Abstract
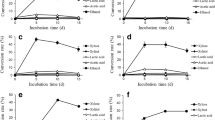
Growth of Fusarium sp. BVKT R2, a potential isolate of forest soils of Eastern Ghats on birchwood xylan in mineral salts medium (MSM) under un-optimized conditions of 30 °C, pH of 5.0, 150 rpm and inoculum size of 5 agar plugs for 7 days, yielded titer of 1290 U/mL of xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8). The effect of various operating parameters such as different substrates and their concentration, additional carbon and nitrogen sources, incubation temperature, initial pH, agitation and inoculum size on the production of xylanase by Fusarium sp. BVKT R2 was studied in shake flask culture by one factor at a time approach. The same culture exhibited higher production of xylanase (4200 U/mL) when grown on birch wood xylan in MSM under optimized conditions with an additional carbon source—sorbitol (1.5%) nitrogen source—yeast extract (1.5%) temperature of 30 °C, pH of 5.0, agitation of 200 rpm and inoculum of 6 agar plugs for only 5 days. There was enhancement in xylanase production under optimized conditions by 3.2 folds over yields under un-optimized conditions. Growth of BVKT R2 culture on locally available lignocelluloses—sawdust, rice straw and cotton stalk—in MSM for 5 days released soluble sugars to the maximum extent of 52.76% with respect to sawdust indicating its greater importance in saccharification essential for biotechnological applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahim AA, Bayoumi A (2011) Thermostable xylanases production by thermophilic fungi from some lignoce llulosic substrates. J Basic Appl Sci Res 1(12):2777–2785
Abdel-Sater MA, El-Said AHM (2001) Xylan-decomposing fungi and xylanolytic activity in agricultural and industrial wastes. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 47:15–21
Aditi K, Ray RR (2014) Effect of salic in on induction and carbon catabolite repression of endoxylanase synthesis in MTCC 10889. Chem Pap 68(4):451–456
Altaf SA, Umar DM, Muhammad MS (2010) Production of xylanase enzyme by Pleurotus eryngii and Flamulina velutipes grown on different carbon sources under submerged fermentation. World Appl Sci J 8:47–49
Altaf SA, Sughra MG, Nasreen K, Umar DM, Sher MM, Noor-e-Saba KM, Fariha RK, Lu C (2016) Characterization of crude xylanase produced by edible mushroom Pleurotus eryngii. J Bioprocess Biotech 6(2):1–6
Anand A, Kumar V, Satyanarayana T (2013) Characteristics of thermostable endoxylanase and b-xylosidase of the extremely thermophilic bacterium Geobacillus thermodenitrificans TSAA1 and its applicability in generating xylooligosaccharides and xylose from agro-residues. Extremophiles 17:357–366
Arabi MIE, Jawhar M, Bakri Y (2011) Effect of additional carbon source and moisture level on xylanase production by Cochliobolus sativus in solid fermentation. Microbiology 80:150–153
Bailey M, Biely J, Poutanen K (1992) Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol 23(3):257–270
Bakir U, Yavascaoglu S, Guvenc F, Ersayin A (2001) An endo-b 1,4- xylanase from Rhizopus oryzae: production, partial purification and biochemical characterization. Enzyme Microb Technol 29:328–334
Bakri Y, Mohammed J, Mohammed IEA (2008) Improvement of xylanase production by Cochliobolus sativus in submerged culture. Food Technol Biotechnol 46(1):116–118
Battan B, Sharma JK, Dhiman SS (2006) High level xylanase production by alkalophilic B. pumilus ASH under solid state fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:1281–1287
Beck CI, Scoot D (1974) Enzymes in foods for better or worse. Adv Chem Ser 138:1–17
Beg QK, Kapoor M, Mahajan L, Hoondal GS (2001) Microbial xylanases and their Industrial applications: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:326–338
Bhosale HJ, Sukalkar SR, Uzma SMZ, Kadam TA (2011) Production of xylanase by Streptomyces rameus grown on agricultural wastes. Biotechnol Bioinf Bioeng 1(4):505–512
Biely P (1985) Microbial xylanolytic systems. Trends Biotechnol 3:288–290
Carmona EC, Fialho MB, Buchgnani EB, Coelho GD, Brocheto-Braga MR, Jorge JA (2005) Production, purification and characterization of a minor form of xylanase from Aspergillus versicolor. Process Biochem 40:359–364
Chakdar H, Kumar M, Pandiyan K, Singh A, Nanjappan K, Kashyap PL, Srivastava AK (2016) Bacterial xylanases: biology to biotechnology. 3 Biotech 6(2):150
Collins T, Gerday C, Feller G (2005) Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:3–23
Damiano VB, Bocchini DA, Gomes E, Da Silva R (2003) Application of crude xylanase from Bacillus licheniformis 77-2 to the bleaching of eucalyptus Kraft pulp. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:139–144
Despres J, Forano E, Lepercq P, Comtet-Marre S, Jubelin G, Chambon C, Yeoman CJ, Berg Miller ME, Fields CJ, Martens E, Terrapon N, Henrissat B, White BA, Moson P (2016) Xylan degradation by the human gut Bacteroides xylanisolvens XB1AT involves two distinct gene clusters that are linked at the transcriptional level. BMC Genomics 17:326
Deswal D, Gupta R, Nandal P, Kuhad RC (2014) Fungal pretreatment improves amenability of lignocellulosic material for its saccharification to sugars. Carbohydr Polym 99:264–269. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.045
de Alencar Guimaraes NC, Sorgatto M, Peixoto-Nogueira S de C, Betini JHA, Zanoelo FF, Marques MR, Lourdes M de, Moraes T de, Polizeli, Giannesi GC (2013) Bioprocess and biotechnology: effect of xylanase from Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus flavus on pulp biobleaching and enzyme production using agro industrial residues as substract. Springer Plus 2:380
Dhillon A, Gupta JK, Jauhari BM, Khanna SA (2000) A cellulase poor, thermostable, alkali-tolerant xylanase produced by Bacillus circulans AB16 grown on rice straw and its application in biobleaching of eucalyptus pulp. Bioresour Technol 73:273–277
Dodd D, Cann IKO (2009) Enzymatic deconstruction of xylan for biofuel production. GCB Bioenergy 1:2–17
Dodd D, Mackie RI, Cann IKO (2011) Xylan degradation, a metabolic property shared by rumen and human colonic Bacteroidetes. Mol Microbiol 79(2):292–304
Fadel M (2001) Production physiology of cellulase and β-glucosidase enzymes of Aspergillus niger grown under solid state fermentation conditions. J Biol Sci 1(5):401–411
Garai D, Kumar V (2013) Response surface optimization for xylanase with high volumetric productivity by indigenous alkali tolerant Aspergillus candidus under submerged cultivation. 3 Biotech 3(2):127–136
Garg N, Mahatma KK, Kumar A (2010) Xylanase: applications and biotechnological aspects. Lambert Academic Publishing AG & Co. KG, Saarbrucken
Gilbert HJ, Hazelwood GP (1999) Bacterial cellulases and xylanases. J Gen Microbiol 139:187–194
Goyal M, Kalra KL, Sareen VK, Soni G (2008) Xylanase production with xylan rich lignocellulosic wastes by a local soil isolate of Trichoderma viride. Braz J Microbiol 39:535–541
Gupta VK, Rajeeva G, Santosh KY, Nandan SD (2009) Optimization of xylanase production from free and immobilized cells of Fusarium solani F7. BioResources 4(3):932–945
Haas H, Herfurth E, Stoffler G, Redl B (1992) Purification, characterization and partial amino acid sequences of a xylanase produced by Penicillium chrysogenum. Biochem Biophys Acta 1117:279–286
Haltrich D, Preiss M, Steiner W (1993) Optimization of a culture medium for increased xylanase production by a wild strain of Schizophyllum commune. Enzyme Microb Technol 15:854–860
Haltrich D, Nidetzky B, Kulbe KD, Steiner W, Zupaneie S (1996) Production of fungal xylanases. Bioresour Technol 58:137–161
Harshvardhan K, Mishra A, Jha B (2013) Purification and characterization of cellulase from a marine Bacillus sp. H1666: a potential agent for single step saccharification of seaweed biomass. J Mol Catal B Enzym 93:51–56
Hoq MM, Carsten H, Wolf-Dieter D (1994) Cellulase-free xylanase by Thermomyces lanuginosus RT9: effect of agitation, aeration, and medium components on production. J Biotechnol 37(1):4958
Irfan M, Muhammad N, Quratulain S (2014) One-factor-at-a-time (OFAT) optimization of xylanase production from Trichoderma viride-IR05 in solid-state fermentation. J Rad Res Appl Sci 7:317–326
Isil S, Nilufer A (2005) Xylanase production from T. harzianum 1073 D3 with alternative carbon and nitrogen sources. Food Technol Biotechnol 43:37–40
Jiang Z, Cong Q, Yan Q, Kumar N, Du X (2010) Characterisation of a thermostable xylanase from Chaetomium sp. and its application in Chinese steamed bread. Food Chem 120:457–462
Joshi C, Khare SK (2012) Induction of xylanase in thermophilic fungi Scytalidium thermophilum and Sporotrichum thermophile. Braz Arch Biol Technol 55:21–27. doi:10.1590/s1516-89132012000100003
Kalogeris E, Iniotaki F, Topakas E, Christakopoulos P, Kekos D, Macris BJ (2003) Performance of an intermittent agitation rotating drum type bioreactor for solid state fermentation of wheat straw. Bioresour Technol 86:207–213
Kheng PP, Omar IC (2005) Xylanase production by a local fungal isolate, Aspergillus niger USM AI 1 via solid state fermentation using palm kernel cake (PKC) as substrate. J Sci Technol 27(2):325–336
Kiddinamoorthy J, Anceno JA, Haki DG, Rakshit SK (2008) Production, purification and characterization of Bacillus sp. GRE7 xylanase and its application in eucalyptus Kraft pulp biobleaching. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:605–612
Knob A, Carmona EC (2008) Xylanase production by Penicillium sclerotiorum and its characterization. World Appl Sci J 4(2):277–283
Kuhad RC, Manchanda M, Singh A (1998) Optimization of xylanase production by a hyperxylanolytic mutant strain of F. oxysporum. Process Biochem 33:641–647
Kumar KS, Ayyachamy M, Kugen P, Suren S (2009) Production of β-xylanase by a Thermomyces lanuginosus MC 134 mutant on corn cobs and its application in biobleaching of bagasse pulp. J Biosci Bioeng 107(5):494–498
Latif F, Asgher M, Saleem R, Akram A, Legge R (2006) Purification and characterization of xylanase produced by C. thermophile NIBGE. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:45–50
Laxmi GS, Sathish T, Subba Rao C, Brahmaiah P, Hymavathi M, Prakasham RS (2008) Palm fiber as novel substrate for enhanced xylanase production by isolated Aspergillus sp. RSP-6. Curr Trends Biotechnol Pharm 2(3):447–455
Lejeune R, Baron GV (1995) Effect of agitation on growth and enzyme production of Trichoderma reesei in batch fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:249–258
Li Y, Lin J, Meng D, Lu J, Gu G, Mao Z (2006) Effect of pH, cultivation time and substrate concentration on the endoxylanase production by Aspergillus awamori ZH-26 under submerged fermentation using central composite rotary design. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:473–477
Lopes F, Motta F, Andrade CCP, Rodrigues MI, Maugeri-Filho F (2011) Thermo-stable xylanases from non conventional yeasts. Microb Biochem Technol 3(3):36–42
Loveleen KS, Maninder A, Sehgal VK (2010) Use of Scopulariopsis acremonium for the production of cellulase and xylanase through submerged fermentation. Afr J Microbiol Res 4(14):1506–1510
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol regent. J Gen Microbiol 131:3017–3027
Mc Cleary BV (1986) Enzymatic modification of plant polysaccharides. Int J Macromole 8:349–354
Milagres AMF, Lacis LS, Prade RA (1993) Characterization of xylanase production by a local isolate of Penicillium janthinellum. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 15:248–253
Miller GL (1959) Use of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Murthy PS, Naidu MM (2012) Production and application of xylanase from Penicillium sp. utilizing coffee by-products. Food Bioprocess Technol 5(2):657–664
Muthezhilan R, Ashok R, Jayalakshmi S (2007) Production and optimization of thermostable alkaline xylanase by Penicillium oxalicum in solid state fermentation. Afr J Microbiol Res 1(2):20–28
Nagar S, Gupta VK, Kumar D, Kumar L, Kuhad RC (2010) Production and optimization of cellulase-free, alkali-stable xylanase by Bacillus pumilus SV-85S in submerged fermentation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:71–83
Nair SG, Sindhu R, Shashidhar S (2008) Fungal xylanase production under solid state and submerged fermentation conditions. Afr J Microbiol Res 2:82–86
Nakamura S, Ishiguro Y, Nakai R, Wakabayashi K, Aono R, Horikoshi K (1995) Purification of a thermophilic alkaline xylanase from thermophilic Bacillus sp. strain TAR-1. J Mol Catal B Enzym 1:7–15
Neves ML, da Silva MF, Souza-Motta CM, Spier MR, Soccol CR, Porto TS, Moreira KA, Porto AL (2011) Lichtheimia blakesleeana as a new potential procedure of phytase and xylanase. Artic Mol 16:4807–4817
Nikhil B, Adhyaru D, Thakor P (2012) Production of xylanase by Aspergillus flavus FPDN1 on Pearl millet bran: optimization of culture conditions and application in bioethanol production. Int J Res Chem Environ 2(3):204–210
Ninawe S, Lal R, Kuhad RC (2006) Isolation of three xylanase-producing strains of actinomycetes and their identification using molecular methods. Curr Microbiol 53(3):178–182
Nochure SV, Roberts MF, Demain AI (1993) True cellulase production by Clostridium thermocellum grown on different carbon sources. Biotechnol Lett 15:641–646
Oakley AJ, Heinrich T, Thompson CA, Wilce MCJ (2003) Characterization of a family 11 from Bacillus subtilis B230 used for paper bleaching. Acta Cryst D 59:627–636
Okafor UA, Emezue TN, Okochi VI, Onyegeme-Okerenta BN, Nwodo-Chinedu S (2007) Xylanase production by Penicillium chrysogenum (PCL501) fermented on cellulosic wastes. Afr J Biochem Res 1:48–53
Otero DM, Cadaval CL, Teixeira LM, Rosa CA, Sanzo AVL, Kalil SJ (2015) Screening of yeasts capable of producing cellulase-free xylanase. Afr J Biotechnol 14(23):1961–1969
Pathak P, Bhardwaj NK, Singh AK (2014) Production of crude cellulase and xylanase from Trichoderma harzianum PPDDN10 NFCCI-2925 and its application in photocopier waste paper recycling. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:3776–3797
Paul J, Varma AK (1990) Influence of sugars on endoxylanase and bxylosidase activities of Bacillus strain. Biotechnol Lett 12:19–27
Petchluan P, Charida P, Nareerat C (2014) Characterization of xylanase and cellulase from Lentinus polychrous Lev. LP-PT-1. Chiang Mai J Sci 41(5.1):1007–1019
Polizeli MLTM, Rizzatti ACS, Monti R, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA, Amorim DS (2005) Xylanases from fungi: properties and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:577–591
Premalatha N, Gopal NO, Jose PA, Anandham R, Kwon SW (2015) Optimization of cellulase production by Enhydrobacter sp. ACCA2 and its application in biomass saccharification. Front Microbiol 6:1046. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.01046
Qinnghe C, Xiaoyu Y, Tiangui N, Cheng J, Qiugang M (2004) The screening of culture condition and properties of xylanase by white-rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Process Biochem 39:1561–1566
Raghukumar C, Muraleedharan U, Gaud VR, Mishra R (2004) Xylanases of marine fungi of potential use for biobleaching of paper pulp. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31:433–441
Rahman AK, Sugitani N, Hatsu M, Takamizawa K (2003) A role of xylanase, α-l-arabinofuranosidase, and xylosidase in xylan degradation. Can J Microbiol 49:58–64
Ramanjaneyulu G, Rajasekhar Reddy B (2016) Optimization of xylanase production through response surface methodology by Fusarium sp. BVKT R2 isolated from forest soil and its application in saccharification. Front Microbiol 7:1450. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.01450
Ramanjaneyulu G, Praveen Kumar Reddy G, Dileep Kumar K, Rajasekhar Reddy B (2015) Isolation and screening of xylanase producing fungi from forest soils. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 4:586–591
Ramanjaneyulu G, Ramya A, Shanthi Kumari B, Dileep Kumar K, Rajasekhar Reddy B (2016) Xylanase producing microflora in Eastern Ghats of Andhra Pradesh, India. J For Res. doi:10.1007/s11676-016-0305-3
Ravichandra K, Yaswanth VVN, Nikhila B, Jamal A, Srinivasa Rao P, Uma A, Ravindrababu V, Prakasham RS (2015) Xylanase production by isolated fungal strain, Aspergillus fumigatus RSP-8 (MTCC 12039): impact of agroindustrial material as substrate. Sugar Tech. doi:10.1007/s12355-014-0357-7
Saha BC, Bothast RJ (1999) Enzymology of xylan degradation. ACS Symp Ser 723:167–194
Saha SP, Ghosh S (2014) Optimization of xylanase production by Penicillium citrinum xym2 and application in saccharification of agro-residues. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3:188–196
Sanghi A, Garg N, Kuhar K, Kuhad RC, Gupta VK (2009) Enhanced production of cellulase-free xylanase by alkalophilic Bacillus subtilis ASH and its application in biobleaching of kraft pulp. BioResources 4:1109–1129
Santhi VS, Bhagat AK, Saranya S, Govindarajan G, Jebakumar SRD (2014) Seaweed (Eucheuma cottonii) associated microorganisms, a versatile enzyme source for the lignocellulosic biomass processing. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 96:144–151. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.08.007
Sepahy AA, Ghazi S, Sepahy MA (2011) Cost-effective production and optimization of alkaline xylanase by indigenous Bacillus mojavensis AG13 fermented on agricultural waste. Enzyme Res. doi:10.4061/2011/593624
Simoes MLG, Tauk-Torniseielo SM (2006) Optimization of xylanase biosynthesis by Aspergillus japonicus isolated from a ‘Caatinga’ area in the Brazilian state of Bahia. Afr J Biotechnol 5:1135–1141
Sridevi A, Sandhya A, Ramanjaneyulu G, Narasimha G, Devi PS (2016) Biocatalytic activity of Aspergillus niger xylanase in paper pulp biobleaching. 3 Biotech 6(165):1–7
Sun J, Wen F, Si T, Xu JH, Zhao H (2012) Direct conversion of xylan to ethanol by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains displaying an engineered minihemicellulosome. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(11):3837–3845
Sunna A, Antranikian G (1997) Xylanolytic enzymes from fungi and bacteria. Crit Rev Biotechnol 17:39–67
Techapu C, Prosesor R (2003) Thermostable and alkaline tolerant microbial cellulose free xylanase produced from agriculture waste. Proc Biochem 38(1):1327–1340
Tony C, Charles G, Georges F (2005) Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:3–23
Torres JM, Cruz DTE (2013) Production of xylanases by mangrove fungi from the Philippines and their application in enzymatic pretreatment of recycled paper pulps. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:645–655
Uday USP, Choudhury P, Bandyopadhyay TK, Bhunia B (2016) Classification, mode of action and production strategy of xylanase and its application for biofuel production from water hyacinth. Int J Biol Macromol 82:1041–1054
Wahyuntari B, Mubarik NR, Setyahadi S (2009) Effect of pH, temperature and medium composition on xylanase production by Bacillus sp. AQ-1 and partial characterization of the crude enzyme. Microbiol Indones 3(1):17–22
Walsh GA, Power RF, Headon DR (1993) Enzymes in animal feed industry. Trends Biotechnol 11:424–430
Wejse PL, Ingvorsen K, Mortensen KK (2005) Salinity and temperature effects on accessibility of soluble and cross-linked insoluble xylans to endoxylanases. IUBMB Life 57(11):761–763
Wong KKY, Saddler JN (1992) Trichoderma xylanases: their properties and application. In: Visser J, Beldman G, Someren MAK, Voragen AGJ (eds) Xylans and xylanases. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 171–186
Yan Q, Hao S, Jiang Z, Zhai Q, Chen W (2009) Properties of a xylanase from Streptomyces matensis being suitable for xylooligosaccharides production. J Mol Catal B Enzym 58:72–77
Yaun Q, Rugyu M (1999) Study on temperature oscillation in production of xylanase by Aspergillus niger. Beijing Hugagong Daxue Xuebao 26:11–16
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial assistance provided by the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, in the form of fellowships to G. Ramanjaneyulu, A. Ramya and K. Dileep Kumar to carry out the above research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramanjaneyulu, G., Sridevi, A., Seshapani, P. et al. Enhanced production of xylanase by Fusarium sp. BVKT R2 and evaluation of its biomass saccharification efficiency. 3 Biotech 7, 351 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0977-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0977-1