Abstract
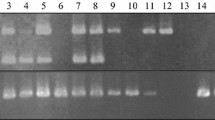
Retrotransposons are major components of eukaryotic genomes and are present in high copy numbers. We developed retrotransposon-based insertion polymorphism (RBIP) markers based on long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences and flanking genome regions by using shotgun genome sequence data of mango (Mangifera indica L.). Three novel LTR sequences were identified based on two LTR retrotransposon structural features; a 5′ LTR located upstream of the primer binding site and a 3′ LTR showing high sequence similarity to the 5′ LTR. Starting with 377 unique sequences containing both 3′ LTR and downstream genome region sequences, we developed 82 RBIP markers that were applied to DNA fingerprinting of 16 mango accession. Five RBIP markers were enough to distinguish all 16 accessions. Our result showed that LTR identification from shotgun genome sequences was effective for development of retrotransposon-based DNA markers without whole-genome sequence information. We discuss application of the developed RBIP markers for identification of genetic diversity and construction of a genetic linkage map.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Report 9:208–218
Boeke JD, Stoye JP (1997) Retrotransposons, endogenous retroviruses and the evolution of retroviruses. In: Coffin J, Hughes S, Varmus H (eds) Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, pp 343–435
Chunwongse C, Phumichai C, Tongyoo P, Juejun N, Chunwongse J (2015) Development of di-nucleotide microsatellite markers and construction of genetic linkage map in mango (Mangifera indica L.) Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 37:119–127
Diwan N, Cregan PB (1997) Automated sizing of fluorescent-labeled simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers to assay genetic variation in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 95:723–733
Duval MF, Bunel J, Sitbon C, Risterucci AM (2005) Development of microsatellite markers of mango. Mol Ecol Notes 5:824–826
Ellinghaus D, Kurtz S, Willhoeft U (2008) LTRharvest, an efficient and flexible software for de novo detection of LTR retrotransposons. BMC Bioinformat 9:18
Evans EA, Mendoza OJ (2009) World mango trade and the economics of mango production. In: Litz RE (ed) The mango: botany, production and uses. CAB International, Oxfordshire, pp 606–627
Flavell AJ, Knox MR, Pearce SR, Ellis TH (1998) Retrotransposon-based insertion polymorphisms (RBIP) for high throughput marker analysis. Plant J 16:643–650
Fujii H, Ogata T, Shimada T, Endo T, Iketani H, Shimizu T, Yamamoto T, Omura M (2013) Minimal marker: an algorithm and computer program for the identification of minimal sets of discriminating DNA markers for efficient variety identification. J Bioinforma Comput Biol 11:1250022
Hollender CA, Dardick C (2015) Molecular basis of angiosperm tree architecture. New Phytol 206:541–556
Honsho C, Nishiyama K, Eiadthong W, Yonemori K (2005) Isolation and characterization of new microsatellites markers in mango. Mol Ecol Notes 5:152–154
Jing R, Vershinin A, Grzebyta J, Shaw P, Smýkal P, Marshall D, Ambrose MJ, Ellis TH, Flavell AJ (2010) The genetic diversity and evolution of field pea (Pisum) studied by high throughput retrotransposon based insertion polymorphism (RBIP) marker analysis. BMC Evol Biol 10:44
Jurka J, Kapitonov VV, Pavlicek A, Klonowski P, Kohany O, Walichiewicz J (2005) Repbase update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:462–467
Kalendar R, Grob T, Regina M, Suoniemi A, Schulman A (1999) IRAP and REMAP: two new retrotransposon-based DNA fingerprinting techniques. Theor Appl Genet 98:704–711
Kalendar R, Antonius K, Smýkal P, Schulman AH (2010) iPBS: a universal method for DNA fingerprinting and retrotransposon isolation. Theor Appl Genet 121:1419–1430
Kashkush K, Jinggui F, Tomer E, Hillel J, Lavi U (2001) Cultivar identification and genetic map of mango (Mangifera indica). Euphytica 122:129–136
Kim H, Yamamoto M, Hosaka F, Terakami S, Nishitani C, Sawamura Y, Yamane H, Wu JZ, Matsumoto T, Matsuyama T, Yamamoto T (2011) Molecular characterization of novel Ty1-copia-like retrotransposons in pear (Pyrus pyrifolia). Tree Genet Genomes 7:845–856
Kim H, Terakami S, Nishitani C, Kurita K, Kanamori H, Katayose Y, Sawamura Y, Saito T, Yamamoto T (2012) Development of cultivar-specific DNA markers based on retrotransposon-based insertional polymorphism in Japanese pear. Breed Sci 62:53–62
Kobayashi S, Goto-Yamamoto N, Hirochika H (2004) Retrotransposon-induced mutations in grape skin color. Science 304:982
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL (1999) Plant retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 33:479–532
Kumar A, Hirochika H (2001) Applications of retrotransposons as genetic tools in plant biology. Trends Plant Sci 6:127–134
Lopez-Valenzuela JA, Martinez O, Paredes-Lopez O (1997) Geographic differentiation and embryo type identification in Mangifera indica L. cultivars using RAPD markers. Hortic Sci 32:1105–1108
Luby JJ, Shaw DV (2001) Does marker-assisted selection make dollars and sense in a fruit breeding program? Hortic Sci 36:872–879
Luo C, Shu B, Yao Q, Wu H, Xu W, Wang S (2016) Construction of a high-density genetic map based on large-scale marker development in mango using specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq). Front Plant Sci 7:1310
Lyer CPA, Schnell RJ (2009) Breeding and genetics. In: Litz RE (ed) The mango: botany, production and uses. CAB International, Oxfordshire, pp 67–96
Mahato AK, Sharma N, Singh A, Srivastav M, Jaiprakash SSK, Singh AK, Sharma TR, Singh NK (2016) Leaf transcriptome sequencing for identifying genic-SSR markers and SNP heterozygosity in crossbred mango variety ‘Amrapali’ (Mangifera indica L.) PLoS ONE 11:e0164325
McCarthy EM, McDonald JF (2003) LTR_STRUC: a novel search and identification program for LTR retrotransposons. Bioinformatics 19:362–367
Monden Y, Tahara M (2015) Plant transposable elements and their application to genetic analysis via high-throughput sequencing platform. Hortic J 84:283–294
Monden Y, Fujii N, Yamaguchi K, Ikeo K, Nakazawa Y, Waki T, Hirashima K, Uchimura Y, Tahara M (2014) Efficient screening of long terminal repeat retrotransposons that show high insertion polymorphism via high-throughput sequencing of the primer binding site. Genome 57:245–252
Monden Y, Hara T, Okada Y, Jahana O, Kobayashi A, Tabushi H, Onaga S, Tahara M (2015) Construction of a linkage map based on retrotransposon insertion polymorphisms in sweetpotato via high-throughput sequencing. Breed Sci 65:143–153
Mukherjee SK (1953) The mango—its botany, cultivation, uses and future improvement, especially as observed in India. Econ Bot 7:130–162
Mukherjee SK, Litz RE (2009) Introduction: botany and importance. In: Litz RE (ed) The mango: botany, production and uses. CAB International, Oxfordshire, pp 1–19
Okada K, Wada M, Moriya S, Katayose Y, Fujisawa H, Wu JZ, Kanamori H, Kurita K, Sasaki H, Fujii H, Terakami S, Iwanami H, Yamamoto T, Abe K (2016) Expression of a putative dioxygenase gene adjacent to an insertion mutation is involved in the short internodes of columnar apples (Malus × domestica). J Plant Res 129:1109–1126
Queen RA, Gribbon BM, James C, Jack P, Flavell AJ (2004) Retrotransposon-based molecular markers for linkage and genetic diversity analysis in wheat. Mol Gen Genomics 271:91–97
Ravishankar KV, Dinesh MR, Nischita P, Sandya BS (2015) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers in mango (Mangifera indica) using next-generation sequencing technology and their transferability across species. Mol Breed 35:93
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYS, numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, ver. 2.01. Exeter Publishing, Ltd., Setauket
Schnell RJ, Ronning CM, Knight RJ (1995) Identification of cultivars and validation of genetic relationships in Mangifera indica L. using RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:269–271
Schnell RJ, Olano CT, Quintanilla WE, Meerow AW (2005) Isolation and characterization of 15 microsatellite loci from mango (Mangifera indica L.) and cross-species amplification in closely related taxa. Mol Ecol Notes 5:625–627
Sherman A, Rubinstein M, Eshed R, Benita M, Ish-Shalom M, Sharabi-Schwager M, Rozen A, Saada D, Cohen Y, Ophir R (2015) Mango (Mangifera indica L.) germplasm diversity based on single nucleotide polymorphisms derived from the transcriptome. BMC Plant Biol 15:277
Shudo A, Tarora K, Makishi Y, Ichi R, Takahashi K, Matsumura M, Shimabukuro S, Matsuda N, Nakasone S, Urasaki N (2013) Development of CAPS markers and their application in breeding for mango, Mangifera indica L. Euphytica 190:345–355
Tahara M, Aoki T, Suzuka S, Yamashita H, Tanaka M, Matsunaga S, Kokumai S (2004) Isolation of an active element from a high-copy-number family of retrotransposons in the sweetpotato genome. Mol Gen Genomics 272:116–127
Vendramin E, Pea G, Dondini L, Pacheco I, Dettori MT, Gazza L, Scalabrin S, Strozzi F, Tartarini S, Bassi D, Verde I, Rossini L (2014) A unique mutation in a MYB gene cosegregates with the nectarine phenotype in peach. PLoS One 9(3):e90574
Viruel MA, Escribano P, Barbieri M, Ferri M, Hormaza JI (2005) Fingerprinting, embryo type and geographic differentiation in mango (Mangifera indica L., Anacardiaceae) with microsatellites. Mol Breed 15:383–393
Vitte C, Ishii T, Lamy F, Brar D, Panaud O (2004) Genomic paleontology provides evidence for two distinct origins of Asian rice (Oryza sativa L). Mol Gen Genomics 272:504–511
Waugh R, McLean K, Flavell AJ, Pearce SR, Kumar A, Thomas BB, Powell W (1997) Genetic distribution of Bare-1-like retrotransposable elements in the barley genome revealed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphisms (S-SAP). Mol Gen Genet 253:687–694
Xu Z, Wang H (2007) LTR_FINDER: an efficient tool for the prediction of full-length LTR retrotransposons. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W265–W268
You FM, Huo N, Gu YQ, Luo MC, Ma Y, Hane D, Lazo GR, Dvorak J, Anderson OD (2008) Batch primer 3: a high throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design. BMC Bioinformat 9:253
Acknowledgements
We thank Mss. F. Hosaka, H. Oshino, N. Shigeta, and N. Yagihashi for their technical help. This study was partially supported by an Okinawa special promotion grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data archiving statement
All sequences obtained by 454 GS FLX Plus sequencing are available in the DDBJ Sequence Read Archive (http://trace.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/dra/index.shtml) under the following accession numbers (Submission, DRA004360; BioProject, PRJDB4532; BioSample, SAMD00046318; experiment, DRX049157; and runs, DRR054307 and DRR054308). Nucleotide sequences of 82 retroratnsposon-based insertion polymorphism markers in mango are available in the DDBJ (http://www.ddbj.nig.ac.jp) under the following accession nos. LC089767–LC089848.
Additional information
Communicated by L. A. Meisel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nashima, K., Terakami, S., Kunihisa, M. et al. Retrotransposon-based insertion polymorphism markers in mango. Tree Genetics & Genomes 13, 110 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1192-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1192-2