Abstract
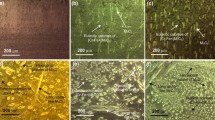
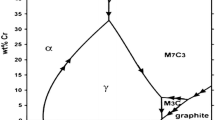
In this investigation, three Fe–Cr–C hardfacing alloys with different carbon and chromium contents and in constant ratio of \( \left( {\frac{Cr}{C} = 6} \right) \) were fabricated by GTAW on AISI 1010 mild steel substrates. The OES, OM, SEM, and XRD techniques and Vickers hardness method were used for determining chemical composition, hardness, and studying the microstructure of the hardface alloys. The OES, OM, and XRD examination results indicated that different carbon and chromium contents of hardface alloys produced hypoeutectic/eutectic/hypereutectic structures. By increasing the carbon and chromium contents in the chemical composition of hardface alloys, the volume fraction of the total (Cr, Fe)7C3 is increased resulting to decreasing in total the austenite volume fraction and increasing the hardness of the surface. Studying the microstructure after wear test (ASTM G65) shows that at the edge of the worn surface, the transformation of austenite to martensite had occurred in all the samples. The wear test results indicate that the highest wear resistance is gained in the hypoeutectic structure with maximum hardness after the wear test. In addition, abrasive wear micromechanisms in hypoeutectic/eutectic/hypereutectic were recognized as: ploughing + cutting/ploughing + cutting + cracking/cracking + cutting, respectively.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng, J.B., Xu, B.S., Liang, X.B., Wu, Y.W.: Microstructure and mechanical characteristics of iron-based coating produced by plasma transferred arc cladding process. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 492, 407–412 (2008)
Liu, Y.F., Xia, Z.Y., Han, J.M., Zhang, G.L., Yang, S.Z.: Microstructure and wear behavior of (Cr, Fe)7C3 reinforced composite coating produced by plasma transferred arc weld-surfacing process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 201, 863–867 (2006)
Coronado, J.J., Caicedo, H.F., Gomez, A.L.: The effects of welding processes on abrasive wear resistance for hard-facing deposits. Trib Int. 42, 745–749 (2009)
Lee, K.Y., Lee, S.H., Kim, Y., Hong, H.S., Oh, Y.M., Kim, S.J.: The effects of additive elements on the sliding wear behavior of fe-base hard-facing alloys. Wear 225, 481–483 (2003)
Buytoz, S., Yildirim, M.M., Eren, H.: Microstructural and Micro-hardness characteristics of gas tungsten arc synthesized Fe–Cr–C coating on AISI 4340. Mat Let 59, 607–614 (2005)
Kirchgabner, M., Badisch, E., Franek, F.: Behavior of iron-based hard-facing alloys under abrasion and impact. Wear 265, 772–779 (2008)
Liu, J., Wang, L., Huang, J.: PTA clad (Cr, Fe)7C3–Fe in situ ceramal composite coating. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beij. 13(6), 538–541 (2006)
Atamert, S., Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.: Microstructure and stability of Fe–Cr–C hardfacing alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 130, 101–111 (1990)
Zumelzu, E., Goyos, I., Cabezas, C., Poitz, O., Parada, A.: Wear and corrosion behaviour of high chromium (14–30%Cr) cast iron alloys. Mat. Proc. Technol. 128, 250–255 (2002)
Lin, C.M., Chang, C.M., Chen, J.H., Hsieh, C.C., Wu, W.: Microstructural evolution of hypereutectic, near eutectic and hypereutectic high-carbon Cr-based hardfacing alloys. Met. Mat. Trans A 40A, 1031–1038 (2009)
Chang, C.M., Lin, C.M., Hsieh, C.C., Chen, J.H., Wu, W.: Micro-structural characteristics of Fe-40%Cr-xC hardfacing alloys with [1.0–4.0 wt%] carbon content. J. Alloy Comp. 487, 83–89 (2009)
Dasgupta, R., Thakur, R., Yadav, M.S., Jha, A.K.: High stress abrasive wear behavior of a hardfacing alloy: effects of some experimental factors. Wear 236, 368–374 (1999)
Dwiredi, D.K.: Microstructure and abrasive wear behavior of iron base hardfacing. Mat. Sci. Tech. 20, 1326–1330 (2004)
Liu, Y.F., Han, J.M., Li, R.H., Li, W.J., Xu, X.Y., Li, W., Yang, S.Z.: Microstructure and dry-sliding resistance of PTA clad (Cr, Fe)7C3/γ-Fe ceramal composite coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 7539–7544 (2006)
Chang, C.M., Chen, L.H., Lin, C.M., Chen, J.H., Fan, C.M., Wu, W.: Microstructure and wear characteristics of hypereutectic Fe–Cr–C cladding with various carbon contents. Surf. Coat. Tech. 205, 245–250 (2010)
Chang, C.M., Chen, Y.C., WU, W.: Microstructural and abrasive characteristics of high carbon Fe–Cr–C hradfacing alloy. Trib. Int. 43, 929–934 (2010)
Eroglu, M., Ozdemir, N.: Tungsten–inert gas surface alloying of a low carbon steel. Surf. Coat Technol. 154, 209–217 (2002)
Collins, W.K., Watson, J.C.: Metallographic etching for carbide volume fraction of high-chromium white cast iron. Mat. Char. 24(4), 379–386 (1990)
Carpenter, S.D., Carpenter, D.: X-ray diffraction of M7C3 carbide within a high chromium white iron. Mat. Let. 57, 4456–4459 (2003)
Bondar, A., Ivanchento, V., Kozbv, A., Todenac, J.C.: Carbon–iron ternary alloy systems phase diagrams–crystallographic and thermodynamic data: MSIT, group IV, vol. 11, pp. 1–56. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg (2008)
Yamamoto, K., Liliac, M.M., Ogi, K.: Thermodynamic evaluation of solidification structure of high chromium white cast iron. Int. J. Cast. Met. Res. 16, 4435–4440 (2003)
Chang, C.M., Lin, C.M., Hsieh, C.C., Chen, J.H., Fan, C.M., Wu, W.: Effect of carbon content on microstructural characteristics of the hypereutectic Fe–Cr–C claddings. Mat. Chem. Phys 117, 257–261 (2009)
Correa, E.O., Alcantara, N.G., Tecco, D.G., Kumar, R.V.: The relationship between the microstructure and abrasive resistance of a hardfacing alloy in the Fe–Cr–C–Nb–V System. Met. Mat. Trans A. 38A, 1671–1680 (2007)
Choteborsky, R., Hrabe, P., Muller, M., Sarkoca, J., Jirkam, M.: Abrasive wear of high chromium Fe–Cr–C hardfacing alloys. Res. Agr. Eng. 4(54), 192–198 (2008)
Chatterjee, S., Pal, T.K.: Wear behavior of hardfacing deposits on cast iron. Wear 255, 417–425 (2003)
Lin, C.M., Chang, C.M., Chen, J.H., Wu, W.: The effects of additive elements on the microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties of Cr–Fe–C hardfacing alloys. J. Alloy Comp. 498, 130–136 (2010)
Buchanan, V.E., Mccartney, D.G., Shipway, P.H.: A comparison of the abrasive wear behavior of iron-chromium based hardfaced coatings deposited by SMAW and electric arc spraying. Wear 267, 542–549 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabet, H., Khierandish, S., Mirdamadi, S. et al. The Microstructure and Abrasive Wear Resistance of Fe–Cr–C Hardfacing Alloys with the Composition of Hypoeutectic, Eutectic, and Hypereutectic at \( \frac{Cr}{C} = 6 \) . Tribol Lett 44, 237 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9842-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9842-2