Abstract
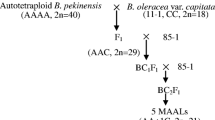
Monosomic addition lines (MALs) are useful materials not only for cytogenetic and molecular genetic studies but also for plant breeding as gene sources. In our previous study, two MALs in the tribe Brassiceae were developed, one being Raphanus sativus lines with alien chromosomes of Brassica rapa (B. rapa-monosomic addition lines; BrMALs) and the second being those with alien chromosomes of Brassica oleracea (B. oleracea-monosomic addition lines; BoMALs). We developed species-specific DNA markers from the genomic sequences of B. rapa and B. oleracea comparing them with those of R. sativus, and identified chromosomes added in BrMALs and BoMALs using these markers. It was revealed that eight types of BrMALs have seven chromosomes of B. rapa and seven types of BoMALs have six chromosomes of B. oleracea. Furthermore, chromosome breakage and homoeologous recombination were suggested to have occurred in some MALs. The developed species-specific DNA markers are considered to be useful for producing MALs and also for assessing chromosome abnormality in MALs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaba M, Kaneko Y, Hatakeyama K, Ishida M, Bang SW, Matsuzawa Y (2009) Identification and evaluation of clubroot resistance of radish chromosome using Brassica napus-Raphanus sativus monosomic addition line. Breed Sci 59:203–206
Chang SB, de Jong H (2005) Production of alien chromosome additions and their utility in plant genetics. Cytogenet Genome Res 109:335–343
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Finch RA, Miller TE, Bennett MD (1984) “Cuckoo” Aegilops addition chromosome in wheat ensures its transmission by causing chromosome breaks in meiospores lacking it. Chromosoma 90:84–88
Friebe B, Qi LL, Nasuda S, Zhang P, Tulee NA, Gill BS (2000) Development of a complete set of Triticum aestivum-Aegilops speltoides chromosome addition lines. Theor Appl Genet 101:51–58
Fu S, Sun C, Yang M, Fei Y, Tan F, Yan B, Ren Z, Tang Z (2013a) Genetic and epigenetic variations induced by wheat-rye 2R and 5R monosomic addition lines. PLoS ONE 8:e54057
Fu S, Yang M, Fei Y, Tan F, Ren Z, Yan B, Zhang H, Tang Z (2013b) Alteration and abnormal mitosis of wheat chromosomes induced by wheat-rye monosomic addition lines. PLoS ONE 8:e70483
Gereta M, Heneen WK, Stoute AI, Muttucumaru N, Scott RJ, King GJ, Kurup S, Bryngelsson T (2012) Assigning Brassica microsatellite markers to the nine C-genome chromosomes using Brassica rapa var. trilocularis-B. oleracea var. alboglabra monosomic alien addition lines. Theor Appl Genet 125:455–466
Hasterok R, Wolny E, Kulak S, Zdziechiewicz A, Maluszynska J, Heneen W (2005) Molecular cytogenetic analysis of Brassica rapa-Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra monosomic addition lines. Theor Appl Genet 111:196–205
Heneen WK, Geleta M, Brismar K, Xiong Z, Pires JC, Hasterok R, Stoute AI, Scott RJ, King GJ, Kurup S (2012) Seed color loci, homoeology and linkage groups of the C genome chromosomes revealed in Brassica rapa-B. oleracea monosomic alien addition lines. Ann Bot 109:1227–1242
Ji Y, Chetelat RT (2003) Homoeologous pairing and recombination in Solanum lycopersicoides monosomic addition and substitution lines of tomato. Theor Appl Genet 106:979–989
Kamstra SA, Ramanna MS, de Jeu M, Kuipers AGJ, Jacobsen E (1999) Homoeologous chromosome pairing in the distant hybrid Alstroemeria aurea × A. inodora and the genome composition of its backcross derivatives determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization with species-specific probes. Heredity 82:69–78
Kaneko Y, Matsuzawa Y, Sarashima M (1987) Breeding of the chromosome addition lines of radish with single kale chromosome. Jpn J Breed 37:438–452
Kaneko Y, Natsuaki T, Bang SW, Matsuzawa Y (1996) Identification and evaluation of turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) resistance gene in kale monosomic addition lines of radish. Breed Sci 46:117–124
Kaneko Y, Bang SW, Matsuzawa Y (2000) Early-bolting trait and RAPD markers in the specific monosomic addition line of radish carrying the e-chromosome of Brassica oleracea. Plant Breed 119:137–140
Kaneko Y, Yano H, Bang SW, Matsuzawa Y (2001) Production and characterization of Raphanus sativus-Brassica rapa monosomic chromosome addition lines. Plant Breed 120:163–168
Kaneko Y, Yano H, Bang SW, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Genetic stability and maintenance of Raphanus sativus lines with an added Brassica rapa chromosome. Plant Breed 122:239–243
Khush GS, Brar DS (1992) Overcoming the barriers in hybridization. In: Kalloo G, Chowdhury JB (eds) Distant hybridization of crop plants. Springer, Berlin, pp 47–61
Leighty CE, Taylor JW (1924) “Hairy neck” wheat segregates from wheat-rye hybrids. J Agr Res 28:567–576
Ma C, Wang Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Chen S, Li H (2011) Identification of a sugar beet BvM14-MADS box gene through differential gene expression analysis of monosomic addition line M14. J Plant Physiol 168:1980–1986
Masuzaki S, Shigyo M, Yamauchi N (2006) Complete assignment of structural genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis influencing bulb color to individual chromosomes of the shallot (Allium cepa L.). Genes Genet Syst 81:255–263
Multani DS, Jena KK, Brar DS, delos Reyes BC, Angeles ER, Khush GS (1994) Development of monosomic alien addition lines and introgression of genes from Oryza australiensis Domin. to cultivated rice O. sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 88:102–109
Peterka H, Budahn H, Schrader O, Ahne R, Schütze W (2004) Transfer of resistance against the beet cyst nematode from radish (Raphanus ativus) to rape (Brassica napus) by monosomic chromosome addition. Theor Appl Genet 109:30–41
Qi L, Friebe B, Zhang P, Gill BS (2007) Homoeologous recombination, chromosome engineering and crop improvement. Chromosome Res 15:3–19
Ren TH, Yang ZJ, Yan BJ, Zhang HQ, Fu SL, Ren ZL (2009) Development and characterization of a new 1BL.1RS translocation line with resistance to stripe rust and powdery mildew of wheat. Euphytica 169:207–213
Schwarzacher T, Leitch AR, Bennett MD, Heslop-Harrison JS (1989) In situ hybridization of parental genomes in a wide hybrid. Ann Bot 64:315–324
Shigyo M, Tashiro Y, Isshiki S, Miyazaki S (1996) Establishment of a series of alien monosomic addition lines of Japanese bunching onion (Allium fistulosum L.) with extra chromosomes from shallot (A. cepa L. Aggregatum group). Genes Genet Syst 71:363–371
Shiokai S, Shirasawa K, Sato Y, Nishio T (2010) Improvement of the dot-blot-SNP technique for efficient and cost-effective genotyping. Mol Breed 25:179–185
Szadkoeski E, Eber F, Huteau V, Lode M, Huneau C, Coriton O, Manzanares-Dauleux MJ, Delourme R, King GJ, Chalhoub B, Jenczewski E, Chèvre A-M (2010) The first meiosis of resynthesized Brassica napus, a genome blender. New Phytol 186:102–112
Tan G, Jin H, Li G, He R, Zhu L, He G (2005) Production and characterization of a complete set of individual chromosome additions from Oryza officinalis to Oryza sativa using RFLP and GISH analysis. Theor Appl Genet 111:1585–1595
Tonosaki K, Michiba K, Bang SW, Kitashiba H, Kaneko Y, Nishio T (2013) Genetic analysis of hybrid seed formation ability of Brassica rapa in intergeneric crossings with Raphanus sativus. Theor Appl Genet 126:837–846
Tsukazaki H, Yamashita K, Yaguchi S, Yamashita K, Hagihara T, Shigyo M, Kojima A, Wako T (2011) Direct determination of the chromosomal location of bunching onion and bulb onion markers using bunching onion-shallot monosomic additions and allotriploid-bunching onion single alien deletions. Theor Appl Genet 122:501–510
van Geyt JPC, Oleo M, Lange W, de Bock TSM (1988) Monosomic additions in beet (Beta vulgaris) carrying extra chromosomes of Beta procumbes. Theor Appl Genet 76:577–586
Wang X, Brassica rapa Genome Sequencing Project Consortium et al. (2011a) The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nature Genet 43: 1035–1039
Wang X, Torres MJ, Pierce G, Lemke C, Nelson LK, Yuksel B, Bowers JE, Marley B, Xiao Y, Lin L, Epps E, Sarazen H, Rogers C, Karunakaran S, Ingles J, Giattina E, Mun JH, Seol YJ, Park BS, Amasino RM, Quiros CF, Pires JC, Osborn TC, Town C, Paterson AH (2011) A physical map of Brassica oleracea shows complexity of chromosomal changes following recursive paleopolyploidizations. BMC Genom 12:470–485
Xiong Z, Gaeta RT, Pires JC (2011) Homoeologous shuffling and chromosome compensation maintain genome balance in resynthesized allopolyploid Brassica napus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:7908–7913
Yaguchi S, Nakajima T, Sumi T, Yamauchi N, Shigyo M (2009) Profiling of nondigestible carbohydrate products in a complete set of alien monosomic addition lines explains genetic controls of its metabolisms in Allium cepa. J Am Soc Hort Sci 134:521–528
Yang L, Ma C, Wang L, Chen S, Li H (2012) Salt stress induced proteome and transcriptome changes in sugar beet monosomic addition line M14. J Plant Physiol 169:839–850
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for Promotion of Basic and Applied Researches for Innovations in Bio-oriented Industry (BRAIN). KT is a recipient of the JSPS fellowship for young scientists (DC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tonosaki, K., Akaba, M., Bang, S.W. et al. The use of species-specific DNA markers for assessing alien chromosome transfer in Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea-monosomic additions of Raphanus sativus . Mol Breeding 34, 1301–1311 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0117-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0117-0