Abstract
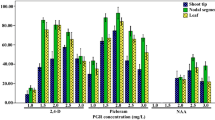
A protocol has been developed for achieving somatic embryogenesis from callus derived from nodal cuttings and production of synthetic seeds in Hemidesmus indicus L. R. Br. a highly traded ethnomedicinal plant. Proembryogenic, friable, light yellowish callus was induced from the basal cut end of the nodal cuttings on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with 3 μM indole-3-butyric acid (IBA). The highest rate of somatic embryogenesis (92 %) was observed when the callus was subcultured on half strength MS medium supplemented with 2 μM IBA. On induction medium somatic embryos were developed up to the torpedo stage. Further elongation and germination of somatic embryos were obtained in MS medium supplemented with 4 μM 6-benzylaminopurine (BA) in combination with 1.5 μM gibberellic acid (GA3). Somatic embryos were collected and suspended in a matrix of MS medium containing sodium alginate (3 % W/V) dropped into 75 mM calcium chloride (CaCl2·2H2O) solution for the production of synthetic seeds and later transferred to MS medium for germination. The synthetic seeds were successfully germinated on medium even after 120 days of storage at 4 °C. The plantlets were eventually transferred to soil with 92 % success.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellic acid
- IBA:
-
Indole-3-butyric acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- NAA:
-
Naphthalene acetic acid
References
Aboshama HMS (2011) Direct somatic embryogenesis of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). World J Agri Sci 7:755–762
Agrawal V, Sardar PR (2007) In vitro regeneration through somatic embryogenesis and organogenesis using cotyledons of Cassia angustifolia Vahl. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:585–592
Alam MI, Auddy B, Gomes A (1996) Viper venom neutralization by Indian medicinal plant (Hemidesmus indicus, Pluchea indica). Phytother Res 10:58–61
Andlib A, Verma RN, Batra A (2011) Synthetic seeds an alternative source for quick regeneration of a zero calorie herb—Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. J Pharm Res 4:2007–2009
Awal A, Taha RM, Hasbullah NA (2007) In vitro formation of synthetic seed of Begonia × Hiemalis fotch. Int J Environ Sci 2:189–192
Bapat VA, Rao PS (1990) In vitro growth of encapsulated axillary buds of mulberry (Morus indica L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 20:69–70
Bekheet SA (2006) A synthetic seed method through encapsulation of in vitro proliferated bulblets of garlic (Allium sativum L.). Arab J Biotech 9:415–426
Capuana M, Petrini G, Di Marco A, Giannini R (2007) Plant regeneration of common ash (Fraxinus excelsior L.) by somatic embryogenesis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:101–110
Castillo B, Smith MAL (1997) Direct somatic embryogenesis from Begonia gracilis explants. Plant Cell Rep 16:385–388
Castillo B, Smith MAL, Yadava UL (1998) Plant regeneration from encapsulated somatic embryos of Carica papaya L. Plant Cell Rep 17:172–176
Chai M, Jia Y, Chen S, Gao Z, Wang H, Liu L, Wang P, Hou D (2011) Callus induction, plant regeneration, and long-term maintenance of embryogenic cultures in Zoysia matrella [L.] Merr. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104:187–192
Chandra R, Deepak D, Khare A (1994) Pregnane glycosides from Hemidesmus indicus. Phytochemistry 35:1545–1548
Chatterjee I, Chakravarthy AK, Gomes A (2006) Daboia russellii and Naja kaouthia venom neutralization by lupeol acetate isolated from the root extract of Indian sarsaparilla Hemidesmus indicus R. Br. J Ethnopharmacol 106:38–43
Corral P, Mallon R, Rodrıguez-Oubina J, Gonzalez ML (2011) Multiple shoot induction and plant regeneration of the endangered species Crepis novoana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 105:211–217
Daud N, Taha RM, Hasbullah NA (2008) Artificial seed production from encapsulated microshoots of Saintpaulia ionantha Wendl. (African violet). J App Sci 8:4662–4667
Deepak S, Srivastava S, Khare A (1995) Indicusin: a pregnane diester triglycoside from Hemidesmus indicus R. Br. Nat Proc Lett 6:81–86
Deepak S, Srivastava S, Khare A (1997) Pregnane glycosides from Hemidesmus indicus. Phytochemistry 44:145–151
Dhandapani M, Kim DH, Hong S (2008) Efficient plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis and organogenesis from the explants of Catharanthus roseus. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 44:18–25
Faisal M, Ahmad N, Anis M (2006) In vitro plant regeneration from Alginate Encapsulated microcuttings of Rauvolfia tetraphylla L. Am Eur J Agric Environ Sci 1:1–6
Ghosh B, Sen S (1994) Plant regeneration from alginate encapsulated somatic embryos of Asparagus cooperi baker. Plant Cell Rep 13:381–385
Gupta MM, Verma RK, Misra LN (1992) Terpenoids from Hemidesmus indicus. Phytochemistry 31:4036–4037
Gurel E, Yucesan B, Aglic E, Gurel S, Verma SK, Sokmen M, Sokmen A (2011) Regeneration and cardiotonic glycoside production in Digitalis davisiana Heywood (Alanya Foxglove). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104:217–225
Hassan NS (2003) In vitro propagation of jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis L.) through alginate-encapsulated shoot apical and axillary buds. Int J Agri Biol 5:513–516
Kirtikar KR, Basu BD (1975) Indian medicinal plants, vol 111. Periodical Experts, Delhi
Kordestani GK, Karami O (2008) Picloram induced somatic embryogenesis in leaves of strawberry (Fragaria ananassa L.). Acta Biol Craco Seri Botanica 50:69–72
Ma G, Lu J, Teixeira da Silva JA, Zhang X, Zhao J (2011) Shoot organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis from leaf and shoot explants of Ochna integerrima (Lour). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104:157–162
Malathy S, Pai JS (1998) In vitro propagation of Hemidesmus indicus. Fitoterapia 69:5333–5536
Mandal S, Das PC, Joshi PC, Das A, Chatterjee A (1991) Hemidesmine a new coumarino lignoid from Hemidesmus indicus R. Br. Ind J Chem 30:712–713
Mathur J, Ahuja PS, Lal N, Mathur AK (1989) Propagation of Valeriana wallichii DC using encapsulated apical and axial shoot buds. Plant Sci 60:111–116
Misra N, Misra P, Datta SK, Mehrotra S (2005) In vitro biosynthesis of antioxidants from Hemidesmus indicus R. Br. cultures. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 41:285–290
Mohanraj R, Ananthan R, Bai VN (2009) Production and storage of synthetic seeds in Coelogyne breviscapa Lindl. Asian J Biotech 1:124–128
Mondal TK, Bhattacharya A, Sood A, Ahuja PS (2002) Factors affecting germination and conversion frequency of somatic embryos of Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O Kuntze. J Plant Physiol 159:1317–1321
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Murthi BR, Seshadri TR (1941) A study of the chemical components of the roots of Decalepis hamiltoni, Part III. Comparison with Hemidesmus indicus (Indian sarsaparilla). Proc Ind Acad Sci 13:399–403
Nadkarni AN (1989) Indian materia medica, vol I. Popular Book Depot, Mumbai
Nagarajan S, Rao LJ (2003) Determination of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde in roots of Decalepis hamiltonii Wight & Arn. and Hemidesmus indicus R. Br. J AOAC Int 86:564–567
Nower AA, Ali EAM, Rizkalla AA (2007) Synthetic seeds of pear (Pyrus communis L.) rootstock storage in vitro. Aus J Basic App Sci 1:262–270
Padhy SN, Mahato SB, Dutta NL (1973) Asclepiadaceae Terpenoides from the roots of Hemidesmus indicus. Phytochemistry 12:217–218
Papanastasiou I, Soukouli K, Moschopoulou G, Kahia J, Kintzios S (2008) Effect of liquid pulses with 6-benzyladenine on the induction of somatic embryogenesis from coffee (Coffea arabica L.) callus cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 92:215–225
Patnaik J, Debata BK (1997) Micropropagation of Hemidesmus indicus (L.) R. Br. through axillary bud culture. Plant Cell Rep 15:427–430
Pattnaik S, Chand PK (2000) Morphogenic response of the alginate encapsulated axillary buds from in vitro shoot cultures of six mulberries. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 64:177–185
Paul S, Dam A, Bhattacharyya A, Bandyopadhyay TK (2011) An efficient regeneration system via direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis for the medicinal tree Murraya koenigii. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 105:271–283
Prakash KA, Sethi D, Deepak A, Khare A, Khare MP (1991) Two pregnane glycosides from Hemidesmus indicus. Phytochemistry 30:297–299
Quiroz-Figueroa FR, Rojas-Herrera R, Galaz-Avalos RM, Loyola-Vargas VM (2006) Embryo production through somatic embryogenesis can be used to study cell differentiation in plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 86:285–301
Ray A, Bhattacharya S (2008) Storage and plant regeneration from encapsulated shoot tips of Rauvolfia serpentina—an effective way of conservation and mass propagation. South Afr J Bot 74:776–779
Roy B, Mandal AB (2008) Development of synthetic seeds involving androgenic and proembryos in elite indica rice. Ind J Biotech 7:515–519
Sakamoto Y, Onishi N, Hirosawa T (1995) Delivery systems for tissue culture by encapsulation. In: Aitken-Christie K, Kozai T, Smith MAL (eds) Automation and environmental control in plant tissue culture. Kluwer Acad. Publ, Dordrecht, pp 215–244
Sarmah DK, Borthakur M, Borua PK (2010) Artificial seed production from encapsulated PLBs regenerated from leaf base of Vanda coerulea Grifft. ex. Lindl. an endangered orchid. Curr Sci 98:686–690
Sharma PK, Dhyani SK, Shankar V (1979) Some useful and medicinal plants of the district Dehradun and Siwalik. J Sci Res Plant Med 1:17–43
Singh SK, Rai MK, Asthana P, Pandey S, Jaiswal VS, Jaiswal U (2009) Plant regeneration from alginate-encapsulated shoot tips of Spilanthes acmella (L.) Murr., a medicinally important and herbal pesticidal plant species. Acta Physiol Plant 31:649–653
Sivanesan I, Lim MY, Jeong BR (2011) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf and petiole explants of Campanula punctata Lam. var. rubriflora Makino. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 107:365–369
Soneji JR, Rao PS, Mhatre M (2002) Germination of synthetic seeds of pineapple (Ananas comosus L.). Plant Cell Rep 20:891–894
Sreekumar S, Seeni S, Pushpangadan P (2000) Micropropagation of Hemidesmus indicus for cultivation and production of 2-hydroxy 4-methoxybenzaldehyde. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 62:211–218
Tejavathi DH, Gayathramma K, Sowmya R (2006) Production of plantlets from encapsulated in vitro shoot buds and somatic embryos of Agave vera-cruz Mill. Plant Cell Biotech Mol Biol 7:183–186
Ved DK, Goraya GS (2007) Demand and supply of medicinal plants in India. Report published by National Medicinal Plants Board, New Delhi and Foundation for Revitalization of Local Health Traditions, Bangalore, p 14
West TP, Ravindra MB, Preece JE (2006) Encapsulation, cold storage, and growth of Hibiscus moscheutos nodal segments. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 87:223–231
Williams EG, Maheswaran G (1986) Somatic embryogenesis: factors influencing coordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann Bot 57:443–462
Acknowledgments
TDT acknowledges the financial assistance from UGC in the form of a major research project (Project no. 38-233/2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Horbowicz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheruvathur, M.K., Najeeb, N. & Thomas, T.D. In vitro propagation and conservation of Indian sarsaparilla, Hemidesmus indicus L. R. Br. through somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seed production. Acta Physiol Plant 35, 771–779 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1117-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1117-5