Abstract
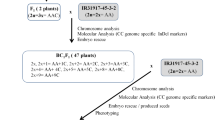
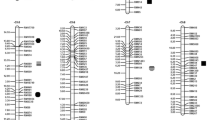
Monosomic alien addition lines (MAALs) are valuable materials for comparative analyses of two distinct genomes, for elucidating introgression mechanisms, and for dissecting genes controlling complex traits. In the study reported here, MAALs of rice containing the complete genome of Oryza sativa and individual chromosomes of Oryza officinalis were produced. Interspecific hybridizations were made between O. sativa L. ssp. Japonica (CV, Hejiang 19, 2 n=24, AA) and O. officinalis (Acc. HY018, 2 n=24, CC). Two backcrosses were made to the cultivated rice to obtain BC2F1 plants. Through RFLP and GISH analyses, 25 MAALs (2 n=25, AA+1C) were identified and divided into 12 syntenic groups, designated MAALs 1–12. MAALs 1, 2, 3, 5, 7 and 10 were each represented by one plant, MAALs 8, 11 and 12 by two plants, MAALs 6 and 9 by four plants, and MAAL 4 by five plants. An ideogram of the C-genome of O. officinalis was constructed, based on GISH analysis of the interspecific hybrid and the MAALs. Comparative RFLP maps showed strong syntenic associations between the A-genomes and C-genomes. Chromosomal arrangements such as translocations and duplications were detected in different alien chromosomes of the MAALs. The complete set of O. officinalis MAALs generated here provides a novel manipulation platform for exploiting and utilizing the O. officinalis genome and carrying out genetic studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal RK, Brar DS, Nandi S, Huang N, Khush GS (1999) Phylogenetic relationships among Oryza species revealed by AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 98:1320–1328
Ahn S, Tanksley SD (1993) Comparative linkage maps of the rice and maize genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7980–7984
Ahn S, Anderson JA, Sorrells ME, Tanksley SD (1993) Homoeologous relationships of rice, wheat and maize chromosomes. Mol Gen Genet 241:483–490
Amante-Bordeos A, Sitch LA, Nelson R, Dalmacio RD, Oliva NP, Aswidinnoor H, Leung H (1992) Transfer of bacterial blight and blast resistance from the tetraploid wild rice Orzya minuta to cultivated rice, Orzya sativa. Theor Appl Genet 84:345–354
Apisitwanich S, Shishido R, Akiyama Y, Fukui K (2001) Quantitative chromosome map of a representative indica rice. Euphytica 118:113–118
Bennetzen JL (2000) Transposable elements contributions to plant gene and genome evolution. Plant Mol Biol 42:351–369
Brar DS, Dalmacio R, Elloran R, Aggarwal R, Angeles R, Khush GS (1996) Gene transfer and molecular characterization of introgression from wild Oryza species into rice. In: Rice genetics III. IRRI, Manila, Philippines, pp 477–486
Cheng ZK, Li X, Yu HX, Gu MH (1996) A new set of primary trisomics in indica rice, its breeding and cytological investigation. Acta Genet Sini 23:363–371
Cheng ZK, Buell CR, Wing RA, Gu M, Jiang J (2001) Toward a cytological characterization of the rice genome. Genome Res 11:2133–2141
Chetelat RT, Rick CM, Cisneros P, Alpert KB, DeVerna JW (1998) Identification, transmission, and cytological behavior of Solanum lycopersicoides Dun. Monosomic alien addition lines in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Genome 41:40–50
Chetelat RT, Meglic V, Cisneros P (2000) A genetic map of tomato based on BC1 Lycopersicon esculentum×Solanum lycopersicoides reveals overall synteny but suppressed recombination between these homoeologous genomes. Genetics 154:857–867
Devos KM, Gale MD (2000) Genome relationships: the grass model in current research. Plant Cell 12:637–646
Ebitani T, Takeuchi Y, Nonoue Y, Yamamoto T, Takeuchi K, Yano M (2005) Construction and evaluation of chromosome segment substitution lines carrying overlapping chromosome segments of indica rice cultivar ‘Kasalath’ in a genetic background of japonica elite cultivar ‘Koshihikari’. Breed Sci 55:65–73
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1995) An introgression line population of Lycopersicon pennellii in the cultivated tomato enables the identification and fine mapping of yield-associated QTL. Genetics 141:1147–1162
Feng Q, Zhang Y, Hao P, Wang S, Fu G, Huang Y, Li Y, Zhu J, Liu Y, Hu X (2002) Sequence and analysis of rice chromosome 4. Nature 420:316–320
Fridman E, Pleban T, Zamir D (2000) A recombination hotspot delimits a wild species QTL for tomato sugar content to 484-bp within an invertase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4718–4723
Fridman E, Carrari F, Liu YS, Fernie AR, Zamir D (2004) Zooming in on a quantitative trait for tomato yield using interspecific introgressions. Science 305:1786–1789
Ge S, Sang T, Lu BR, Hong DY (1999) Phylogeny of rice genomes with emphasis on origins of allotetraploid species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14400–14405
He RF, Wang YY, Shi ZY, Ren X, Zhu LL, Weng QM, He GC (2003) Construction of genomic library of wild rice and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of large insert DNA linked to BPH resistance locus. Gene 321:113–121
Huang Z, He GC, Shu LH, Li XH, Zhang QF (2001) Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper genes in rice. Theor Appl Genet 102:929–934
Jena KK, Khush GS (1989) Monosomic alien addition lines of rice: production, morphology, cytology, and breeding behavior. Genome 32:449–455
Jena KK, Khush GS (1990) Introgression of genes from Oryza officinalis Well ex Watt to cultivated rice, O. sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 80:737–745
Jena KK, Khush GS, Kochert G (1994) Comparative RFLP mapping of a wild rice, Oryza officinalis, and cultivated rice, O. sativa. Genome 37:382–389
Keller B, Feuillet C (2000) Colinearity and gene density in grass genomes. Trends Plant Sci 5:246–251
Khush GS, Singh RJ, Sur SC, Librojo A (1984) Primary trisomics of rice: origin, morphology, cytology, and use in linkage mapping. Genetics 107:141–163
Kowalski SP, Lan TH, Feldmann KA, Paterson AH (1994) Comparative mapping of Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica oleracea chromosomes reveals islands of conserved organization. Genetics 138:449–510
Kubo T, Aida Y, Nakamura K, Tsunematsu H, Doi K, Yoshimura A (2002) Reciprocal chromosome segment substitution series derived from Japonica and Indica cross of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 52:319–325
Kurakazu T, Sobrizal, Ikeda K, Sanchez PL, Doi K, Angeles ER, Khush G.S, Yoshimura A (2001) Oryza meridionalis chromosomal segment introgression lines in cultivated rice, O. sativa L. Rice Genet Newsl 18:81–82
Kurata N, Omura T (1984) Chromosome analysis. In: Tsunoda ST, Takahashi N (eds) Biology of rice. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo and Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 305–320
Lagercrantz U, Putteril J, Coupland G, Lydiate D (1996) Comparative mapping in Arabidopsis and Brassica, fine scale genome collinearity and congruence of genes controlling flowering time. Plant J 9:13–20
Multani DS, Jena KK, Brar DS, Delos Reyes BG, Angeles ER, Khush GS (1994) Development of monosomic alien addition lines and introgression of genes from Oryza australiensis Donin. to cultivated rice O. sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 88:102–109
Multani DS, Khush GS, Delos Reyes BG, Brar DS (2003) Alien genes introgression and development of monosomic alien addition lines from Oryza latifolia Desv. to rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 107:395–405
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high-molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Prince JP, Pochard E, Tanksley SD (1993) Construction of a molecular map of pepper and comparisons of syntenic relationships with tomato. Genome 36:404–417
Song YC, Gustafson JP (1995) The physical location of fourteen RFLP markers in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 90:113–119
Suen DF, Wang CK, Lin RF, Kao YY, Lee FM, Chen CC (1997) Assignment of DNA markers to Nicotiana syvestris chromosomes using monosomic alien addition lines. Theor Appl Genet 94:331–337
Tan GX, Huang Z, Weng QM, Ren X, Zhu LL, He GC (2004a) Two whitebacked planthopper resistance genes shared the same genomic intervals with brown planthopper resistance genes. Heredity 92:212a–217a
Tan GX, Weng QM, Ren X, Shi ZY, Zhu LL, He GC (2004b) Mapping of a new resistance gene to bacterial blight in rice line introgressed from Oryza officinalis. Acta Genetica Sinica 31:724b–729b
Tanksley SD, Berantzky R, Lapitan NL, Prince JP (1988) Conservation of gene repertoire but not gene order in pepper and tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6419–6423
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066
Uozu S, Ikehashi H, Ohmido N, Ohtsubo H, Ohtsubo E, Fukui K (1997). Repetitive sequences: cause for variation in genome size and chromosome morphology in the genus Oryza. Plant Mol Biol 35:791–799
Vaughan DA, Morishima H, Kadowaki K (2003) Diversity in the Oryza genus. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:139–146
Yan HH, Min SK, Zhu LH (1999) Visualization of Oryza eichingeri chromosomes in intergenomic hybrid plants from O. sativa× O. eichingeri via fluorescent in situ hybridization. Genome 42:48–51
Yasui H, Yoshimura A, Iwata N (1992) Characterization of monosomic alien chromosomes of O. punctata transferred to O. sativa using RFLP markers. Rice Genet Newsl 9:139–142
Zamir D (2001) Improving plant breeding with exotic genetic libraries. Nat Rev Genet 2:983–989
Zamir D, Tadmor Y (1986) Unequal segregation of nuclear genes in plants. Bot Gaz 147:355–358
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Dr. T. Sasaki for kindly providing the RFLP probes. This study was supported by grants from the National Program of High Technology Development and the Key Project of the Chinese Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. J. Mackill
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, G., Jin, H., Li, G. et al. Production and characterization of a complete set of individual chromosome additions from Oryza officinalis to Oryza sativa using RFLP and GISH analyses. Theor Appl Genet 111, 1585–1595 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0090-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0090-4