Abstract
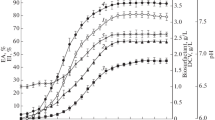
The Leucobacter komagatae 183 strain, isolated from mangrove sediment in Trang, southern Thailand, was evaluated as a potential biosurfactant producer. The biosurfactant production was carried out by using a mineral salt medium with commercial sugar and monosodium glutamate as the carbon and nitrogen source, respectively. The microbial growth was investigated and the best cultivation time for the biosurfactant was found to be 54 h. After the microbial cultivation at 30°C under optimized conditions, the biosurfactant produced was found to reduce the surface tension of pure water to 26.5 mN/m with the critical micelle concentration of about 9 mg/l. The stability of the biosurfactant at different salinities, pH and temperature and also its emulsifying activity has been investigated. It is an effective surfactant at very low concentrations over a wide range of temperatures, pHs and salt concentrations. The crude biosurfactant showed a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity and also had the ability to emulsify oil and enhance PAHs solubility.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RC, Yu PK (2005) Factors affecting the antimicrobial activity of ovine-dervied cathelicidins aginst Escherichia coli O157:H7. Int J Antimicrob Ag 25:205–210
Banat IM, Franzetti A, Gandolfi I, Bestetti G, Martinotti MG, Fracchia L, Smyth TJ, Marchant R (2010) Microbial biosurfactants production, applications and future potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:427–444
Barkay T, Navon-Venezia S, Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (1999) Enhancement of solubilization and biodegradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons by the bioemulsifier alasan. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2697–2702
Benincasa M, Contiero J, Manresa MA, Moraes IO (2002) Rhamnolipid production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBI growing on soap stock as the sole carbon source. J Food Eng 54:283–288
Candan F, Unlu M, Tepe B, Daferera D, Polissiou M, Sokmen A, Akpulat HA (2003) Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil and methanol extracts of Achillea millefolium subsp. millefolium Afan. (Asteraceae). J Ethnopharmacol 87:215–220
Chayabutra C, Wu J, Ju LK (2001) Rhamnolipid production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa under denitrification: effects of limiting nutrients and carbon substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 72:25–33
Cooper DG, Goldenberg BG (1987) Surface-active agents from two Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:224–229
Das K, Mukherjee AK (2007) Crude petroleum-oil biodegradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from petroleum oil contaminated soil from North-East India. Bioresource Technol 98:1339–1345
Das P, Mukherjee S, Sen R (2008) Antimicrobial potential of a lipopeptide biosurfactant derived from a marine Bacillus circulans. J Appl Microbiol 104:1675–1684
Dastgheib SMM, Amoozegar MA, Elahi E, Asad S, Banat IM (2008) Bioemulsifier production by a halothermophilic Bacillus strain with potential applications in microbially enhanced oil recovery. Biotechnol Lett 30:263–270
Fathabad EG (2011) Biosurfactants in pharmaceutical industry. Am J Drug Discov Dev 1:58–69
Ghojavand H, Vahabzadeh F, Roayaei E, Khodabandeh A (2008) Production and properties of a biosurfactant obtained from a member of the Bacillus subtilis group (PTCC 1696). J Colloid Interf Sci 324:172–176
Gudina EJ, Rocha V, Teixeira JA, Rodrigues LR (2010) Antimicrobial and antiadhesive properties of a biosurfactant isolated from Lactobacillus paracasei ssp. paracasei A20. Lett Appl Microbiol 50:419–424
Haddad NI, Wang J, Mu B (2008) Isolation and characterization of a biosurfactant producing strain, Brevibacilis brevis HOB1. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1597–1604
Ilori MO, Amobi CJ, Odocha AC (2005) Factors affecting biosurfactant production by oil degrading Aeromonas sp., isolated from a tropical environment. Chemosphere 61:985–992
Janek T, Lukaszewicz M, Rezanka T, Krasowska A (2010) Isolation and characterization of two new lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens BD5 isolated from water from the arctic archipelago of Svalbard. Bioresource Technol 101:6118–6123
Jeong HS, Lim DJ, Hwang SH, Ha SD, Kong JY (2004) Rhamnolipid production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa immobilized in polyvinyl alcohol beads. Biotechnol Lett 26:35–39
Joshi S, Bharucha C, Jha S, Yadav S, Nerurkar A, Desai AJ (2008) Biosurfactant production using molasses and whey under thermophilic conditions. Bioresource Technol 99:195–199
Kim HS, Jeon JW, Kim BH, Ahn CY, Oh HM, Yoon BD (2006) Extracellular production of a glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, by Candida sp. SY16 using fed-batch fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:391–396
Kim SY, Kim JY, Kim SH, Bae HJ, Yi H, Yoon SH, Koo BS, Kwon M, Cho JY, Lee CE, Hong S (2007) Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis displays anti-proliferative effect via apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest and survival signaling suppression. FEBS Lett 581:865–871
Kuyukina MS, Ivshina IB, Makarov SO, Litvinenko LV, Cunningham CJ, Philip JC (2005) Effect of biosurfactants on crude oil desorption and mobilization in a soil system. Environ Int 31:155–161
Maneerat S, Phetrong K (2007) Isolation of biosurfactant-producing marine bacteria and characteristics of selected biosurfactant. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 29:781–791
Mulligan CN (2009) Recent advances in the environmental applications of biosurfactants. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 14:372–378
Negi PS, Chauhan AS, Sadia GA, Rohinishree YS, Ramteke RS (2005) Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of various seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed extracts. Food Chem 92:119–124
Nitschke M, Coast SG (2007) Biosurfactants in food industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 18:252–259
Obayori O, Ilori M, Adebusoye S, Oyetibo G, Omotayo A, Amund O (2009) Degradation of hydrocarbons and biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas sp. strain LP1. World J Microb Biot 25:1615–1623
Pornsunthorntawee O, Wongpanit P, Chavadej S, Abe M, Rujiravanit R (2008) Structural and physicochemical characterization of crude biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa SP4 isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil. Bioresource Technol 99:1589–1595
Rahman KSM, Rahman TJ, McClean S, Marchant R, Banat IM (2002) Rhamnolipid biosurfactant production by strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa using low-cost raw materials. Biotechnol Prog 18:1277–1281
Rodrigues L, Banat IM, Teixeira J, Oliveira R (2006) Biosurfactants: potential applications in medicine. J Antimicrob Chemoth 57:609–618
Roongsawang N, Thaniyavarn J, Thaniyavarn S, Kameyama T, Haruki M, Imanaka T, Morikawa M, Kanaya S (2002) Isolation and characterization of a halotolerant Bacillus subtilis BBK-1 which produces three kinds of lipopeptides: bacillomycin L, plipastatin, and surfactin. Extremophiles 6:499–506
Saimmai A, Tani A, Kimbara K, Sobhon V, Maneerat S (2010) Mangrove sediment, a new source of potential biosurfactant producing bacteria. World J Microb Biot (in press)
Sangster J (1989) Octanol-water partition coefficients of simple organic compounds. J Phys Chem Ref Data 18:3
Santos AS, Sampaio AP, Vasquez GS, Santa Anna LM, Pereira N Jr, Freire DM (2002) Evaluation of different carbon and nitrogen sources in the production of rhamnolipids by a strain of Pseudomonas. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 98:1025–1035
Seydlova G, Svobodova J (2008) Review of surfactin chemical properties and the potential biomedical applications. Cent Eur J Med 3:123–133
Singh P, Cameotra SS (2004) Potential applications of microbial surfactants in biomedical sciences. Trends Biotechnol 22:142–146
Sobrinho HBS, Rufino RD, Luna JM, Salgueiro AA, Campos-Takaki GM, Leite LFC, Sarubbo LA (2008) Utilization of two agroindustrial by-products for the production of a surfactant by Candida sphaerica UCP0995. Process Biochem 43:912–917
Tabatabaee A, Assadi MM, Noohi AA, Sajadian VA (2005) Isolation of biosurfactant producing bacteria from oil reservoirs. Iranian J Env Health Sci Eng 2:6–12
Thavasi R, Jayalakshmi S, Balasubramanian T, Banat IM (2007) Biosurfactant production by Corynebacterium kutscheri from waste motor lubricant oil and peanut oil cake. Lett Appl Microbiol 45:686–691
Wei YH, Choub CL, Changb JH (2005) Rhamnolipid production by indigenous Pseudomonas aeruginosa J4 originating from petrochemical wastewater. Biochem Eng 27:146–154
Wu JY, Yeh KL, Lu WB, Lin CL, Chang JS (2008) Rhamnolipid production with indigenous Pseudomonas aeruginosa EM1 isolated from oil-contaminated site. Bioresource Technol 99:157–1164
Yin B, Gu JD, Wan N (2005) Degradation of indole by enrichment culture and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gs isolated from mangrove sediment. Int Biodeter Biodegr 56:243–248
Yin H, Qiang J, Jia Y, Ye J, Peng H, Qin H, Zhang N, He B (2009) Characteristics of biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa S6 from oil-containing wastewater. Process Biochem 44:302–308
Zhou M, Rhue RD (2000) Screening commercial surfactants suitable for remeditating DNAPL source zones by solubility. Environ Sci Technol 34:1985–1990
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Program Strategic Scholarships for Frontier Research Network for the PhD Program Thai Doctoral degree from the Office of the Higher Education Commission, Thailand for providing a scholarship to A.S. This work was also funded by the Faculty of Agro-Industry and Graduate School, Prince of Songkla University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saimmai, A., Sobhon, V. & Maneerat, S. Production of biosurfactant from a new and promising strain of Leucobacter komagatae 183. Ann Microbiol 62, 391–402 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0275-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0275-9