Abstract
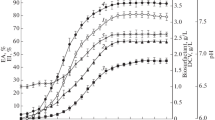
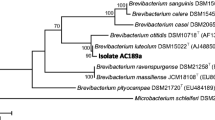
Inquilinus limosus strain KB3, isolated from marine sediment in the south of Thailand, was used to produce a biosurfactant from a mineral salts medium (MSM) with palm oil decanter cake (PODC) as a carbon source. It was found that cellular growth and biosurfactant production in MSM were greatly affected by the medium components. I. limosus KB3 was able to grow and to produce surfactant reducing the surface tension of medium to 28.2 mN/m and giving a crude surfactant concentration of 5.13 g/l after 54 h. The biosurfactant obtained was found to reduce the surface tension of pure water to 25.5 mN/m with the critical micelle concentration of 9 mg/l, and retained its properties during exposure to elevated temperatures (121 °C), high salinity (12 % NaCl), and a wide range of pH values. Chemical characterization by FT-IR, NMR, and ESI-MS revealed that the biosurfactant has a lipopeptide composition with molecular mass (m/z) of 1,032. The biosurfactant was capable of forming stable emulsions with various hydrocarbons and had the ability to enhance oil recovery, PAHs solubility, and antimicrobial activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Aboulwafa AM, Hassouna NAH (2008) Optimization of surfactin production by Bacillus subtilis isolate BS5. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 150:305–325
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Aboulwafa MM, Hassouna NAH (2009) Characterization of rhamnolipid produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolate Bs20. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 157:329–345
Anderson RC, Yu PK (2005) Factors affecting the antimicrobial activity of ovine-dervied cathelicidins aginst Escherichia coli O157:H7. Int J Antimicrob Ag 25:205–210
Aniszewski E, Peixoto SR, Mota FF, Leite SGF, Rosado SA (2010) Bioemulsifier production by Microbacterium sp. strains isolated from mangrove and their application to remove cadmium and zinc from hazardous industrial residue. Braz J Microbiol 41:235–245
Banat IM, Franzetti A, Gandolfi I, Bestetti G, Martinotti MG, Fracchia L, Smyth TJ, Marchant R (2010) Microbial biosurfactants production, applications and future potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:427–444
Barber WP, Stuckey DC (2000) Nitrogen removal in a modified anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR): 1, denitrification. Water Res 10:2413–2422
Barkay T, Navon-Venezia S, Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (1999) Enhancement of solubilization and biodegradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons by the bioemulsifier alasan. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2697–2702
Benincasa M, Contiero J, Manresa MA, Moraes IO (2002) Rhamnolipid production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBI growing on soapstock as the sole carbon source. J Food Eng 54:283–288
Candan F, Unlu M, Tepe B, Daferera D, Polissiou M, Sokmen A, Akpulat HA (2003) Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil and methanol extracts of Achillea millefolium subsp. millefolium Afan. (Asteraceae). J Ethnopharmacol 87:215–220
Chayabutra C, Wu J, Ju LK (2001) Rhamnolipid production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa under denitrification: effects of limiting nutrients and carbon substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 72:25–33
Chen HL, Juang RS (2008) Recovery and separation of surfactin from pretreated fermentation broths by physical and chemical extraction. Biochem Eng J 38:39–46
Das K, Mukherjee AK (2007) Comparison of lipopeptide biosurfactants production by Bacillus subtilis strains in submerged and solid state fermentation systems using a cheap carbon source: some industrial applications of biosurfactants. Process Biochem 42:1191–1199
Das P, Mukherjee S, Sen R (2009) Substrate dependent production of extracellular biosurfactant by a marine bacterium. Bioresource Technol 100:1015–1019
Ghojavand H, Vahabzadeh F, Roayaei E, Khodabandeh A (2008) Production and properties of a biosurfactant obtained from a member of the Bacillus subtilis group (PTCC 1696). J Colloid Interf Sci 324:172–176
Gudina EJ, Teixeira JA, Rodrigues LR (2011) Isolation and functional characterization of a biosurfactant produced by Lactobacillus paracasei. Colloid Surf B 76:298–304
Ilori MO, Amobi CJ, Odocha AC (2005) Factors affecting biosurfactant production by oil degrading Aeromonas sp., isolated from a tropical environment. Chemosphere 61:985–992
Intergovernmental oceanographic commission manuals and guide No.13 (1982) Manual for monitoring oil and dissolved/dispersed petroleum hydrocarbons in marine waters and beaches. UNESCO
Joshi S, Bharucha C, Jha S, Yadav S, Nerurkar A, Desai AJ (2008) Biosurfactant production using molasses and whey under thermophilic conditions. Bioresource Technol 99:195–199
Li JL, Chen BH (2009) Surfactant-mediated biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Materials 2:76–94
Makkar R, Cameotra SS (2002) An update on the use of unconventional substrates for biosurfactant production and their new applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:428–434
Maneerat S (2009) Biosurfactants from marine microorganisms. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 27:1263–1272
Muthusamy K, Gopalakrishnan S, Ravi TK, Sivachidambaram P (2008) Biosurfactants: properties, commercial production and application. Curr Microbiol 94:736–747
Negi PS, Chauhan AS, Sadia GA, Rohinishree YS, Ramteke RS (2005) Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of various seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed extracts. Food Chem 92:119–124
Nitschke M, Pastore G (2006) Production and properties of a surfactant obtained from Bacillus subtilis grown on cassava wastewater. Bioresource Technol 97:336–341
Obayori O, Ilori M, Adebusoye S, Oyetibo G, Omotayo A, Amund O (2009) Degradation of hydrocarbons and biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas sp. strain LP1. World J Microb Biot 25:1615–1623
Roongsawang N, Thaniyavarn J, Thaniyavarn S, Kameyama T, Haruki M, Imanaka T, Morikawa M, Kanaya S (2002) Isolation and characterization of a halotolerant Bacillus subtilis BBK-1 which produces three kinds of lipopeptides: bacillomycin L, plipastatin, and surfactin. Extremophiles 6:499–506
Saimmai A, Sobhon V, Maneerat S (2011) Molasses a whole medium for bosurfactants production by Bacillus strains and their application. Appl Biochem Biotech 165:315–335
Saimmai A, Sobhon V, Maneerat S (2012a) Mangrove sediment, a new source of potential biosurfactant producing bacteria. Ann Microbiol. doi:10.1007/s13213-012-0424-9
Saimmai A, Sobhon V, Maneerat S (2012b) Production of biosurfactant from a new and promising strain of Leucobacter komagatae 183. Ann Microbiol 62:391–402
Santos AS, Sampaio AP, Vasquez GS, Anna LMS Jr, Pereira N, Freire DM (2002) Evaluation of different carbon and nitrogen sources in the production of rhamnolipids by a strain of Pseudomonas. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 98:1025–1035
Singh P, Cameotra SS (2004) Potential applications of microbial surfactants in biomedical sciences. Trends Biotechnol 22:142–146
Sobrinho HBS, Rufino RD, Luna JM, Salgueiro AA, Campos-Takaki GM, Leite LFC, Sarubbo LA (2008) Utilization of two agroindustrial by-products for the production of a surfactant by Candida sphaerica UCP0995. Process Biochem 43:912–917
Tabatabaee A, Assadi MM, Noohi AA, Sajadian VA (2005) Isolation of biosurfactant producing bacteria from oil reservoirs. J Environ Health Sci Eng 2:6–12
Tang JS, Gao H, Hong K, Yu Y, Jiang MM, Lin HP, Ye WC, Yao XS (2007) Complete assignments of 1H- and 13C-NMR spectral data of nine surfactin isomers. Magn Reson Chem 45:792–796
Thavasi R, Jayalakshmi S, Banat IM (2001) Effect of biosurfactant and fertilizer on biodegradation of crude oil by marine isolates of Bacillus megaterium, Corynebacterium kutscheri and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioresource Technol 102:772–778
Thavasi R, Jayalakshmi S, Balasubramaniam T, Banat IM (2008) Production and characterization of a glycolipid biosurfactant from Bacillus megaterium using economically cheaper sources. World J Microb Biot 24:917–925
Wu JY, Yeh KL, Lu WB, Lin CL, Chang JS (2008) Rhamnolipid production with indigenous Pseudomonas aeruginosa EM1 isolated from oil-contaminated site. Bioresource Technol 99:1157–1164
Yahya A, Sye CP, Ishola TA, Suryanto H (2010) Effect of adding palm oil mill decanter cake slurry with regular turning operation on the composting process and quality of compost from oil palm empty fruit bunches. Bioresource Technol 101:8736–8741
Zhou M, Rhue RD (2000) Screening commercial surfactants suitable for remeditating DNAPL source zones by solubility. Environ Sci Technol 34:1985–1990
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Phuket Rajabhat University for providing a scholarship to A.S. This work was supported by the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of Thailand, Office of the Higher Education Commission and the Postdoctoral Fellowship from Prince of Songkla University. The work was also funded by the Graduate School, Prince of Songkla University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saimmai, A., Udomsilp, S. & Maneerat, S. Production and characterization of biosurfactant from marine bacterium Inquilinus limosus KB3 grown on low-cost raw materials. Ann Microbiol 63, 1327–1339 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0592-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0592-7