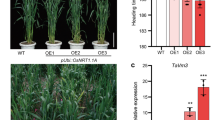
Abstract
Serine/threonine protein phosphatases (PPs) can be grouped into PP1 and PP2 based on enzymological criteria using specific inhibitors and activators. PP2 receives abscisic acid as signal and negative regulation of tolerance of high salt, drought, and cold stresses, yet the role of PP1 in stress tolerance remains unknown. The objective of this study was to transfer OsPP1a cDNA to rice via Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105 to assess the mechanisms by which it can confer tolerance to salt treatment. All OsPP1a transcript levels except for OsPP1a-4 detected in transgenic lines were significantly higher than in non-transgenic (NT) plants. Transgenic plants overexpressing OsPP1a showed enhanced tolerance to high salt treatment, SnRK1A, and two stress-responsive genes, OsNAC5 and OsNAC6, which were up-regulated in transgenic OsPP1a-2, OsPP1a-3, and OsPP1a-6 lines. The gene expression profiles of lines OsPP1a-2, -3, and -6 were well-matched with the data for ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, scavenging the DPPH radical, and malondialdehyde content in NT and transgenic plants under salt stress treatment. In addition, transgenic rice plants also exhibited higher survival rates and plant heights, fewer oxidative injuries, and grew faster than NT plants exposed to salt treatment. Thus, the overexpression of OsPP1a in rice may be useful for enhancing tolerance in high-salt areas.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aida M, Ishida T, Fukaki H, Fujisawa H, Tasaka M (1997) Genes involved in organ separation in Arabidopsis: an analysis of the cup-shaped cotyledon mutant. Plant Cell 9(6):841–857
Amor NB, Jimènez A, Megdiche W, Lundqvist M, Sevilla F, Abdelly C (2006) Response of antioxidant systems to NaCl stress in the halophyte Cakile maritima. Physiol Plant 126:446–457
Anil VS, Krishnamurthy P, Kuruvilla S, Sucharitha S, Thomas G, Mathew MK (2005) Regulation of the uptake and distribution of Na+ in shoots of rice (Oryza sativa) variety Pokkali: role of Ca+2 in salt tolerance response. Physiol Plant 124:451–464
Bakker E, Qin Y (2006) Electrochemical sensors. Anal Chem 78(12):3965–3984
Bohm S, Buchberger A (2013) The budding yeast Cdc48 (Shp1) complex promotes cell cycle progression by positive regulation of protein phosphatase 1 (Glc7). PLoS ONE 8:e56486
Ceulemans H, Bollen M (2004) Functional diversity of protein phosphatase-1, a cellular economizer and reset button. Physiol Rev 84:1–39
Chen Q, Wang Q, Xiong L, Lou Z (2011) A structural view of the conserved domain of rice stress- responsive NAC1. Protein Cell 2:55–63
Chiang CM, Chen SP, Chen LFO, Chiang MC, Chien HL, Lin KH (2014) Expression of the broccoli catalase gene (BoCAT) enhances heat tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 23(3):266–277
Choe YH, Kim YS, Kim YH, Park HM, Yoon HS (2013) Homologous expression of r-glutamylcysteine synthetase increases grain yield and tolerance of transgenic rice plants to environmental stresses. J Plant Physiol 170:610–618
Chung PJ, Kim YS, Jeong JS, Park SH, Nahm BH, Kim JK (2009) The histone deacetylase OsHDAC1 epigenetically regulates the OsNAC6 gene that controls seedling root growth in rice. Plant J 59:764–776
Counce PA, Keisling TC, Mitchell AJ (2000) A uniform, objective, and adaptive system for expressing rice development. Crop Sci 40:436–443
Diaz-Vivancos P, Faize M, Barba-Espin G, Faize L, Petri C, Hernández JA, Burgos L (2013) Ectopic expression of cytosolic superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase leads to salt stress tolerance in transgenic plums. Plant Biotechnol J 11(8):976–985
Djanaguiraman M, Prasad PV, Seppanen M (2010) Selenium protects sorghum leaves from oxidative damage under high temperature stress by enhancing antioxidant defense system. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(12):999–1007
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Foyer CH, Lopez DH, Date JF, Scott IM (1997) Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione associated mechanisms of acclamatory stress tolerance and signaling. Physiol Plant 100:241–254
Gabor BL (1981) Determination of sodium with ion-selective electrodes. Clin Chem 27(8):1435–1438
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Phys Biochem 48:909–930
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
He XJ, MuRL Cao WH, Zhang ZG, Zhang JS, Chen YS (2005) AtNAC2, a transcription factor downstream of ethylene and auxin signaling pathways, is involved in salt stress response and lateral root development. Plant J 44(6):903–916
Hoque A, Banu NA, Okuma E, Amakpo K, Nakamura Y, Shimoishi Y, Murata Y (2007) Exogenous proline and glycinebetaine increase NaCl-induced ascorbate-glutathione cycle enzyme activities, and proline improves salt tolerance more than glycinebetaine in tobacco bright yellow-2 suspension- cultured cells. J Plant Physiol 164:1457–1468
Hu H, Dai M, Yao J, Xiao B, Li X, Zhang Q, Xiong L (2006) Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 35:12987–12992
Hu H, You J, Fang Y, Zhu X, Qi Z, Xiong L (2008) Characterization of transcription factor gene SNAC2 conferring cold and salt tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 67:169–181
Hu K, Li W, Wang H, Chen K, Wang Y, Sang J (2012) Shp1, a regulator of protein phosphatase 1 Glc7, has important roles in cell morphogenesis, cell cycle progression and DNA damage response in Candida albicans. Fungal Gene Biol 49:433–442
Hwang SY, VanToai TT (1991) Abscisic acid induces anaerobiosis tolerance in corn. Plant Physiol 97:593–597
Ismail AM, Ella ES, Vergara GV, Mackill DJ (2009) Mechanisms associated with tolerance to flooding during germination and early seedling growth in rice (Oryza sativa L). Ann Bot 103:197–209
Jyothishwaran G, Kotresha D, Selvaraj T, Srideshikan S, Rajvanshi P, Jayabaskaran C (2007) A modified freeze and thaw method for efficient transformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Curr Sci 93:770–772
Kim SI, Veena SB, Gelvin SB (2007) Genome-wide analysis of Agrobacterium T-DNA integration sites in the Arabidopsis genome generated under non-selective conditions. Plant J 51:779–791
Kleinow T, Himbert S, Krenz B, Jeske H, Koncz C (2009) NAC domain transcription factor ATAF1 interacts with SNF1-related kinases and silencing of its subfamily causes severe developmental defects in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 177:360–370
Kosugi H, Kikugawa K (1985) Thiobarbituric acid reaction of aldehydes and oxidized lipids in glacial acetic acid. Lipids 20:915–920
Kumar M, Sirhindi G, Bhardwaj R, Jain G (2001) Effect of exogenous H2O2 on antioxidant enzymes of Brassica juncea L. seedlings in relation to 24-epibrassinolide under chilling stress. Indian J Biochem Biophys 47:378–382
Lee YP, Kim SH, Bang JW, Lee HS, Kwak SS, Kwon SY (2007) Enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress in transgenic tobacco plants expressing three antioxidant enzymes in chloroplasts. Plant Cell Rep 26:591–598
Lesage B, Qian J, Bollen M (2011) Spindle checkpoint silencing: PP1 tips the balance. Curr Biol 21:R898–R903
Lin KH, Pu SF (2010) Tissue- and genotype-specific ascorbate peroxidase expression in sweet potato in response to salt stress. Biol Plant 54(4):664–670
Lu CA, Lin CC, Lee KW, Chen JL, Huang LF, Ho SL, Liu HJ, Hsing YI, Yu SM (2007) The SnRK1A protein kinase plays a key role in sugar signaling during germination and seedling growth of rice. Plant Cell 9(8):2484–2499
Masaru O, Yasuyuki H, Akira H, Akira T, Tatsunosuke N, Takahiko H (2002) Introduction of a Nat/H+ antiporter gene from Atriplex gmelini confers salt tolerance to rice. FEBS Lett 532:279–282
McClung CR (1997) The regulation of catalase in Arabidopsis. Free Rad Biol Med 23:489–496
Meloni DA, Oliva MA, Martinez CA, Cambraia J (2003) Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 49:69–76
Miller G, Shulaev V, Mittler R (2008) Reactive oxygen signaling and abiotic stress. Physiol Plant 133:481–489
Munns R (2005) Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. N Phytol 167:645–663
Murgia I, Tarantion D, Vannini C, Bracale M, Carravieri S, Soave C (2004) Arabidopsis thaliana plants overexpressing thylakoidal ascorbate peroxidase show increased resistance to paraquat induced photoxidative stress and to nitric oxide-induced cell death. Plant J 38:940–953
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Nakashima K, Tran LSP, Van Nguyen D, Fujita M, Maruyama K, Todaka D, Ito Y, Hayashi N, Shinozaki KY (2007) Functional analysis of a NAC type transcription factor OsNAC6 involved in abiotic and biotic stress responsive gene expression in rice. Plant J 51:617–630
Nakashima K, Ito Y, Shinozaki KY (2009) Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol 149:88–95
Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Shinozaki KY (2012) NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:97–103
Nuruzzaman M, Manimekalai R, Sharoni AM, Satoh K, Kondoh H, Ooka H, Kikuchi S (2010) Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Gene 465:30–44
Ogawa D, Abe K, Miyao A, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Mizutani M, Morita H, Toda Y, Hobo T, Sato Y, Hattori T, Hirochika H, Takeda S (2011) RSS1 regulates the cell cycle and maintains meristematic activity under stress conditions in rice. Nature Commu 2:278
Ogawa D, Morita H, Hattori T, Takeda S (2012) Molecular characterization of the rice protein RSS1 required for meristematic activity under stressful conditions. Plant Physiol Biochem 61:54–60
Passaia G, Spagnolo FL, Caverzan A, Jardim-Messeder D, Christoff AP, Gaeta ML, de Araujo Mariath JE, Margis R, Margis-Pinheiro M (2013) The mitochondrial glutathione peroxidase GPX3 is essential for H2O2 homeostasis and root and shoot development in rice. Plant Sci 208:93–101
Peng A, Lewellyn AL, Schiemann WP, Maller JL (2010) Repo-man controls a protein phosphatase 1-dependent threshold for DNA damage checkpoint activation. Curr Biol 20:387–396
Prashanth SR, Sadhasivam V, Parida A (2008) Over expression of cytosolic copper/zinc superoxide dismutase from a mangrove plant Avicennia marina in indica Rice var Pusa Basmati-1 confers abiotic stress. Transgenic Res 17:281–291
Puranik S, Sahu PP, Srivastava PS, Prasad M (2012) NAC proteins: regulation and role in stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 17:369–381
Qin Q, Wang W, Guo X, Yue J, Huang Y, Xu X, Li J, Hou S (2014) Arabidopsis DELLA protein degradation is controlled by a type-one protein phosphatase, TOPP4. PLoS Genet 10(7):e1004464
Rabbani M, Maruyama K, Abe H, Khan MA, Katsura K, Ito Y, Yoshiwara K, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Shinozaki KY (2003) Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol 133:1755–1767
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1992) A simple method for estimating and testing minimum evolution trees. Mol Biol Evol 9:945–967
Saad AS, Xu L, Li HP, Huang T, Gao CS, Guo MW, Cheng W, Zhao GY, Liao YC (2013) A rice stress-responsive NAC gene enhances tolerance of transgenic wheat to drought and salt stresses. Plant Sci 203:33–40
Sanz P, Ludin K, Carlson M (2000) Sip5 interacts with both the Reg1 Glc7 protein phosphatase and the Snf1 protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 154:99–107
Sheu JJ, Yu TS, Tong WF, Yu SM (1996) Carbohydrate starvation stimulates differential expression of rice alpha-amylase genes that is modulated through complicated transcriptional and posttranscriptional processes. J Biol Chem 271:26998–27004
Song SY, Chen Y, Chen J, Dai XY, Zhang WH (2011) Physiological mechanisms underlying OsNAC5-dependent tolerance of rice plants to abiotic stress. Planta 234(2):331–345
Swati P, Pranav PS, Srivastava PS, Manoj P (2012) NAC proteins: regulation and role in stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 17(6):369–381
Tähtiharju S (2002) The role of calcium and protein phosphatases in cold signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. University of Helsinki, Viikinkaari
Takasaki H, Maruyama K, Kidokoro S, Ito Y, Fujita Y, Shinozaki K, Shinozaki KY, Nakashima K (2010) The abiotic stress-responsive NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC5 regulates stress-inducible genes and stress tolerance in rice. Mol Genet Genomics 284:173–183
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Toki S (1997) Rapid and efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 15:16–21
Verslues PE, Agarwal M, Agarwal SK, Zhu J, Zhu K (2006) Methods and concepts in quantifying resistance to drought, salt and freezing, abiotic stresses that affect water status. Plant J 45:523–539
Wang W, Vignani R, Scali M, Cresti M (2006) A universal and rapid protocol for protein extraction from recalcitrant plant tissues for proteomic analysis. Electrophoresis 27:2782–2786
Wang R, Che S, Zhou X, Shen X, Deng L, Poll A (2008) Ionic homeostasis and reactive oxygen species control in leaves and xylem sap of two poplars subjected to NaCl stress. Tree Physiol 28:947–957
Xi DM, Liu WS, Yang GD, Wu CA, Zheng CC (2010) Seed-specific overexpression of antioxidant genes in Arabidopsis enhances oxidative stress tolerance during germination and early seedling growth. Plant Biotech J 8:796–806
Xiong L, Zhu JK (2002) Molecular and genetic aspects of plant responses to osmotic stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:131–139
Yamaquchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Yang Y, Tang RJ, Jiang CM, Li B, Kang T, Liu H, Zhao N, Ma XJ, Yang L, Chen SL, Zhang HX (2015) Overexpression of the PtSOS2 gene improves tolerance to salt stress in transgenic poplar plants. Plant Biotechnol J. doi:10.1111/pbi.12335
Yoshiki Y, Kahhara T, Sakabe Y, Yamasaki T (2001) Superoxide and DPPH radical-scavenging activities of soyasponin β related to gallic acid. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:2162–2165
Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Wu J, Zheng X, Zheng S, Sun X, Qiu Q, Lu T (2013) Gene knockout study reveals that cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 2 (OsAPX2) plays a critical role in growth and reproduction in rice under drought, salt and cold. PLoS ONE 8(2):e57472
Zheng J, Zhao JF, Tao YZ, Wang JH, Liu YJ, Fu JJ, Jin Y, Gao P, Zhang JP, Bai YF, Wang GY (2004) Isolation and analysis of water stress induced genes in maize seedlings by subtractive PCR and cDNA microarray. Plant Mol Biol 55:807–823
Zhou J, Wang J, Bi Y, Wang L, Tang L, Yu X, Ohtani M, Demura T, Zhuge Q (2014) Overexpression of PtSOS2 enhances salt tolerance in transgenic poplars. Plant Mol Biol Report 32:185–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yu-Duan Laio and Kuan-Hung Lin contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2016_446_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Supplemental Fig. S2 Analysis of transgenic rice by genomic PCR and Southern blot analysis for HPT genes. (A) The expected size of the HPT gene fragment (indicated by arrowhead) was 689 bp. M, 100 bp marker; NT, non-transgenic rice; P, positive control (using pPZP200/OsPP1a plasmid as the template); lanes 4–9, OsPP1a-1, OsPP1a-2, OsPP1a-3, OsPP1a-4, OsPP1a-5, and OsPP1a-6, respectively. (B) Genomic DNA (15 μg/lane) from NT and OsPP1a-1, -2, -3, -4, -5, and -6 transgenic plants were digested with restriction enzyme HindIII and electrophoresed through 1 % agarose gel. 32P-labeled hyg DNA was used as a probe (DOCX 124 kb)
11032_2016_446_MOESM3_ESM.docx
Supplemental Fig. S3 Phylogenetic tree inferred from the Protein Phosphatase amino acid sequences by the Neighbor Joining method. Numbers indicate bootstrap support for individual nodes. Similarities of amino acids (%) between OsPP1a and others are also shown using OsPP1a as 100 % (DOCX 212 kb)
11032_2016_446_MOESM4_ESM.docx
Supplemental Fig. S4 RNA expression in the OsNAC gene family and SnRK1 genes under salt stress by RT-PCR (A) in NT plant and T1 transgenic lines (OsPP1a-2, OsPP1a-3, and OsPP1a-6). The transcript levels of OsNAC5 and OsNAC6 were also assessed in NT and transgenic plants receiving sodium butyrate (NaB) treatments and without NaB as control (B). Total RNA in all tested plants was extracted from 5-day-old plants (DOCX 302 kb)
11032_2016_446_MOESM5_ESM.docx
Supplemental Fig. S5 Measurement of the seed germination rate in salt-containing solutions with 0, 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 mM of NaCl. All tested plants were germinated for 5 days and for high-salt stress treatment. Transgenic plants were grown in nutrient soil under normal conditions for 14 days and transferred to 150 mM NaCl for 3 days (DOCX 73 kb)
11032_2016_446_MOESM6_ESM.docx
Supplemental Fig. S6 Endogenous OsPP1a was expressed in different tissues of germinating rice seedling by RT-PCR. Paired primers OsPP1a 5F and OsPP1a 3R (Table 1) were used for confirmation of OsPP1a expression in endosperm, embryo, root, and leaf tissues of NT seedlings. Tubulin (TUB) gene was used as internal control (DOCX 59 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, YD., Lin, KH., Chen, CC. et al. Oryza sativa protein phosphatase 1a (OsPP1a) involved in salt stress tolerance in transgenic rice. Mol Breeding 36, 22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0446-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0446-2