Abstract
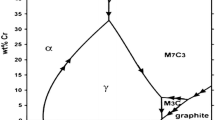
The aim of this study was the investigation of the effect of different Y2O3 additives on wear resistance of the hypereutectic Fe–Cr–C hardfacing coatings. The microstructures were observed by optical microscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy, respectively. Meanwhile, the hardness was measured and the wear resistance was evaluated. Finally, the role of Y2O3 was discussed. The microstructures of the coatings consist of the primary (Cr, Fe)7C3 carbide and eutectic structure [austenite + (Cr, Fe)7C3 carbide]. Moreover, Y2O3 can refine the M7C3 carbide and improve the wear resistance of coatings obviously. Y2O3 can absorb at the surface of the M7C3 carbide and improve the wear resistance of the hypereutectic Fe–Cr–C hardfacing coatings.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raheleh, A.P., Reza, S.R., Reza, M., Hossein, J.: Improving the hot corrosion resistance of plasma sprayed ceria–yttria stabilized zirconia thermal barrier coatings by laser surface treatment. Mater. Des. 57, 336–341 (2014)
Kazemipour, M., Shokrollahi, H., Sharafi, S.: The Influence of the matrix microstructure on abrasive wear resistance of heat-treated Fe–32Cr–4.5C wt% hardfacing alloy. Tribol. Lett. 39, 181–192 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11249-010-9634-0
Ji, J., Niu, Y., Wu, J., Yu, Z.: Improvement of properties of TiN coating by optimising microstructural design. Surf. Eng. 30(1), 36–40 (2014)
Lin, C.M., Chang, C.M., Chen, Y.C., Chen, J.H., Hsieh, C.C., Wu, W.T.: Microstructural evolution of hypoeutectic, near-eutectic, and hypereutectic high-carbon Cr-based hard-facing alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 40(5), 1031–1038 (2009)
Coronado, J.J., Caicedo, H.F., Gómez, A.L.: The effects of welding processes on abrasive wear resistance for hardfacing deposits. Tribol. Int. 42, 745–749 (2009)
Buchanan, V.E.: Solidification and microstructural characterisation of iron–chromium based hardfaced coatings deposited by SMAW and electric arc spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 203, 3638–3646 (2009)
Sabet, H., Khierandish, Sh, Mirdamadi, Sh, Goodarzi, M.: The microstructure and abrasive wear resistance of Fe–Cr–C hardfacing alloys with the composition of hypoeutectic, eutectic, and hypereutectic at Cr/C = 6. Tribol. Lett. 44, 237–245 (2011). doi:10.1007/s11249-011-9842-2
Hanlon, D.N., Rainforth, W.M., Sellars, C.M.: The rolling/sliding wear response of conventionally processed and spray formed high chromium content cast iron at ambient and elevated temperature. Wear 225–229, 587–599 (1999)
Carpenter, S.D., Carpenter, D.: Stacking faults and superlattice observations during transmission electron microscopy of a (Fe, Cr)7C3 carbide. Mater. Lett. 57, 4456–4465 (2003)
Carpenter, S.D., Carpenter, D., Pearce, J.T.H.: XRD and electron microscope study of a heat treated 26.6 % chromium white iron microstructure. Mater. Chem. Phy. 101, 49–55 (2007)
Carpenter, S.D., Carpenter, D.E.O.S., Pearce, J.T.H.: The nature of stacking faults within iron-chromium carbide of the type (Fe, Cr)7C3. J. Alloys Compd. 494, 245–251 (2010)
Chang, C.M., Chen, L.H., Lin, C.M., Chen, J.H., Fan, C.M., Wu, W.T.: Microstructure and wear characteristics of hypereutectic Fe–Cr–C cladding with various carbon contents. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205(2), 245–250 (2010)
Coronado, J.J.: Effect of (Fe, Cr)7C3 carbide orientation on abrasion wear resistance and fracture toughness. Wear 270, 287–293 (2011)
Veinthal, R., Sergejev, F., Zikin, A., Tarbe, R., Hornung, J.: Abrasive impact wear and surface fatigue wear behavior of Fe–Cr–C PTA overlays. Wear 301, 102–108 (2013)
Hornung, J., Zikin, A., Pichelbauer, K., Kalin, M., Kirchgaßner, M.: Influence of cooling speed on the microstructure and wear behavior of hypereutectic Fe–Cr–C hardfacings. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 576, 243–251 (2013)
Wang, S.R., Song, L.H., Yang, Q., Wang, M.: Effect of carbide orientation on impact-abrasive wear resistance of high-Cr iron used in shot blast machine. Tribol. Lett. 50, 439–448 (2013)
Wang, K.L., Zhang, Q.B., Sun, M.L., Wei, X.G., Zhu, Y.M.: Microstructure and corrosion resistance of laser clad coatings with rare earth elements. Appl. Sur. Sci. 174, 191–200 (2001)
Qu, Y.H., Xing, J., Zhi, X., Peng, J., Fu, H.: Effect of cerium on the as-cast microstructure of a hypereutectic high chromium cast iron. Mater. Lett. 62, 3024–3027 (2008)
Liu, X.B., Yu, R.L.: Effects of La2O3 on microstructure and wear properties of laser clad γ/Cr7C3/TiC composite coatings on TiAl intermetallic alloy. Mater. Chem. Phy. 101, 448–454 (2007)
Yang, J., Hao, F.F., Li, D., Zhou, Y.F., Ren, X.J., Yang, Y.L., Yang, Q.X.: Effect of RE oxide on growth dynamics of primary austenite grain in hardfacing layer of medium-high carbon steel. J. Rare. Earth. 30, 814–819 (2012)
Yang, J., Hou, X.R., Zhang, P.F., Zhou, Y.F., Xing, X.L., Ren, X.J., Yang, Q.X.: First-principles calculations on LaAlO3 as the heterogeneous nucleus of the austenite. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1029, 48–56 (2014)
Hao, F.F., Liao, B., Li, D., Dan, T., Ren, X.J., Yang, Q.X.: Effects of rare earth oxide on hardfacing metal microstructure of medium carbon steel and its refinement mechanism. J. Rare. Earth. 29(6), 609–613 (2011)
Zhou, Y.F., Yang, Y.L., Jiang, Y.W., Yang, J., Ren, X.J., Yang, Q.X.: Fe-24 wt% Cr-4.1 wt% C hardfacing alloy: microstructure and carbide refinement mechanisms with ceria additive. Mater. Charact. 72, 77–86 (2012)
Tian, Y.S., Chen, C.Z., Chen, L.X., Huo, Q.H.: Effect of RE oxides on the microstructure of the coatings fabricated on titanium alloys by laser alloying technique. Scripta Mater. 54, 847–852 (2006)
Wu, C.M.L., Yu, D.Q., Law, C.M.T., Wang, L.: Properties of lead-free solder alloys with rare earth element additions. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44, 1–44 (2004)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude for projects supported by Program for National Nature Science Foundation of China (51271163) and (51471148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, X., Zhou, Y.F., Zhao, B. et al. Influence of Nano-Y2O3 on Wear Resistance of Hypereutectic Fe–Cr–C Hardfacing Coating. Tribol Lett 58, 23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0475-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0475-8