Abstract
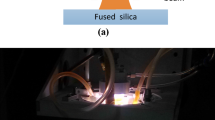
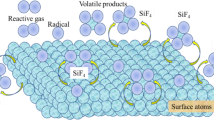
Atmospheric plasma etching has been increasingly applied in the fabrication of optical elements for high efficiency and near-zero damage to optical surfaces. However, the non-linearity of material removal rate is inevitable because of the thermal effect of inductively coupled plasma (ICP) etching for fused silica. To apply ICP to figure fused silica surface, the time-varying non-linearity between material removal rate and dwell time is analyzed. An experimental model of removal function is established considering the time-varying non-linearity. According to this model, an algorithm based on nested pulsed iterative method is proposed for calculating and compensating this time-varying non-linearity by varying the dwell time. Simulation results show that this algorithm can calculate and adjust the dwell time accurately and remove surface errors with rapid convergence. Surface figuring experiments were set up on the fused silica planar work-pieces with a size of 100 mm (width) × 100 mm (length) × 10 mm (thickness). With the compensated dwell time, the surface error converges rapidly from 4.556 λ PV (peak-to-valley) to 0.839 λ PV within 13.2 min in one iterative figuring. The power spectral density analysis indicates that the spatial frequency errors between 0.01 and 0.04 mm−1 are smoothed efficiently, and the spatial frequency errors between 0.04 and 0.972 mm−1 are also corrected. Experimental results demonstrate that the ICP surface figuring can achieve high convergence for surface error reduction using the compensated dwell time. Therefore, the ICP surface figuring can greatly improve surface quality and machining efficiency for fused silica optical elements.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li N, Wang B, Jin H (2014) Harbin Inst Technol 21(5):124–128
Wang Z, Wu Y, Dai Y (2007) Aviat Precis Manuf Technol 43(5):1–5
Nie X, Li S, Dai Y, Song C (2013) Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng 8786(22):11306–11312
Shen J, Liu S, Yi K, He H, Shao J, Fan Z (2005) Optik Int J Light Electron Opt 116(6):288–294
Wang Y, Hang L, Hu M (2008) Surf Technol 37(1):51–53
Meister J, Arnold T (2011) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 31:91–107
Mori Y, Yamamura K, Sano Y (2000) Rev Sci Instrum 71(12):4620–4626
Takino H, Yamamura K, Sano Y, Mori Y (2010) Appl Opt 49:4434–4440
Eichentopf I-M, Böhm G, Meister J, Arnold T (2010) Plasma Process Polym 6(S10):S204–S208
Arnold T, Böhm G, Fechner R, Meister J, Nickel A, Frost F, Hansel T, Schindler A (2010) Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A 616:147–156
Arnold T, Böhm G (2012) Precis Eng 36(4):546–553
Eichentopf I-M, Böhm G, Arnold T (2011) Surf Coat Technol 205(205):S430–S434
Fanara C, Shore P, Nicholls J-R, Lyford N, Sommer P, Fiske P (2006) SPIE Astron Telesc Instrum Int Soc Opt Photonics 10:933–939
Jourdain R, Castelli M, Shore P, Sommer P, Proscia D (2013) Prod Eng Res Devel 7:665–673
Zhang J, Wang B, Dong S (2008) Int J Precis Eng Manuf 9(2):39–43
Jia G, Li B, Zhang J (2016) Mater Sci Forum 878:83–88
Shi B, Dai Y, Xie X, Li S, Zhou L (2016) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 36(3):1–10
Shi B, Xie X, Dai Y, Liao C (2014) Proc SPIE 9281:928104
Greenfield S, Jones I (1964) Analyst 89(1064):713–720
Castelli M, Jourdain R, Morantz P, Shore P (2012) Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng 8450:34
Wendt R, Fassel V (1965) Anal Chem 37(7):920–922
Castelli M, Jourdain R, Morantz P, Shore P (2012) Precis Eng 36(3):467–476
Liao W, Dai Y, Xie X (2014) Opt Eng 53(9):095101
Arnold T, Böhm G, Paetzelt H (2016) Nonconventional ultra-precision manufacturing of ULE mirror surfaces using atmospheric reactive plasma jets. In: SPIE astronomical telescopes and instrumentation, p 99123N
Acknowledgements
This research work was supported by the project “Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET) (No. 130165)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Z., Xie, X., Chen, H. et al. Non-linear Compensated Dwell Time for Efficient Fused Silica Surface Figuring Using Inductively Coupled Plasma. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 38, 443–459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-018-9873-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-018-9873-7