Abstract
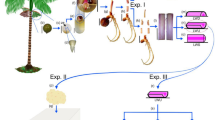
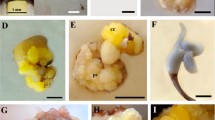
Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from young leaf explants (5–10 mm long) adjacent to the apex of 5–6 year old offshoots of Tunisian date palm (Phœnix dactylifera L.), cultivar Boufeggous was successfully achieved. Factors affecting embryogenic callus initiation, including plant growth regulators and explant size, were investigated. The highest induction frequencies of embryogenic calli occurred after 6–7 months on MS medium supplemented with 10 mg l−1 2,4-D and 0.3 mg l−1 activated charcoal. The subculture of these calli onto maintenance medium resulted in the formation of proembryos. Fine chopping and partial desiccation (6 and 12 h) of embryogenic calli with proembryos prior to transfer to MS medium supplemented with 1 mg l−1 ABA stimulated the rapid maturation of somatic embryos. Maturated somatic embryo yield per 0.5 g FW of embryogenic callus was 51 embryos with an average maturation time of 55 days. This was increased to 422 with finely chopped callus, and 124 and 306 embryos following 6 and 12 h desiccation treatments, respectively. The average time to maturation for these 3 treatments was 35, 43 and 38 days, respectively. Subsequent substitution of ABA in MS medium with 1 mg l−1 NAA resulted in the germination and conversion of 81% of the somatic embryos into plantlets with normal roots and shoots. The growth of regenerated somatic plants was also monitored in the field.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- AC:
-
Activated charcoal
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- IBA:
-
Indole-3-butyric acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
- NAA:
-
α-Naphthalenacetic acid
- PGRs:
-
Plant growth regulators
References
Ammirato PV (1983) Embryogenesis. In: Evans DA, Sharp WR, Ammirato PV, Yamado Y (eds) Handbook of plant cell culture. Macmillan, New York, pp 82–123
Attree SM, Fowke LC (1993) Somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seeds of conifers. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 35:1–35. doi:10.1007/BF00043936
Barbier-Brygoo H, Ephritikhine G, Klambt D, Ghislain M, Guern J (1989) Functional evidence for an auxin receptor at the plasmalemma of tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:891–895. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.3.891
Benkirane H, Sabounji K, Chlyah A, Chlyah H (2000) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from fragments of immature inflorescence and coleoptiles of Durum wheat. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 61:107–113. doi:10.1023/A:1006464208686
Bhaskaran S, Smith R (1992) Somatic embryogenesis from shoot tip and immature inflorescence of Phoenix dactylifera L. cv. Barhee. Plant Cell Rep 12:22–25. doi:10.1007/BF00232416
Carpenter JB, Ream CL (1976) Date palm breeding, a review. Date Grow Inst Rep 53:23–33
Chand S, Sahrawat AK (2001) Stimulatory effect of partial desiccation on plant regeneration in Indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 10:43–47
Cuenca B, San-Josë MC, Martinez MT, Ballester A, Vieitez AM (1999) Somatic embryogenesis from stem and leaf explants of Quercus robur L. Plant Cell Rep 18:538–543. doi:10.1007/s002990050618
Daguin F, Letouzé R (1997) Le clonage végétal. Cahier no 88. Biofutur 163:1–12
De Jong AJ, Schmidt EDL, De Vriess SC (1993) Early events in higher-plant embryogenesis. Plant Mol Biol 22:367–377. doi:10.1007/BF00014943
Delporte F, Mostade O, Jacquemin JM (2001) Plant regeneration through callus initiation from thin mature embryo fragments of wheat. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 67:73–80. doi:10.1023/A:1011697316212
De Touchet B, Duval Y, Pannetier C (1991) Plant regeneration from embryogenic suspension cultures of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). Plant Cell Rep 10:522–532
Drira N (1983) Multiplication végétative du palmier dattier (Phoenix dactylifera L.) par la culture in vitro de bourgeons axillaires et de feuilles qui en dérivent. C R Acad Sci Paris 296:1077–1082
Drira N, Benbadis A (1985) Multiplication végétative du palmier dattier (Phoenix dactylifera L.) par reversion, en culture in vitro, d’ébauches florales de pieds femelles adultes. J Plant Physiol 119:227–235
Duditis D, Boogre L, Gyorgyey JC (1991) Molecular and cellular approaches to the analysis of plant embryo development from somatic cells in vitro. J Cell Sci 99:475–484
El Hadrami I, El Bellaj M, El Idrissi A, J’Aiti F, El Jaafari S, Daayf F (1998) Biotechnologie végétales et amelioration du palmier dattier (phoenix dactylifera L.) Pivot de l’agriculture oasienne Marocaine. Cah Agric 7:463–468
Feher A, Pasternak TP, Duditis D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cell to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74:201–228. doi:10.1023/A:1024033216561
Fki L, Masmoudi R, Drira N, Rival A (2003) An optimised protocol for plant regeneration from embryogenic suspension cultures of date palm, Phoenix dactylifera L., cv. Deglet Nour. Plant Cell Rep 21:517–524
Jones MPA, Yi Z, Murch SJ, Saxena PK (2007) Thidiazuron-induced regeneration of Echinacea purpurea L.: micropropagation in solid and liquid cultures systems. Plant Cell Rep 26:13–19. doi:10.1007/s00299-006-0209-3
Kermode AR, Dumbroff EB, Bewley JD (1989) The role of maturation drying in the transition from seed development to germination. J Exp Bot 40:303–313. doi:10.1093/jxb/40.2.303
Klimaszewska K, Smith DR (1997) Maturation of somatic embryos of Pinus strobes is promoted by a high concentration of gellan gum. Physiol Plant 100:949–957. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb00022.x
Lelu MA, Bastien C, Drugeault A, Gouez ML, Klimaszewska K (1999) Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet development in Pinus sylvestris and Pinus pinaster on medium with and without growth regulators. Physiol Plant 105:719–728. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3054.1999.105417.x
Levee V, Lelu MA, Jouanin L, Cornu K, Pilate G (1997) Agrobacterium-tumefaciens-mediated transformation of hybrid larch (Larix kaempferi x L. deciduas) and transgenic plant regeneration. Plant Cell Rep 16:680–685. doi:10.1007/s002990050301
Lowe K, Taylor DB, Ryan P, Paterson KE (1985) Plant regeneration via organogenesis and embryogenesis in the maize inbred line B73. Plant Sci 41:125–132. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(85)90114-1
Lu C, Chandler SF, Vasil IK (1984) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from cultured immature embryos of rye (Secale cereale L.). J Plant Physiol 115:237–244
Malabadi R, Choudhury H, Tandon P (2004) Initiation, maintenance and maturation of somatic embryos from thin apical dome sections in Pinus kesiya (Royle ex. Gord) promoted by partial desiccation and gellan gum. Sci Hortic 102:449–459. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2004.06.001
Maruyama E, Hosoi Y, Ishii K (2007) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in yakutanegoyou, Pinus armandii Franch. Var. amamiana (Koidz.) Hatusima, an endemic and endangered species in Japan. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:28–34. doi:10.1007/s11627-006-9003-8
Michalczuk L, Cooke TJ, Cohen JD (1992) Auxin levels at different stages of carrot somatic embryogenesis. Phytochemistry 31:1097–1103. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(92)80241-6
Muniswamy B, Sreenath HL (1996) Effect of kanamycin on callus induction and somatic embryogenesis in cultured leaf tissues on coffea canephora Pierre (Robusta). J Coffee Res 26:44–51
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio-assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Perez-Nunez MT, Chan JL, Saenz L, Gonzalez T, Verdeil JL, Oropeza C (2006) Improved somatic embryogenesis from Coco nucifera (L) plumule explants. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:37–47. doi:10.1079/IVP2005722
Pliego-Alfaro F, Monsalud MJR, Litz RE, Gray DJ, Moon PA (1996) Effect of abscisic acid osmolarity and partial desiccation on the development of recalcitrant mango somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 44:63–70. doi:10.1007/BF00045914
Pullman GS, Gupta PK (1991) Method for reproducing coniferous plants by somatic embryogenesis using adsorbent materials in the development stage media. US Patent 5,034,326
Rance IM, Tian W, Mathews H, Kochko A, Beachy RN, Fauquet C (1994) Partial desiccation of mature embryo-derived calli, a simple treatment that dramatically enhances the regeneration ability of Indica rice. Plant Cell Rep 13:647–651. doi:10.1007/BF00232938
Rhouma A (1994) Le palmier dattier en Tunisie. Le patrimoine génétique, Vol 1. PNUD/FAO/RAB/88/024
Sané D, Aberlenc-Bertossi F, Gassama-Dia YK, Sagna M, Trouslot MF, Duval Y, Borgel A (2006) Histocytological analysis of callogenesis and somatic embryogenesis from cell suspensions of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Ann Bot (Lond) 98:301–308. doi:10.1093/aob/mcl104
Sharma DR, Kumari R, Chowdhury JB (1980) In vitro culture of female date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) tissues. Euphytica 29:169–174. doi:10.1007/BF00037263
Steinmacher DA, Cangahuala-Inocente GC, Clement CR, Guerra MP (2007a) Somatic embryogenesis from peach palm zygotic embryos. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:124–132. doi:10.1007/s11627-007-9032-y
Steinmacher DA, Clement CR, Guerra MP (2007b) Somatic embryogenesis from immature peach palm inflorescence explants: towards development of an efficient protocol. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 89:15–22. doi:10.1007/s11240-007-9207-6
Teisson C, Alvard D (1995) A new concept of plant in vitro cultivation liquid medium: temporary immersion. In: Terzi M, Cella R, Falavigna A (eds) Current Plant Science and Biotechnology in Agriculture. Current issue in Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology, vol 22. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, pp 105–110
Teixeira JB, Sondahl MR, Nakamura T, Kirby EG (1995) Establishment of oil palm cell suspensions and plant regeneration. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 40:105–111. doi:10.1007/BF00037662
Tisserat B (1979) Propagation of date palm (phoenix dactylifera L.) in vitro. J Exp Bot 30:1275–1283. doi:10.1093/jxb/30.6.1275
Tran Thanh Van K, Bui VL (2000) Current status of thin cell layer method for the induction of organogenesis or somatic embryogenesis. In: Mohan SJ, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 51–92
Trigiano RN (1997) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension of Acanthopanax Koreanum nakai. Plant Cell Rep 17:84–88. doi:10.1007/s002990050357
Valverde R, Arias O, Thorpe TA (1987) Picloram-induced embryogenesis in pejibaye palm (Bactris gasipaes HBK). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 10:149–156. doi:10.1007/BF00035913
Vieitez AM (1995) Somatic embryogenesis in Camellia spp. In: Jain SM, Gupta PK, Newton R (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Angiosperm vol 2. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, pp 235–276
Zouine J, El Hadrami I (2007) Effect of 2,4-D, glutamine and BAP on embryogenic suspension culture of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Sci Hortic 112:221–226. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2006.12.041
Zuo JR, Niu QW, Frugis G, Chua NH (2002) The wuschel gene promotes vegetative-to-embryonic transition in Arabidopsis. Plant J 30:349–359. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01289.x
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Alain Poupet for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was financial supported by grants from the IPGRI “CRPh Degache, Projet FEM-PNUD-IPGRI, RAB 98 G31”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Othmani, A., Bayoudh, C., Drira, N. et al. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in date palm Phœnix dactylifera L., cv. Boufeggous is significantly improved by fine chopping and partial desiccation of embryogenic callus. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 97, 71–79 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9500-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9500-7