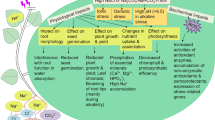
Abstract
Key message
The mechanism of conferring salt tolerance by AtTPS9 involves enhanced deposition of suberin lamellae in the Arabidopsis root endodermis, resulting in reduction of Na+ transported to the leaves.
Abstract
Members of the class I trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) enzymes are known to play an important role in plant growth and development in Arabidopsis. However, class II TPSs and their functions in salinity stress tolerance are not well studied. We characterized the function of a class II TPS gene, AtTPS9, to understand its role in salt stress response and root development in Arabidopsis. The attps9 mutant exhibited significant reduction of soluble sugar levels in the leaves and formation of suberin lamellae (SL) in the endodermis of roots compared to the wild type (WT). The reduction in SL deposition (hydrophobic barriers) leads to increased apoplastic xylem loading, resulting in enhanced Na+ content in the plants, which explains salt sensitivity of the mutant plants. Conversely, AtTPS9 overexpression lines exhibited increased SL deposition in the root endodermis along with increased salt tolerance, showing that regulation of SL deposition is one of the mechanisms of action of AtTPS9 in conferring salt tolerance to Arabidopsis plants. Our data showed that besides salt tolerance, AtTPS9 also regulates seed germination and root development. qRT-PCR analyses showed significant downregulation of selected SNF1-RELATED PROTEIN KINASE2 genes (SnRK2s) and ABA-responsive genes in the mutant, suggesting that AtTPS9 may regulate the ABA-signaling intermediates as part of the mechanism conferring salinity tolerance.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are provided in the main text and the supplementary materials.
References
Afzal S, Chaudhary N, Singh NK (2021) Role of soluble sugars in metabolism and sensing under abiotic stress. In: Aftab T, Hakeem KR (eds) Plant growth regulators: signalling under stress conditions. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 305–334
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Avonce N, Leyman B, Mascorro-Gallardo JO, Van Dijck P, Thevelein JM, Iturriaga G (2004) The arabidopsis trehalose-6-P synthase AtTPS1 gene is a regulator of glucose, abscisic acid, and stress signaling. Plant Physiol 136:3649–3659
Avonce N, Mendoza-Vargas A, Morett E, Iturriaga G (2006) Insights on the evolution of trehalose biosynthesis. BMC Evol Biol 6:109
Barberon M, Vermeer JE, De Bellis D, Wang P, Naseer S, Andersen TG, Humbel BM, Nawrath C, Takano J, Salt DE, Geldner N (2016) Adaptation of root function by nutrient-induced plasticity of endodermal differentiation. Cell 164:447–459
Chae MJ, Lee JS, Nam MH, Cho K, Hong JY, Yi SA, Suh SC, Yoon IS (2007) A rice dehydration-inducible SNF1-related protein kinase 2 phosphorylates an abscisic acid responsive element-binding factor and associates with ABA signaling. Plant Mol Biol 63:151–169
Chary SN, Hicks GR, Choi YG, Carter D, Raikhel NV (2008) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase regulates cell shape and plant architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146:97–107
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Cortina C, Culiáñez-Macià FA (2005) Tomato abiotic stress enhanced tolerance by trehalose biosynthesis. Plant Sci 169:75–82
De Smet I, Signora L, Beeckman T, Inze D, Foyer CH, Zhang H (2003) An abscisic acid-sensitive checkpoint in lateral root development of Arabidopsis. Plant J 33:543–555
Dellaporta S (1994) Plant DNA miniprep and microprep: versions 2.1–2.3. In: Freeling M, Walbot V (eds) The maize handbook. Springer, Berlin, pp 522–525
Delorge I, Figueroa CM, Feil R, Lunn JE, Van Dijck P (2015) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is not the only active TPS in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem J 466:283–290
Elbein AD (1974) The metabolism of α, α-trehalose. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 30:227–256
Elbein AD, Pan Y, Pastuszak I, Carroll D (2003) New insights on trehalose: a multifunctional molecule. Glycobiol 13:17R-27R
Fernandez O, Bethencourt L, Quero A, Sangwan RS, Clement C (2010) Trehalose and plant stress responses: friend or foe? Trends Plant Sci 15:409–417
Fichtner F, Lunn JE (2021) The role of Trehalose 6-Phosphate (Tre6P) in plant metabolism and development. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72:737–760
Furihata T, Maruyama K, Fujita Y, Umezawa T, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:1988–1993
Geng Y, Wu R, Wee CW, Xie F, Wei X, Chan PM, Tham C, Duan L, Dinneny JR (2013) A spatio-temporal understanding of growth regulation during the salt stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:2132–2154
Goddijn OJ, van Dun K (1999) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Trends Plant Sci 4:315–319
Gómez LD, Gilday A, Feil R, Lunn JE, Graham IA (2010) AtTPS1-mediated trehalose 6-phosphate synthesis is essential for embryogenic and vegetative growth and responsiveness to ABA in germinating seeds and stomatal guard cells. Plant J 64:1–13
Guan H, Liu X, Fu Y, Han X, Wang Y, Li Q, Guo L, Mur LAJ, Wei Y, He W (2023) The locoweed endophyte Alternaria oxytropis affects root development in Arabidopsis in vitro through auxin signaling and polar transport. J Exp Bot 74:931–944
Hirayama T, Umezawa T (2010) The PP2C–SnRK2 complex: the central regulator of an abscisic acid signaling pathway. Plant Signal Behav 5:160–163
Islam MA, Rahman MM, Rahman MM, Jin X, Sun L, Zhao K, Wang S, Sikdar A, Noor H, Jeon J-S (2021) In silico and transcription analysis of trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene family of wheat: trehalose synthesis genes contribute to salinity, drought stress and leaf senescence. Genes 12(11):1652
Jacobs A, Lunde C, Bacic A, Tester M, Roessner U (2007) The impact of constitutive heterologous expression of a moss Na+ transporter on the metabolomes of rice and barley. Metabolomics 3:307–317
Kerbler SML, Armijos-Jaramillo V, Lunn JE, Vicente R (2023) The trehalose 6-phosphate phosphatase family in plants. Physiol Plant 175:e14096
Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Minami H, Kagaya Y, Hattori T (2004) Differential activation of the rice sucrose nonfermenting1-related protein kinase2 family by hyperosmotic stress and abscisic acid. Plant Cell 16:1163–1177
Kong L, Liu J, Zhang W, Li X, Zhang Y, Chen X, Zhan Z, Piao Z (2023) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthetase gene family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa) and Plasmodiophora brassicae during theirinteraction. Intl J Mol Sci 24:929
Krishnamurthy P, Jyothi-Prakash PA, Qin L, He J, Lin Q, Loh CS, Kumar PP (2014) Role of root hydrophobic barriers in salt exclusion of a mangrove plant Avicennia officinalis. Plant, Cell Environ 37:1656–1671
Krishnamurthy P, Ranathunge K, Nayak S, Schreiber L, Mathew MK (2011) Root apoplastic barriers block Na+ transport to shoots in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot 62:4215–4228
Krishnamurthy P, Vishal B, Bhal A, Kumar PP (2021) WRKY9 transcription factor regulates cytochrome P450 genes CYP94B3 and CYP86B1, leading to increased root suberin and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plant 172:1673–1687
Krishnamurthy P, Vishal B, Ho WJ, Lok FCJ, Lee FSM, Kumar PP (2020) Regulation of a cytochrome P450 gene CYP94B1 by WRKY33 transcription factor controls apoplastic barrier formation in roots to confer salt tolerance. Plant Physiol 184:2199–2215
Kubo M, Udagawa M, Nishikubo N, Horiguchi G, Yamaguchi M, Ito J, Mimura T, Fukuda H, Demura T (2005) Transcription switches for protoxylem and metaxylem vessel formation. Genes Dev 19:1855–1860
Kupnik K, Primožič M, Knez Ž, Leitgeb M (2023) Trehalose. In: Gupta VK (ed) Valorization of biomass to bioproducts. Elsevier, pp 163–207
Lee J, Jeong B, Bae HR, Jang HA, Kim JK (2023) Trehalose biosynthesis gene otsA protects against stress in the initial infection stage of Burkholderia-bean bug symbiosis. Microbiol Spectr 11:e03510-03522
Leyman B, Van Dijck P, Thevelein JM (2001) An unexpected plethora of trehalose biosynthesis genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Trends Plant Sci 6:510–513
Li HW, Zang BS, Deng XW, Wang XP (2011) Overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene OsTPS1 enhances abiotic stress tolerance in rice. Planta 234:1007–1018
Li Y, Chu Y, Yao K, Shi C, Deng X, Lin J (2023a) Response of sugar metabolism in the cotyledons and roots of Ricinus communis subjected to salt stress. Plant Biol 25:62–71
Li Z, Wang Y, Yu L, Gu Y, Zhang L, Wang J, Qiu L (2023b) Overexpression of the purple perilla (Perilla frutescens L.) FAD3a gene enhances salt tolerance in soybean. Intl J Mol Sci 24(13):10533
Liu L, Wang H, Fu Y, Tang W, Zhao P, Ren Y, Liu Z, Wu K, Zhang X (2023) Turnip crinkle virus-encoded suppressor of RNA silencing interacts with Arabidopsis SGS3 to enhance virus infection. Mol Plant Pathol 24:154–166
McMillan SD, Oberlie NR, Hardtke HA, Montes MM, Brown DW, McQuade KL (2023) A secondary function of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase is required for resistance to oxidative and desiccation stress in Fusarium verticillioides. Fungal Biol 127:918–926
Mollavali M, Börnke F (2022) Characterization of Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase and Trehalose-6-Phosphate Phosphatase genes of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and analysis of their differential expression in response to temperature. Intl J Mol Sci 23:11436
Morabito C, Secchi F, Schubert A (2021) Grapevine TPS (trehalose-6-phosphate synthase) family genes are differentially regulated during development, upon sugar treatment and drought stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 164:54–62
Munns R, Day DA, Fricke W, Watt M, Arsova B, Barkla BJ, Bose J, Byrt CS, Chen ZH, Foster KJ, Gilliham M, Henderson SW, Jenkins CLD, Kronzucker HJ, Miklavcic SJ, Plett D, Roy SJ, Shabala S, Shelden MC, Soole KL, Taylor NL, Tester M, Wege S, Wegner LH, Tyerman SD (2020) Energy costs of salt tolerance in crop plants. New Phytol 225:1072–1090
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nawaz M, Hassan MU, Chattha MU, Mahmood A, Shah AN, Hashem M, Alamri S, Batool M, Rasheed A, Thabit MA, Alhaithloul HAS, Qari SH (2022) Trehalose: a promising osmo-protectant against salinity stress-physiological and molecular mechanisms and future prospective. Mol Biol Rep 49:11255–11271
Nuccio ML, Wu J, Mowers R, Zhou H-P, Meghji M, Primavesi LF, Paul MJ, Chen X, Gao Y, Haque E, Basu SS, Lagrimini LM (2015) Expression of trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in maize ears improves yield in well-watered and drought conditions. Nat Biotechnol 33:862–869
Ramon M, De Smet I, Vandesteene L, Naudts M, Leyman B, Van Dijck P, Rolland F, Beeckman T, Thevelein JM (2009) Extensive expression regulation and lack of heterologous enzymatic activity of the Class II trehalose metabolism proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 32:1015–1032
Reichelt N, Korte A, Krischke M, Mueller MJ, Maag D (2023) Natural variation of warm temperature-induced raffinose accumulation identifies TREHALOSE-6-PHOSPHATE SYNTHASE 1 as a modulator of thermotolerance. Plant Cell Environ 46:3392–3404
Rojas BE, Tonetti T, Figueroa CM (2023) Trehalose 6-phosphate metabolism in C4 species. Curr Opin Plant Biol 72:102347
Romero C, Bellés JM, Vayá JL, Serrano R, Culiáñez-Macià FA (1997) Expression of the yeast trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene in transgenic tobacco plants: pleiotropic phenotypes include drought tolerance. Planta 201:293–297
Rosa M, Prado C, Podazza G, Interdonato R, Gonzalez JA, Hilal M, Prado FE (2009) Soluble sugars—Metabolism, sensing and abiotic stress: a complex network in the life of plants. Plant Signal Behav 4:388–393
Shkolnik-Inbar D, Bar-Zvi D (2010) ABI4 mediates abscisic acid and cytokinin inhibition of lateral root formation by reducing polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:3560–3573
Suzuki N, Bajad S, Shuman J, Shulaev V, Mittler R (2008) The transcriptional co-activator MBF1c is a key regulator of thermotolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 283:9269–9275
Swida-Barteczka A, Pacak A, Kruszka K, Nuc P, Karlowski WM, Jarmolowski A, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z (2023) MicroRNA172b-5p/trehalose-6-phosphate synthase module stimulates trehalose synthesis and microRNA172b-3p/AP2-like module accelerates flowering in barley upon drought stress. Front Plant Sci 14:1124785
Tavakkoli E, Fatehi F, Coventry S, Rengasamy P, McDonald GK (2011) Additive effects of Na+ and Cl– ions on barley growth under salinity stress. J Exp Bot 62:2189–2203
Ursache R, Andersen TG, Marhavy P, Geldner N (2018) A protocol for combining fluorescent proteins with histological stains for diverse cell wall components. Plant J 93:399–412
van Dijken AJ, Schluepmann H, Smeekens SC (2004) Arabidopsis trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is essential for normal vegetative growth and transition to flowering. Plant Physiol 135:969–977
Vandesteene L, Ramon M, Le Roy K, Van Dijck P, Rolland F (2010) A single active trehalose-6-P synthase (TPS) and a family of putative regulatory TPS-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 3:406–419
Vishal B (2017) OsTPS8 controls salt stress tolerance and agronomic traits in rice. National University of Singapore, ScholarBank@NUS Repository
Vishal B, Krishnamurthy P, Ramamoorthy R, Kumar PP (2019) OsTPS8 controls yield-related traits and confers salt stress tolerance in rice by enhancing suberin deposition. New Phytol 221:1369–1386
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Yang B, Zhang L, Xiang S, Chen H, Qu C, Lu K, Li J (2023) Identification of Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase (TPS) genes associated with both source-/sink-related yield traits and drought response in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Plants 12:981
Yang HL, Liu YJ, Wang CL, Zeng QY (2012) Molecular evolution of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family in Populus. Arabidopsis and Rice Plos One 7:e42438
Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Sayama H, Kidokoro S, Maruyama K, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010) AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. Plant J 61:672–685
Zang B, Li H, Li W, Deng XW, Wang X (2011) Analysis of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family suggests the formation of TPS complexes in rice. Plant Mol Biol 76:507–522
Funding
This study was funded in part by grant number A-8000149-03-00 from the National University of Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BV, PK and PPK conceived the research plans; BV and PK designed and carried out the experiments, analyzed the data and all authors contributed to writing the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Prakash Lakshmanan.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vishal, B., Krishnamurthy, P. & Kumar, P.P. Arabidopsis class II TPS controls root development and confers salt stress tolerance through enhanced hydrophobic barrier deposition. Plant Cell Rep 43, 115 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-024-03215-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-024-03215-w