy [18]. A prospective Italian study in 200 patients found that, at the mean follow-up of 42.3 months, PC accounted for 32.9% of recurrence [19]. Another Italian study with 441 gastric cancer patients showed 17% PC recurrence at the median follow-up of 48 months [20]. Therefore, synchronous and metachronous PC is the most important problem of gastric cancer recurrence and metastasis. Such gastric PC is associated with poor prognosis with median survival ranging from 1-1.6 months [21, 22] to 3.1-9 months [1, 15]. As is rightly stated, the risk of peritoneal recurrence of gastric cancer is particularly high in patients with diffuse-mixed tumors and infiltration of the serosa, against which surgery alone, no matter how radical, can offer little possibility of a cure [20]. Therefore, new comprehensive treatment strategies are required.
Clinical studies suggest that CRS plus HIPEC could achieve good efficacy in selected patients with PC. To our knowledge there are 4 institutional studies on CRS plus HIPEC in patients with gastric cancer, 2 retrospective (42 and 26 patients, respectively) [3, 23], 1 prospective (49 patients) [4] and 1 comparative non-randomized (34 patients) studies [24]. The median survival ranged from 6.6 months [24], 8 months [23] to 10-11 months [3, 4], and the 5-year survival ranged from 6% [3, 25] to 16% [4]. These clinical studies are based on non-homogenous and non-standardized groups of patients. In order to more objectively evaluate such treatment, it is necessary to study this treatment modality under experimental conditions.
Small animal models of PC have been established, including nude mice models and rat models [26–29]. In most of these animal models, cancer cells are injected directly into the peritoneum, which will result in widespread PC in due time [25, 30–32]. All these small animal models are only suitable for HIPEC alone because the small body size and limited blood supply cannot stand major surgical interventions. The establishment of large animal model of PC from gastric cancer is necessary for experimental studies testing CRS and HIPEC.
VX2 carcinoma is a rabbit tumor of epithelial origin, established from a virus-induced papilloma by Rous and coworkers [12]. Characterized by rapid tumor growth and early metastasis, this tumor is extremely malignant and can be allogeneously transplanted almost anywhere in rabbits. Although VX2 is a squamous cell carcinoma model, which may be different from adenocarcinoma, it has been used in many experimental studies on head and neck cancer [33–36], lung cancer [37], esophageal cancer [38, 39], breast cancer [40], gastric cancer [41, 42], liver cancer [43, 44], colon cancer [45, 46], kidney cancer [47–49], bladder cancer [50], bone tumor [51] and simple peritoneal carcinomatosis [52]. In this study we constructed a rabbit model of gastric cancer with PC. Our results demonstrated that the orthotopic inoculation of tumor cells into the stomach is the most appropriate method, resulting in typical ulcerative gastric cancer and progressive PC, all features similar to the clinico-pathologic progression of gastric cancer patients. In comparison, percutaneous injection of cancer cells into the abdominal cavity could result in intestinal injury by mistake. No ulcerative gastric cancer could be induced, and the tumor take rate is low. These results support the notion that orthotopic tumor model is preferred for the study of tumor biological behaviors and interventions [53]. The natural history of this model is about 4 weeks, including a subclinical stage in the first week, clinical stage in the second week, accelerated PC stage in the third week and terminal stage in the fourth week. Typical PC features are peritoneal cancer nodules of various sizes throughout the whole abdominal cavity, "omentum cake", intestinal obstruction and bloody ascites. The end of the first week could be considered as the early PC, while the end of the second week as the advanced PC. Therefore, specific treatment approaches could be designed to target either early PC or advanced PC.
Conclusions
A rabbit model of gastric cancer with PC has been established by injecting VX2 cancer cells into the submucosal layer of the stomach. The model is characterized by typical ulcerative gastric cancer with progressive PC, making it more suitable for surgical interventional studies to evaluate CRS and HIPEC against gastric PC.
References
Sadeghi B, Arvieux C, Glehen O, Beaujard AC, Rivoire M, Baulieux J, Fontaumard E, Brachet A, Caillot JL, Faure JL, Porcheron J, Peix JL, François Y, Vignal J, Gilly FN: Peritoneal carcinomatosis from non-gynecologic malignancies: results of the EVOCAPE 1 multicentric prospective study. Cancer. 2000, 88: 358-363. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(20000115)88:2<358::AID-CNCR16>3.0.CO;2-O.
al-Shammaa HAH, Li Y, Yonemura Y: Current status and future strategies of cytoreductive surgery plus intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemotherapy for peritoneal carcinomatosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008, 14: 1159-1166. 10.3748/wjg.14.1159.
Yonemura Y, Kawamura T, Bandou E, Takahashi S, Sawa T, Matsuki N: Treatment of peritoneal dissemination from gastric cancer by peritonectomy and chemohyperthermic peritoneal perfusion. Br J Surg. 2005, 92: 370-375. 10.1002/bjs.4695.
Glehen O, Schreiber V, Cotte E, Sayag-Beaujard AC, Osinsky D, Freyer G, François Y, Vignal J, Gilly FN: Cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemohyperthermia for peritoneal carcinomatosis arising from gastric cancer. Arch Surg. 2004, 139: 20-26. 10.1001/archsurg.139.1.20.
Mori T, Fujiwara Y, Sugita Y, Azama T, Ishii T, Taniguchi K, Yamazaki K, Takiguchi S, Yasuda T, Yano M, Monden M: Application of molecular diagnosis for detection of peritoneal micrometastasis and evaluation of preoperative chemotherapy in advanced gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004, 11: 14-20. 10.1007/BF02524340.
Yang XJ, Li Y, al-shammaa Hassan AH, Yang GL, Liu SY, Lu YL, Zhang JW, Yonemura Y: Cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy improves survival in selected patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis from abdominal and pelvic malignancies: results of 21 cases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009, 16: 345-351. 10.1245/s10434-008-0226-2.
Li PC, Chen LD, Zheng F, Li Y: Intraperitoneal chemotherapy with hydroxycamptothecin reduces peritoneal carcinomatosis: results of an experimental study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008, 134: 37-44. 10.1007/s00432-007-0242-9.
Hartmann J, Kilian M, Atanassov V, Braumann C, Ordemann J, Jacobi CA: First surgical tumour reduction of peritoneal surface malignancy in a rat's model. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2008, 25: 445-449. 10.1007/s10585-008-9150-x.
Aarts F, Hendriks T, Boerman OC, Oyen WJ, Bleichrodt RP: Hyperthermia and fibrinolytic therapy do not improve the beneficial effect of radioimmunotherapy following cytoreductive surgery in rats with peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal origin. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2008, 23: 301-309. 10.1089/cbr.2007.0455.
Aarts F, Bleichrodt RP, de Man B, Lomme R, Boerman OC, Hendriks T: The effects of adjuvant experimental radioimmunotherapy and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy on intestinal and abdominal healing after cytoreductive surgery for peritoneal carcinomatosis in the rat. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008, 15: 3299-3307. 10.1245/s10434-008-0070-4.
Gesson-Paute A, Ferron G, Thomas F, de Lara EC, Chatelut E, Querleu D: Pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin during open versus laparoscopically assisted heated intraoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC): an experimental study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008, 15: 339-344. 10.1245/s10434-007-9571-9.
Kidd JG, Rous P: A transplantable rabbit carcinoma originating in a virus-induced papilloma and containing the virus in masked or altered form. J Exp Med. 1940, 71: 813-838. 10.1084/jem.71.6.813.
Workman P, Balmain A, Hickman JA, McNally NJ, Rohas AM, Mitchison NA, Pierrepoint CG, Raymond R, Rowlatt C, Stephens TC, Wallace J, Straughan DW: UKCCCR guidelines for the welfare of animals in experimental neoplasia. Cancer Metast Rev. 1989, 8: 82-88. 10.1007/BF00047059.
Bozzetti F, Yu W, Baratti D, Kusamura S, Deraco M: Logoregional treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2008, 98: 273-276. 10.1002/jso.21052.
Okajima K, Yamada S: Surgical treatment of far-advanced gastric cancer. Jpn J Cancer Clin. 1986, 32: 1203-1209.
Sugarbaker PH, Yonemura Y: Clinical pathway for the management of respectable gastric cancer with peritoneal seeding: Best palliation with a ray of hope for cure. Oncology. 2000, 58: 96-107. 10.1159/000012086.
Moon YW, Jeung HC, Rha SY, Yoo NC, Roh JK, Noh SH, Kim BS, Chung HC: Changing patterns of prognosticators during 15-year follow-up of advanced gastric cancer after radical gastrectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy: a 15-year follow-up study at a single Korean institute. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007, 14: 2730-2737.
Sakuramoto S, Sasako M, Yamaguchi T, Kinoshita T, Fujii M, Nashimoto A, Furukawa H, Nakajima T, Ohashi Y, Imanura H, Higashino M, Yamamura Y, Kurita A, Arai K: Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer with S-1, an oral fluoropyrimidine. N Engl J Med. 2007, 357: 1810-1820. 10.1056/NEJMoa072252.
Muratore A, Zimmitti G, Tesoriere RL, Mellano A, Massucco P, Capussotti L: Low rates of loco-regional recurrence following extended lymph node dissection for gastric cancer. EJSO. 2009, 35: 588-592.
Roviello F, Marrelli D, Manzoni GD, Morgagni P, Leo AD, Saragoni L, Stefano AD: Prospective study of peritoneal recurrence after curative surgery for gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2003, 90: 1113-1119. 10.1002/bjs.4164.
Chu DZ, Lang NP, Thompson C, Osteen PK, Westbrook KC: Peritoneal carcinomatosis in nongynecologic malignancy. A prospective study of prognostic factors. Cancer. 1989, 63: 364-367. 10.1002/1097-0142(19890115)63:2<364::AID-CNCR2820630228>3.0.CO;2-V.
Yamada S, Takeda T, Matsumoto K: Prognostic analysis of malignant pleural and peritoneal effusions. Cancer. 1983, 51: 136-140. 10.1002/1097-0142(19830101)51:1<136::AID-CNCR2820510127>3.0.CO;2-X.
Scaringi S, Kianmanesh R, Sabate JM, Facchiano E, Jouet P, Coffin B, Parmentier G, Hay JM, Flamant Y, Msika S: Advanced gastric cancer with or without peritoneal carcinomatosis treated with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy: a single western center experience. EJSO. 2008, 34: 1246-1252.
Hall JJ, Loggie BW, Shen P, Beamer S, Douglas Case L, McQuellon R, Geisinger KR, Levine EA: Cytoreductive surgery with intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Surg. 2004, 8: 454-463. 10.1016/j.gassur.2003.12.014.
Pelz JO, Doerfer J, Decker M, Dimmler A, Hohenberger W, Meyer T: Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemoperfusion (HIPEC) decrease wound strength of colonic anastomosis in a rat model. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007, 22: 941-947. 10.1007/s00384-006-0246-y.
Flatmark K, Reed W, Halvorsen T, Sørensen O, Wiig JN, Larsen SG, Fodstad Ø, Giercksky KE: Pseudomyxoma peritonei--two novel orthotopic mouse models portray the PMCA-I histopathologic subtype. BMC Cancer. 2007, 7: 116-10.1186/1471-2407-7-116.
Pelz JO, Doerfer J, Hohenberger W, Meyer T: A new survival model for hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in tumor-bearing rats in the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis. BMC Cancer. 2005, 5: 56-10.1186/1471-2407-5-56.
Braumann C, Stuhldreier B, Bobrich E, Menenakos C, Rogalla S, Jacobi CA: High doses of taurolidine inhibit advanced intraperitoneal tumor growth in rats. J Surg Res. 2005, 129: 129-135. 10.1016/j.jss.2005.03.012.
Braumann C, Jacobi CA, Rogalla S, Menenakos C, Fuehrer K, Trefzer U, Hofmann M: The tumor suppressive reagent taurolidine inhibits growth of malignant melanoma--a mouse model. J Surg Res. 2007, 143: 327-378. 10.1016/j.jss.2007.01.041.
Pelz JO, Doerfer J, Dimmler A, Hohenberger W, Meyer T: Histological response of peritoneal carcinomatosis after hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemoperfusion (HIPEC) in experimental investigations. BMC Cancer. 2006, 6: 162-10.1186/1471-2407-6-162.
Otto J, Jansen PL, Lucas S, Schumpelick V, Jansen M: Reduction of peritoneal carcinomatosis by intraperitoneal administration of phospholipids in rats. BMC Cancer. 2007, 7: 104-10.1186/1471-2407-7-104.
Monneuse O, Mestrallet JP, Quash G, Gilly FN, Glehen O: Intraperitoneal treatment with dimethylthioampal DIMATE combined with surgical debulking is effective for experimental peritoneal carcinomatosis in a rat model. J Gastrointest Surg. 2005, 9: 769-774. 10.1016/j.gassur.2005.02.006.
van Es RJ, Dullens HF, Bilt van der A, Koole R, Slootweg PJ: Evaluation of the VX2 rabbit auricle carcinoma as a model for head and neck caner in humans. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2000, 28: 300-307.
Sapundzhiev NR, Dunne AA, Ramaswamy A, Sitter H, Davis RK, Werner JA: Lymph node metastasis in an animal model: effect of piecemeal laser surgical resection. Lasers Surg Med. 2005, 36: 371-376. 10.1002/lsm.20184.
Matsumura T, Sugahara T, Yui S, Kobayashi S, Ishihara Y, Nakamura M, Fuchihata H: Effect of irradiation on lung metastasis of VX2 carcinoma in maxillary sinus of rabbit. Oral Radiol. 1985, 1: 117-123. 10.1007/BF02350164.
Schulz S, Haussler U, Mandic R, Heverhagen JT, Neubauer A, Dunne AA, Werner JA, Weihe E, Bette M: Treatment with ozone/oxygen-penumoperitoneum results in complete remission of rabbit squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 2008, 122: 2360-2367. 10.1002/ijc.23382.
Shomura Y, Saito Y, Minami K, Imamura H: A new method for establishing an intrapulmonary tumor in the rabbit. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003, 51: 337-343. 10.1007/BF02719464.
Mine H, Nakamura T: Mode of lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer induced in rabbits with VX2 carcinoma. Jpn J Surg. 1983, 13: 236-245. 10.1007/BF02469483.
Sheyhedin I, Okunaka T, Kato H, Yamamoto Y, Sakaniwa N, Konaka C, Aizawa K: Localization of experimental submucosal esophageal tumor in rabbits by using mono-L-aspartyl chlorine e6 and long-wavelength photodynamic excitation. Lasers Surg Med. 2000, 26: 83-89. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9101(2000)26:1<83::AID-LSM12>3.0.CO;2-1.
Wang L, Yao Q, Wang J, Wei G, Li G, Li D, Ling R, Chen J: MRI and hybrid PET/CT for monitoring tumour metastasis in a metastatic breast cancer model in rabbit. Nucl Med Commun. 2008, 29: 137-143. 10.1097/MNM.0b013e3282f258c1.
Tabuchi Y, Nakamura T, Saitoh Y: Liver metastases induced by implantation of VX2 cancer into the gastrointestine. J Surg Res. 1991, 50: 216-222. 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90181-K.
Hagiwara A, Takahashi T, Ueda T, Lee R, Takeda M, Itoh T: Intraoperative chemotherapy with carbon particles adsorbing mitomycin C for gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination in rabbits. Surgery. 1988, 104: 874-881.
Nakakuma K, Tashiro S, Hiraoka T, Ogata K, Ootsuka K: Hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic cancer detected by iodized oil. Radiology. 1985, 154: 15-17.
Sano B, Sugiyama Y, Kunieda K, Sano J, Saji S: Antitumor effects induced by the combination of TNP-470 as an angiogenesis inhibitor and lentinan as a biological response modifier in a rabbit spontaneous liver metastasis model. Surg Today. 2002, 32: 503-509. 10.1007/s005950200085.
Sakane M, Tabuchi Y, Saitoh Y: Suppressive effect of doxorubicin on liver recurrence after resection of colonic VX2 cancer lesions: differences in efficacy according to the injection protocol. Surg Today. 1993, 23: 514-520. 10.1007/BF00730627.
Nagamitsu A, Konno T, Oda T, Kabaru K, Ishimaru Y, Kitamura N: Targeted cancer chemotherapy for VX2 tumor implanted in the colon with lipiodol as a carrier. Eur J Cancer. 1998, 34: 1764-1769. 10.1016/S0959-8049(98)00153-1.
Gadeholt-Gothlin G, Gothlin JH: Comparison of nephrectomy and/or doxorubicin treatment in rabbit VX-2 carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 1995, 58: 134-145. 10.1002/jso.2930580213.
Bruners P, Braunschweig T, Hodenius M, Pietsch H, Penzkofer T, Baumann M, Gunther RW, Schmitz-Rode T: Thermoablation of malignant kidney tumor using magnetic nanoparticles: an in vivo feasibility study in a rabbit model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010, 33: 127-134. 10.1007/s00270-009-9583-x.
Miao Y, Ni Y, Hosmans H, Yu J, Vaninbroukx J, Dymarkowski S, Zhang H, Marchal G: Radiofrequency ablation for eradication of renal tumor in a rabbit model by using a cooled-tip electrode technique. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001, 8: 651-657. 10.1007/s10434-001-0651-y.
Yang WH, Liebert M, Price RE, Cromeens DM, Lin JSN, Grossman HB: Extravesical cryosurgical approach for VX2 bladder tumor in rabbits. Urol Res. 2001, 29: 345-349. 10.1007/s002400100204.
Yamaguchi H, Mochizuki K, Ishii Y: Experimental study of chemical embolus therapy combined with radiotherapy for VX2 bone tumors. Int J Clin Oncol. 2000, 5: 386-394. 10.1007/PL00012068.
Murata N, Ishida H, Nomura T, Yamada H, Idezuki Y: The facilitation of peritoneal dissemination of a tumor by laparotomy in a rabbit model. Surg Today. 2000, 30: 54-58. 10.1007/PL00010047.
Talmadge JE, Singh RK, Fidler IJ, Raz A: Murine models to evaluate novel and conventional therapeutic strategies for cancer. Am J Pathol. 2007, 170: 793-804. 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060929.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/10/124/prepub
Acknowledgements
This work was supported Foundation for the Author of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of China (No FANEDD-200464); the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20621502, 20921062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
LI Y conceived, designed and partly conducted the study. Mei LJ, Yang XJ, Tang L, and Hassan AHA conducted the study and drafted the manuscript. Yonemura Y gave technique instructions and revised the manuscript. All authors have read the approved the final manuscript.
Lie-Jun Mei, Xiao-Jun Yang contributed equally to this work.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Mei, LJ., Yang, XJ., Tang, L. et al. Establishment and identification of a rabbit model of peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 10, 124 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-124
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-124